ThreadPoolExecutor源码注释
Java线程池实现原理及其在美团业务中的实践
寒食君
面试必问的线程池,你懂了吗?
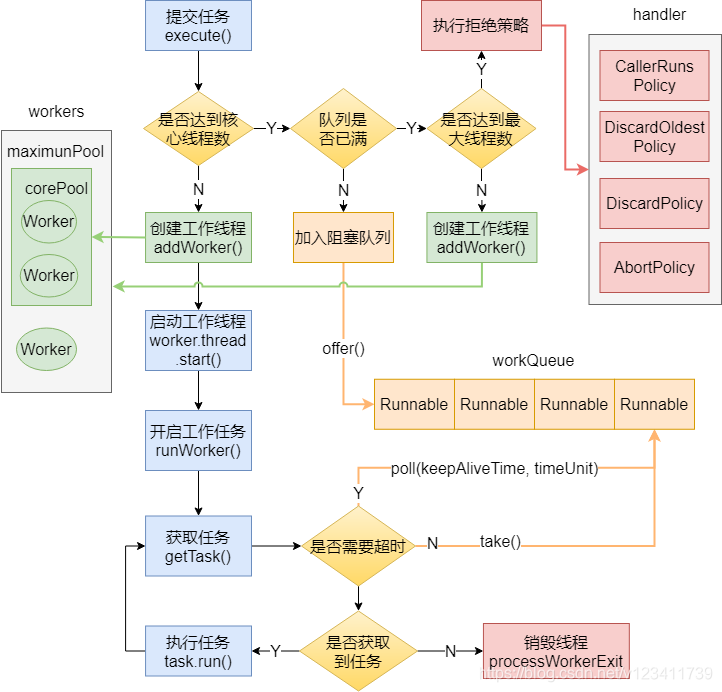
简易流程
- 调用
submit方法提交任务
- 如果此时工作线程数
workCount小于corePoolSize,调用addWorker()方法创建一个核心线程处理这个Task(核心线程与其他线程的区别在于运行的时候会立马执行这个提交的Task,等该Task运行完毕后再从workQueue拉取任务,而其他的线程只能从workQueue拉取任务)。
- 如果此时工作线程数
workCount不小于corePoolSize,尝试向workQueue添加这个任务,如果此时workQueue未满,将Task加入队列,等待getTask()方法抓取给runWorker()执行。
- 如果添加
workQueue失败(队列已满),若此时workCount小于maximumPoolSize则调用addWorker()方法创建非核心线程提交这个任务。
- 若此时
workCount不小于maximumPoolSize,执行拒绝策略,结束。
- 调用
addWorker()添加任务成功后,运行worker.Thread.strat()方法,此时线程就绪,等待JVM调用执行Work本身的的run()方法执行任务。
run()方法内部只是调用了runWorker()方法,在runWorker()方法中,若Worker持有的firstTask不为null,则先执行这个Task,之后再通过getTask()方法从workQueue拉取Task执行run()方式立即执行。getTask()返回为null,则执行Worker回收。getTask()方法有两种方式从workQueue抓取任务,不需要超时使用task()方法,需要超时使用poll()方法。并在以下特殊情况下返回null,提醒runWorker()方法对当前线程进行回收。
- 线程池已经停止
- 线程数现阶段过多
- Worker回收过程:从
workers中移除remove掉该worker,如有必要添加工作线程处理workerQueue的任务
流程图
源码注释
package com.my.threadpool;
import java.security.AccessControlContext;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.AbstractQueuedSynchronizer;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
public class MyThreadPoolExecutor {
/**
* The main pool control state, ctl, is an atomic integer packing
* two conceptual fields
* workerCount, indicating the effective number of threads
* runState, indicating whether running, shutting down etc
*
* In order to pack them into one int, we limit workerCount to
* (2^29)-1 (about 500 million) threads rather than (2^31)-1 (2
* billion) otherwise representable. If this is ever an issue in
* the future, the variable can be changed to be an AtomicLong,
* and the shift/mask constants below adjusted. But until the need
* arises, this code is a bit faster and simpler using an int.
*
* The workerCount is the number of workers that have been
* permitted to start and not permitted to stop. The value may be
* transiently different from the actual number of live threads,
* for example when a ThreadFactory fails to create a thread when
* asked, and when exiting threads are still performing
* bookkeeping before terminating. The user-visible pool size is
* reported as the current size of the workers set.
*
* The runState provides the main lifecycle control, taking on values:
*
* RUNNING: Accept new tasks and process queued tasks
* SHUTDOWN: Don't accept new tasks, but process queued tasks
* STOP: Don't accept new tasks, don't process queued tasks,
* and interrupt in-progress tasks
* TIDYING: All tasks have terminated, workerCount is zero,
* the thread transitioning to state TIDYING
* will run the terminated() hook method
* TERMINATED: terminated() has completed
*
* The numerical order among these values matters, to allow
* ordered comparisons. The runState monotonically increases over
* time, but need not hit each state. The transitions are:
*
* RUNNING -> SHUTDOWN
* On invocation of shutdown(), perhaps implicitly in finalize()
* (RUNNING or SHUTDOWN) -> STOP
* On invocation of shutdownNow()
* SHUTDOWN -> TIDYING
* When both queue and pool are empty
* STOP -> TIDYING
* When pool is empty
* TIDYING -> TERMINATED
* When the terminated() hook method has completed
*
* Threads waiting in awaitTermination() will return when the
* state reaches TERMINATED.
*
* Detecting the transition from SHUTDOWN to TIDYING is less
* straightforward than you'd like because the queue may become
* empty after non-empty and vice versa during SHUTDOWN state, but
* we can only terminate if, after seeing that it is empty, we see
* that workerCount is 0 (which sometimes entails a recheck -- see
* below).
*/
/**
* ctl保存线程池状态和工作线程数,高3位保存状态,低29位保存线程有效数
* 当我们的线程池运行状态为 RUNNING,工作线程个数为 3,则此时 ctl 的原码为:1110 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0011
*/
private final AtomicInteger ctl = new AtomicInteger(ctlOf(RUNNING, 0));
/**
* 32 -3 = 29
*/
private static final int COUNT_BITS = Integer.SIZE - 3;
/**
* 1的二进制表示:0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0001
* 1 << 29:0010 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000
* CAPACITY = (1 << COUNT_BITS) - 1 = 0001 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 = 29个1
*/
private static final int CAPACITY = (1 << COUNT_BITS) - 1;
// runState is stored in the high-order bits
/**
* -1原码:1000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0001
* -1反码:1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1110
* -1补码:1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111
* RUNNING = -1 << COUNT_BITS = 1110 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 取3位:111
*/
private static final int RUNNING = -1 << COUNT_BITS;
/**
* 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 取前3位:000
*/
private static final int SHUTDOWN = 0 << COUNT_BITS;
/**
* 0010 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 取前3位:001
*/
private static final int STOP = 1 << COUNT_BITS;
/**
* 0100 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 取前3位:010
*/
private static final int TIDYING = 2 << COUNT_BITS;
/**
* 0110 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 取前3位:011
*/
private static final int TERMINATED = 3 << COUNT_BITS;
// Packing and unpacking ctl
/**
* 获取线程池状态
* ctl跟CAPACITY取反后的结果取&,CAPACITY高3位变1,后29位变0,跟ctl取&值,得到高三位置均为真实值、低29位均为0的值
* @param c ctl
* @return runState
*/
private static int runStateOf(int c) { return c & ~CAPACITY; }
/**
* 获取工作线程数
* ctl跟CAPACITY取&,得到高3位均为0,低29位真实值表示工作线程数
* @param c ctl
* @return workerCount
*/
private static int workerCountOf(int c) { return c & CAPACITY; }
/**
* 计算ctl
* runState的高3位跟workerCount的低29位做|
* @param rs runState
* @param wc workerCount
* @return ctl
*/
private static int ctlOf(int rs, int wc) { return rs | wc; }
/**
* 只要状态比SHUTDOWN(0)小就是running?
* @param c ctl
* @return true/false
*/
private static boolean isRunning(int c) {
return c < SHUTDOWN;
}
/**
* 一些静态参数
*/
/**
* The queue used for holding tasks and handing off to worker
* threads. We do not require that workQueue.poll() returning
* null necessarily means that workQueue.isEmpty(), so rely
* solely on isEmpty to see if the queue is empty (which we must
* do for example when deciding whether to transition from
* SHUTDOWN to TIDYING). This accommodates special-purpose
* queues such as DelayQueues for which poll() is allowed to
* return null even if it may later return non-null when delays
* expire.
*/
/**
* 用来存储积压任务的阻塞队列,实现类由用户自己确定
* 线程池中是以生产者消费者模式,通过这个阻塞队列来实现的。阻塞队列缓存任务,工作线程从阻塞队列中获取任务。
* 举例如下
* @see ArrayBlockingQueue 基于数组的有界阻塞队列,按先进先出对元素进行排序
* @see LinkedBlockingQueue 基于链表结构的有界/无界阻塞队列,按先进先出对元素进行排序,吞吐量通常高于 ArrayBlockingQueue。默认长度为Integer.MAX_VALUE。Executors.newFixedThreadPool 使用了该队列
* @see SynchronousQueue 一个不存储元素的阻塞队列,每一个put操作必须等待take操作,否则不能添加元素,支持公平锁和非公平锁。Executors.newCachedThreadPool 使用了该队列,这个线程池在新任务到来时创建新的线程,如有空闲线程重复使用
* @see PriorityBlockingQueue 具有优先级的无界队列,按优先级对元素进行排序。元素的优先级是通过自然顺序或Comparator来定义
*/
private final BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue = null;
/**
* Lock held on access to workers set and related bookkeeping.
* While we could use a concurrent set of some sort, it turns out
* to be generally preferable to use a lock. Among the reasons is
* that this serializes interruptIdleWorkers, which avoids
* unnecessary interrupt storms, especially during shutdown.
* Otherwise exiting threads would concurrently interrupt those
* that have not yet interrupted. It also simplifies some of the
* associated statistics bookkeeping of largestPoolSize etc. We
* also hold mainLock on shutdown and shutdownNow, for the sake of
* ensuring workers set is stable while separately checking
* permission to interrupt and actually interrupting.
*/
/**
* 用于同步线程池的一些操作
*/
private final ReentrantLock mainLock = new ReentrantLock();
/**
* Set containing all worker threads in pool. Accessed only when
* holding mainLock.
*/
/**
* 对工作线程以及一些状态的封装,所有Worker的集合,操作workers需要持有锁
*/
private final HashSet<Worker> workers = new HashSet<>();
/**
* Wait condition to support awaitTermination
*/
/**
* 由mainLock创建的Condition,用于terminal调用时的线程同步
*/
private final Condition termination = mainLock.newCondition();
/**
* Tracks largest attained pool size. Accessed only under mainLock.
*/
/**
* 线程池中最多有过多少个活跃线程数
*/
private int largestPoolSize;
/**
* Counter for completed tasks. Updated only on termination of
* worker threads. Accessed only under mainLock.
*/
/**
* 统计线程池总共处理了多少任务
*/
private long completedTaskCount;
/*
* All user control parameters are declared as volatiles so that
* ongoing actions are based on freshest values, but without need
* for locking, since no internal invariants depend on them
* changing synchronously with respect to other actions.
*/
/**
* 以下参数支持用户自定义,声明为volatile类型
*/
/**
* Factory for new threads. All threads are created using this
* factory (via method addWorker). All callers must be prepared
* for addWorker to fail, which may reflect a system or user's
* policy limiting the number of threads. Even though it is not
* treated as an error, failure to create threads may result in
* new tasks being rejected or existing ones remaining stuck in
* the queue.
*
* We go further and preserve pool invariants even in the face of
* errors such as OutOfMemoryError, that might be thrown while
* trying to create threads. Such errors are rather common due to
* the need to allocate a native stack in Thread.start, and users
* will want to perform clean pool shutdown to clean up. There
* will likely be enough memory available for the cleanup code to
* complete without encountering yet another OutOfMemoryError.
*/
/**
* 创建工作线程的工程,用户可自定义
*/
private volatile ThreadFactory threadFactory;
/**
* Handler called when saturated or shutdown in execute.
*/
/**
* 拒绝策略,workQueue满载时触发
*/
private volatile RejectedExecutionHandler handler;
/**
* Timeout in nanoseconds for idle threads waiting for work.
* Threads use this timeout when there are more than corePoolSize
* present or if allowCoreThreadTimeOut. Otherwise they wait
* forever for new work.
*/
/**
* 工作线程空闲时依然保持存活的时间 || 空闲线程回收时间
*/
private volatile long keepAliveTime;
/**
* If false (default), core threads stay alive even when idle.
* If true, core threads use keepAliveTime to time out waiting
* for work.
*/
/**
* 是否需要保持核心线程始终存活
*/
private volatile boolean allowCoreThreadTimeOut;
/**
* Core pool size is the minimum number of workers to keep alive
* (and not allow to time out etc) unless allowCoreThreadTimeOut
* is set, in which case the minimum is zero.
*/
/**
* 核心线程数,可看作稳定的工作线程数,当阻塞队列未满载时线程池将保持核心线程数
*/
private volatile int corePoolSize;
/**
* Maximum pool size. Note that the actual maximum is internally
* bounded by CAPACITY.
*/
/**
* 最大线程数,可看做弹性的工作线程数,当阻塞线程满载时,线程池会在核心线程数的基础上创建新线程处理任务,直至最大线程数
*/
private volatile int maximumPoolSize;
/**
* The default rejected execution handler
*/
/**
* 默认拒绝策略
*/
private static final RejectedExecutionHandler defaultHandler =
new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy();
/**
* Permission required for callers of shutdown and shutdownNow.
* We additionally require (see checkShutdownAccess) that callers
* have permission to actually interrupt threads in the worker set
* (as governed by Thread.interrupt, which relies on
* ThreadGroup.checkAccess, which in turn relies on
* SecurityManager.checkAccess). Shutdowns are attempted only if
* these checks pass.
*
* All actual invocations of Thread.interrupt (see
* interruptIdleWorkers and interruptWorkers) ignore
* SecurityExceptions, meaning that the attempted interrupts
* silently fail. In the case of shutdown, they should not fail
* unless the SecurityManager has inconsistent policies, sometimes
* allowing access to a thread and sometimes not. In such cases,
* failure to actually interrupt threads may disable or delay full
* termination. Other uses of interruptIdleWorkers are advisory,
* and failure to actually interrupt will merely delay response to
* configuration changes so is not handled exceptionally.
*/
private static final RuntimePermission shutdownPerm =
new RuntimePermission("modifyThread");
/* The context to be used when executing the finalizer, or null. */
private final AccessControlContext acc = null;
/**
* 以下是内部类
*/
/**
* Class Worker mainly maintains interrupt control state for
* threads running tasks, along with other minor bookkeeping.
* This class opportunistically extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer
* to simplify acquiring and releasing a lock surrounding each
* task execution. This protects against interrupts that are
* intended to wake up a worker thread waiting for a task from
* instead interrupting a task being run. We implement a simple
* non-reentrant mutual exclusion lock rather than use
* ReentrantLock because we do not want worker tasks to be able to
* reacquire the lock when they invoke pool control methods like
* setCorePoolSize. Additionally, to suppress interrupts until
* the thread actually starts running tasks, we initialize lock
* state to a negative value, and clear it upon start (in
* runWorker).
*/
/**
* 继承AQS:Worker内部存在同步需求
* 实现Runnable接口:Worker本身就是一个异步的任务调度器
*
* 一个worker持有一个线程,可能持有一个firstTask。
* 执行runWorker方法执行这个firstTask或者从阻塞队列获取任务来执行
* 当getTask返回空时,说明此时已经没有Task供这个worker处理,此时可执行该worker的回收,
*/
private final class Worker
extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer
implements Runnable
{
/**
* This class will never be serialized, but we provide a
* serialVersionUID to suppress a javac warning.
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = 6138294804551838833L;
/** Thread this worker is running in. Null if factory fails. */
/**
* 在调用构造方法时通过ThreadFactory来创建线程,可以用来执行任务
*/
final Thread thread;
/** Initial task to run. Possibly null. */
/**
* 保存传入的第一个任务,这个任务可以有也可以为null,由addWorker方法确定。
* 如果这个值是非空的,那么线程就会在启动初期立即执行这个任务,也就对应核心线程创建时的情况;
* 如果这个值是null,那么就需要创建一个线程去执行任务列表(workQueue)中的任务,也就是非核心线程的创建。
*/
Runnable firstTask;
/** Per-thread task counter */
volatile long completedTasks;
/**
* Creates with given first task and thread from ThreadFactory.
* @param firstTask the first task (null if none)
*/
Worker(Runnable firstTask) {
setState(-1); // inhibit interrupts until runWorker
this.firstTask = firstTask;
this.thread = getThreadFactory().newThread(this);
}
/** Delegates main run loop to outer runWorker */
/**
* Worker类最主要的方法
*/
public void run() {
runWorker(this);
}
// Lock methods
//
// The value 0 represents the unlocked state.
// The value 1 represents the locked state.
protected boolean isHeldExclusively() {
return getState() != 0;
}
protected boolean tryAcquire(int unused) {
if (compareAndSetState(0, 1)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());
return true;
}
return false;
}
protected boolean tryRelease(int unused) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);
setState(0);
return true;
}
public void lock() { acquire(1); }
public boolean tryLock() { return tryAcquire(1); }
public void unlock() { release(1); }
public boolean isLocked() { return isHeldExclusively(); }
void interruptIfStarted() {
Thread t;
if (getState() >= 0 && (t = thread) != null && !t.isInterrupted()) {
try {
t.interrupt();
} catch (SecurityException ignore) {
}
}
}
}
/**
* Main worker run loop. Repeatedly gets tasks from queue and
* executes them, while coping with a number of issues:
*
* 1. We may start out with an initial task, in which case we
* don't need to get the first one. Otherwise, as long as pool is
* running, we get tasks from getTask. If it returns null then the
* worker exits due to changed pool state or configuration
* parameters. Other exits result from exception throws in
* external code, in which case completedAbruptly holds, which
* usually leads processWorkerExit to replace this thread.
*
* 2. Before running any task, the lock is acquired to prevent
* other pool interrupts while the task is executing, and then we
* ensure that unless pool is stopping, this thread does not have
* its interrupt set.
*
* 3. Each task run is preceded by a call to beforeExecute, which
* might throw an exception, in which case we cause thread to die
* (breaking loop with completedAbruptly true) without processing
* the task.
*
* 4. Assuming beforeExecute completes normally, we run the task,
* gathering any of its thrown exceptions to send to afterExecute.
* We separately handle RuntimeException, Error (both of which the
* specs guarantee that we trap) and arbitrary Throwables.
* Because we cannot rethrow Throwables within Runnable.run, we
* wrap them within Errors on the way out (to the thread's
* UncaughtExceptionHandler). Any thrown exception also
* conservatively causes thread to die.
*
* 5. After task.run completes, we call afterExecute, which may
* also throw an exception, which will also cause thread to
* die. According to JLS Sec 14.20, this exception is the one that
* will be in effect even if task.run throws.
*
* The net effect of the exception mechanics is that afterExecute
* and the thread's UncaughtExceptionHandler have as accurate
* information as we can provide about any problems encountered by
* user code.
*
* @param w the worker
*/
/**
* Work主要的运行方法,循环从阻塞队列中获取任务并执行
* 1.while循环不断地通过getTask()方法获取任务。
* 2.getTask()方法从阻塞队列中取任务。
* 3.如果线程池正在停止,那么要保证当前线程是中断状态,否则要保证当前线程不是中断状态。
* 4.执行任务。
* 5.如果getTask结果为null则跳出循环,执行processWorkerExit()方法,销毁线程。
* @param w worker
*/
final void runWorker(Worker w) {
Thread wt = Thread.currentThread();
Runnable task = w.firstTask;
w.firstTask = null;
w.unlock(); // allow interrupts
boolean completedAbruptly = true;
try {
/**
* 任务的执行有两种可能:
* 一种是任务直接由新创建的线程执行。
* 另一种是线程从任务队列中获取任务然后执行,执行完任务的空闲线程会再次去从队列中申请任务再去执行。
* 第一种情况仅出现在线程初始创建的时候,第二种是线程获取任务绝大多数的情况。
* 线程需要从任务缓存模块中不断地取任务执行,帮助线程从阻塞队列中获取任务,实现线程管理模块和任务管理模块之间的通信。这部分策略由getTask方法实现
*/
while (task != null || (task = getTask()) != null) {
// 加锁标记当前工作线程正在执行任务,不接收中断
w.lock();
// If pool is stopping, ensure thread is interrupted;
// if not, ensure thread is not interrupted. This
// requires a recheck in second case to deal with
// shutdownNow race while clearing interrupt
if ((runStateAtLeast(ctl.get(), STOP) ||
(Thread.interrupted() &&
runStateAtLeast(ctl.get(), STOP))) &&
!wt.isInterrupted())
wt.interrupt();
try {
// 线程池的切面
beforeExecute(wt, task);
Throwable thrown = null;
try {
task.run();
} catch (RuntimeException x) {
thrown = x; throw x;
} catch (Error x) {
thrown = x; throw x;
} catch (Throwable x) {
thrown = x; throw new Error(x);
} finally {
// 线程池的切面
afterExecute(task, thrown);
}
} finally {
task = null;
// 完成任务数++
w.completedTasks++;
// 释放锁
w.unlock();
}
}
completedAbruptly = false;
} finally {
// 工作线程Worker接收不到任务的时候,就会开始被回收
processWorkerExit(w, completedAbruptly);
}
}
/**
* Performs blocking or timed wait for a task, depending on
* current configuration settings, or returns null if this worker
* must exit because of any of:
* 1. There are more than maximumPoolSize workers (due to
* a call to setMaximumPoolSize).
* 2. The pool is stopped.
* 3. The pool is shutdown and the queue is empty.
* 4. This worker timed out waiting for a task, and timed-out
* workers are subject to termination (that is,
* {@code allowCoreThreadTimeOut || workerCount > corePoolSize})
* both before and after the timed wait, and if the queue is
* non-empty, this worker is not the last thread in the pool.
*
* @return task, or null if the worker must exit, in which case
* workerCount is decremented
*/
/**
* 线程从任务队列中获取任务然后执行。getTask方法帮助线程从阻塞队列中获取任务,实现线程管理模块和任务管理模块之间的通信
*/
private Runnable getTask() {
// 上一次从阻塞队列poll任务是否超时
boolean timedOut = false; // Did the last poll() time out?
for (;;) {
// 获取当前线程池状态
int c = ctl.get();
int rs = runStateOf(c);
// Check if queue empty only if necessary.
// 如果线程池状态是STOP、TIDYING、TERMINATED,或者SHUTDOWN并且工作队列为空,那么返回null,代表当前worker可回收
if (rs >= SHUTDOWN && (rs >= STOP || workQueue.isEmpty())) {
decrementWorkerCount();
return null;
}
// wc:当前worker数量
int wc = workerCountOf(c);
// Are workers subject to culling?
// 如果核心线程空闲时需要回收 || 当前worker数大于核心线程数
boolean timed = allowCoreThreadTimeOut || wc > corePoolSize;
// 如果当前工作线程数超过了最大线程数,或者达到了核心线程数的回收条件
// 并且池中还有其他线程在工作 || 阻塞队列空闲
// 则尝试回收当前worker
if ((wc > maximumPoolSize || (timed && timedOut))
&& (wc > 1 || workQueue.isEmpty())) {
if (compareAndDecrementWorkerCount(c))
return null;
continue;
}
// 如果不满足回收条件,那么从阻塞队列获取任务
// poll在队列为空时返回null,take会等待直到队列中有任务可取出
try {
Runnable r = timed ?
// keepAliveTime:队列里无任务需要处理,代表该线程空闲,可以尝试回收判断
workQueue.poll(keepAliveTime, TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS) :
workQueue.take();
if (r != null)
return r;
timedOut = true;
} catch (InterruptedException retry) {
timedOut = false;
}
}
}
/**
* Executes the given task sometime in the future. The task
* may execute in a new thread or in an existing pooled thread.
*
* If the task cannot be submitted for execution, either because this
* executor has been shutdown or because its capacity has been reached,
* the task is handled by the current {@code RejectedExecutionHandler}.
*
* @param command the task to execute
* @throws RejectedExecutionException at discretion of
* {@code RejectedExecutionHandler}, if the task
* cannot be accepted for execution
* @throws NullPointerException if {@code command} is null
*/
/**
* 线程池最重要的execute方法
* 任务提交入口,提交的Task不能为空,线程池状态必须是RUNNING,提交的任务可能被如下处理
* 1、创建核心线程执行(wc < corePoolSize)
* 2、放入缓存队列workQueue(wc > corePoolSize && workQueue没满)
* 3、创建工作线程执行(wc < maximumPoolSize)
* 4、执行拒绝策略(wc >= maximumPoolSize)
* @param command Task
*/
public void execute(Runnable command) {
if (command == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
/*
* Proceed in 3 steps:
*
* 1. If fewer than corePoolSize threads are running, try to
* start a new thread with the given command as its first
* task. The call to addWorker atomically checks runState and
* workerCount, and so prevents false alarms that would add
* threads when it shouldn't, by returning false.
*
* 2. If a task can be successfully queued, then we still need
* to double-check whether we should have added a thread
* (because existing ones died since last checking) or that
* the pool shut down since entry into this method. So we
* recheck state and if necessary roll back the enqueuing if
* stopped, or start a new thread if there are none.
*
* 3. If we cannot queue task, then we try to add a new
* thread. If it fails, we know we are shut down or saturated
* and so reject the task.
*/
int c = ctl.get();
// 1、当前线程数小于核心线程数,addWorker(核心线程),存在并发可能
if (workerCountOf(c) < corePoolSize) {
if (addWorker(command, true))
return;
// 1、1并发添加失败了
c = ctl.get();
}
// 2、并发添加核心线程失败,尝试向阻塞队列offer这个Task
if (isRunning(c) && workQueue.offer(command)) {
int recheck = ctl.get();
// 2、1 添加阻塞队列后检查线程池状态是否还是运行中,如果不是需要remove这个Task并执行拒绝策略
if (! isRunning(recheck) && remove(command))
reject(command);
// 2、2 如果此时恰好worker等于0或者移除失败,add非核心线程worker,给Task一次执行的机会
else if (workerCountOf(recheck) == 0)
addWorker(null, false);
}
// 3、阻塞队列已满,直接尝试addWorker(最大线程)
else if (!addWorker(command, false))
// add最大线程worker失败触发拒绝策略
reject(command);
}
/**
* Checks if a new worker can be added with respect to current
* pool state and the given bound (either core or maximum). If so,
* the worker count is adjusted accordingly, and, if possible, a
* new worker is created and started, running firstTask as its
* first task. This method returns false if the pool is stopped or
* eligible to shut down. It also returns false if the thread
* factory fails to create a thread when asked. If the thread
* creation fails, either due to the thread factory returning
* null, or due to an exception (typically OutOfMemoryError in
* Thread.start()), we roll back cleanly.
*
* @param firstTask the task the new thread should run first (or
* null if none). Workers are created with an initial first task
* (in method execute()) to bypass queuing when there are fewer
* than corePoolSize threads (in which case we always start one),
* or when the queue is full (in which case we must bypass queue).
* Initially idle threads are usually created via
* prestartCoreThread or to replace other dying workers.
*
* @param core if true use corePoolSize as bound, else
* maximumPoolSize. (A boolean indicator is used here rather than a
* value to ensure reads of fresh values after checking other pool
* state).
* @return true if successful
*/
/**
* 该方法的功能就是增加一个线程,该方法不考虑线程池是在哪个阶段增加的该线程,这个分配线程的策略是在上个步骤完成的,该步骤仅仅完成增加线程,并使它运行,最后返回是否成功这个结果
* @param firstTask 指定新增的线程执行的第一个任务,该参数可以为空
* @param core true表示在新增线程时会判断当前活动线程数是否少于corePoolSize,false表示新增线程前需要判断当前活动线程数是否少于maximumPoolSize
* @return true/false
*/
private boolean addWorker(Runnable firstTask, boolean core) {
retry:
for (;;) {
int c = ctl.get();
int rs = runStateOf(c);
// Check if queue empty only if necessary.
if (rs >= SHUTDOWN &&
! (rs == SHUTDOWN &&
firstTask == null &&
! workQueue.isEmpty()))
return false;
for (;;) {
int wc = workerCountOf(c);
if (wc >= CAPACITY ||
wc >= (core ? corePoolSize : maximumPoolSize))
return false;
if (compareAndIncrementWorkerCount(c))
break retry;
c = ctl.get(); // Re-read ctl
if (runStateOf(c) != rs)
continue retry;
// else CAS failed due to workerCount change; retry inner loop
}
}
// 以上逻辑主要对当前线程池的一系列状态进行判断,判断当下是否还需要继续创建worker
// 如果执行完没有退出,说明CAS成功,有机会创建worker
boolean workerStarted = false;
boolean workerAdded = false;
Worker w = null;
try {
w = new Worker(firstTask);
final Thread t = w.thread;
if (t != null) {
final ReentrantLock mainLock = this.mainLock;
// 为了防止超过核心线程数以及最大线程数,需要加独占锁
mainLock.lock();
try {
// Recheck while holding lock.
// Back out on ThreadFactory failure or if
// shut down before lock acquired.
int rs = runStateOf(ctl.get());
// 如果线程池非SHUTDOWN状态
// 或者线程池状态为SHUTDOWN且当前worker是为了消费阻塞队列里缓存的任务
if (rs < SHUTDOWN ||
(rs == SHUTDOWN && firstTask == null)) {
if (t.isAlive()) // precheck that t is startable
throw new IllegalThreadStateException();
// 向works中添加worker
workers.add(w);
int s = workers.size();
// 更新曾持有的最大线程数量
if (s > largestPoolSize)
largestPoolSize = s;
// 标记worker已添加
workerAdded = true;
}
} finally {
// 释放锁
mainLock.unlock();
}
// 如果添加了worker,启动工作
if (workerAdded) {
t.start();
workerStarted = true;
}
}
} finally {
// 如果启动失败,执行清理工作
if (! workerStarted)
addWorkerFailed(w);
}
return workerStarted;
}
/**
* 构建线程池需要的参数
* @param corePoolSize 核心线程数:线程池中一直保持的活跃线程数量,即使啥也不干。如果allowCoreThreadTimeOut为true则在空闲的时候会过期
* 当线程池运行的线程少于 corePoolSize 时,将创建一个新线程来处理请求
* @param maximumPoolSize 最大线程数:线程池中运行开启的最大线程数量
* @param keepAliveTime 当线程数大于核心线程数时,多余的线程超过这个时间就终止了
* @param unit 过期时间单位
* @param workQueue 保存待执行的Task,这个Task必须是@see Runnable 类型,由 execute 方法提交
* @param threadFactory 线程工厂:用来创建新线程
* @param handler 拒绝策略处理器:达到线程边界(thread bounds?)或者线程池容量已满时,处理新进来的Task。默认是AbortPolicy
* 1、线程池运行状态不是 RUNNING;2、线程池已经达到最大线程数,并且阻塞队列已满时。
*/
public MyThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
ThreadFactory threadFactory,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
// 校验corePoolSize大于等于0,maximumPoolSize大于corePoolSize
if (corePoolSize < 0 ||
maximumPoolSize <= 0 ||
maximumPoolSize < corePoolSize ||
keepAliveTime < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
if (workQueue == null || threadFactory == null || handler == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
}
/**------------------以下辅助------------**/
public ThreadFactory getThreadFactory() {
return threadFactory;
}
public void setThreadFactory(ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
this.threadFactory = threadFactory;
}
/*
* Bit field accessors that don't require unpacking ctl.
* These depend on the bit layout and on workerCount being never negative.
*/
private static boolean runStateLessThan(int c, int s) {
return c < s;
}
private static boolean runStateAtLeast(int c, int s) {
return c >= s;
}
protected void beforeExecute(Thread t, Runnable r) { }
protected void afterExecute(Runnable r, Throwable t) { }
/**
* Performs cleanup and bookkeeping for a dying worker. Called
* only from worker threads. Unless completedAbruptly is set,
* assumes that workerCount has already been adjusted to account
* for exit. This method removes thread from worker set, and
* possibly terminates the pool or replaces the worker if either
* it exited due to user task exception or if fewer than
* corePoolSize workers are running or queue is non-empty but
* there are no workers.
*
* @param w the worker
* @param completedAbruptly if the worker died due to user exception
*/
private void processWorkerExit(Worker w, boolean completedAbruptly) {
if (completedAbruptly) // If abrupt, then workerCount wasn't adjusted
decrementWorkerCount();
final ReentrantLock mainLock = this.mainLock;
mainLock.lock();
try {
completedTaskCount += w.completedTasks;
workers.remove(w);
} finally {
mainLock.unlock();
}
tryTerminate();
int c = ctl.get();
if (runStateLessThan(c, STOP)) {
if (!completedAbruptly) {
int min = allowCoreThreadTimeOut ? 0 : corePoolSize;
if (min == 0 && ! workQueue.isEmpty())
min = 1;
if (workerCountOf(c) >= min)
return; // replacement not needed
}
addWorker(null, false);
}
}
/**
* Decrements the workerCount field of ctl. This is called only on
* abrupt termination of a thread (see processWorkerExit). Other
* decrements are performed within getTask.
*/
private void decrementWorkerCount() {
do {} while (! compareAndDecrementWorkerCount(ctl.get()));
}
/**
* Attempts to CAS-decrement the workerCount field of ctl.
*/
private boolean compareAndDecrementWorkerCount(int expect) {
return ctl.compareAndSet(expect, expect - 1);
}
public boolean remove(Runnable task) {
boolean removed = workQueue.remove(task);
tryTerminate(); // In case SHUTDOWN and now empty
return removed;
}
final void tryTerminate() {
for (;;) {
int c = ctl.get();
if (isRunning(c) ||
runStateAtLeast(c, TIDYING) ||
(runStateOf(c) == SHUTDOWN && ! workQueue.isEmpty()))
return;
if (workerCountOf(c) != 0) { // Eligible to terminate
interruptIdleWorkers(ONLY_ONE);
return;
}
final ReentrantLock mainLock = this.mainLock;
mainLock.lock();
try {
if (ctl.compareAndSet(c, ctlOf(TIDYING, 0))) {
try {
terminated();
} finally {
ctl.set(ctlOf(TERMINATED, 0));
termination.signalAll();
}
return;
}
} finally {
mainLock.unlock();
}
// else retry on failed CAS
}
}
/**
* Invokes the rejected execution handler for the given command.
* Package-protected for use by ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor.
*/
final void reject(Runnable command) {
handler.rejectedExecution(command, null);
}
/**
* Attempts to CAS-increment the workerCount field of ctl.
*/
private boolean compareAndIncrementWorkerCount(int expect) {
return ctl.compareAndSet(expect, expect + 1);
}
private void interruptIdleWorkers(boolean onlyOne) {
final ReentrantLock mainLock = this.mainLock;
mainLock.lock();
try {
for (Worker w : workers) {
Thread t = w.thread;
if (!t.isInterrupted() && w.tryLock()) {
try {
t.interrupt();
} catch (SecurityException ignore) {
} finally {
w.unlock();
}
}
if (onlyOne)
break;
}
} finally {
mainLock.unlock();
}
}
private static final boolean ONLY_ONE = true;
protected void terminated() { }
/**
* Rolls back the worker thread creation.
* - removes worker from workers, if present
* - decrements worker count
* - rechecks for termination, in case the existence of this
* worker was holding up termination
*/
private void addWorkerFailed(Worker w) {
final ReentrantLock mainLock = this.mainLock;
mainLock.lock();
try {
if (w != null)
workers.remove(w);
decrementWorkerCount();
tryTerminate();
} finally {
mainLock.unlock();
}
}
}
j
