背景
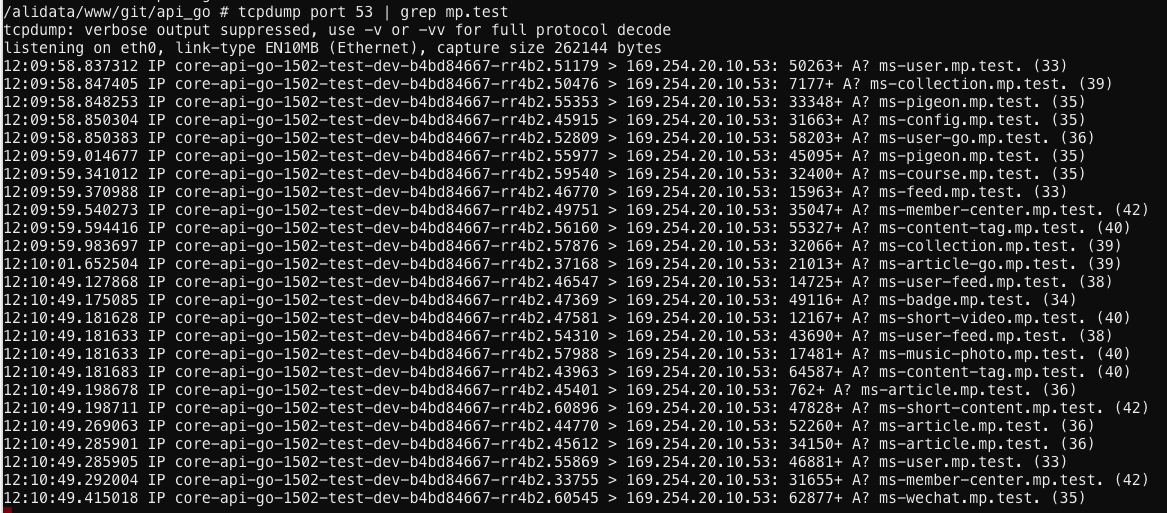
有同学通过zipkin发现dns解析偶尔会花费40ms(预期是1ms以内),并且猜测和alpine镜像有关系。
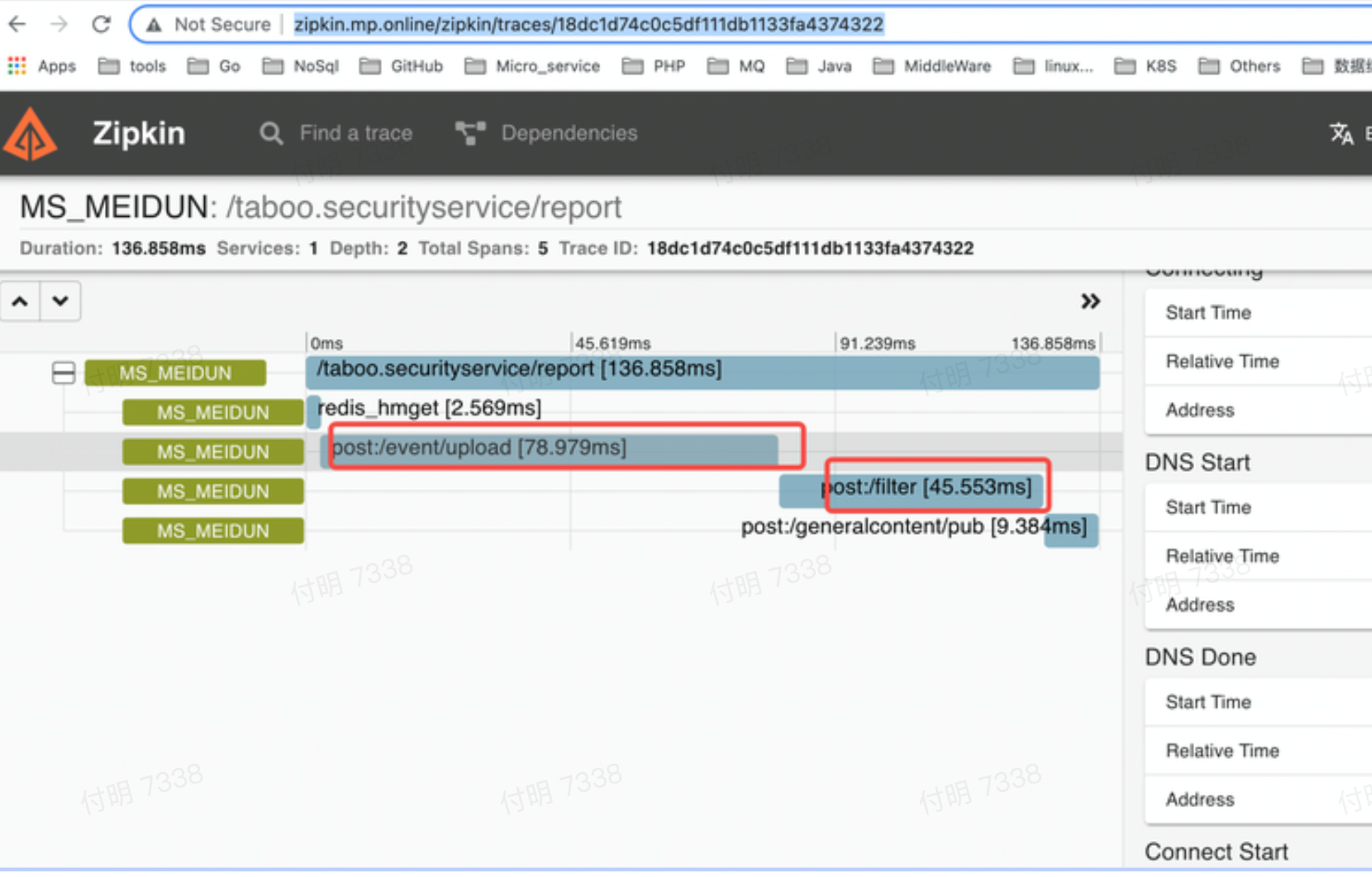
第一反应不太可能是alpine镜像的问题(alpine镜像使用这么频繁,如果有问题应该早就修复了),下面针对这个问题进行分析。
Go中dns解析过程
首先我们了解下golang中如何进行dns解析的。直接看代码,关键函数goLookupIPCNAMEOrder
// src/net/dnsclient_unix.go func (r *Resolver) goLookupIPCNAMEOrder(ctx context.Context, network, name string, order hostLookupOrder) (addrs []IPAddr, cname dnsmessage.Name, err error) { // 省略检查代码 // 读取/etc/resolv.conf,防止读取频繁,5秒钟生效一次 resolvConf.tryUpdate("/etc/resolv.conf") // ... // 默认解析ipv4和ipv6 qtypes := []dnsmessage.Type{dnsmessage.TypeA, dnsmessage.TypeAAAA} // 【关键】根据network的不同,4结尾的只解析ipv4,6结尾的只解析ipv6 switch ipVersion(network) { case '4': qtypes = []dnsmessage.Type{dnsmessage.TypeA} case '6': qtypes = []dnsmessage.Type{dnsmessage.TypeAAAA} } // ... // 判断/etc/resolv.conf里面的single-request和single-request-reopen参数,如果设置的话,就是串行请求,否者是并行请求 if conf.singleRequest { queryFn = func(fqdn string, qtype dnsmessage.Type) {} responseFn = func(fqdn string, qtype dnsmessage.Type) result { dnsWaitGroup.Add(1) defer dnsWaitGroup.Done() p, server, err := r.tryOneName(ctx, conf, fqdn, qtype) return result{p, server, err} } } else { queryFn = func(fqdn string, qtype dnsmessage.Type) { dnsWaitGroup.Add(1) // 看到go关键字了么?没有设置single-request就是并发解析 go func(qtype dnsmessage.Type) { p, server, err := r.tryOneName(ctx, conf, fqdn, qtype) lane <- result{p, server, err} dnsWaitGroup.Done() }(qtype) } responseFn = func(fqdn string, qtype dnsmessage.Type) result { return <-lane } } // 下面代码也很重要 var lastErr error // len(namelist) = len(search domain) + 1 // 遍历nameserver,resolv.conf中可以配置多个nameserver,比如下面的配置namelist长度就是4: // nameserver 169.254.20.10 // nameserver 172.16.0.10 // search meipian-test.svc.cluster.local svc.cluster.local cluster.local for _, fqdn := range conf.nameList(name) { // ... // 遍历解析类型,这里就是ipv4和ipv6 for _, qtype := range qtypes { // .... } } // ... return addrs, cname, nil }
通过以上代码我们可以得出以下结论:
go实现了dns解析
Dns解析跟是不是alpine镜像没有关系,因为go 中dns解析是自己实现的,不依赖于系统调用。go build tag也证明了这一点
//go:build aix || darwin || dragonfly || freebsd || linux || netbsd || openbsd || solaris // +build aix darwin dragonfly freebsd linux netbsd openbsd solaris
内置解析器会读取配置文件
go程序会读取并解析/etc/resolv.conf文件,并且标准选项都有实现,包括single-request和single-request-reopen option设置。
// src/net/dnsconfig_unix.go case s == "single-request" || s == "single-request-reopen": // Linux option: // http://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man5/resolv.conf.5.html // "By default, glibc performs IPv4 and IPv6 lookups in parallel [...] // This option disables the behavior and makes glibc // perform the IPv6 and IPv4 requests sequentially." conf.singleRequest = true
single-request参数是有效的
如果设置了single request选项,dns解析的时候是串行的
if conf.singleRequest { queryFn = func(fqdn string, qtype dnsmessage.Type) {} responseFn = func(fqdn string, qtype dnsmessage.Type) result { dnsWaitGroup.Add(1) defer dnsWaitGroup.Done() p, server, err := r.tryOneName(ctx, conf, fqdn, qtype) return result{p, server, err} } }
如果没有设置single-request选项,dns解析是并行的(真实情况是并行和串行结合的)。
if conf.singleRequest { // ... } else { queryFn = func(fqdn string, qtype dnsmessage.Type) { dnsWaitGroup.Add(1) go func(qtype dnsmessage.Type) { p, server, err := r.tryOneName(ctx, conf, fqdn, qtype) lane <- result{p, server, err} dnsWaitGroup.Done() }(qtype) } responseFn = func(fqdn string, qtype dnsmessage.Type) result { return <-lane } }
解析过程和配置相关
dns解析策略、次数和ndots、search domain和nameserver配置强相关:
默认情况下dns查询会同时解析IPv4和IPv6地址(不论容器是否支持IPv6)
ndots和待解析的域名决定要不要优先使用search domain,通俗一点说,如果你的域名请求参数中,点的个数比配置的ndots小,则会优先拼接search domain后去解析,比如有如下配置:
search meipian-test.svc.cluster.local svc.cluster.local cluster.local options ndots:3
如果现在解析的域名是www.baidu.com,ndots配置的是3,待解析域名中的点数(2)比 ndots 小,所以会优先拼接搜索域名去解析,解析顺序如下:
- www.baidu.com.meipian-test.svc.cluster.local.
- www.baidu.com.svc.cluster.local.
- www.baidu.com.cluster.local.
- www.baidu.com.
如果配置文件中ndots等于2,则解析顺序如下:
www.baidu.com.
www.baidu.com.meipian-test.svc.cluster.local.
www.baidu.com.svc.cluster.local.
www.baidu.com.cluster.local.
serach domain和nameserver决定了dns最多查询的次数,即查询次数等于搜素域的数量+1乘以dnsserver的数量。比如有以下配置:
nameserver 169.254.20.10 nameserver 172.16.0.10 search meipian-test.svc.cluster.local svc.cluster.local cluster.local options ndots:3
当我们解析www.baidu.com域名时,解析顺序如下:
|
解析域名
|
查询类型
|
dns server
|
|
www.baidu.com.meipian-test.svc.cluster.local.
|
A
|
169.254.20.10
|
|
www.baidu.com.meipian-test.svc.cluster.local.
|
A
|
172.16.0.10
|
|
www.baidu.com.meipian-test.svc.cluster.local.
|
AAAA
|
169.254.20.10
|
|
www.baidu.com.meipian-test.svc.cluster.local.
|
AAAA
|
172.16.0.10
|
|
www.baidu.com.svc.cluster.local.
|
A
|
169.254.20.10
|
|
www.baidu.com.svc.cluster.local.
|
A
|
172.16.0.10
|
|
www.baidu.com.svc.cluster.local.
|
AAAA
|
169.254.20.10
|
|
www.baidu.com.svc.cluster.local.
|
AAAA
|
172.16.0.10
|
|
www.baidu.com.cluster.local.
|
A
|
169.254.20.10
|
|
www.baidu.com.cluster.local.
|
A
|
172.16.0.10
|
|
www.baidu.com.cluster.local.
|
AAAA
|
169.254.20.10
|
|
www.baidu.com.cluster.local.
|
AAAA
|
172.16.0.10
|
|
www.baidu.com.
|
A
|
169.254.20.10
|
|
www.baidu.com.
|
A
|
172.16.0.10
|
|
www.baidu.com.
|
AAAA
|
169.254.20.10
|
|
www.baidu.com.
|
AAAA
|
172.16.0.10
|
一共16次,是不是很恐怖?当然只有在最坏的情况(比如域名确实不存在时)才会有这么多次请求。
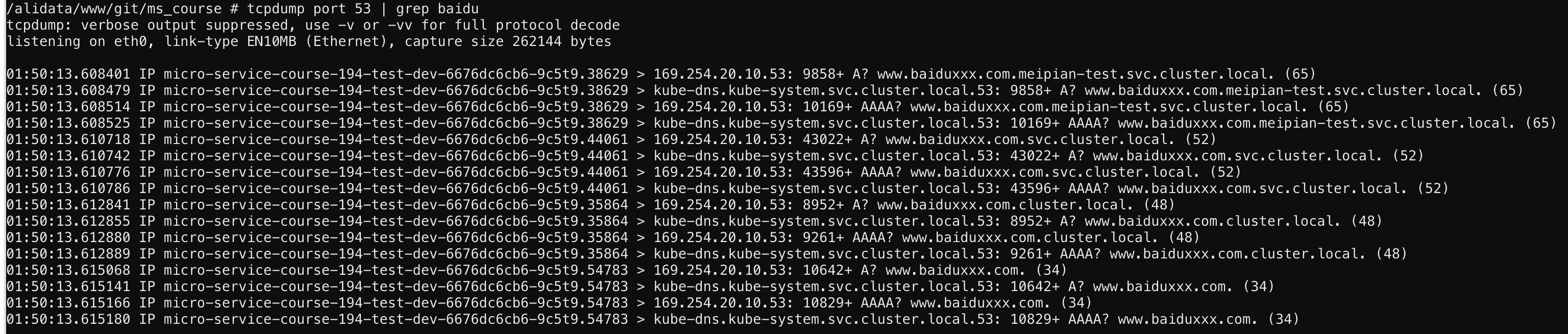
⚠️ 串行和并行请求是如何结合的?
并行是指同一个域名的去同一个dns server解析不同的类型时是并行的,不同的域名之间还是串行的。
把请求放在时间线上就像下面这样:
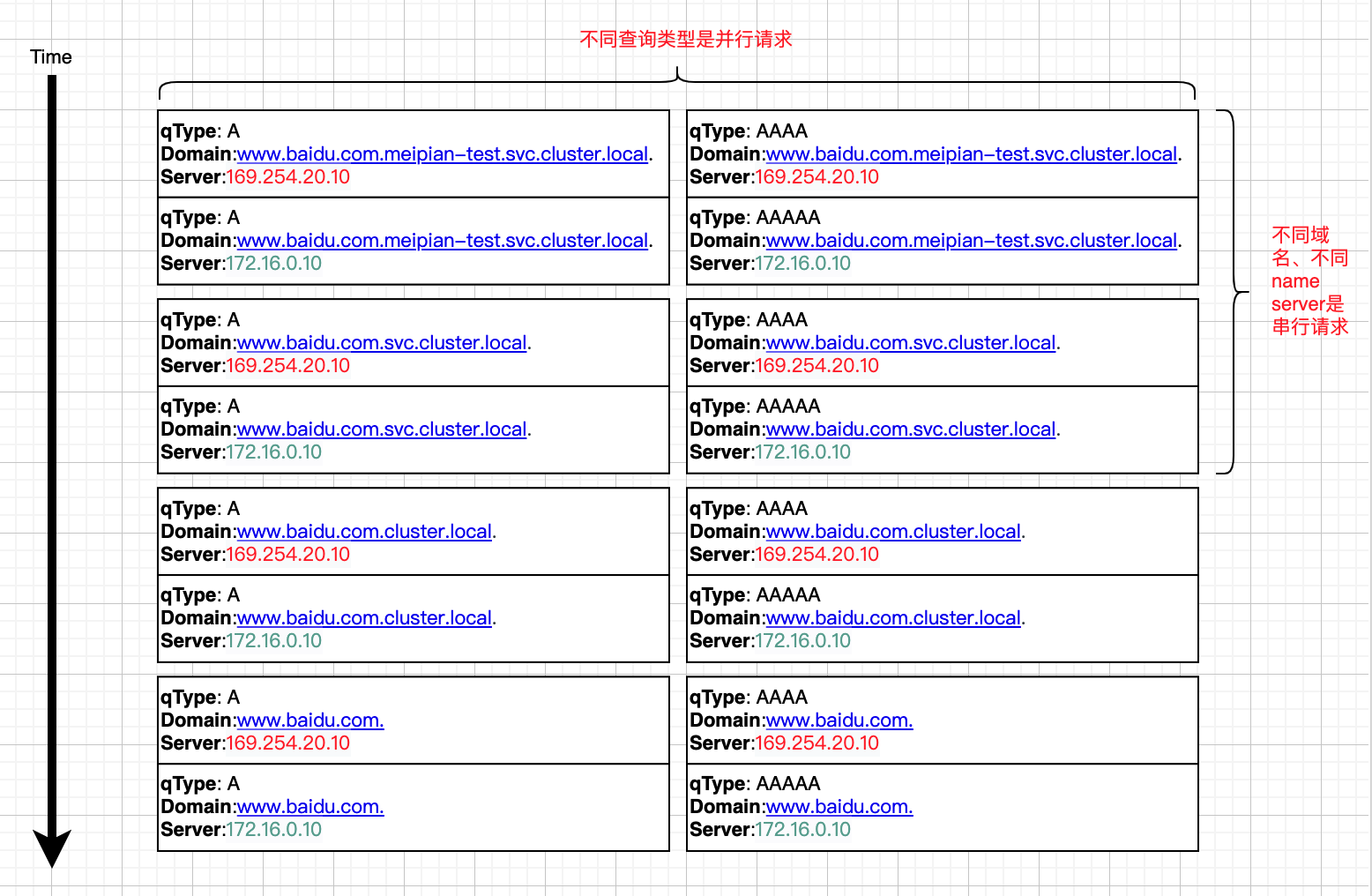
上图话的是最坏的情况,实际上过程中只要有一次解析成功就返回了。
内置解析器参数默认值
ndots: 1, timeout: 5 * time.Second, // dns解析超时时间为5秒,有点太长了 attempts: 2, // 解析失败,重试两次 defaultNS = []string{"127.0.0.1:53", "[::1]:53"} // 默认dns server search:os.Hostname //
其中需要注意的就是timeout,建议在resolv.conf上加上这个参数,并且写个较小的值。因为dns解析默认是udp请求(不可靠),如果发生丢包情况就会等5s。
Dns 解析策略
上面说到go使用的是内置解析器,其实并不是所有情况都是这样的。
两种解析器
golang有两种域名解析方法:内置go解析器和基于cgo的系统解析器。
// src/net/cgo_stub.go //go:build !cgo || netgo // +build !cgo netgo func init() { netGo = true } // src/net/conf_netcgo.go //go:build netcgo // +build netcgo func init() { netCgo = true }
默认情况下用的是内置解析,如果你想指定使用cgo解析器,可以build的时候指定。
export GODEBUG=netdns=go # force pure Go resolver
export GODEBUG=netdns=cgo # force cgo resolver
内置解析器解析策略
当goos=linux下使用的是 hostLookupFilesDNS ,也就是说,hosts解析优先dns解析(go1.17.5)。
const ( // hostLookupCgo means defer to cgo. hostLookupCgo hostLookupOrder = iota hostLookupFilesDNS // files first hostLookupDNSFiles // dns first hostLookupFiles // only files hostLookupDNS // only DNS ) var lookupOrderName = map[hostLookupOrder]string{ hostLookupCgo: "cgo", hostLookupFilesDNS: "files,dns", hostLookupDNSFiles: "dns,files", hostLookupFiles: "files", hostLookupDNS: "dns", }
根据操作系统的不同,使用的解析策略也会略有不同,比如android平台就会强制使用cgo
// src/net/conf.go fallbackOrder := hostLookupCgo // ... if c.forceCgoLookupHost || c.resolv.unknownOpt || c.goos == "android" { return fallbackOrder }
禁用IPv6解析
在go1.17之前是没有办法禁用ipv6解析的。1.17之后go提供了一些方式
// 默认是IPv4和IPv6都解析 qtypes := []dnsmessage.Type{dnsmessage.TypeA, dnsmessage.TypeAAAA} // 根据network的不同可以只解析ipv4或者只解析ipv6 switch ipVersion(network) { case '4': qtypes = []dnsmessage.Type{dnsmessage.TypeA} case '6': qtypes = []dnsmessage.Type{dnsmessage.TypeAAAA} } // ipVersion returns the provided network's IP version: '4', '6' or 0 // if network does not end in a '4' or '6' byte. func ipVersion(network string) byte { if network == "" { return 0 } n := network[len(network)-1] if n != '4' && n != '6' { n = 0 } return n }
所以想要禁用IPv6解析的话就很容易了,我们只需要在建立连接的时候指定network类型。以http为例,重写Transport的DialContext方法,将原来的network(默认是tcp)强制写成tcp4。
&http.Client{ Transport: &http.Transport{ // .... DialContext: func(ctx context.Context, network, addr string) (net.Conn, error) { // 强制使用ipv4解析 return zeroDialer.DialContext(ctx, "tcp4", addr) }, } }
总结
- go默认使用内置dns解析器,不依赖操作系统,跟基础镜像无关
- go内置解析器会读取/etc/resov.conf配置,标准配置都有实现,手动修改配置5秒后生效
- Go1.17之后可以禁用ipv6解析
- go内置解析器解析过程默认是并行和串行结合的
- 相同域名的不同请求类型是并行的
- 不同域名之间是串行的
优化建议
修改ndots为合适的值
推荐部署 Nodelocal DNS Cache 扩展来解决这个问题,同时也提升 DNS 解析的性能
k8s中如何配置的dnsPolicy是ClusterFist,默认ndots会是5`
- 如果微服务之前请求使用的是service name,那么不需要修改(拼接搜索域名之后是可以成功解析的)
- 如果微服务之间请求使用的是域名(或者说拼接搜索域名之后一定解析不到的情况下),需要将ndots设置成合适值,目标是把原始域名放在前面解析(拼接搜索域名放在后面)
修改timeout为合适的值
go默认是5s,因为udp请求的不可靠性,一旦遇到丢包情况,就会让程序等到天荒地老
禁用Ipv6解析开启single-request
对于go内置解析器而言single-request和single-request-reopen是同一个意思,这决定了不同解析请求(A或者AAAA)是并发还是串行,默认是并行。如果禁用了IPv6,就没有并发解析的必要了,建议开始single-request
优化效果
dns解析只有有效的A记录查询了,世界突然安静了。