谈谈对SpringBoot的认识(Spring 和 Spring Boot 有什么区别?)
Spring框架是一个轻量级的企业级开发的一站式解决方案,提供了IoC容器、AOP、数据访问、Web开发、消息、测试等相关技术的支持,这些模块的出现,大大的缩短了应用程序的开发时间,同时提高了应用开发的效率。
Spring Boot 本质上是 Spring 框架的延伸和扩展,它的诞生目的是为了简化 Spring 框架初始搭建以及开发的过程,使用它可以不再依赖 Spring 应用程序中的 XML 配置,为更快、更高效的开发 Spring 提供更加有力的支持,是一种遵循“习惯优于配置”原则的框架。
Spring Boot有哪些优点(特性)?为什么要用Spring Boot?
1)更快速的构建能力,Spring Boot 提供了更多的 Starters 用于快速构建业务框架,Starters 可以理解为启动器,它包含了一系列可以集成到应用里面的依赖包,你可以一站式集成 Spring 及其他技术,而不需要到处找依赖包。
例如在 Spring 中如果要创建 Web 应用程序的最小依赖项为:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-web</artifactId>
<version>xxx</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>xxx</version>
</dependency>
而 Spring Boot 只需要一个依赖项就可以来启动和运行 Web 应用程序。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
当我们添加了 Starter 模块支持之后,在项目的构建期,它就会把所有其他依赖项将自动添加到项目中。
常见的 Starters 有以下几个:
spring-boot-starter-test
spring-boot-starter-web
spring-boot-starter-data-jpa
spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf
2)起步依赖,也就是在创建 Spring Boot 时可以直接勾选依赖模块,这样在项目初始化时就会把相关依赖直接添加到项目中,大大缩短了查询并添加依赖的时间。
3)内嵌容器支持,Spring Boot 内嵌了 Tomcat、Jetty、Undertow 三种容器,其默认嵌入的容器是 Tomcat,我们启动 Spring Boot 项目的时候,在控制台上就能看到。

我们可以通过修改 pom.xml 来移除内嵌的 Tomcat 更换为其他的容器,比如更换为 Jetty 容器,配置如下:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<!-- 移处 Tomcat -->
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<!-- 移处 jetty 容器 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jetty</artifactId>
</dependency>
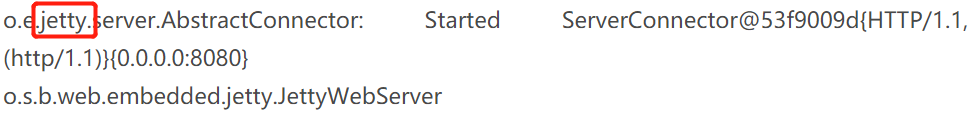
当我们添加完成之后,再重新生成 pom.xml 文件,然后再启动 Spring Boot 项目容器信息就为我们指定的Jetty 容器启动了,如下所示:
4)Actuator [ˈæktjuˌeɪtər] 监控,Spring Boot 自带了 Actuator 监控功能,主要用于提供对应用程序监控,以及控制的能力,比如监控应用程序的运行状况,或者内存、线程池、Http 请求统计等,同时还提供了关闭应用程序等功能。
Actuator 提供了 19 个接口,接口请求地址和代表含义如下表所示:

SpringBoot的核心注解是哪个?它主要由哪几个注解组成的?
SpringBoot的核心注解是@SpringBootApplication,由以下3个注解组成:
(1)@SpringBootConfiguration:它组合了Configuration注解实现了配置文件的功能。
(2)@EnableAutoConfiguration:打开自动配置功能,Spring Boot根据类路径中的jar包依赖为当前项目进行自动配置。例如,添加了spring-boot-starter-web依赖,会自动添加Tomcat和Spring MVC的依赖,那么Spring Boot会对Tomcat和Spring MVC进行自动配置。
(3)@ComponentScan:Spring扫描组件。

Spring Boot 的启动流程是怎么样的?
我们知道 Spring Boot 程序的入口是 SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args) 方法,那么就从 run() 方法开始分析吧,它的源码如下:
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) { // 1.创建并启动计时监控类 StopWatch = new StopWatch(); stopWatch.start(); // 2.声明应用上下文对象和异常报告集合 ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null; Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList(); // 3.设置系统属性 headless 的值 this.configureHeadlessProperty(); // 4.创建所有 Spring 运行监听器并发布应用启动事件 SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = this.getRunListeners(args); listeners.starting(); Collection exceptionReporters; try { // 5.处理 args 参数 ApplicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args); // 6.准备环境 ConfigurableEnvironment environment = this.prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments); this.configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment); // 7.创建 Banner 的打印类 Banner printedBanner = this.printBanner(environment); // 8.创建应用上下文 context = this.createApplicationContext(); // 9.实例化异常报告器 exceptionReporters = this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringBootExceptionReporter.class, new Class[]{ConfigurableApplicationContext.class}, context); // 10.准备应用上下文 this.prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner); // 11.刷新应用上下文 this.refreshContext(context); // 12.应用上下文刷新之后的事件的处理 this.afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments); // 13.停止计时监控类 stopWatch.stop(); // 14.输出日志记录执行主类名、时间信息 if (this.logStartupInfo) { (new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass)).logStarted(this.getApplicationLog(), stopWatch); } // 15.发布应用上下文启动完成事件 listeners.started(context); // 16.执行所有 Runner 运行器 this.callRunners(context, applicationArguments); } catch (Throwable var10) { this.handleRunFailure(context, var10, exceptionReporters, listeners); throw new IllegalStateException(var10); } try { // 17.发布应用上下文就绪事件 listeners.running(context); // 18.返回应用上下文对象 return context; } catch (Throwable var9) { this.handleRunFailure(context, var9, exceptionReporters, (SpringApplicationRunListeners)null); throw new IllegalStateException(var9); } }
从以上源码可以看出 Spring Boot 的启动总共分为以下 18 个步骤。
1.创建并启动计时监控类
此计时器是为了监控并记录 Spring Boot 应用启动的时间的,它会记录当前任务的名称,然后开启计时器。
2.声明应用上下文对象和异常报告集合
此过程声明了应用上下文对象和一个异常报告的 ArrayList 集合。
3.设置系统属性 headless 的值
设置 Java.awt.headless = true,其中 awt(Abstract Window Toolkit)的含义是抽象窗口工具集。设置为 true 表示运行一个 headless 服务器,可以用它来作一些简单的图像处理。
4.创建所有 Spring 运行监听器并发布应用启动事件
此过程用于获取配置的监听器名称并实例化所有的类。
5.初始化默认应用的参数类
也就是说声明并创建一个应用参数对象。
6.准备环境
创建配置并且绑定环境(通过 property sources 和 profiles 等配置文件)。
7.创建 Banner 的打印类
Spring Boot 启动时会打印 Banner 图片,如下图所示:

此 banner 信息是在 SpringBootBanner 类中定义的,我们可以通过实现 Banner 接口来自定义 banner 信息,然后通过代码 setBanner() 方法设置 Spring Boot 项目使用自己自定义 Banner 信息,或者是在 resources 下添加一个 banner.txt,把 banner 信息添加到此文件中,就可以实现自定义 banner 的功能了。
8.创建应用上下文
根据不同的应用类型来创建不同的 ApplicationContext 上下文对象。
9.实例化异常报告器
它调用的是 getSpringFactoriesInstances() 方法来获取配置异常类的名称,并实例化所有的异常处理类。
10.准备应用上下文
此方法的主要作用是把上面已经创建好的对象,传递给 prepareContext 来准备上下文,例如将环境变量 environment 对象绑定到上下文中、配置 bean 生成器以及资源加载器、记录启动日志等操作。
11.刷新应用上下文
此方法用于解析配置文件,加载 bean 对象,并且启动内置的 web 容器等操作。
12.应用上下文刷新之后的事件处理
这个方法的源码是空的,可以做一些自定义的后置处理操作。
13.停止计时监控类
停止此过程第一步中的程序计时器,并统计任务的执行信息。
14.输出日志信息
把相关的记录信息,如类名、时间等信息进行控制台输出。
15.发布应用上下文启动完成事件
触发所有 SpringApplicationRunListener 监听器的 started 事件方法。
16.执行所有 Runner 运行器
执行所有的 ApplicationRunner 和 CommandLineRunner 运行器。
17.发布应用上下文就绪事件
触发所有的 SpringApplicationRunListener 监听器的 running 事件。
18.返回应用上下文对象
到此为止 Spring Boot 的启动程序就结束了,我们就可以正常来使用 Spring Boot 框架了。
常见面试题:
(1)为什么现在越爱越多的公司用Spring Boot?(蓝月亮1年)
(2)SpringBoot的核心注解是哪个?它主要由哪几个注解组成的?(蓝月亮1年)
(3)Spring Boot 的启动流程是怎么样的?
参考好文:
(1)《Spring Boot实战》-- 汪云飞 编著
(2)拉钩教育 -- https://kaiwu.lagou.com/course/courseInfo.htm?courseId=59#/detail/pc?id=1774