这两周学习了巡风扫描器的搭建,也在学长的带领下看了各部分的下源代码,为了加深记忆,梳理一下巡风大体的工作流程,主要通过web端的页面分析,错误的地方还请大佬们多多指正。
整体看一下巡风的扫描流程:登陆->配置页面进行配置->到统计页面查看记录总数、IP总数、以及漏斗分析->到搜索页面输入搜索条件->选中一个或多个搜索结果,右上角新增任务->输入任务名称,选择插件->点击任务名称,即可查看任务详情
一:登陆页面
看一下后端的登陆函数,获取前端输入的用户名、密码,并通过app验证,app在__init.py__这个脚本里被初始化,是连接数据库的对象。
# 登录 @app.route('/login', methods=['get', 'post']) def Login(): if request.method == 'GET': return render_template('login.html') else: # 获取前端输入的用户名密码 account = request.form.get('account') password = request.form.get('password') if account == app.config.get('ACCOUNT') and password == app.config.get('PASSWORD'): session['login'] = 'loginsuccess' return redirect(url_for('Search')) else: return redirect(url_for('Login'))
二:配置页面
登录之后,点击配置页面,默认是爬虫引擎配置,还有一种是扫描引擎配置,后端是通过get请求的参数区分,在配置页面,可以自定义扫描方式、线程数、超时时间、资产列表等。更改配置后,后端通过UpdateConfig这个视图函数更新配置,
下面让看下每一项配置的作用:
资产探测周期配置:
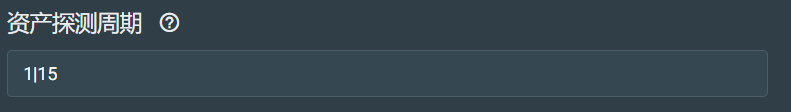
每天固定的时间点扫描,进行资产探测收集。
网络资产探测列表配置
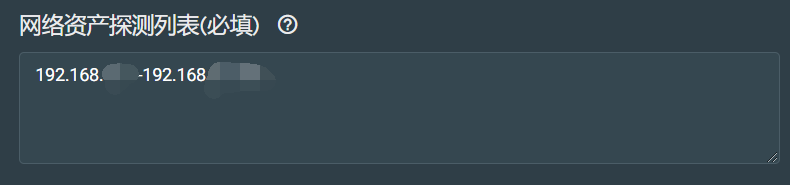
在这个地方,可以设置需要探测的内网的地址段,可以设置成图中格式,也可以设置成cidr(https://www.cnblogs.com/liangxiyang/p/11628000.html)地址格式,另外,探测列表一旦更改,则会立即触发扫描,进行资产收集。
启用MASSCAN

启用端口探测列表配置:

这两个配置都是用来探测端口的,默认是ICMP方式,只对存活的IP地址进行指定端口的探测,MASSCAN方式探测1-65535的端口,第一个方框内为路径地址,第二个方框内为发包速率。
服务类型识别配置:
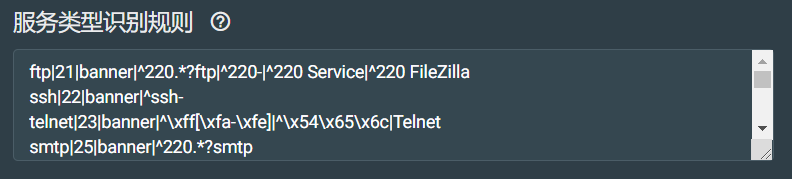
用于识别开放端口上所运营的服务。
cms识别规则配置:
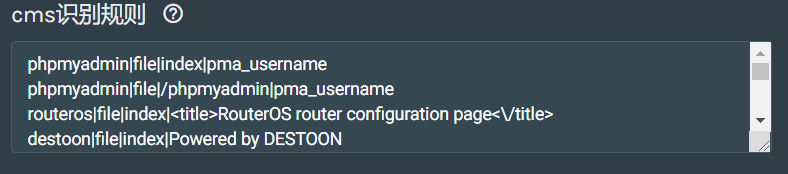
CMS英文全称是:Content Management System 中文名称是: 网站内容管理系统 (CMS最擅长的就是建设网站,最流行的CMS有:国外的:Wordpress,Drupal,Joomla,这是国外最流行的3大CMS。国内则是DedeCMS和帝国,PHPCMS等)。CMS识别原理就是得到一些CMS的一些固有特征,通过得到这个特征来判断CMS的类别。 比如使用MD5识别和正则表达式识别的方式,就是用特定的文件路径访问网站,获得这个文件的MD5或者用正则表达式匹配某个关键词,如果匹配成功就说明这个是这个CMS。 所以,这个识别的成功率是根据我们的字典来的。
代码语言识别规则配置:
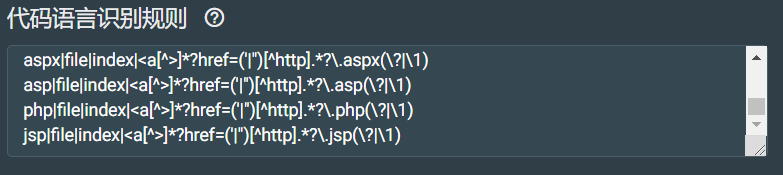
用于识别web网站的开发语言,通过响应头、文件等
组件容器识别配置:
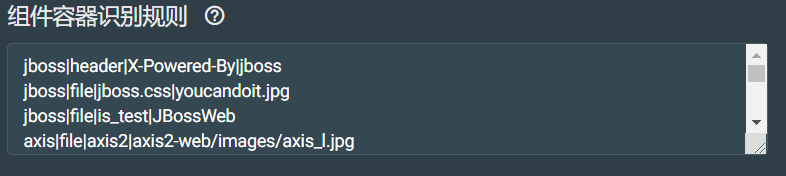
用于识别web的容器、中间件等组件。对容器、中间件等不了解,网上搜了一下:容器作为操作系统和应用程序之间的桥梁,给处于其中的应用程序组件提供一个环境,使应用程序直接跟容器中的环境变量交互,不必关注其它系统问题。
下面是配置更新页面的视图函数以及数据库里面的内容:

# 配置更新异步 @app.route('/updateconfig', methods=['get', 'post']) @logincheck def UpdateConfig(): rsp = 'fail' name = request.form.get('name', 'default') # 配置名 value = request.form.get('value', '') # 配置值 conftype = request.form.get('conftype', '') # 配置类型 print name," ",value," ",conftype # 根据name来判断是哪个配置,就从数据库去取对应的值,然后把提交过来的value加上去更新 # 如果三个值都存在 if name and value and conftype: # 判断所要更新的配置 # 端口列表或MAsscan配置 if name == 'Masscan' or name == 'Port_list': origin_value = Mongo.coll['Config'].find_one({'type': 'nascan'})["config"][name]["value"] value = origin_value.split('|')[0] + '|' + value # 判断是否启用存活探测ICMP elif name == 'Port_list_Flag': name = 'Port_list' origin_value = Mongo.coll['Config'].find_one({'type': 'nascan'})["config"]['Port_list']["value"] value = value + '|' + origin_value.split('|')[1] # 判断是否启用MASSCAN elif name == 'Masscan_Flag': name = 'Masscan' path = Mongo.coll['Config'].find_one({'type': 'nascan'})["config"]["Masscan"]["value"] if len(path.split('|')) == 3: path = path.split('|')[1] + "|" + path.split('|')[2] else: path = path.split('|')[1] if value == '1': value = '1|' + path else: value = '0|' + path result = Mongo.coll['Config'].update({"type": conftype}, {'$set': {'config.' + name + '.value': value}}) if result: rsp = 'success' return rsp
三:统计页面
配置页面完成后,立即开始进行资产探测、可以在统计页面看到资产探测结果(获取数据库数据并在前端进行展示):
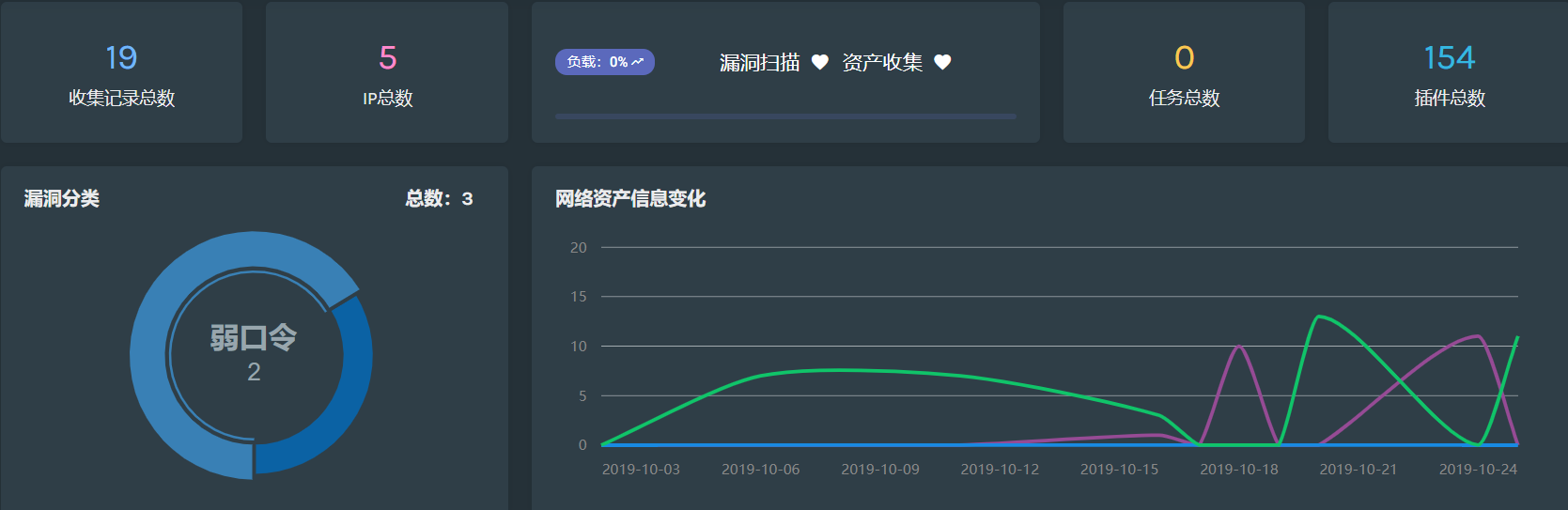
下面是加了注释的视图函数源码

# 统计页面 @app.route('/analysis') @logincheck def Analysis(): # distinct获取集合中指定字段的不重复值,以集合的形式返回,就是去重 ip = len(Mongo.coll['Info'].distinct('ip')) print 'ip总数', ip # 获取数量 record = Mongo.coll['Info'].find().count() print '记录总数', record # 获取任务数量 task = Mongo.coll['Task'].find().count() print '任务总数', task # group是mongodb中自带的三种聚合函数之一 # count:简单统计集合中符合某种条件的文档数量。 # distinct:用于对集合中的文档针进行去重处理。 # group:用于提供比count、distinct更丰富的统计需求,可以使用js函数控制统计逻辑 vul = int(Mongo.coll['Plugin'].group([], {}, {'count': 0},'function(doc,prev){prev.count = prev.count + doc.count}')[0]['count']) plugin = Mongo.coll['Plugin'].find().count() print "插件总数", plugin vultype = Mongo.coll['Plugin'].group(['type'], {"count":{"$ne":0}}, {'count': 0},'function(doc,prev){prev.count = prev.count + doc.count}') print "漏斗类型", vultype # sort根据date字段降序排列,limit指定读取的数据数量 cur = Mongo.coll['Statistics'].find().sort('date', -1).limit(30) trend = [] for i in cur: trend.append( {'time': i['date'], 'add': i['info']['add'], 'update': i['info']['update'], 'delete': i['info']['delete']}) # 找到Heartbeat集合中的两个文档 vulbeat = Mongo.coll['Heartbeat'].find_one({'name': 'load'}) scanbeat = Mongo.coll['Heartbeat'].find_one({'name': 'heartbeat'}) if vulbeat == None or scanbeat == None: taskpercent = 0 taskalive = False scanalive = False else: taskpercent = vulbeat['value'] * 100 taskalive = (datetime.now() - vulbeat['up_time']).seconds scanalive = (datetime.now() - scanbeat['up_time']).seconds taskalive = True if taskalive < 120 else False scanalive = True if scanalive < 120 else False # aggregate主要用于处理数据(诸如统计平均值,求和等),并返回计算后的数据结果。有点类似sql语句中的 count(*)。 server_type = Mongo.coll['Info'].aggregate( [{'$group': {'_id': '$server', 'count': {'$sum': 1}}}, {'$sort': {'count': -1}}]) web_type = Mongo.coll['Info'].aggregate([{'$match': {'server': 'web'}}, {'$unwind': '$webinfo.tag'}, {'$group': {'_id': '$webinfo.tag', 'count': {'$sum': 1}}}, {'$sort': {'count': -1}}]) #把数据传到analysis.html页面进行渲染 return render_template('analysis.html', ip=ip, record=record, task=task, vul=vul, plugin=plugin, vultype=vultype, trend=sorted(trend, key=lambda x: x['time']), taskpercent=taskpercent, taskalive=taskalive, scanalive=scanalive, server_type=server_type, web_type=web_type)
三:搜索页面
资产探测完成后,就可以根据搜索规则,搜索需要的端口,ip等。
比如:查看所有开放25端口的IP,在搜索框输入port:25。 查看指定IP、IP段等
前端输入搜索条件后,后端在search.html接受,并命名为q:
<input type="text" class="form-control" placeholder="Example: ip: 192.168.1.1; port: 22" style="color: #797979;" id="filter" name="q">
搜索完成后,会直接对结果展示
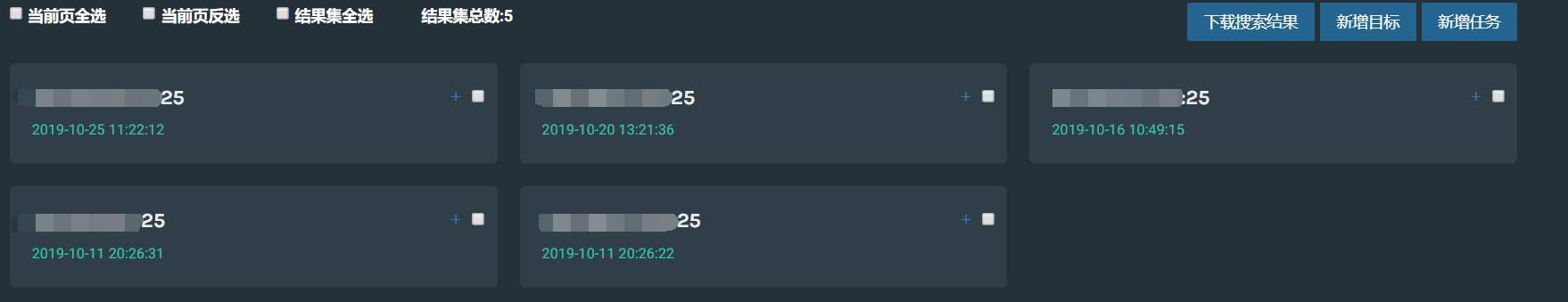
四:任务页面
搜索出结果后,可以选中其中的一个或多个(作为目标),然后新增任务,选择插件类型,根据选择的插件数量创建任务,后端就会进行任务扫面扫描,点击任务名称,即可查看该任务的详情。
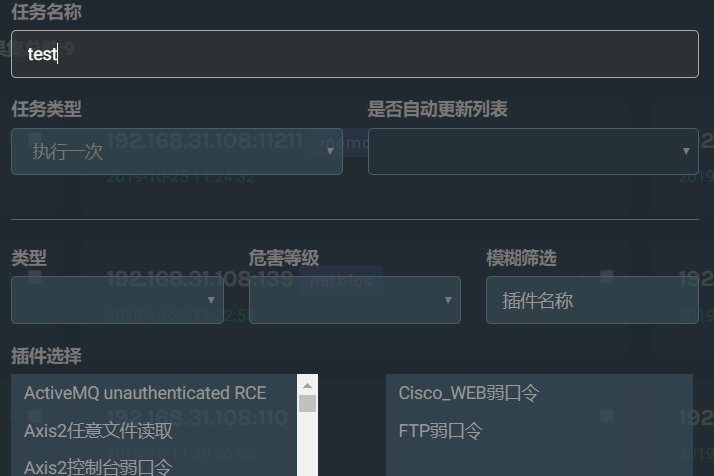
下面是加了注释的视图函数源码

# 新增任务异步 @app.route('/addtask', methods=['get', 'post']) @logincheck def Addtask(): # 先获取了页面传了的值 先默认result为fail # 没有plugin的话直接返回fail # 有的话,先判断结果集是否全选,将结果集的ip和port都加入列表,否则将当前页的ip将入列表。 title = request.form.get('title', '') # 任务名称 plugin = request.form.get('plugin', '') # 从插件列表里所选择的插件 condition = unquote(request.form.get('condition', '')) # 所选结果的ip地址 print 222222,condition plan = request.form.get('plan', 0) # 执行周期 print 33333,plan ids = request.form.get('ids', '') # 所选地址的 ip:端口 print 44444,ids isupdate = request.form.get('isupdate', '0') # 是否自动更新列表 resultcheck = request.form.get('resultcheck', '0') # 结果集是否全选 print title,plugin,condition,plan,ids,isupdate,resultcheck result = 'fail' if plugin: targets = [] if resultcheck == 'true': # 结果集全选 list = condition.strip().split(';') print list query = querylogic(list) cursor = Mongo.coll['Info'].find(query) for i in cursor: tar = [i['ip'], i['port']] targets.append(tar) else: # 当前页结果选择 for i in ids.split(','): tar = [i.split(':')[0], int(i.split(':')[1])] targets.append(tar) temp_result = True for p in plugin.split(','): query = querylogic(condition.strip().split(';')) item = {'status': 0, 'title': title, 'plugin': p, 'condition': condition, 'time': datetime.now(), 'target': targets, 'plan': int(plan), 'isupdate': int(isupdate), 'query': dumps(query)} # 插入到数据库 insert_reuslt = Mongo.coll['Task'].insert(item) if not insert_reuslt: temp_result = False if temp_result: result = 'success' return result
五:插件页面
插件的展示主要是获取数据库内容,并传到前端,主要看一下插件的增加

# 插件列表页 @app.route('/plugin') @logincheck def Plugin(): # 获取前端页面 page = int(request.args.get('page', '1')) print 1111,page # 从数据库里面找到有关插件数据 cursor = Mongo.coll['Plugin'].find().limit(page_size).skip((page - 1) * page_size) # 在前端页面展示 return render_template('plugin.html', cursor=cursor, vultype=cursor.distinct('type'), count=cursor.count())
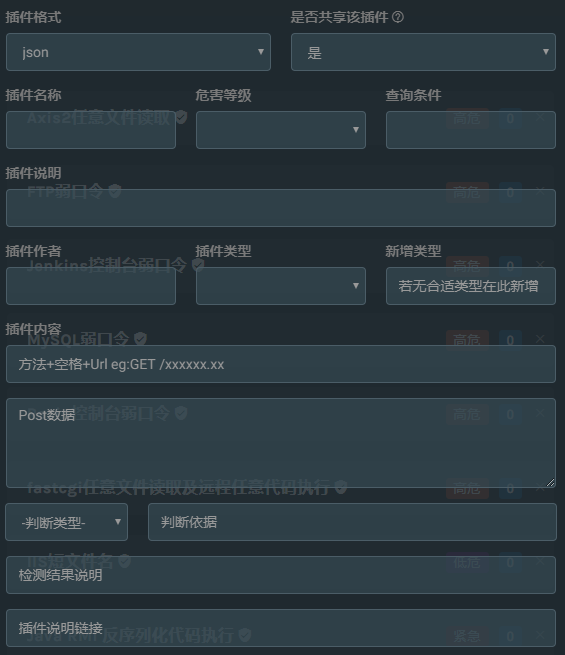
插件有两种格式,一是json格式,二是py脚本格式。
json格式的上传较为简单,只需要在前端填写对应的内容就行
而py脚本方式,则需要按指定的格式编写代码,大概如下:

def get_plugin_info(): plugin_info = { "name": "MySQL弱口令", "info": "导致数据库敏感信息泄露,严重可导致服务器直接被入侵。", "level": "高危", "type": "弱口令", "author": "wolf@YSRC", "url": "", "keyword": "server:mysql", "source": 1 } return plugin_info def get_hash(password, scramble): hash_stage1 = hashlib.sha1(password).digest() hash_stage2 = hashlib.sha1(hash_stage1).digest() to = hashlib.sha1(scramble + hash_stage2).digest() reply = [ord(h1) ^ ord(h3) for (h1, h3) in zip(hash_stage1, to)] hash = struct.pack('20B', *reply) return hash def get_scramble(packet): tmp = packet[15:] m = re.findall("x00?([x01-x7F]{7,})x00", tmp) if len(m) > 3: del m[0] scramble = m[0] + m[1] try: plugin = m[2] except: plugin = '' return plugin, scramble def get_auth_data(user, password, scramble, plugin): user_hex = binascii.b2a_hex(user) pass_hex = binascii.b2a_hex(get_hash(password, scramble)) if not password: data = "85a23f0000000040080000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000" + user_hex + "0000" else: data = "85a23f0000000040080000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000" + user_hex + "0014" + pass_hex if plugin: data += binascii.b2a_hex( plugin) + "0055035f6f73076f737831302e380c5f636c69656e745f6e616d65086c69626d7973716c045f7069640539323330360f5f636c69656e745f76657273696f6e06352e362e3231095f706c6174666f726d067838365f3634" len_hex = hex(len(data) / 2).replace("0x", "") auth_data = len_hex + "000001" + data return binascii.a2b_hex(auth_data) def check(ip, port, timeout): socket.setdefaulttimeout(timeout) user_list = ['root'] for user in user_list: for pass_ in PASSWORD_DIC: try: pass_ = str(pass_.replace('{user}', user)) sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM) sock.connect((ip, int(port))) packet = sock.recv(254) # print packet plugin, scramble = get_scramble(packet) auth_data = get_auth_data(user, pass_, scramble, plugin) sock.send(auth_data) result = sock.recv(1024) if result == "x07x00x00x02x00x00x00x02x00x00x00": return u"存在弱口令,账号:%s,密码:%s" % (user, pass_) except Exception, e: if "Errno 10061" in str(e) or "timed out" in str(e): return
其中get_plugin_info()与check()方法是必须的,用来获取插件信息和检查。
***************不积跬步无以至千里***************
