1.commonjs 模块管理
所有代码都运行在模块作用域,不会污染全局作用域。
模块可以多次加载,但是只会在第一次加载时运行一次,然后运行结果就被缓存了,以后再加载,就直接读取缓存结果。要想让模块再次运行,必须清除缓存。
模块加载的顺序,按照其在代码中出现的顺序。
2.module对象
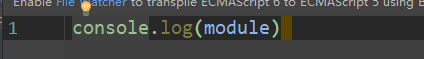

2.1 module.exports属性
module.exports属性表示当前模块对外输出的接口,其他文件加载该模块,实际上就是读取module.exports变量。
2.2 exports变量
为了方便,Node为每个模块提供一个exports变量,指向module.exports。这等同在每个模块头部,有一行这样的命令:
var exports = module.exports;(commonJS隐式做了这个赋值)
2.3 js文件就是一个函数
console.log(arguments) { '0': {}, '1': { [Function: require] resolve: { [Function: resolve] paths: [Function: paths] }, main: Module { id: '.', exports: {}, parent: null, filename: 'C:\Users\liang\Desktop\node\hello.js', loaded: false, children: [], paths: [Array] }, extensions: { '.js': [Function], '.json': [Function], '.node': [Function] }, cache: { 'C:UsersliangDesktop odehello.js': [Object] } }, '2': Module { id: '.', exports: {}, parent: null, filename: 'C:\Users\liang\Desktop\node\hello.js', loaded: false, children: [], paths: [ 'C:\Users\liang\Desktop\node\node_modules', 'C:\Users\liang\Desktop\node_modules', 'C:\Users\liang\node_modules', 'C:\Users\node_modules', 'C:\node_modules' ] }, '3': 'C:\Users\liang\Desktop\node\hello.js', '4': 'C:\Users\liang\Desktop\node' }
console.log(arguments.callee)
[Function]
console.log(arguments.length)
5
(function (exports, require, module, __filename, __dirname){})()
exports是module.exports的一个引用
require引用模块后,返回给调用者的是module.exports而不是exports
exports.xxx,相当于在导出对象上挂属性,该属性对调用模块直接可见
exports =相当于给exports对象重新赋值,调用模块不能访问exports对象及其属性
如果此模块是一个类,就应该直接赋值module.exports,这样调用者就是一个类构造器,可以直接new实例
这是两种暴漏的方式,都可以使用
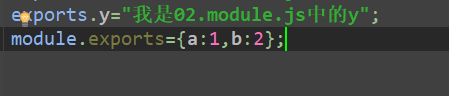
下面是引入方式,及结果
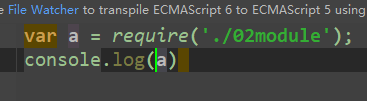
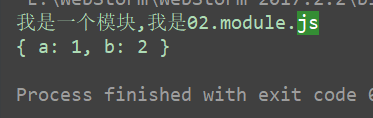
我们可以看成 exports = module.exports = {} 就是exports 指针指向module.exports的对象
关于rfequire 引入的返回值是module.exports

2.4 require 规则
(1)如果参数字符串以“/”开头,则表示加载的是一个位于绝对路径的模块文件。比如,require('/home/marco/foo.js')将加载/home/marco/foo.js。
(2)如果参数字符串以“./”开头,则表示加载的是一个位于相对路径(跟当前执行脚本的位置相比)的模块文件。比如,require('./circle')将加载当前脚本同一目录的circle.js。
(3)如果参数字符串不以“./“或”/“开头,则表示加载的是一个默认提供的核心模块(位于Node的系统安装目录中),或者一个位于各级node_modules目录的已安装模块(全局安装或局部安装)
(4)如果参数字符串不以“./“或”/“开头,而且是一个路径,比如require('example-module/path/to/file'),则将先找到example-module的位置,然后再以它为参数,找到后续路径。
(5)如果指定的模块文件没有发现,Node会尝试为文件名添加.js、.json、.node后,再去搜索。.js件会以文本格式的JavaScript脚本文件解析,.json文件会以JSON格式的文本文件解析,.node文件会以编译后的二进制文件解析。
(6)如果想得到require命令加载的确切文件名,使用require.resolve()方法。
2.5模块缓存
第一次加载某个模块时,Node会缓存该模块。以后再加载该模块,就直接从缓存取出该模块的module.exports属性。
require('./example.js');require('./example.js').message = "hello";require('./example.js').message// "hello"
上面代码中,连续三次使用require命令,加载同一个模块。第二次加载的时候,为输出的对象添加了一个message属性。但是第三次加载的时候,这个message属性依然存在,这就证明require命令并没有重新加载模块文件,而是输出了缓存。
如果想要多次执行某个模块,可以让该模块输出一个函数,然后每次require这个模块的时候,重新执行一下输出的函数。
所有缓存的模块保存在require.cache之中,如果想删除模块的缓存,可以像下面这样写。
2.6require.main
require.main === module// true