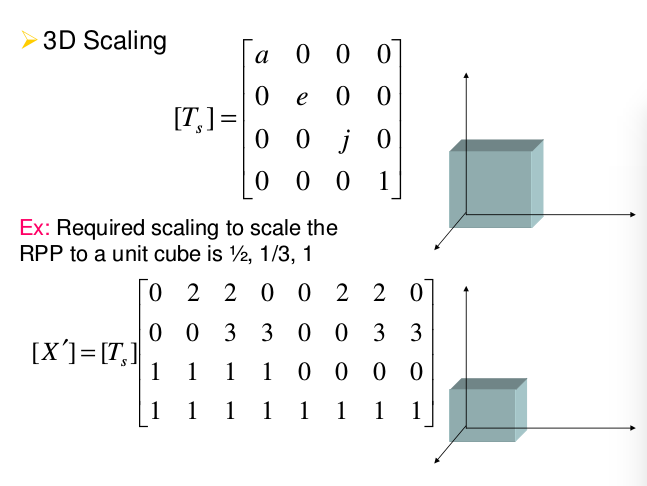
对点云的操作可以直接应用变换矩阵,即旋转,平移,尺度,3D的变换就是要使用4*4 的矩阵,例如:



等等模型
在这里直接使用程序开实现一个点云的旋转,新建文件matrix.cpp
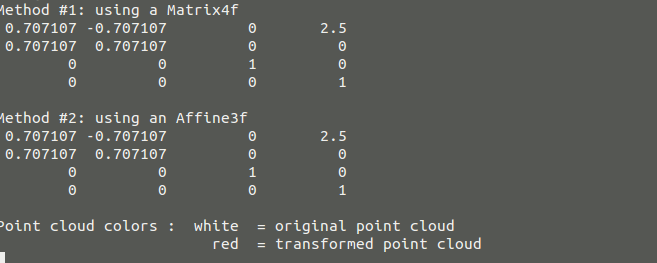
#include <iostream> #include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h> #include <pcl/io/ply_io.h> #include <pcl/point_cloud.h> #include <pcl/console/parse.h> #include <pcl/common/transforms.h> #include <pcl/visualization/pcl_visualizer.h> // 命令行的帮助提示 void showHelp(char * program_name) { std::cout << std::endl; std::cout << "Usage: " << program_name << " cloud_filename.[pcd|ply]" << std::endl; std::cout << "-h: Show this help." << std::endl; } int main (int argc, char** argv) { if (pcl::console::find_switch (argc, argv, "-h") || pcl::console::find_switch (argc, argv, "--help")) { showHelp (argv[0]); return 0; } // 读取文件 std::vector<int> filenames; bool file_is_pcd = false; filenames = pcl::console::parse_file_extension_argument (argc, argv, ".ply"); if (filenames.size () != 1) { filenames = pcl::console::parse_file_extension_argument (argc, argv, ".pcd"); if (filenames.size () != 1) { showHelp (argv[0]); return -1; } else { file_is_pcd = true; } } //载入文件 pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr source_cloud (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ> ()); if (file_is_pcd) { if (pcl::io::loadPCDFile (argv[filenames[0]], *source_cloud) < 0) { std::cout << "Error loading point cloud " << argv[filenames[0]] << std::endl << std::endl; showHelp (argv[0]); return -1; } } else { if (pcl::io::loadPLYFile (argv[filenames[0]], *source_cloud) < 0) { std::cout << "Error loading point cloud " << argv[filenames[0]] << std::endl << std::endl; showHelp (argv[0]); return -1; } } /* Reminder: how transformation matrices work : |-------> This column is the translation | 1 0 0 x | | 0 1 0 y | }-> The identity 3x3 matrix (no rotation) on the left | 0 0 1 z | / | 0 0 0 1 | -> We do not use this line (and it has to stay 0,0,0,1) METHOD #1: Using a Matrix4f This is the "manual" method, perfect to understand but error prone ! */ Eigen::Matrix4f transform_1 = Eigen::Matrix4f::Identity(); // Define a rotation matrix 定义旋转的角度 再有角度计算出旋转矩阵 float theta = M_PI/4; // The angle of rotation in radians transform_1 (0,0) = cos (theta); transform_1 (0,1) = -sin(theta); transform_1 (1,0) = sin (theta); transform_1 (1,1) = cos (theta); // (row, column) // Define a translation of 2.5 meters on the x axis. transform_1 (0,3) = 2.5;//意思就是在第一行第四个元素的值为2.5,也就是在x轴的平移为2.5 // Print the transformation 打印出这个变换矩阵 printf ("Method #1: using a Matrix4f "); std::cout << transform_1 << std::endl; /* METHOD #2: Using a Affine3f 第二种方案 This method is easier and less error prone 更简单的方案 */ Eigen::Affine3f transform_2 = Eigen::Affine3f::Identity(); // Define a translation of 2.5 meters on the x axis. transform_2.translation() << 2.5, 0.0, 0.0; // The same rotation matrix as before; theta radians arround Z axis transform_2.rotate (Eigen::AngleAxisf (theta, Eigen::Vector3f::UnitZ())); // Print the transformation printf (" Method #2: using an Affine3f "); std::cout << transform_2.matrix() << std::endl; // Executing the transformation pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr transformed_cloud (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ> ()); // 你可以使用 transform_1 或者 transform_2;效果都是一样的 pcl::transformPointCloud (*source_cloud, *transformed_cloud, transform_2); // 可视化的 printf( " Point cloud colors : white = original point cloud " " red = transformed point cloud "); pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer viewer ("Matrix transformation example"); // 为点云设置RGB的值 pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<pcl::PointXYZ> source_cloud_color_handler (source_cloud, 255, 255, 255); // We add the point cloud to the viewer and pass the color handler viewer.addPointCloud (source_cloud, source_cloud_color_handler, "original_cloud"); pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<pcl::PointXYZ> transformed_cloud_color_handler (transformed_cloud, 230, 20, 20); // Red viewer.addPointCloud (transformed_cloud, transformed_cloud_color_handler, "transformed_cloud"); viewer.addCoordinateSystem (1.0, 0); viewer.setBackgroundColor(0.05, 0.05, 0.05, 0); //设置背景颜色 viewer.setPointCloudRenderingProperties (pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 2, "original_cloud"); viewer.setPointCloudRenderingProperties (pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 2, "transformed_cloud"); //viewer.setPosition(800, 400); // Setting visualiser window position while (!viewer.wasStopped ()) { // Display the visualiser until 'q' key is pressed viewer.spinOnce (); } return 0; }
编译后我们随便找一个PCD文件查看效果,也可以该程序的参数,查看不同的参数的结果
命令窗口打印的结果
可视化的结果

(2)移除 NaNs:
从传感器获得的点云可能包含几种测量误差和/或不准确。其中之一是在一些点的坐标中存在NaN(不是数)值,正如你在下面的文件中看到的那样:
# .PCD v0.7 - Point Cloud Data file format VERSION 0.7 FIELDS x y z rgba SIZE 4 4 4 4 TYPE F F F U COUNT 1 1 1 1 WIDTH 640 HEIGHT 480 VIEWPOINT 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 POINTS 307200 DATA ascii nan nan nan 10135463 nan nan nan 10398635 nan nan nan 10070692 nan nan nan 10268071 ...
点云对象的成员函数有称为“is_dense()”,如果所有的点都有效的返回true是为有限值。一个NaNs表明测量传感器距离到该点的距离值是有问题的,可能是因为传感器太近或太远,或者因为表面反射。那么当存在无效点云的NaNs值作为算法的输入的时候,可能会引起很多问题,比如“"Assertion `point_representation_->isValid (point) && "Invalid (NaN, Inf) point coordinates given to radiusSearch!"' failed."”如果发生这样的错误就要移除这些点,那么下面就是为了解决移除无效点的程序
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h> #include <pcl/filters/filter.h> #include <iostream> #include <pcl/visualization/cloud_viewer.h> int main(int argc,char** argv) { if(argc !=3) { std::cout <<" Usage: "<<argv[0] <<"<input cloud> <output cloud>" <<std::endl; return -1; } //object for string the point cloud pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZRGBA>::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZRGBA>); //read a PCDfile from disk if(pcl::io::loadPCDFile<pcl::PointXYZRGBA>(argv[1],*cloud) !=0) { return -1; } //the mapping tells you to that points of the oldcloud the new ones correspond //but we will not use it std::vector<int> mapping; pcl::removeNaNFromPointCloud(*cloud, *cloud, mapping); //pcl::removeNaNFromPointCloud(*cloud, *cloud, mapping); //save it back pcl::io::savePCDFileASCII(argv[2],*cloud); pcl::visualization::CloudViewer viewer(argv[2]); viewer.showCloud(cloud); while (!viewer.wasStopped()) { // Do nothing but wait. } }
然后可以显示移除NaNs点后的可视图,

这张点云是我自己用kinect 生成的点云,在没有移除NaNs的时候可以先读取以下,显示他的点云数值在命令窗口,你会发现会有很多的NaNs的无效点,经过
移除这些点之后在read一些打印处的结果就不会存在NaNs的无效点,这样在后期的使用算法的时候就不会出现错误了。

这种方法的问题是它不会保持点云仍然是有序点云。所有的点云都存储一个“宽度”和“高度”变量。在无序点云,总数为宽度相同,而高度设置为1。在有序的点云(像从相机拍摄像传感器如Kinect或Xtion的),宽度和高度都相同的像素的图像分辨率传感器的工作。点云分布在深度图像的行中,每一个点对应一个像素。成员函数”isorganized()”如果高度大于1时返回真。
由于移除NaNs无效点会改变点云的点的数量,它不再能保持组织与原来的宽高比,所以函数将设置高度1。这不是一个大问题,只有少数的PCL的算法工作明确要求是有序的点云(大多这样情况下会使用在优化上),但你必须考虑其中的影响。
暂时就到这里了。。。。。。
微信公众号号可扫描二维码一起共同学习交流
