(1)点云到深度图与可视化的实现
区分点云与深度图本质的区别
1.深度图像也叫距离影像,是指将从图像采集器到场景中各点的距离(深度)值作为像素值的图像。获取方法有:激光雷达深度成像法、计算机立体视觉成像、坐标测量机法、莫尔条纹法、结构光法。
2.点云:当一束激光照射到物体表面时,所反射的激光会携带方位、距离等信息。若将激光束按照某种轨迹进行扫描,便会边扫描边记录到反射的激光点信息,由
于扫描极为精细,则能够得到大量的激光点,因而就可形成激光点云。点云格式有*.las ;*.pcd; *.txt等。
深度图像经过坐标转换可以计算为点云数据;有规则及必要信息的点云数据可以反算为深度图像
rangeimage是来自传感器一个特定角度拍摄的一个三维场景获取的有规则的有焦距等基本信息的深度图。
深度图像的像素值代表从传感器到物体的距离或者深度值。
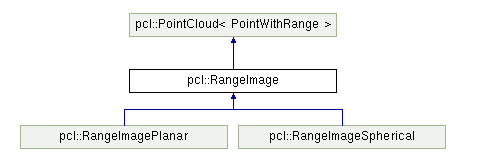
RangeImage类的继承于PointCloud主要的功能实现一个特定的视点得到的一个三维场景的深度图像,继承关系为
所以我们知道有规则及必要信息就可以反算为深度图像。那么我们就可以直接创建一个有序的规则的点云,比如一张平面,或者我们直接使用Kinect获取的点云来可视化深度的图,所以首先分析程序中是如果实现的点云到深度图的转变的,(程序的注释是我自己的理解,注释的比较详细)
#include <iostream> #include <boost/thread/thread.hpp> #include <pcl/common/common_headers.h> #include <pcl/range_image/range_image.h> //关于深度图像的头文件 #include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h> #include <pcl/visualization/range_image_visualizer.h> //深度图可视化的头文件 #include <pcl/visualization/pcl_visualizer.h> //PCL可视化的头文件 #include <pcl/console/parse.h> typedef pcl::PointXYZ PointType; //参数 float angular_resolution_x = 0.5f,//angular_resolution为模拟的深度传感器的角度分辨率,即深度图像中一个像素对应的角度大小 angular_resolution_y = angular_resolution_x; pcl::RangeImage::CoordinateFrame coordinate_frame = pcl::RangeImage::CAMERA_FRAME;//深度图像遵循坐标系统 bool live_update = false; //命令帮助提示 void printUsage (const char* progName) { std::cout << " Usage: "<<progName<<" [options] <scene.pcd> " << "Options: " << "------------------------------------------- " << "-rx <float> angular resolution in degrees (default "<<angular_resolution_x<<") " << "-ry <float> angular resolution in degrees (default "<<angular_resolution_y<<") " << "-c <int> coordinate frame (default "<< (int)coordinate_frame<<") " << "-l live update - update the range image according to the selected view in the 3D viewer. " << "-h this help " << " "; } void setViewerPose (pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer& viewer, const Eigen::Affine3f& viewer_pose) { Eigen::Vector3f pos_vector = viewer_pose * Eigen::Vector3f(0, 0, 0); Eigen::Vector3f look_at_vector = viewer_pose.rotation () * Eigen::Vector3f(0, 0, 1) + pos_vector; Eigen::Vector3f up_vector = viewer_pose.rotation () * Eigen::Vector3f(0, -1, 0); viewer.setCameraPosition (pos_vector[0], pos_vector[1], pos_vector[2], look_at_vector[0], look_at_vector[1], look_at_vector[2], up_vector[0], up_vector[1], up_vector[2]); } //主函数 int main (int argc, char** argv) { //输入命令分析 if (pcl::console::find_argument (argc, argv, "-h") >= 0) { printUsage (argv[0]); return 0; } if (pcl::console::find_argument (argc, argv, "-l") >= 0) { live_update = true; std::cout << "Live update is on. "; } if (pcl::console::parse (argc, argv, "-rx", angular_resolution_x) >= 0) std::cout << "Setting angular resolution in x-direction to "<<angular_resolution_x<<"deg. "; if (pcl::console::parse (argc, argv, "-ry", angular_resolution_y) >= 0) std::cout << "Setting angular resolution in y-direction to "<<angular_resolution_y<<"deg. "; int tmp_coordinate_frame; if (pcl::console::parse (argc, argv, "-c", tmp_coordinate_frame) >= 0) { coordinate_frame = pcl::RangeImage::CoordinateFrame (tmp_coordinate_frame); std::cout << "Using coordinate frame "<< (int)coordinate_frame<<". "; } angular_resolution_x = pcl::deg2rad (angular_resolution_x); angular_resolution_y = pcl::deg2rad (angular_resolution_y); //读取点云PCD文件 如果没有输入PCD文件就生成一个点云 pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::Ptr point_cloud_ptr (new pcl::PointCloud<PointType>); pcl::PointCloud<PointType>& point_cloud = *point_cloud_ptr; Eigen::Affine3f scene_sensor_pose (Eigen::Affine3f::Identity ()); //申明传感器的位置是一个4*4的仿射变换 std::vector<int> pcd_filename_indices = pcl::console::parse_file_extension_argument (argc, argv, "pcd"); if (!pcd_filename_indices.empty ()) { std::string filename = argv[pcd_filename_indices[0]]; if (pcl::io::loadPCDFile (filename, point_cloud) == -1) { std::cout << "Was not able to open file ""<<filename<<"". "; printUsage (argv[0]); return 0; } //给传感器的位姿赋值 就是获取点云的传感器的的平移与旋转的向量 scene_sensor_pose = Eigen::Affine3f (Eigen::Translation3f (point_cloud.sensor_origin_[0], point_cloud.sensor_origin_[1], point_cloud.sensor_origin_[2])) * Eigen::Affine3f (point_cloud.sensor_orientation_); } else { //如果没有给点云,则我们要自己生成点云 std::cout << " No *.pcd file given => Genarating example point cloud. "; for (float x=-0.5f; x<=0.5f; x+=0.01f) { for (float y=-0.5f; y<=0.5f; y+=0.01f) { PointType point; point.x = x; point.y = y; point.z = 2.0f - y; point_cloud.points.push_back (point); } } point_cloud.width = (int) point_cloud.points.size (); point_cloud.height = 1; } // -----从创建的点云中获取深度图--// //设置基本参数 float noise_level = 0.0; float min_range = 0.0f; int border_size = 1; boost::shared_ptr<pcl::RangeImage> range_image_ptr(new pcl::RangeImage); pcl::RangeImage& range_image = *range_image_ptr; /* 关于range_image.createFromPointCloud()参数的解释 (涉及的角度都为弧度为单位) : point_cloud为创建深度图像所需要的点云 angular_resolution_x深度传感器X方向的角度分辨率 angular_resolution_y深度传感器Y方向的角度分辨率 pcl::deg2rad (360.0f)深度传感器的水平最大采样角度 pcl::deg2rad (180.0f)垂直最大采样角度 scene_sensor_pose设置的模拟传感器的位姿是一个仿射变换矩阵,默认为4*4的单位矩阵变换 coordinate_frame定义按照那种坐标系统的习惯 默认为CAMERA_FRAME noise_level 获取深度图像深度时,邻近点对查询点距离值的影响水平 min_range 设置最小的获取距离,小于最小的获取距离的位置为传感器的盲区 border_size 设置获取深度图像边缘的宽度 默认为0 */ range_image.createFromPointCloud (point_cloud, angular_resolution_x, angular_resolution_y,pcl::deg2rad (360.0f), pcl::deg2rad (180.0f),scene_sensor_pose, coordinate_frame, noise_level, min_range, border_size); //可视化点云 pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer viewer ("3D Viewer"); viewer.setBackgroundColor (1, 1, 1); pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<pcl::PointWithRange> range_image_color_handler (range_image_ptr, 0, 0, 0); viewer.addPointCloud (range_image_ptr, range_image_color_handler, "range image"); viewer.setPointCloudRenderingProperties (pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 1, "range image"); //viewer.addCoordinateSystem (1.0f, "global"); //PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<PointType> point_cloud_color_handler (point_cloud_ptr, 150, 150, 150); //viewer.addPointCloud (point_cloud_ptr, point_cloud_color_handler, "original point cloud"); viewer.initCameraParameters (); //range_image.getTransformationToWorldSystem ()的作用是获取从深度图像坐标系统(应该就是传感器的坐标)转换为世界坐标系统的转换矩阵 setViewerPose(viewer, range_image.getTransformationToWorldSystem ()); //设置视点的位置 //可视化深度图 pcl::visualization::RangeImageVisualizer range_image_widget ("Range image"); range_image_widget.showRangeImage (range_image); while (!viewer.wasStopped ()) { range_image_widget.spinOnce (); viewer.spinOnce (); pcl_sleep (0.01); if (live_update) { //如果选择的是——l的参数说明就是要根据自己选择的视点来创建深度图。 // live update - update the range image according to the selected view in the 3D viewer. scene_sensor_pose = viewer.getViewerPose(); range_image.createFromPointCloud (point_cloud, angular_resolution_x, angular_resolution_y, pcl::deg2rad (360.0f), pcl::deg2rad (180.0f), scene_sensor_pose, pcl::RangeImage::LASER_FRAME, noise_level, min_range, border_size); range_image_widget.showRangeImage (range_image); } } }
在代码利解释的十分详细,编译查看结果

没有输入PCD点云文件的结果

输入点云的原始图

输入的结果及其深度图
(2)如何从深度图像中提取边界
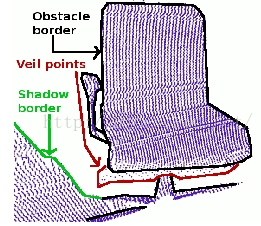
从深度图像中提取边界(从前景跨越到背景的位置定义为边界),对于物体边界:这是物体的最外层和阴影边界的可见点集,阴影边界:毗邻与遮挡的背景上的点集,Veil点集,在被遮挡物边界和阴影边界之间的内插点,它们是有激光雷达获取的3D距离数据中的典型数据类型,这三类数据及深度图像的边界如图:
代码解析:从磁盘中读取点云,创建深度图像并使其可视化,提取边界信息很重要的一点就是区分深度图像中当前视点不可见点几何和应该可见但处于传感器获取距离范围之外的点集 ,后者可以标记为典型边界,然而当前视点不可见点则不能成为边界,因此,如果后者的测量值存在,则提供那些超出传感器距离获取范围之外的数据对于边界的提取是非常重要的,
新建文件range_image_border_extraction.cpp:
#include <iostream> #include <boost/thread/thread.hpp> #include <pcl/range_image/range_image.h> #include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h> #include <pcl/visualization/range_image_visualizer.h> #include <pcl/visualization/pcl_visualizer.h> #include <pcl/features/range_image_border_extractor.h> #include <pcl/console/parse.h> typedef pcl::PointXYZ PointType; // -------------------- // -----Parameters----- // -------------------- float angular_resolution = 0.5f; pcl::RangeImage::CoordinateFrame coordinate_frame = pcl::RangeImage::CAMERA_FRAME; bool setUnseenToMaxRange = false; // -------------- // -----Help----- // -------------- void printUsage (const char* progName) { std::cout << " Usage: "<<progName<<" [options] <scene.pcd> " << "Options: " << "------------------------------------------- " << "-r <float> angular resolution in degrees (default "<<angular_resolution<<") " << "-c <int> coordinate frame (default "<< (int)coordinate_frame<<") " << "-m Treat all unseen points to max range " << "-h this help " << " "; } // -------------- // -----Main----- // -------------- int main (int argc, char** argv) { // -------------------------------------- // -----Parse Command Line Arguments----- // -------------------------------------- if (pcl::console::find_argument (argc, argv, "-h") >= 0) { printUsage (argv[0]); return 0; } if (pcl::console::find_argument (argc, argv, "-m") >= 0) { setUnseenToMaxRange = true; cout << "Setting unseen values in range image to maximum range readings. "; } int tmp_coordinate_frame; if (pcl::console::parse (argc, argv, "-c", tmp_coordinate_frame) >= 0) { coordinate_frame = pcl::RangeImage::CoordinateFrame (tmp_coordinate_frame); cout << "Using coordinate frame "<< (int)coordinate_frame<<". "; } if (pcl::console::parse (argc, argv, "-r", angular_resolution) >= 0) cout << "Setting angular resolution to "<<angular_resolution<<"deg. "; angular_resolution = pcl::deg2rad (angular_resolution); // ------------------------------------------------------------------ // -----Read pcd file or create example point cloud if not given----- // ------------------------------------------------------------------ pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::Ptr point_cloud_ptr (new pcl::PointCloud<PointType>); pcl::PointCloud<PointType>& point_cloud = *point_cloud_ptr; pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointWithViewpoint> far_ranges; Eigen::Affine3f scene_sensor_pose (Eigen::Affine3f::Identity ()); //传感器的位置 std::vector<int> pcd_filename_indices = pcl::console::parse_file_extension_argument (argc, argv, "pcd"); if (!pcd_filename_indices.empty ()) { std::string filename = argv[pcd_filename_indices[0]]; if (pcl::io::loadPCDFile (filename, point_cloud) == -1) //打开文件 { cout << "Was not able to open file ""<<filename<<"". "; printUsage (argv[0]); return 0; } scene_sensor_pose = Eigen::Affine3f (Eigen::Translation3f (point_cloud.sensor_origin_[0], point_cloud.sensor_origin_[1], point_cloud.sensor_origin_[2])) * Eigen::Affine3f (point_cloud.sensor_orientation_); //仿射变换矩阵 std::string far_ranges_filename = pcl::getFilenameWithoutExtension (filename)+"_far_ranges.pcd"; if (pcl::io::loadPCDFile(far_ranges_filename.c_str(), far_ranges) == -1) std::cout << "Far ranges file ""<<far_ranges_filename<<"" does not exists. "; } else { cout << " No *.pcd file given => Genarating example point cloud. "; for (float x=-0.5f; x<=0.5f; x+=0.01f) //填充一个矩形的点云 { for (float y=-0.5f; y<=0.5f; y+=0.01f) { PointType point; point.x = x; point.y = y; point.z = 2.0f - y; point_cloud.points.push_back (point); } } point_cloud.width = (int) point_cloud.points.size (); point_cloud.height = 1; } // ----------------------------------------------- // -----Create RangeImage from the PointCloud----- // ----------------------------------------------- float noise_level = 0.0; //各种参数的设置 float min_range = 0.0f; int border_size = 1; boost::shared_ptr<pcl::RangeImage> range_image_ptr (new pcl::RangeImage); pcl::RangeImage& range_image = *range_image_ptr; range_image.createFromPointCloud (point_cloud, angular_resolution, pcl::deg2rad (360.0f), pcl::deg2rad (180.0f), scene_sensor_pose, coordinate_frame, noise_level, min_range, border_size); range_image.integrateFarRanges (far_ranges); if (setUnseenToMaxRange) range_image.setUnseenToMaxRange (); // -------------------------------------------- // -----Open 3D viewer and add point cloud----- // -------------------------------------------- pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer viewer ("3D Viewer"); //创建视口 viewer.setBackgroundColor (1, 1, 1); //设置背景颜色 viewer.addCoordinateSystem (1.0f); //设置坐标系 pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<PointType> point_cloud_color_handler (point_cloud_ptr, 0, 0, 0); viewer.addPointCloud (point_cloud_ptr, point_cloud_color_handler, "original point cloud"); //添加点云 //PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<pcl::PointWithRange> range_image_color_handler (range_image_ptr, 150, 150, 150); //viewer.addPointCloud (range_image_ptr, range_image_color_handler, "range image"); //viewer.setPointCloudRenderingProperties (PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 2, "range image"); // ------------------------- // -----Extract borders提取边界的部分----- // ------------------------- pcl::RangeImageBorderExtractor border_extractor (&range_image); pcl::PointCloud<pcl::BorderDescription> border_descriptions; border_extractor.compute (border_descriptions); //提取边界计算描述子 // ------------------------------------------------------- // -----Show points in 3D viewer在3D 视口中显示点云----- // ---------------------------------------------------- pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointWithRange>::Ptr border_points_ptr(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointWithRange>), //物体边界 veil_points_ptr(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointWithRange>), //veil边界 shadow_points_ptr(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointWithRange>); //阴影边界 pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointWithRange>& border_points = *border_points_ptr, & veil_points = * veil_points_ptr, & shadow_points = *shadow_points_ptr; for (int y=0; y< (int)range_image.height; ++y) { for (int x=0; x< (int)range_image.width; ++x) { if (border_descriptions.points[y*range_image.width + x].traits[pcl::BORDER_TRAIT__OBSTACLE_BORDER]) border_points.points.push_back (range_image.points[y*range_image.width + x]); if (border_descriptions.points[y*range_image.width + x].traits[pcl::BORDER_TRAIT__VEIL_POINT]) veil_points.points.push_back (range_image.points[y*range_image.width + x]); if (border_descriptions.points[y*range_image.width + x].traits[pcl::BORDER_TRAIT__SHADOW_BORDER]) shadow_points.points.push_back (range_image.points[y*range_image.width + x]); } } pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<pcl::PointWithRange> border_points_color_handler (border_points_ptr, 0, 255, 0); viewer.addPointCloud<pcl::PointWithRange> (border_points_ptr, border_points_color_handler, "border points"); viewer.setPointCloudRenderingProperties (pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 7, "border points"); pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<pcl::PointWithRange> veil_points_color_handler (veil_points_ptr, 255, 0, 0); viewer.addPointCloud<pcl::PointWithRange> (veil_points_ptr, veil_points_color_handler, "veil points"); viewer.setPointCloudRenderingProperties (pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 7, "veil points"); pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<pcl::PointWithRange> shadow_points_color_handler (shadow_points_ptr, 0, 255, 255); viewer.addPointCloud<pcl::PointWithRange> (shadow_points_ptr, shadow_points_color_handler, "shadow points"); viewer.setPointCloudRenderingProperties (pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 7, "shadow points"); //------------------------------------- // -----Show points on range image----- // ------------------------------------ pcl::visualization::RangeImageVisualizer* range_image_borders_widget = NULL; range_image_borders_widget = pcl::visualization::RangeImageVisualizer::getRangeImageBordersWidget (range_image, -std::numeric_limits<float>::infinity (), std::numeric_limits<float>::infinity (), false, border_descriptions, "Range image with borders"); // ------------------------------------- //-------------------- // -----Main loop----- //-------------------- while (!viewer.wasStopped ()) { range_image_borders_widget->spinOnce (); viewer.spinOnce (); pcl_sleep(0.01); } }
编译的运行的结果./range_image_border_extraction -m

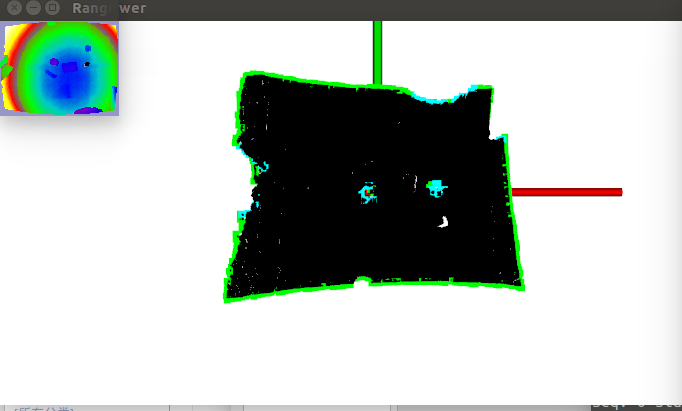
这将一个自定生成的,矩形状浮点型点云,有显示结果可以看出检测出的边界用绿色较大的点表示,其他的点用默认的普通的大小点来表示.
因为有人问我为什么使用其他的PCD文件来运行这个程序的时候会提示 Far ranges file far_ranges_filename does not exists 这是因为在深度传感器得带深度图像并可视化图像的时候,我们都知道传感器的测量距离受硬件的限制,所以在这里就是要定义传感器看不到的距离,所以当我们自己使用kinect获取深度图像运行这个程序的时候直接使用命令
./range_image_border_extraction -m out0.pcd 使用-m的原因是要设置传感器看不见的位置 Setting unseen values in range image to maximum range readings
那么对于我们使用自己使用的PCD文件并且设置 -m后的一个结果比如
忘了宣传我的微信公众号了,所以微信里会有更多的人分享,同时也希望积极关注分享你的学习

未完待续*****************8888888