filter是过滤的意思:在web开发中,是请求会先到过滤器,然后由过滤器再转发到具体的借口上去,此时过滤器就可以对捕捉到的请求作出适当的逻辑了。
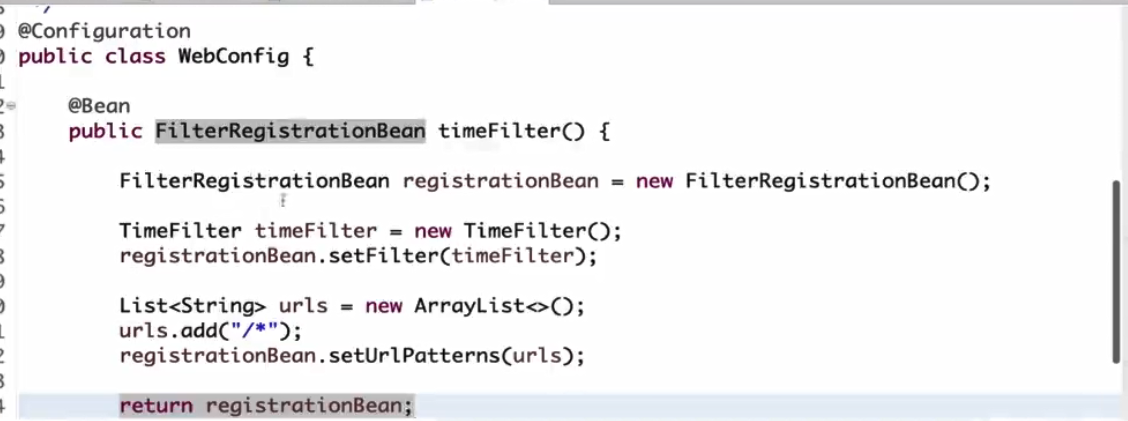
一般如果用第三方的filter但是此filter又不是专门服务于spring开发环境,此时就不会被扫描到,因此需要加个@Configuration注解,有了此注解spring会在启动之初就去加载该filter这和以前在spring.xml中配置创建类是一样的效果,urls是指定要过滤那些请求,没有指定的则直接去访问不需要过滤器。
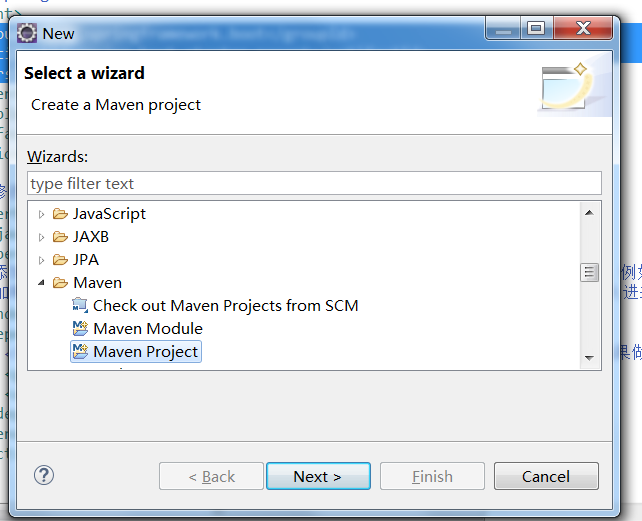
创建一个maven项目,然后此项目继承一个父项目:org.springframework.boot
1.创建一个maven项目:
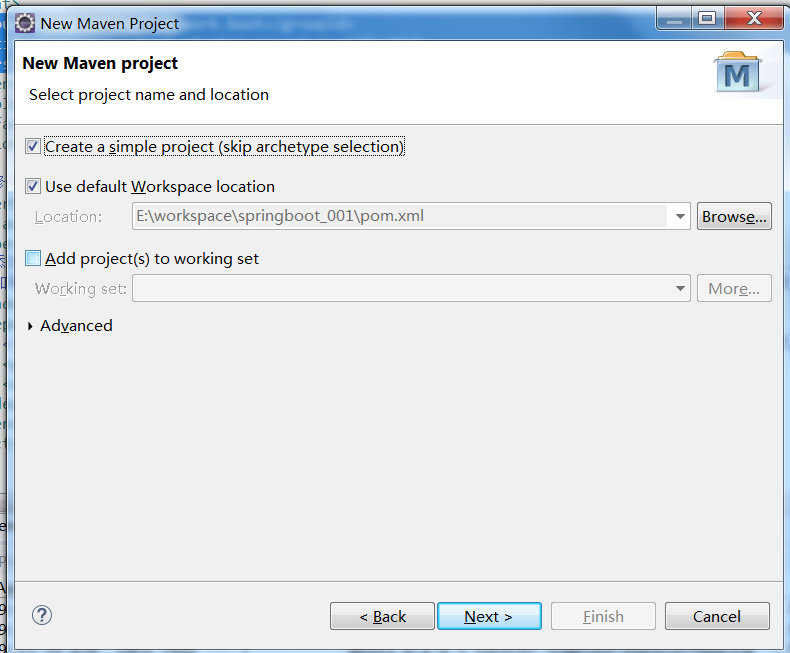
2.点击next后配置父项目及版本号
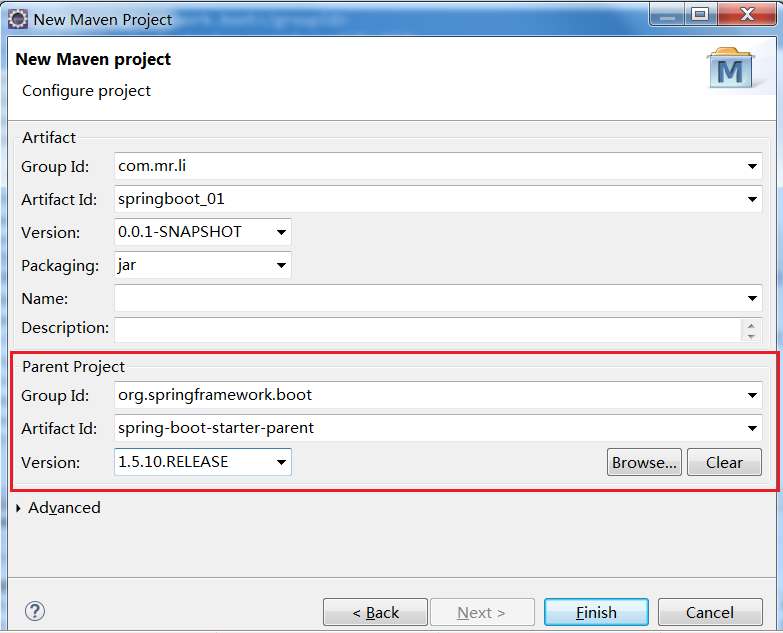
3.点击finish后就可查看pom.xml文件中已经有父级项目了。
好了,创建项目演示已经做完,现在粘贴整个各个组件的代码:说明在注释中
1.启动类:
package com.mr.li; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.FilterRegistrationBean; import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.ServletComponentScan; import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.ServletListenerRegistrationBean; /** * 启动类: * 1.@springBootApplication:表示此类是spring boot的启动类. * 2.@ServletComponentScan:此注解的意思是在spring boot启动时,主动去扫描所有的Servlet类,filter类.... * @author Administrator * */ import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.ServletRegistrationBean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import com.mr.li.filter.MyFilter2; import com.mr.li.listener.MyListener2; import com.mr.li.servlet.MyServlet; @SpringBootApplication @ServletComponentScan public class Application { public static void main(String[] args) { //此方法是spring boot启动时必须调用的一个静态方法,第一个参数是启动类的模板,第二个参数就是main方法中的参数。 SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args); } //方法名叫什么无所谓:在启动类中创建一个新的filter @Bean public ServletRegistrationBean getServletRegistrationBean() { ServletRegistrationBean bean = new ServletRegistrationBean(new MyServlet(), "/hhhh"); return bean; } //过滤器方式二:在启动类中创建一个新的filter对象,加载到spring容器中,然后但凡以他配置的过滤的后缀名结束的请求都会过滤掉, @Bean public FilterRegistrationBean getFilterRegistrationBean() { FilterRegistrationBean bean = new FilterRegistrationBean(new MyFilter2()); bean.addUrlPatterns("/hhhh","/my"); return bean; } //注册Listener监听器方式二:启动类中方法注册Listener类。 @Bean public ServletListenerRegistrationBean<MyListener2> getListenerRegistrationBean(){ ServletListenerRegistrationBean<MyListener2> bean = new ServletListenerRegistrationBean<MyListener2>(new MyListener2()); return bean; } }
2.整合servlet
package com.mr.li.servlet; import java.io.IOException; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; /** * spring boot整合Servlet: * 在spring boot中演示:正常的web项目下的Servlet编写方式。现在在spring boot中编写是当前这种方式的,简化了非常多。 * 其中 * 1.@WebServlet注解中my和/my相当于以前web.xml中配置的servlet标签和servlet-mapping标签的所有内容。 相当于web.xml中的: <servlet> <servlet-name>my</servlet-name> <servlet-class>com.mr.li.servlet.MyServlet</servlet-class> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>my</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/my</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> */ @WebServlet(name = "my", urlPatterns = "/my") public class MyServlet extends HttpServlet{ private static final long serialVersionUID = 8908779617494799833L; @Override protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { System.out.println("访问到MyServlet"); // resp.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8"); resp.getWriter().write("你好,世界"); } }
3.整合filter方式一:
package com.mr.li.filter; import java.io.IOException; import javax.servlet.Filter; import javax.servlet.FilterChain; import javax.servlet.FilterConfig; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.ServletRequest; import javax.servlet.ServletResponse; import javax.servlet.annotation.WebFilter; /** * spring boot整合filter方式一: * 编写Filter,是Servlet的拦截器,指定某个请求到达此请求(一般是servlet)之前就将一些条件过滤掉 * 相当于web.xml中的: * <filter> * <filter-name>MyFilter</filter-name> * <filter-class>com.mr.li.filter.MyFilter</filter-class> * </filter> * <filter-mapping> * <filter-name>MyFilter</filter-name> * <url-parrern>/my</url-parrern> * </filter-mapping> * 本filter的名字叫:MyFilter * 拦截:/my 结尾的请求 * @author Administrator * */ @WebFilter(filterName = "MyFilter", urlPatterns = {"/my"}) public class MyFilter implements Filter { @Override public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException { System.out.println("filter初始化了"); } @Override public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException { System.out.println("进入:MyFilter"); chain.doFilter(request, response);//放行 System.out.println("离开:MyFilter"); } @Override public void destroy() { System.out.println("filter销毁了"); } }
4.整合filter方式2:方法注册,注册方法在启动类中,这里只提供对象
package com.mr.li.filter; import java.io.IOException; import javax.servlet.Filter; import javax.servlet.FilterChain; import javax.servlet.FilterConfig; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.ServletRequest; import javax.servlet.ServletResponse; /** * spring boot整合filter方式二:在启动类中调用 */ public class MyFilter2 implements Filter { @Override public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException { System.out.println("filter222初始化了"); } @Override public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException { System.out.println("进入:MyFilter222"); chain.doFilter(request, response);//放行 System.out.println("离开:MyFilter222"); } @Override public void destroy() { System.out.println("filter销毁了"); } }
5.整合Listener方式一:
package com.mr.li.listener; import javax.servlet.ServletContextEvent; import javax.servlet.ServletContextListener; import javax.servlet.annotation.WebListener; /** * spring boot整合Listener监听器方式一:配置监听器,主要看针对哪个去配置监听器,这里配置的监听器主要是针对Servlet配置的监听器。 * 此配置相当于web.xml中: *<listener-calss>com.mr.li.listener.MyListener</listener-calss> */ @WebListener public class MyListener implements ServletContextListener { @Override public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce) { System.out.println("Listener监听器开始工作了。。。init。。。。。"); } @Override public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent sce) { } }
6.整合Listener方式二:整合方法在启动类中,这里只提供对象
package com.mr.li.listener; import javax.servlet.ServletContextEvent; import javax.servlet.ServletContextListener; /** * spring boot整合Listener监听器方式二:通过在启动类中的方法注册Listener监听器。 * 此配置相当于web.xml中: *<listener-calss>com.mr.li.listener.MyListener</listener-calss> */ public class MyListener2 implements ServletContextListener { @Override public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce) { System.out.println("Listener2222监听器开始工作了。。。init。。。。。"); } @Override public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent sce) { } }
7.controller
package com.mr.li.controller; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody; /** * 单独演示Controller * */ @Controller public class HelloWorld { @RequestMapping("/show") @ResponseBody public Map<String, Object> show(){ Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>(); map.put("hello", "world"); return map; } }
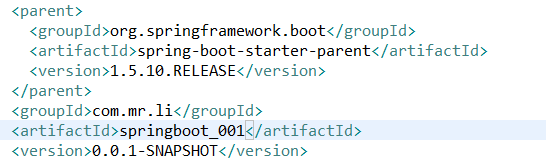
8.pom.xml
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <!-- spring boot项目需要继承父项目,现为2.1.4版本的父项目 --> <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>1.5.10.RELEASE</version> </parent> <groupId>com.mr.li</groupId> <artifactId>springboot_001</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <!-- 修改jdk版本 --> <properties> <java.version>1.7</java.version> </properties> <!-- 添加启动器:spring boot启动器中包含各个项目所需要的jar包,总共有44个启动器,例如web,jdbc,redis...想要使用哪个技术 就要添加哪个启动器。启动器是各个技术的组件,想用哪个技术就将哪个技术的启动器加入进来,这样此服务器就会拥有哪个技术的组件 --> <dependencies> <dependency> <!-- web启动器:此启动器中包含:tomcat + spring mvc的所有jar包,所以如果做web项目就必须有此启动器 --> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> </dependencies> </project>
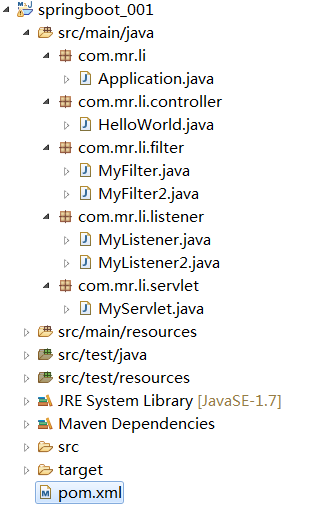
具体的项目结构如下:
*如果jdk不对就项目右键 -> maven -> updata Project... 一下
*访问的url:http: //localhost:8080/my 这里是访问的servlet , controller一样可以访问,将my换为show即可