原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/wanmeishenghuo/p/9678143.html参考狄泰软件相关教程
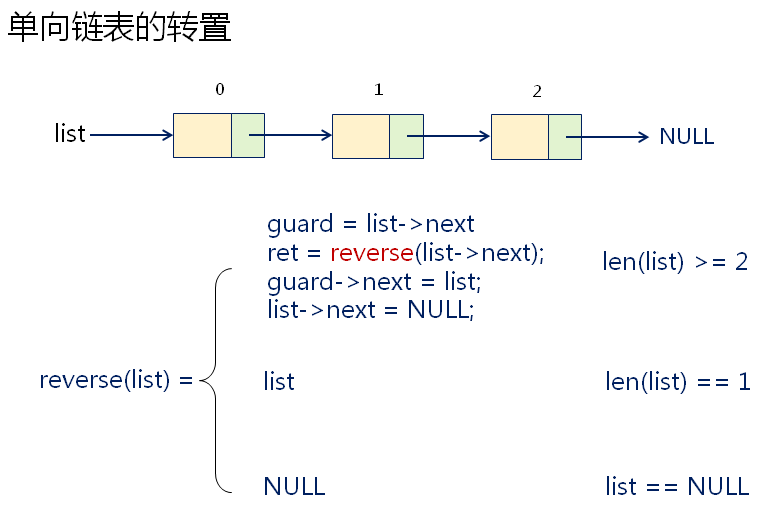
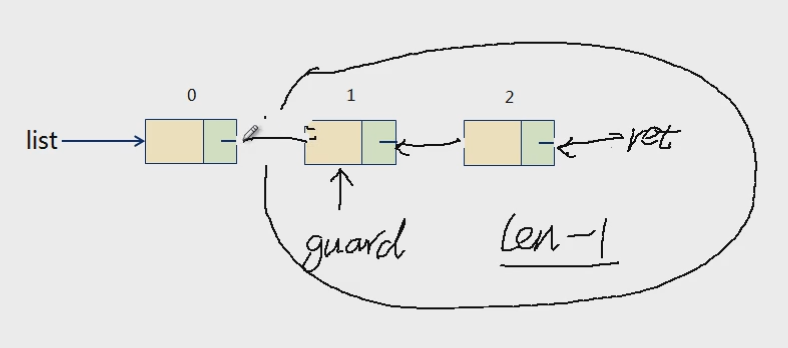
将大问题分解,先将第一个节点拿出来,将其它的节点看成一个整体。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include "DTString.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace DTLib;
struct Node
{
int value;
Node* next;
};
Node* create_list(int v, int len) // v:数据元素从哪一个之开始。 len:长度
{
Node* ret = NULL;
Node* slider = NULL;
for(int i=0; i<len; i++)
{
Node* n = new Node();
n->value = v++;
n->next = NULL;
if( slider == NULL )
{
slider = n;
ret = n;
}
else
{
slider->next = n;
slider = n;
}
}
return ret;
}
void destroy_list(Node* list)
{
while( list )
{
Node* del = list;
list = list->next;
delete del;
}
}
void print_list(Node* list)
{
while( list )
{
cout << list->value << "->";
list = list->next;
}
cout << "NULL" << endl;
}
Node* reverse(Node* list)
{
if( (list == NULL) || (list->next == NULL) )
{
return list;
}
else
{
Node* guard = list->next;
Node* ret = reverse(list->next);
guard->next = list;
list->next = NULL;
return ret;
}
}
int main()
{
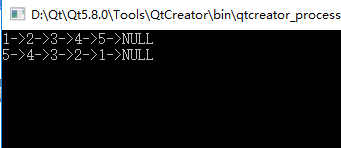
Node* list = create_list(1, 5);
print_list(list);
list = reverse(list);
print_list(list);
destroy_list(list);
return 0;
}
实验2:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include "DTString.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace DTLib;
struct Node
{
int value;
Node* next;
};
Node* create_list(int v, int len) // v:数据元素从哪一个之开始。 len:长度
{
Node* ret = NULL;
Node* slider = NULL;
for(int i=0; i<len; i++)
{
Node* n = new Node();
n->value = v++;
n->next = NULL;
if( slider == NULL )
{
slider = n;
ret = n;
}
else
{
slider->next = n;
slider = n;
}
}
return ret;
}
void destroy_list(Node* list)
{
while( list )
{
Node* del = list;
list = list->next;
delete del;
}
}
void print_list(Node* list)
{
while( list )
{
cout << list->value << "->";
list = list->next;
}
cout << "NULL" << endl;
}
Node* reverse(Node* list)
{
if( (list == NULL) || (list->next == NULL) )
{
return list;
}
else
{
Node* guard = list->next;
Node* ret = reverse(list->next);
guard->next = list;
list->next = NULL;
return ret;
}
}
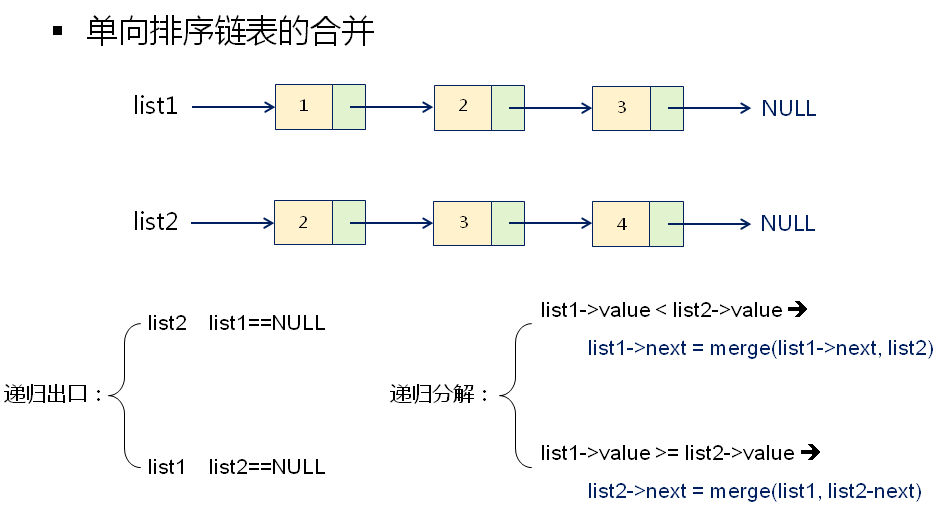
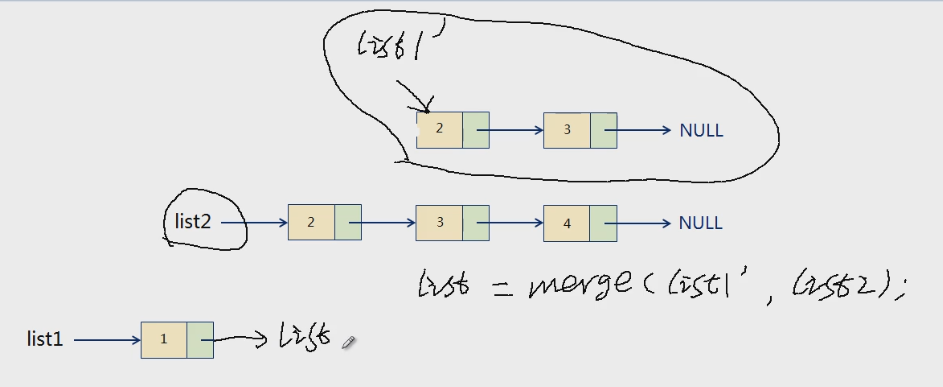
Node* merge(Node* list1, Node* list2)
{
if( list1 == NULL )
{
return list2;
}
else if( list2 == NULL )
{
return list1;
}
else if( list1->value < list2->value )
{
/*
Node* list1_ = list1->next;
Node* list = merge(list1_, list2);
list1->next = list;
return list1;
*/
return (list1->next = merge(list1->next, list2), list1); //逗号表达式
}
else
{
/*
Node* list2_ = list2->next;
Node* list = merge(list1, list2_);
list2->next = list;
return list2;
*/
return (list2->next = merge(list2->next, list1), list2); //逗号表达式
}
}
int main()
{
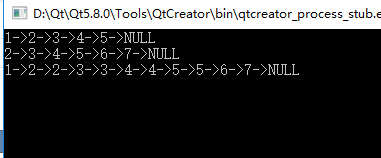
Node* list1 = create_list(1, 5);
Node* list2 = create_list(2, 6);
print_list(list1);
print_list(list2);
Node* list = merge(list1, list2);
print_list(list);
destroy_list(list);
return 0;
}
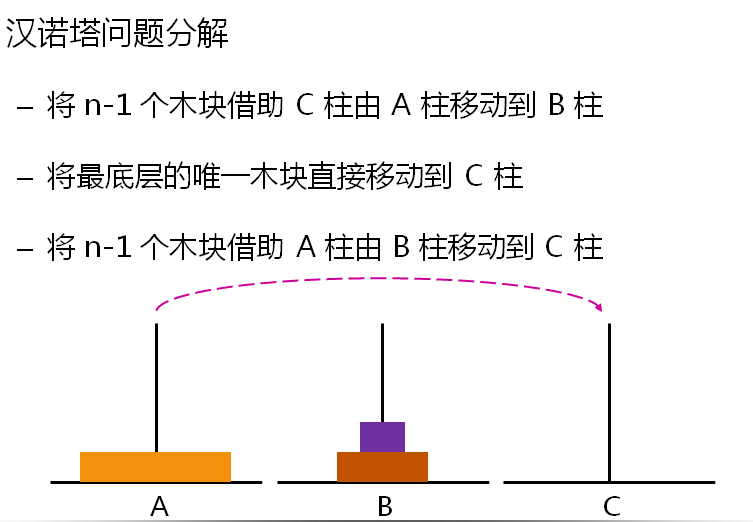
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include "DTString.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace DTLib;
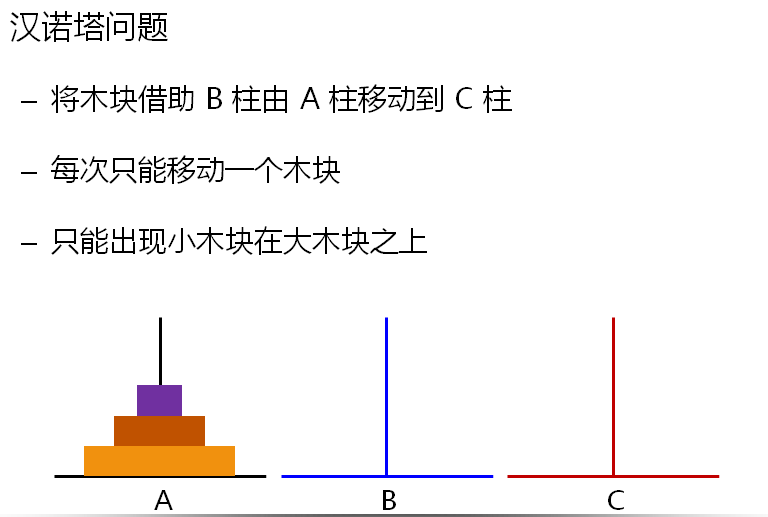
void HanoiTower(int n, char a, char b, char c) // a ==> src b ==> middle c ==> dest
{
if( n == 1 )
{
cout << a << "-->" << c << endl;
}
else
{
HanoiTower(n-1, a, c, b);
HanoiTower(1, a, b, c);
HanoiTower(n-1, b, a, c);
}
}
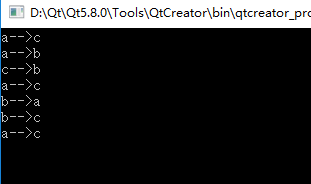
int main()
{
HanoiTower(3, 'a', 'b', 'c');
return 0;
}
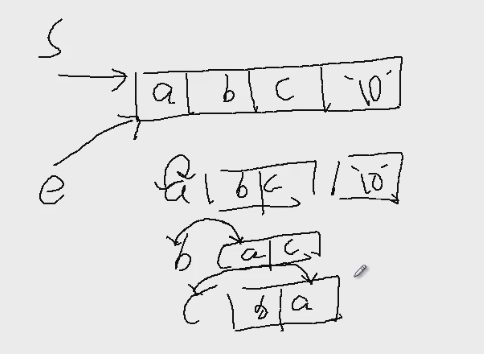
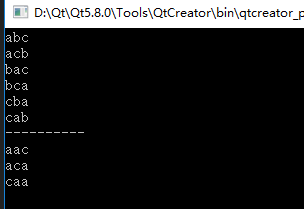
e始终指向字符串的开头,用来打印,s用来控制交换。
一开始,a和a交换,全排列b、c。
然后,a和b交换,全排列a、c。
然后交换a和c,全排列b、a。
如果两个字符是一样的,就没有必要交换,否则全排列有重复的现象。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include "DTString.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace DTLib;
void HanoiTower(int n, char a, char b, char c) // a ==> src b ==> middle c ==> dest
{
if( n == 1 )
{
cout << a << "-->" << c << endl;
}
else
{
HanoiTower(n-1, a, c, b);
HanoiTower(1, a, b, c);
HanoiTower(n-1, b, a, c);
}
}
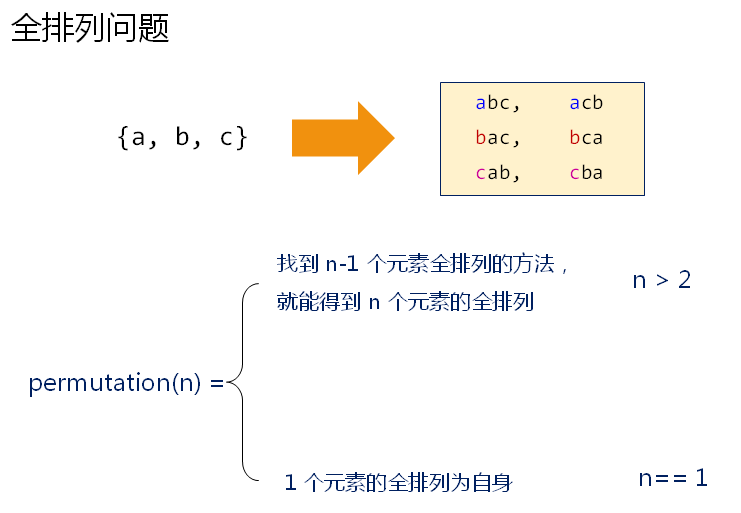
void permutation(char* s, char* e) // e始终指向字符串开头,用于打印
{
if( *s == '�' )
{
cout << e << endl;
}
else
{
int len = strlen(s);
for(int i=0; i<len; i++) //第一个字符一次和后面的元素交换
{
if( (i == 0) || (s[0] != s[i]) )
{
swap(s[0], s[i]); // 交换
permutation(s+1, e); // 交换之后将子串全排列
swap(s[0], s[i]); // 再交换回来
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
char s[] = "abc";
char s1[] = "aac";
permutation(s, s);
cout << "----------" << endl;
permutation(s1, s1);
return 0;
}