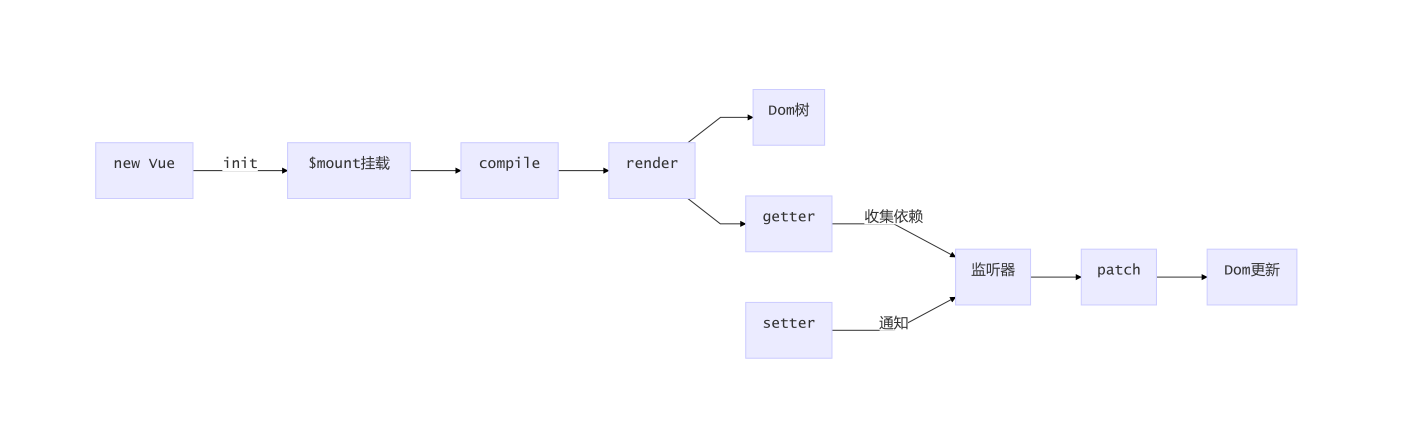
Vue工作机制
- vue工作机制
- Vue响应式的原理
- 依赖收集与追踪
- 编译compile
html:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <!-- 插值绑定 --> <p>{{name}}</p> <!-- 指令系统 --> <p k-text="name"></p> <p>{{age}}</p> <p>{{doubleAge}}</p> <!-- 双向绑定 --> <input type="text" k-model="name"> <!-- 事件处理 --> <button @click="changeName">呵呵</button> <!-- html内容解析 --> <div k-html="html"></div> </div> <script src='./compile.js'></script> <script src='./kvue.js'></script> <script> new KVue({ el: '#app', data: { name: "I am test.", age: 17, html: '<button>这是一个按钮</button>' }, created() { console.log('开始啦'); setTimeout(() => { this.name = '我是异步事件' }, 1500) }, methods: { changeName() { this.name = '哈喽,哈哈哈哈'; this.age = 20; this.id = 'xx' ; console.log(1, this) ; } } }) </script> </body> </html>
kvue.js
/* * @Author: liguowei01 * @Date: 2019-12-31 11:17:12 * @Last Modified by: liguowei01 * @Last Modified time: 2020-01-02 17:55:53 */ // 用法: new KVue({data:{...}}) class KVue { constructor(options) { this.$options = options; //数据的响应化 this.$data = options.data; this.observe(this.$data); //观察数据 //模拟一下watcher创建 // new Watcher(); //实例一 // this.$data.test; // new Watcher(); //实例二 实例二不等于实例一 // this.$data.foo.bar; new Compile(options.el, this); //生命周期函数 //created if (options.created) { //options.created(); //本来是这样执行,下面的调用call()方法,为函数指定执行作用域 options.created.call(this); //这样就可以在created函数中用this了。 } } observe(obj) { //检验数据类型必须是对象 if (!obj || typeof obj !== 'object') { return; } //遍历该对象 Object.keys(obj).forEach(key => { this.defineReactive(obj, key, obj[key]); //代理配置项 data 中的属性到vue实例上 this.proxyData(key); }) } //数据响应化(数据劫持) defineReactive(obj, key, val) { this.observe(val); //递归解决数据的嵌套 const dep = new Dep(); Object.defineProperty(obj, key, { get() { Dep.target && dep.addDep(Dep.target); return val }, set(newVal) { if (newVal === val) { return; } val = newVal; // console.log(`${key}属性更新了:${newVal}`) dep.notify(); } }) } //代理函数() proxyData(key) { Object.defineProperty(this, key, { get() { return this.$data[key]; }, set(newVal) { this.$data[key] = newVal; } }) } } //vue 数据绑定的原理是什么? //首先,把vue选项里的data中的每个属性都利用了Object.defineProperty()定义了一个属性, //都定义了get和set这样的话让我们的机会监听数据和变化, //当这些属性发生变化时,我们可以通知那些需要更新的地方去更新 //依赖搜集 //Dep: 用来管理 Watcher class Dep { constructor() { //这里存在若干依赖(watcher,一个watcher对应一个属性) this.deps = []; } //添加依赖的方法,搜集依赖时,往这里面放东西 addDep(dep) { this.deps.push(dep) } //通知方法,用来通知所有的watcher 去更新 notify() { this.deps.forEach(dep => dep.updata()) } } //Watcher 用来做具体更新的对象 class Watcher { constructor(vm, key, cb) { this.vm = vm; this.key = key; this.cb = cb; //将当前watcher实例指定到Dep静态属性target Dep.target = this; this.vm[this.key]; //触发getter,添加依赖 Dep.target = null; } updata() { // console.log('属性更新了'); this.cb.call(this.vm, this.vm[this.key]) } }
Compile.js
/* * @Author: liguowei01 * @Date: 2020-01-02 10:34:50 * @Last Modified by: liguowei01 * @Last Modified time: 2020-01-03 09:18:12 */ //用法 new Compile(el,vm) class Compile { constructor(el, vm) { //要遍历的宿主节点 this.$el = document.querySelector(el); this.$vm = vm; //在其他方法中方便使用 //编译 if (this.$el) { //转换内部内容为片段Fragment this.$fragment = this.node2Fragment(this.$el); //执行编译 this.compile(this.$fragment); //将编译完的html追加到$el this.$el.appendChild(this.$fragment); } } //将宿主元素中的代码片段拿出来遍历,这样做比较高效 node2Fragment(el) { //创建一个代码块 const frag = document.createDocumentFragment(); //将el中所有子元素“搬家”(移动)到frag中 let child; while (child = el.firstChild) { frag.appendChild(child); } return frag; } compile(el) { const childNodes = el.childNodes; Array.from(childNodes).forEach(node => { //判断类型 if (this.isElement(node)) { //元素 console.log('编译元素', node.nodeName); //查找k-, @, : const nodeAttrs = node.attributes; Array.from(nodeAttrs).forEach(attr => { const attrName = attr.name; const exp = attr.value; if (this.isDirective(attrName)) { //k-text const dir = attrName.substring(2); //执行指令 this[dir] && this[dir](node, this.$vm, exp); } if (this.isEvent(attrName)) { //@click let dir = attrName.substring(1); // text this.eventHandler(node, this.$vm, exp, dir); } }) } else if (this.isInterpolation(node)) { //插值文本{{}} console.log('编译文本', node.nodeName); this.compileText(node); } //递归子节点 if (node.childNodes && node.childNodes.length > 0) { this.compile(node) } }) } isDirective(attr) { return attr.indexOf('k-') == 0; } isEvent(attr) { return attr.indexOf('@') == 0; } isElement(node) { return node.nodeType === 1; } //插值文本 isInterpolation(node) { return node.nodeType === 3 && /{{(.*)}}/.test(node.textContent); } //编译文本 compileText(node) { //console.log(RegExp.$1); //正则对象RegExp的静态属性$1就是第一个匹配的值 就是上面'name' //node.textContent = this.$vm.$data[RegExp.$1]; this.updata(node, this.$vm, RegExp.$1, 'text'); } /* * @作用: 更新函数 根据指令决定是哪个更新器 它将来需要知道(参数) * @params: node 更新的节点 * @params: vm kvue的实例 * @params: exp 正则表达式 匹配的结果 如:name * @params: dir 指令(文本、事件、其他) 如:text,html,model * 这个方法是个通用方法,将来要被调用很多次 */ updata(node, vm, exp, dir) { const updaterFn = this[dir + 'Updater']; //在当前的类里面组合一个函数名 /*这种写法和 this.a 一样,this是代表当前对象,也是一个对象, 对象名.方法名 或 对象名.属性名 调用对象中的属性和方法 还有一种调用方式:对象名['方法名'] 或 对象名['属性名'] 也可以使用 对象名['方法名']() 执行此方法 */ //先判断updaterFn是否存在,如果存在则执行 updaterFn && updaterFn(node, vm[exp]); //初始化(第一次) //依赖收集 new Watcher(vm, exp, function(value) { //观察vm 里的exp(属性),并在属性变化时,如何更新 updaterFn && updaterFn(node, value); }) } //更新的具体操作 textUpdater(node, value) { node.textContent = value; } text(node, vm, exp) { this.updata(node, vm, exp, 'text'); } // 事件处理 eventHandler(node, vm, exp, dir) { let fn = vm.$options.methods && vm.$options.methods[exp]; if (dir && fn) { node.addEventListener(dir, fn.bind(vm), false); } } model(node, vm, exp) { this.updata(node, vm, exp, 'model'); let val = vm.exp; node.addEventListener('input', (e) => { let newValue = e.target.value; vm[exp] = newValue; val = newValue; }) } modelUpdater(node, value) { node.value = value; } html(node, vm, exp) { this.updata(node, vm, exp, 'html'); } htmlUpdater(node, value) { node.innerHTML = value; } }
/*
问题1:vue编译过程是怎样的?
遵循3W1H原则,什么是编译,为什么要编译。
首先写的这些模板的语句,html根本就不能识别,
我们通过编译的过程,可以进行依赖的收集,
进行依赖收集以后,我们就把data中的数据模型和视图之间产生了绑定关系
产生了依赖关系,那么以后模型发生变化的时候,
我们就会通知这些依赖的地方让他们进行更新,
这就是我们执行编译的目的,这样就做到了模型驱动视图的变化。
问题2:双向绑定的原理是什么?
做双向绑定时,通常在表单元素上绑定一个v-model,
我们在编译的时候,可以解析到v-model
操作时做了两件事:
1.在表单元素上做了事件监听(监听input、change事件)
2.如果值发生变化时,在事件回调函数把最新的值设置到vue的实例上
3.因为vue的实例已经实现了数据的响应化,
它的响应化的set函数会触发,通知界面中所有模型的依赖的更新。
所以界面中的,跟这个数据相关的部分就更新了
*/