There is a kind of balanced binary search tree named red-black tree in the data structure. It has the following 5 properties:
- (1) Every node is either red or black.
- (2) The root is black.
- (3) Every leaf (NULL) is black.
- (4) If a node is red, then both its children are black.
- (5) For each node, all simple paths from the node to descendant leaves contain the same number of black nodes.
For example, the tree in Figure 1 is a red-black tree, while the ones in Figure 2 and 3 are not.
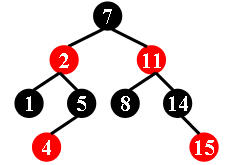 | 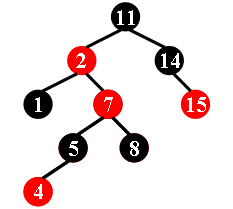 | 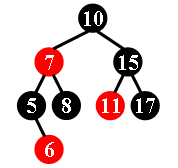 |
|---|---|---|
| Figure 1 | Figure 2 | Figure 3 |
For each given binary search tree, you are supposed to tell if it is possible to color the nodes and turn it into a legal red-black tree.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains several test cases. The first line gives a positive integer K (≤10) which is the total number of cases. For each case, the first line gives a positive integer N (≤30), the total number of nodes in the binary search tree. The second line gives the postorder traversal sequence of the tree. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print in a line Yes if the given tree can be turned into a legal red-black tree, or No if not.
Sample Input:
3
9
1 4 5 2 8 15 14 11 7
9
1 4 5 8 7 2 15 14 11
8
6 5 8 7 11 17 15 10
Sample Output:
Yes No Yes
AC代码:

1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 typedef long long ll; 4 const int maxn=111; 5 struct node 6 { 7 int l,r,tol; 8 }stu[maxn]; 9 int n,a[maxn],root,tot; 10 void handle(int l,int r,int pre) 11 { 12 if(l==r) return ; 13 int pos=r; 14 for(int i=r-1;i>=l;--i) if(a[i]>a[r]) pos=i; 15 if(pos==r){ 16 int cnt=++tot; 17 stu[cnt].l=0; 18 stu[cnt].r=0; 19 handle(l,pos-1,cnt); 20 stu[pre].l=cnt; 21 } 22 else if(pos==l){ 23 int cnt=++tot; 24 stu[cnt].l=0; 25 stu[cnt].r=0; 26 handle(pos,r-1,cnt); 27 stu[pre].r=cnt; 28 } 29 else{ 30 int cnt=++tot; 31 stu[cnt].l=0; 32 stu[cnt].r=0; 33 handle(l,pos-1,cnt); 34 stu[pre].l=cnt; 35 cnt=++tot; 36 stu[cnt].l=0; 37 stu[cnt].r=0; 38 handle(pos,r-1,cnt); 39 stu[pre].r=cnt; 40 } 41 } 42 vector<int> solve(vector<int> p,vector<int> q) 43 { 44 vector<int> res; 45 res.clear(); 46 for(int i=0;i<(int)p.size();++i){ 47 int u=p[i]; 48 for(int j=0;j<(int)q.size();++j){ 49 if(u==q[j]){ 50 res.push_back(u); 51 break; 52 } 53 } 54 } 55 return res; 56 } 57 int tol; 58 vector<int> red[maxn],black[maxn]; 59 bool flag; 60 void dfs(int cur) 61 { 62 if(flag==false) return ; 63 if(stu[cur].l>0 && stu[cur].r>0){ 64 dfs(stu[cur].l); 65 if(flag==false) return ; 66 dfs(stu[cur].r); 67 if(flag==false) return ; 68 vector<int> x=solve(black[stu[stu[cur].l].tol],black[stu[stu[cur].r].tol]); 69 int cnt=++tol; 70 stu[cur].tol=cnt; 71 red[cnt]=x; 72 black[cnt].clear(); 73 vector<int> y=solve(black[stu[stu[cur].l].tol],red[stu[stu[cur].r].tol]); 74 vector<int> z=solve(red[stu[stu[cur].l].tol],black[stu[stu[cur].r].tol]); 75 vector<int> w=solve(red[stu[stu[cur].l].tol],red[stu[stu[cur].r].tol]); 76 set<int> se; 77 se.clear(); 78 for(int i=0;i<(int)x.size();++i) se.insert(x[i]); 79 for(int i=0;i<(int)y.size();++i) se.insert(y[i]); 80 for(int i=0;i<(int)z.size();++i) se.insert(z[i]); 81 for(int i=0;i<(int)w.size();++i) se.insert(w[i]); 82 set<int>::iterator it; 83 for(it=se.begin();it!=se.end();++it){ 84 black[cnt].push_back((*it)+1); 85 } 86 if((int)red[cnt].size()==0 && (int)black[cnt].size()==0){ 87 flag=false; 88 return ; 89 } 90 } 91 else if(stu[cur].l>0){ 92 dfs(stu[cur].l); 93 if(flag==false) return ; 94 int id=stu[stu[cur].l].tol; 95 bool have0=false; 96 for(int i=0;i<(int)red[id].size();++i){ 97 if(red[id][i]==0){ 98 have0=true; 99 break; 100 } 101 } 102 if(have0==false){ 103 flag=false; 104 return ; 105 } 106 int cnt=++tol; 107 stu[cur].tol=cnt; 108 red[cnt].clear(); 109 black[cnt].clear(); 110 black[cnt].push_back(1); 111 } 112 else if(stu[cur].r>0){ 113 dfs(stu[cur].r); 114 if(flag==false) return ; 115 int id=stu[stu[cur].r].tol; 116 bool have0=false; 117 for(int i=0;i<(int)red[id].size();++i){ 118 if(red[id][i]==0){ 119 have0=true; 120 break; 121 } 122 } 123 if(have0==false){ 124 flag=false; 125 return ; 126 } 127 int cnt=++tol; 128 stu[cur].tol=cnt; 129 red[cnt].clear(); 130 black[cnt].clear(); 131 black[cnt].push_back(1); 132 } 133 else{ 134 int cnt=++tol; 135 stu[cur].tol=cnt; 136 red[cnt].clear(); 137 red[cnt].push_back(0); 138 black[cnt].clear(); 139 black[cnt].push_back(1); 140 } 141 } 142 int main() 143 { 144 int t; 145 for(scanf("%d",&t);t;--t){ 146 scanf("%d",&n); 147 for(int i=1;i<=n;++i){ 148 scanf("%d",&a[i]); 149 } 150 tot=0; 151 root=++tot; 152 stu[root].l=0; 153 stu[root].r=0; 154 handle(1,n,1); 155 flag=true; 156 tol=0; 157 dfs(root); 158 if(flag) printf("Yes "); 159 else printf("No "); 160 } 161 return 0; 162 }
