列表:
比较:如果有多个元素,默认从第一个元素开始比较,比较对应的ASCII码值大小;
逻辑(and or):
连接(+):[1, 2, 3] + [4, 5, 6] 结果是 [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
重复(*):['Hi!'] * 4 结果是 ['Hi!', 'Hi!', 'Hi!', 'Hi!']
成员关系(in 和 not in):3 in [1, 2, 3] 结果是 True
定义:在[ ]内,可以存放多个任意类型的值,以逗号隔开。
定义一个学生列表
students=[ '钱垚',‘李小龙‘,’张全蛋‘]
print(students[1]) #李小龙
student_info=['杨波',84,'female',['泡8',’喝9‘]]
#取杨波同学的所有爱好
print(student_info[3])
#取杨波同学的第二个爱好
print(student_info[3][1]
2切片(顾头不顾尾,步长)
student_info=['杨波',84,'female',['泡8',’喝9‘]]
print(student_info[0:4:2(步长)]) #['杨波','female']
print(student_info[0] #'杨波'
print(student_info[0:1]) #['杨波']
注意以上两个是不一样的。
list1 = [1, 3, 2, 9, 7, 8]

我们从上图可以看到:-2表示的是从开始到倒数第二个
4:表示的是从索引4到最后

这是一种简单的按照步长为2,进行分片。一个是从正向开始,一个是从负向开始
4。成员运算in和not in
print('杨波' in student_info) #True
print('杨波' not in student_info) #False
5追加
student_info=['杨波',84,'female',['泡8',’喝9‘]]
#在student_info列表末尾追加一个值
student_info.append('安徽最牛的学院,合肥学院')
print(student_info)
![]()
6删除
删除列表中索引为2的值
del student_info[2]
print(student_info)
需要掌握的:
1、index
2、count
3、pop
4、remove
5、insert
6、extend
student_info = ['尹浩卿', 95, 'female', ['尬舞', '喊麦'], 95]
1index获取列表中某个值(如果有相同的,就获取第一个值)的索引
print(student_info.index(95)) #1
print(student_info.index(95,2,5 )) #4 2表示起始位置,5表示结束位置
2count获取列表中某个值的数量
print(student_info.count(95)) #2
3pop取值。
默认取列表中最后一个值
如果pop括号中写了索引,那就取索引中的值。
print(student_info.pop())
sex=student_info.pop(2)
print(sex) #female
print(student_info)

其实取出和移除的区别就在于有没有又没有保存被取出的值,pop是保存的,而remove是不保存的,而且pop()的括号里面加的是要删除的索引,而remove()括号里面加的是需要删除的元素。
4移除 把列表中的某个值的第一个值给去掉
student_info = ['尹浩卿', 95, 'female', ['尬舞', '喊麦'], 95]
student_info.remove(95)
print(student_info) # ['尹浩卿', 'female', ['尬舞', '喊麦'], 95]
name=student_info.remove('伊浩卿')
print(name) #None
print(student_info) #['female', ['尬舞', '喊麦'], 95]
5 插入值
student_info = ['尹浩卿', 95, 'female', ['尬舞', '喊麦'], 95]
在student_info的索引位置为3,插入一个‘合肥学院’
student_info.insert(3,'合肥学院')
print(student_info)
![]()
6.extend 合并列表
student_info1 = ['尹浩卿', 95, 'female', ['尬舞', '喊麦'], 95]
student_info2 = ['娄逸夫', 94, 'male', ['尬舞1', '喊麦2']]
student_info1.extend(student_info2)
print(student_info1)
student_info1.append(student_info2) #append是把它当作一个元素添加到student_info1中。
print(student_info1)
![]()
![]()
7reverse翻转(重要的内置方法)
只有列表有reverse(),元组,字典,字符串都没有。
列表名.reverse()的返回值是None,所以不可以出现list2=list1.reverse()这样的操作。其作用的结果,需要通过打印被作用的列表才可以查看出具体的效果。
可以在list1.reverse()之后,用list2=list1来表示反转之后的字符串,也可以直接打印list1。
reversed():
reverse(sequence) - >反转迭代器的序列值
返回反向迭代器
也就是说,在经过reversed()的作用之后,返回的是一个把序列值经过反转之后的迭代器,所以,需要通过遍历,或者List,或者next()等方法,获取作用后的值;
1.列表的反转:
>>> bb = [1,3,5,7]
>>> print(list(reversed(bb)))
[7, 5, 3, 1]
2.元组的反转:
>>> aa = (1, 2, 3)
>>> print(tuple(reversed(aa)))
(3, 2, 1)
3.字符串的反转
>>> aa = 'asbdamfgh'
>>> ''.join(reversed(aa)) 不可套用str(reversed(aa))
'hgfmadbsa'
![]()
student_info[::-1]这样也可以进行反转

综上所看,实现翻转至少有四种方法:
reversed()
reverse()
[::-1]
for i in range(len())
8sort排序


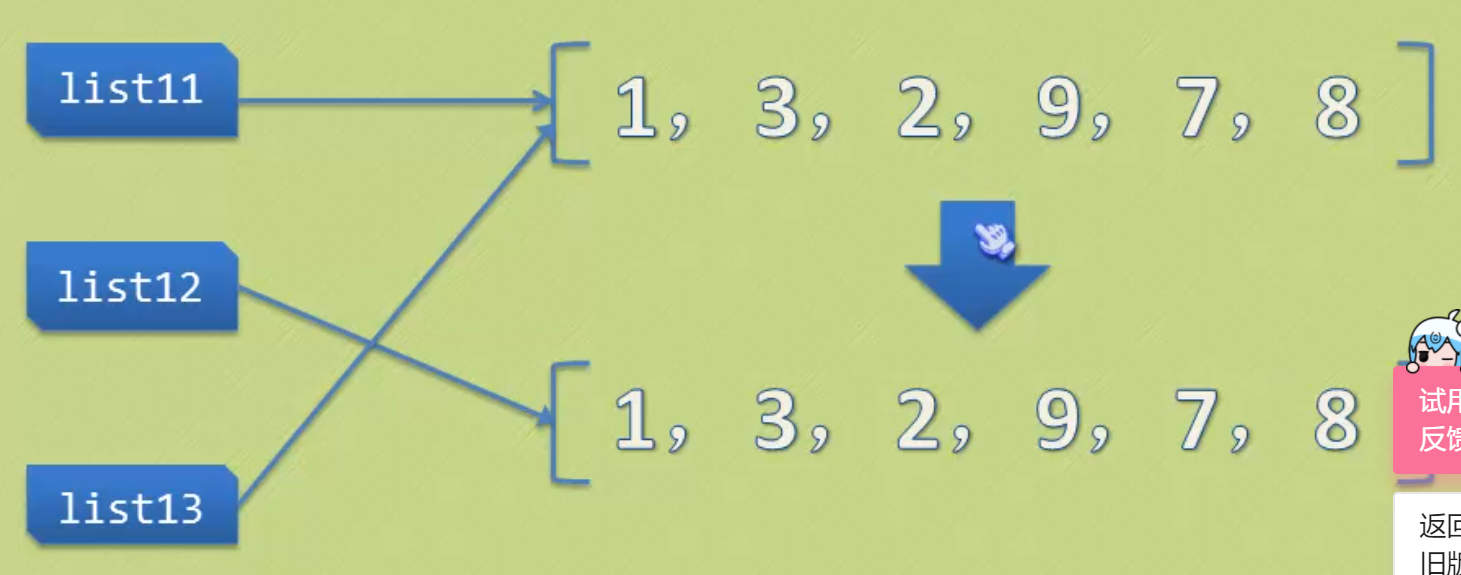
9.拷贝。
list2=list1.copy()和list2=list1[:],这才是真正的拷贝,
list2=list1,这只是又给list1多起一个名字而已。

如果只是直接把一个名字赋给另外一个名字,只是让这个变量的值多了一个标签而已,并没有实现真正的拷贝。
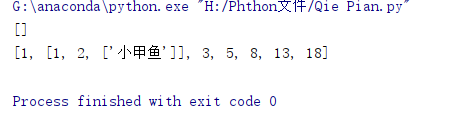
10 清除 clear
list1 = [1, [1, 2, ['小甲鱼']], 3, 5, 8, 13, 18]
list2 = list1.copy()
list1.clear()
print(list1)
print(list2)
11.列表推导式或者列表解析式
list1=[x**2 for x in range(10)]
print(list1)
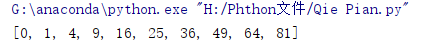
list1 = ['1.Jost do It','2.一切皆有可能','3.让变成改变世界','4.Impossible is nothing']
list2 = ['4.阿迪达斯','2.李宁','3.鱼C工作室','1.耐克']
list3 = [name+':'+slogan[2:] for slogan in list1 for name in list2 if name[0]==slogan[0]]
print(list3)
for each in list3:
print(each)
