实验二 动态高优先权优先调度
实验内容
模拟实现动态高优先权优先(若数值越大优先权越高,每运行一个时间单位优先权-n,若数值越小优先权越高,没运行一个时间单位优先权+n),具体如下:
设置进程体:进程名,进程的到达时间,服务时间,初始优先权,进程状态(W——等待,R——运行,F——完成),进程间的链接指针
进程初始化:由用户输入进程名、服务时间、初始优先权进行初始化,同时,初始化进程的状态为W。
显示函数:在进程调度前、调度中和调度后进行显示。
排序函数:对就绪状态的进程按照优先权排序。优先权相同时进入等待队列时间早的进程在前。注意考虑到达时间
调度函数:每次从等待队列队首调度优先权最高的进程执行,状态变化。并在执行一个时间单位后优先权变化,服务时间变化,状态变化。当服务时间为0时,状态变为F。
删除函数:撤销状态为F的进程。
实验要求
1、 测试数据可以随即输入或从文件中读入。
2、 必须要考虑到进程的到达时间
3、 最终能够计算每一个进程的周转时间。
实验代码
1.txt
process1 1 5 2 W process2 1 4 7 W process3 1 8 3 W process5 1 6 9 W process4 1 15 6 W
main.go
package main import ( "bufio" "container/heap" "fmt" "os" "strconv" "strings" "time" ) type Item struct { name string priority int index int arrival int service int oldservice int state string } type PriorityQueue []*Item func (pq PriorityQueue) Len() int { return len(pq) } func (pq PriorityQueue) Less(i, j int) bool { if pq[i].priority == pq[j].priority { return pq[i].service < pq[i].service } return pq[i].priority > pq[j].priority } func (pq PriorityQueue) Swap(i, j int) { pq[i], pq[j] = pq[j], pq[i] pq[i].index = i pq[j].index = j } func (pq *PriorityQueue) Push(x interface{}) { n := len(*pq) item := x.(*Item) item.index = n *pq = append(*pq, item) } //优先队列的Pop并不是用这个Pop,最后的元素并不是优先级最高的! func (pq *PriorityQueue) Pop() interface{} { old := *pq n := len(old) item := old[n-1] item.index = -1 *pq = old[0 : n-1] return item } func (pq *PriorityQueue) Top() *Item { item := heap.Pop(pq).(*Item) heap.Push(pq, item) return item } func (pq *PriorityQueue) update(item *Item, priority, service int, state string) { item.priority = priority item.service = service item.state = state heap.Fix(pq, item.index) } //创建优先队列 var pq = make(PriorityQueue, 0) func main() { f, err := os.OpenFile("1.txt", os.O_RDONLY, 0777) if err != nil { fmt.Println("没有找到1.txt!") os.Exit(1) } fmt.Println("请输入每秒改变优先级n") n := 1 fmt.Scan(&n) reader := bufio.NewReader(f) for i := 0; i < 5; i++ { //每次读取一行 buf, _, _ := reader.ReadLine() sli := strings.Fields(string(buf)) priint, _ := strconv.Atoi(sli[3]) arrint, _ := strconv.Atoi(sli[1]) serint, _ := strconv.Atoi(sli[2]) //创建实例 one := &Item{ name: sli[0], priority: priint, index: i, arrival: arrint, service: serint, oldservice: serint, state: sli[4], } heap.Push(&pq, one) } //初始化堆 heap.Init(&pq) fmt.Println("请输入第x秒后的状态:") x := 0 fmt.Scan(&x) //执行, 初始总数n为5,x为循环次数 num := 5 for second := 1; second <= x; second++ { time.Sleep(time.Second) // pq[num] != heap.Pop(*pq)!!! //临时优先队列 var tempq = make(PriorityQueue, 0) //遍历所有堆元素,仅pq[0]优先级最高! for i := 0; i < num; i++ { onepq := pq[i] if onepq.state == "F" { //添加到tempq tempq = append(tempq, onepq) continue } //服务时间不为0,就让其-1,state设为R if onepq.service != 0 { if i == 0 { //优先级最高 onepq.priority = pq[i].priority - n onepq.service = pq[i].service - 1 onepq.state = "R" } else { //堆里其他元素 onepq.priority = pq[i].priority + n onepq.state = "W" } } else { //service=0, state设为F onepq.state = "F" } //添加到tempq tempq = append(tempq, onepq) } //删除堆里所有元素 for pq.Len() > 0 { heap.Pop(&pq) } //把所有元素加到堆里 for _, v := range tempq { heap.Push(&pq, v) } //输出 fmt.Printf(" 第%d秒的状态表示 ", second) fmt.Println("进程名 | 服务时间 | 目前优先级 | 进程状态 | 平均周转时间") //输出堆 for i := 0; i < num; i++ { if pq[i].oldservice == pq[i].service { fmt.Printf("%v %v %v %v 0 ", pq[i].name, pq[i].service, pq[i].priority, pq[i].state) } else { fmt.Printf("%v %v %v %v %v ", pq[i].name, pq[i].service, pq[i].priority, pq[i].state, (second-pq[i].arrival)*1.0/(pq[i].oldservice-pq[i].service)) } } } } /* 使用了golang的container/heap包,需要手动实现less/len/swap/push/pop方法,这里也自定义了update和top方法,需要注意有以下几点: 1. heap并不是按优先级排序的,所以不能用for遍历,仅pq[0]优先级最高 2. 在遍历堆内所有节点时不能直接update,因为fix方法会重新构建堆,我这里使用的方式是用切片来保存堆中所有的元素,空堆后再一次性push */
实验截图
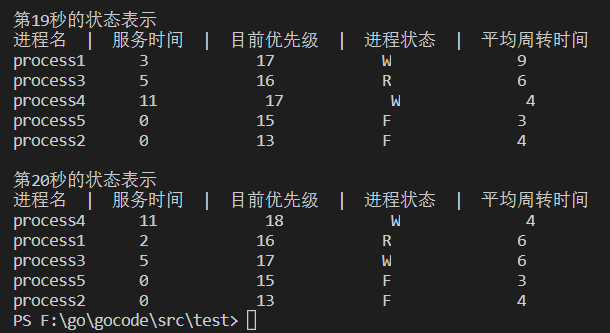
前4秒状态:
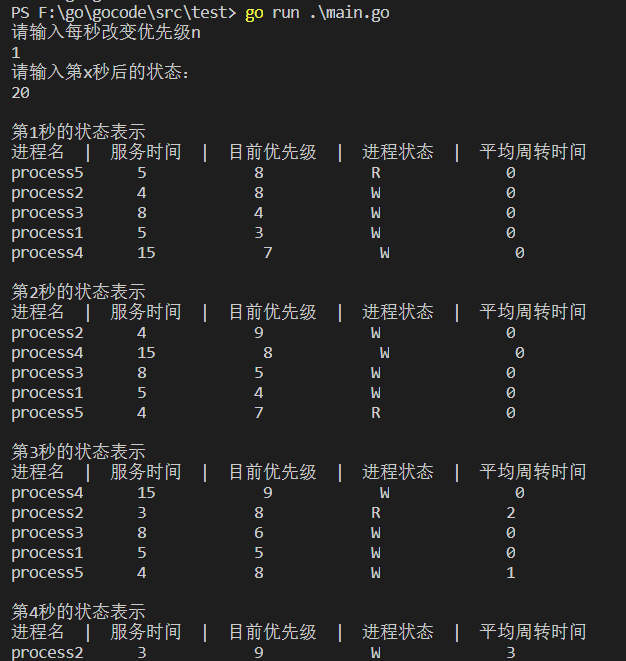
后2秒状态: