点击查看AngularJS系列目录
转载请注明出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/leosx/
Angular的表达式
Angular的表达式和JavaScript代码很像,不过通常Angular的表达式的作用是进行数据绑定。
Angular表达式 PK JavaScript表达式
Angular的表达式和JavaScript的表达式很相像,它们之间有如下不同:
1、Context(上下文): JavaScript 表达式的求值针对全局对象
window的,在Angular中,表达式的求值只是针对于scope对象。2、Forgiving(容错性):在JavaScript中,尝试访问一个为undefined的属性,你会收到一个异常的。但是在Angular中,会忽略
undefined和null。3、没有流程控制语句:在Angular表达式中,你不能使用条件判断、循环语句、或者异常。
4、没有函数声明:您不能在Angular表达式中声明function,哪怕在
ng-init指令中也不行!5、没有正则表达式:你不能再Angular表达式中使用正则表达式。
6、没有空操作和void方法:你不能再Angular表达式中使用void方法。
7、Filters过滤器:你可以在Angular表达式中使用过滤器去格式化显示。
如果你想运行更复杂的JavaScript代码,你应该在controller里面去声明,在模板中调用。注意,如果我们通常会使用 $eval() 方法去代替eval() 方法。
来一个例子:
文件一:index.html
<span>
1+2={{1+2}}
</span>
it('should calculate expression in binding', function() {
expect(element(by.binding('1+2')).getText()).toEqual('1+2=3');
});
你也可以动态计算不同的表达式:
文件一:index.html
<div ng-controller="ExampleController" class="expressions">
Expression:
<input type='text' ng-model="expr" size="80"/>
<button ng-click="addExp(expr)">Evaluate</button>
<ul>
<li ng-repeat="expr in exprs track by $index">
[ <a href="" ng-click="removeExp($index)">X</a> ]
<code>{{expr}}</code> => <span ng-bind="$parent.$eval(expr)"></span>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
文件二:script.js
angular.module('expressionExample', [])
.controller('ExampleController', ['$scope', function($scope) {
var exprs = $scope.exprs = [];
$scope.expr = '3*10|currency';
$scope.addExp = function(expr) {
exprs.push(expr);
};
$scope.removeExp = function(index) {
exprs.splice(index, 1);
};
}]);
文件三:protractor.js
it('should allow user expression testing', function() {
element(by.css('.expressions button')).click();
var lis = element(by.css('.expressions ul')).all(by.repeater('expr in exprs'));
expect(lis.count()).toBe(1);
expect(lis.get(0).getText()).toEqual('[ X ] 3*10|currency => $30.00');
});
上下文(context)
Angular不会使用JavaScript的eval() 方法去计算表达式,而是使用$parse 服务去处理表达式。在Angular中,我们会使用$window 服务和 $location 服务代替JavaScript的全局变量window和location变量。
文件一:index.html
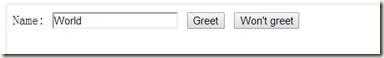
<div class="example2" ng-controller="ExampleController">
Name: <input ng-model="name" type="text"/>
<button ng-click="greet()">Greet</button>
<button ng-click="window.alert('Should not see me')">Won't greet</button>
</div>
文件二:script.js
angular.module('expressionExample', [])
.controller('ExampleController', ['$window', '$scope', function($window, $scope) {
$scope.name = 'World';
$scope.greet = function() {
$window.alert('Hello ' + $scope.name);
};
}]);
文件三:protractor.js
it('should calculate expression in binding', function() {
if (browser.params.browser == 'safari') {
// Safari can't handle dialogs.
return;
}
element(by.css('[ng-click="greet()"]')).click();
// We need to give the browser time to display the alert
browser.wait(protractor.ExpectedConditions.alertIsPresent(), 1000);
var alertDialog = browser.switchTo().alert();
expect(alertDialog.getText()).toEqual('Hello World');
alertDialog.accept();
});
容错性
在Angular中,表达式会忽略undefined 和 null的对象,而不会像JavaScript中一样,会报错!
$event指令
像ngClick 和 ngFocus 指令,在他们的表达式中,有一个$event 对象。如果引用了jQuery的haunted,该对象是一个jQuery事件对象的实例。
文件一:index.html
<div ng-controller="EventController">
<button ng-click="clickMe($event)">Event</button>
<p><code>$event</code>: <pre> {{$event | json}}</pre></p>
<p><code>clickEvent</code>: <pre>{{clickEvent | json}}</pre></p>
</div>
文件二:script.js
angular.module('eventExampleApp', []).
controller('EventController', ['$scope', function($scope) {
/*
* expose the event object to the scope
*/
$scope.clickMe = function(clickEvent) {
$scope.clickEvent = simpleKeys(clickEvent);
console.log(clickEvent);
};
/*
* return a copy of an object with only non-object keys
* we need this to avoid circular references
*/
function simpleKeys (original) {
return Object.keys(original).reduce(function (obj, key) {
obj[key] = typeof original[key] === 'object' ? '{ ... }' : original[key];
return obj;
}, {});
}
}]);
点击这里,进行查看。
注意上面的例子中,我们使用$event去调用clickMe来实现事件的。但是在 {{$event}}中,却不会显示出任何信息,因为$event 是一个来自于scope之外的binding(绑定)。
一次性绑定
使用:: 开头的表达式被Angular认作是一次性绑定。一次性表达式不会在值发生变化的时候重新计算。第一次绑定完成之后,就再也不会跟着数据变化而变化了。
第一个文件:index.html
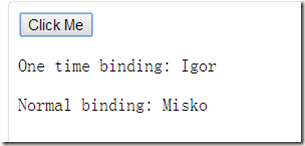
<div ng-controller="EventController">
<button ng-click="clickMe($event)">Click Me</button>
<p id="one-time-binding-example">One time binding: {{::name}}</p>
<p id="normal-binding-example">Normal binding: {{name}}</p>
</div>
第二个文件:script.js
angular.module('oneTimeBidingExampleApp', []).
controller('EventController', ['$scope', function($scope) {
var counter = 0;
var names = ['Igor', 'Misko', 'Chirayu', 'Lucas'];
/*
* expose the event object to the scope
*/
$scope.clickMe = function(clickEvent) {
$scope.name = names[counter % names.length];
counter++;
};
}]);
第三个文件:protractor.js
it('should freeze binding after its value has stabilized', function() {
var oneTimeBiding = element(by.id('one-time-binding-example'));
var normalBinding = element(by.id('normal-binding-example'));
expect(oneTimeBiding.getText()).toEqual('One time binding:');
expect(normalBinding.getText()).toEqual('Normal binding:');
element(by.buttonText('Click Me')).click();
expect(oneTimeBiding.getText()).toEqual('One time binding: Igor');
expect(normalBinding.getText()).toEqual('Normal binding: Igor');
element(by.buttonText('Click Me')).click();
expect(oneTimeBiding.getText()).toEqual('One time binding: Igor');
expect(normalBinding.getText()).toEqual('Normal binding: Misko');
element(by.buttonText('Click Me')).click();
element(by.buttonText('Click Me')).click();
expect(oneTimeBiding.getText()).toEqual('One time binding: Igor');
expect(normalBinding.getText()).toEqual('Normal binding: Lucas');
});
效果图:
使用一次性绑定的示例:
如果我们只需要我们的表达式执行第一个有效的时候,我们就可以使用我们的一次性表达式。下面,我们有三种用法:
1、在花括号或者属性中使用:
<div name="attr: {{::color}}">text: {{::name | uppercase}}</div>
2、我们在双向绑定中,不希望参数发生变化的时候:
someModule.directive('someDirective', function() {
return {
scope: {
name: '=',
color: '@'
},
template: '{{name}}: {{color}}'
};
});
<div some-directive name="::myName" color="My color is {{::myColor}}"></div>
3、在一个指令中使用:
<ul>
<li ng-repeat="item in ::items | orderBy:'name'">{{item.name}};</li>
</ul>