以前使用过DS和DF,最近使用Spark ML跑实验,再次用到简单复习一下。
//案例数据 1,2,3 4,5,6 7,8,9 10,11,12 13,14,15 1,2,3 4,5,6 7,8,9 10,11,12 13,14,15 1,2,3 4,5,6 7,8,9 10,11,12 13,14,15
1:DS与DF关系?
type DataFrame = Dataset[Row]
2:加载txt数据
val rdd = sc.textFile("data")
val df = rdd.toDF()
这种直接生成DF,df数据结构为(查询语句:df.select("*").show(5)):
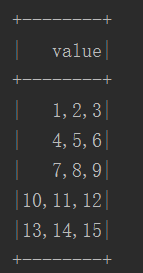
只有一列,属性为value。
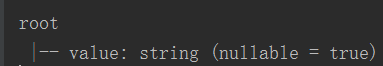
3: df.printSchema()
4:case class 可以直接就转成DS
// Note: Case classes in Scala 2.10 can support only up to 22 fields. To work around this limit, // you can use custom classes that implement the Product interface case class Person(name: String, age: Long) // Encoders are created for case classes val caseClassDS = Seq(Person("Andy", 32)).toDS()
5:直接解析主流格式文件
val path = "examples/src/main/resources/people.json"
val peopleDS = spark.read.json(path).as[Person]
6:RDD转成DataSet两种方法
数据格式:
xiaoming,18,iPhone mali,22,xiaomi jack,26,smartisan mary,16,meizu kali,45,huawei
(a):使用反射推断模式
val persons = rdd.map { x => val fs = x.split(",") Person(fs(0), fs(1).toInt, fs(2)) } persons.toDS().show(2) persons.toDF("newName", "newAge", "newPhone").show(2) persons.toDF().show(2)
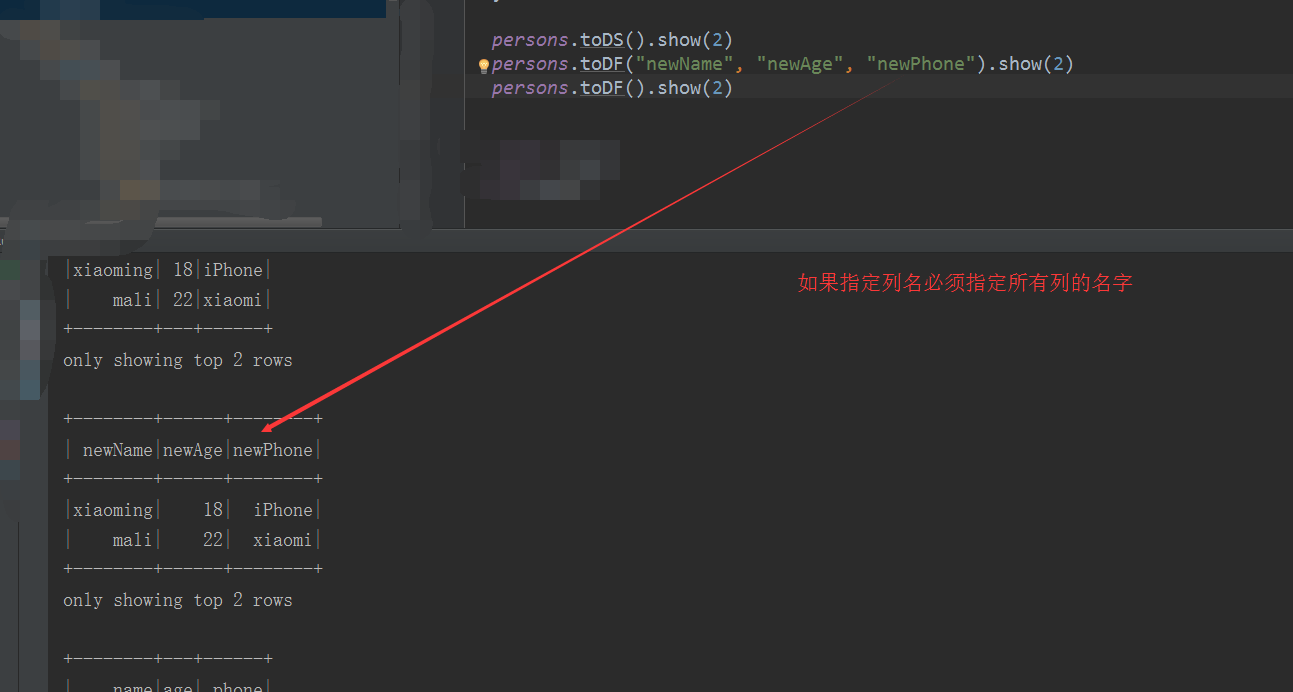
(b):编程方式指定模式
步骤:
import org.apache.spark.sql.types._ //1:创建RDD val rddString = sc.textFile("C:\Users\Daxin\Documents\GitHub\OptimizedRF\sql_data") //2:创建schema val schemaString = "name age phone" val fields = schemaString.split(" ").map { filedName => StructField(filedName, StringType, nullable = true) } val schema = StructType(fields) //3:数据转成Row val rowRdd = rddString.map(_.split(",")).map(attributes => Row(attributes(0), attributes(1), attributes(2))) //创建DF val personDF = spark.createDataFrame(rowRdd, schema) personDF.show(5)
7:注册视图
//全局表,生命周期多个session可以共享并且创建该视图的sparksession停止该视图也不会过期 personDF.createGlobalTempView("GlobalTempView_Person") //临时表,存在的话覆盖。生命周期和sparksession相同 personDF.createOrReplaceTempView("TempView_Person") //personDF.createTempView("TempView_Person") //如果视图已经存在则异常 // Global temporary view is tied to a system preserved database `global_temp` //全局视图存储在global_temp数据库中,如果不加数据库前缀异常,提示找不到视图 spark.sql("select * from global_temp.GlobalTempView_Person").show(2) //临时表不需要添加数据库 spark.sql("select * from TempView_Person").show(2)

8:UDF 定义:
Untyped User-Defined Aggregate Functions
package com.daxin.sq.df import org.apache.spark.sql.expressions.MutableAggregationBuffer import org.apache.spark.sql.expressions.UserDefinedAggregateFunction import org.apache.spark.sql.types._ import org.apache.spark.sql.Row /** * Created by Daxin on 2017/11/18. * url:http://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/sql-programming-guide.html#untyped-user-defined-aggregate-functions */ //Untyped User-Defined Aggregate Functions object MyAverage extends UserDefinedAggregateFunction { // Data types of input arguments of this aggregate function override def inputSchema: StructType = StructType(StructField("inputColumn", IntegerType) :: Nil) //2 // Updates the given aggregation buffer `buffer` with new input data from `input` //TODO 第一个缓冲区是sum,第二个缓冲区是元素个数 override def update(buffer: MutableAggregationBuffer, input: Row): Unit = { if (!input.isNullAt(0)) { buffer(0) = buffer.getInt(0) + input.getInt(0) // input.getInt(0)是中inputSchema定义的第0个元素 buffer(1) = buffer.getInt(1) + 1 println() } } // Data types of values in the aggregation buffer //TODO 定义缓冲区的模型(也就是数据结构) override def bufferSchema: StructType = StructType(StructField("sum", IntegerType) :: StructField("count", IntegerType) :: Nil) // Merges two aggregation buffers and stores the updated buffer values back to `buffer1` //TODO MutableAggregationBuffer 是Row子类 override def merge(buffer1: MutableAggregationBuffer, buffer2: Row): Unit = { //TODO 合并分区,将结果更新到buffer1 buffer1(0) = buffer1.getInt(0) + buffer2.getInt(0) buffer1(1) = buffer1.getInt(1) + buffer2.getInt(1) println() } // Initializes the given aggregation buffer. The buffer itself is a `Row` that in addition to // standard methods like retrieving a value at an index (e.g., get(), getBoolean()), provides // the opportunity to update its values. Note that arrays and maps inside the buffer are still // immutable. override def initialize(buffer: MutableAggregationBuffer): Unit = { buffer(0) = 0 buffer(1) = 0 } // Whether this function always returns the same output on the identical input override def deterministic: Boolean = true // Calculates the final result override def evaluate(buffer: Row): Int = buffer.getInt(0) / buffer.getInt(1) // The data type of the returned value,返回值类型 override def dataType: DataType = IntegerType // 1 }
测试代码:
spark.udf.register("myAverage", MyAverage)
val result = spark.sql("SELECT myAverage(age) FROM TempView_Person")
result.show()
8:关于机器学习中的DataFrame的schema定:
一列名字为 label,另一列名字为 features。一般可以使用case class完成转换
case class UDLabelpOint(label: Double, features: org.apache.spark.ml.linalg.Vector)