本节目标: exec替换进程映像 exec关联函数组(execl、execlp、execle、execv、execvp) 一,exec替换进程映像 在进程的创建上Unix采用了一个独特的方法,它将进程创建与加载一个新进程映象分离。这样的好处是有更多的余地对两种操作进行管理。 当我们创建了一个进程之后,通常将子进程替换成新的进程映象,这可以用exec系列的函数来进行。当然,exec系列的函数也可以将当前进程替换掉。 例如:在shell命令行执行ps命令,实际上是shell进程调用fork复制一个新的子进程,在利用exec系统调用将新产生的子进程完全替换成ps进程。 二,exec系列函数(execl、execlp、execle、execv、execvp) 包含头文件<unistd.h> 功能: 用exec函数可以把当前进程替换为一个新进程,且新进程与原进程有相同的PID。exec名下是由多个关联函数组成的一个完整系列, 头文件<unistd.h> extern char **environ; 原型: int execl(const char *path, const char *arg, ...); int execlp(const char *file, const char *arg, ...); int execle(const char *path, const char *arg, ..., char * const envp[]); int execv(const char *path, char *const argv[]); int execvp(const char *file, char *const argv[]); 参数: path参数表示你要启动程序的名称包括路径名 arg参数表示启动程序所带的参数,一般第一个参数为要执行命令名,不是带路径且arg必须以NULL结束 返回值:成功返回0,失败返回-1 注:上述exec系列函数底层都是通过execve系统调用实现: #include <unistd.h> int execve(const char *filename, char *const argv[],char *const envp[]); DESCRIPTION: execve() executes the program pointed to by filename. filename must be either a binary executable, or a script starting with a line of the form 以上exec系列函数区别: 1,带l 的exec函数:execl,execlp,execle,表示后边的参数以可变参数的形式给出且都以一个空指针结束。 示例:
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <unistd.h> int main(void) { printf("entering main process--- "); execl("/bin/ls","ls","-l",NULL); printf("exiting main process ---- "); return 0; }
利用execl将当前进程main替换掉,所有最后那条打印语句不会输出
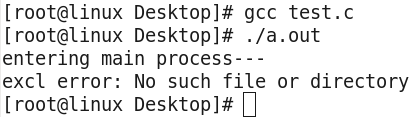
2,带 p 的exec函数:execlp,execvp,表示第一个参数path不用输入完整路径,只有给出命令名即可,它会在环境变量PATH当中查找命令 示例: 当不带p但没给出完整路径时: #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <unistd.h> int main(void) { printf("entering main process--- "); if(execl("ls","ls","-l",NULL)<0) perror("excl error"); return 0; }
结果显示找不到,所有替换不成功,main进程继续执行
现在带p:
if(execlp("ls","ls","-l",NULL)<0)
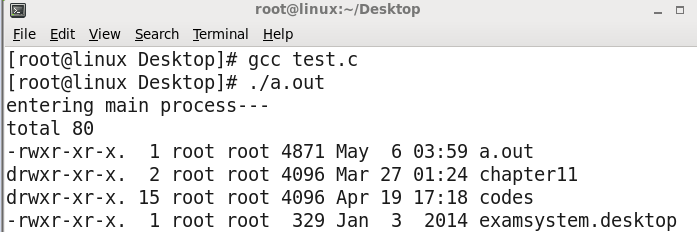
替换成功
3,不带 l 的exec函数:execv,execvp表示命令所需的参数以char *arg[]形式给出且arg最后一个元素必须 是NULL 示例: #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <unistd.h> int main(void) { printf("entering main process--- "); int ret; char *argv[] = {"ls","-l",NULL}; ret = execvp("ls",argv); if(ret == -1) perror("execl error"); printf("exiting main process ---- "); return 0; }
替换成功
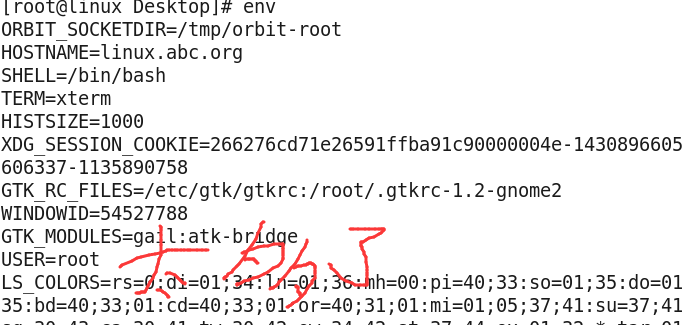
4,带 e 的exec函数:execle表示,将环境变量传递给需要替换的进程 从上述的函数原型中我们发现: extern char **environ; 此处的environ是一个指针数组,它当中的每一个指针指向的char为“XXX=XXX” environ保存环境信息的数据可以env命令查看:
它由shell进程传递给当前进程,再由当前进程传递给替换的新进程
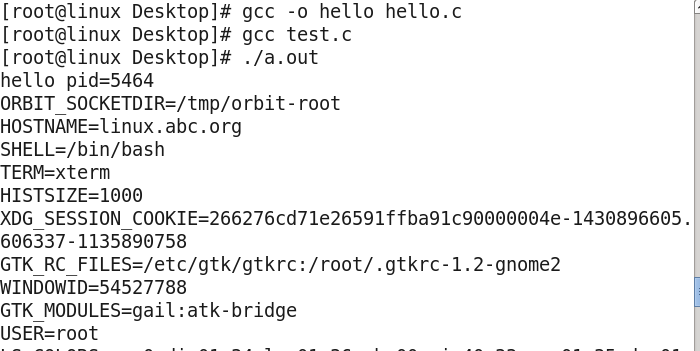
示例:execle.c #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <unistd.h> int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { //char * const envp[] = {"AA=11", "BB=22", NULL}; printf("Entering main ... "); int ret; ret =execl("./hello", "hello", NULL); //execle("./hello", "hello", NULL, envp); if(ret == -1) perror("execl error"); printf("Exiting main ... "); return 0; } hello.c #include <unistd.h> #include <stdio.h> extern char** environ; int main(void) { printf("hello pid=%d ", getpid()); int i; for (i=0; environ[i]!=NULL; ++i) { printf("%s ", environ[i]); } return 0; }
可知原进程确实将环境变量信息传递给了新进程
那么现在我们可以利用execle函数自己给的需要传递的环境变量信息:
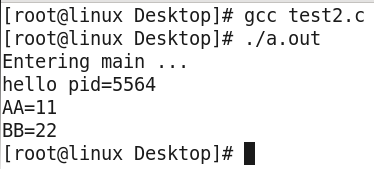
示例程序:execle.c #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <unistd.h> int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { char * const envp[] = {"AA=11", "BB=22", NULL}; printf("Entering main ... "); int ret; //ret =execl("./hello", "hello", NULL); ret =execle("./hello", "hello", NULL, envp); if(ret == -1) perror("execl error"); printf("Exiting main ... "); return 0; } hello.c #include <unistd.h> #include <stdio.h> extern char** environ; int main(void) { printf("hello pid=%d ", getpid()); int i; for (i=0; environ[i]!=NULL; ++i) { printf("%s ", environ[i]); } return 0; }
确实将给定的环境变量传递过来了
http://bbs.csdn.net/topics/350057686

要怎样做才能正常执行(主要是execl函数运行php文件。),并输入exit退出?
execl会载入你调用的程序,覆盖原有代码段,相当于你本来的程序的代码段被替换成execl执行的了。
所以execl后面的都不会输出了。
正确的应该是fork一个子进程,在子进程中调用execl。
如果我把execl 放到用pthread_create创建的线程是不是也一样会覆盖原有的代码?
我测试过也是一样会退出。。
一定要用fork 吗?
execl是覆盖进程的代码段,所以如果你原来的程序还需要正常退出的话,就要fork一个子进程。
另外,如果需要execl调用的这个程序执行完成,就需要在父进程中等待,可以调用waitpid。
具体的你man一下看看。
如果用了fork 。执行execl 后会不会停止 子进程的呢?
fork以后,子进程拷贝父进程的几乎所有特性,包括pc,也就是说,在子进程中,还是从你fork的地方开始运行的。然后你execl,覆盖掉的是子进程的代码段,与父进程无关。
pthread_create创建的子线程与父线程共用同一代码段!只是寄存器和栈不同!
execl不是创建一个新进程,Linux只有fork能创建新进程
execl成功是不会返回的,会执行新的程序。
execl失败才会返回
http://bbs.chinaunix.net/thread-4168834-1-1.html

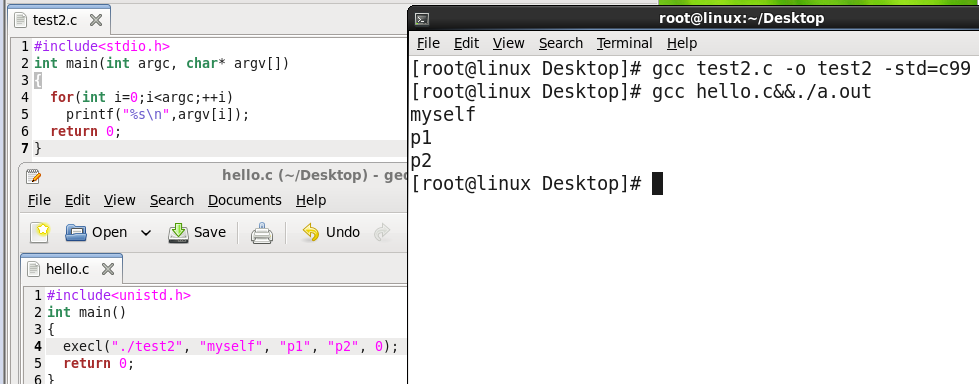
我感觉execl的第一个参数和第二个参数有重叠,帮我 ... 如题,我学习了一下execl函数的用法: #include<unistd.h> int main() { execl("ls", "ls", "-al"); return 0; } OK,什么也不打印,于是我改了一下: #include<unistd.h> int main() { execl("/bin/ls", "ls", "-al", 0); return 0; } 很奇怪啊,execl第一个参数必须是path,我如果把调用语句改成execl("/bin", "ls", "-al", 0); 发现也不行。那岂不是说这个path参数必须包含可执行程序的名字本身? 可是这样的话,execl的第二个参数就是文件名啊,第二个参数岂不是多余了? 非常疑惑,求解释! path里面包含了file的名字,那还要第二个file参数干什么呢? 感觉多余? 第2个参数将传给进程,也就是argv[0],进程可以通过查看面子有多大,就能看人下菜碟-哦是随机应变了!。 果然是高手!我验证了你的说法,第二个参数是argv[0],可以是任何东西,不必是可执行文件名。如下图所示:
三,fcntl()函数中的FD_CLOEXEC标识在exec系列函数中的作用
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
int fcntl(int fd, int cmd, ... /* arg */ );
File descriptor flags
The following commands manipulate the flags associated with a file
descriptor. Currently, only one such flag is defined: FD_CLOEXEC, the
close-on-exec flag. If the FD_CLOEXEC bit is 0, the file descriptor
will remain open across an execve(2), otherwise it will be closed.
//如果FD_CLOEXEC标识位为0,则通过execve调用后fd依然是打开的,否则为关闭的
F_GETFD (void)
Read the file descriptor flags; arg is ignored.
F_SETFD (long)
Set the file descriptor flags to the value specified by arg.
如:fcntl(fd, F_SETFD, FD_CLOEXEC);
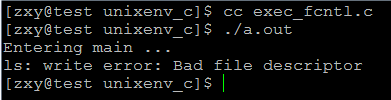
1关闭(标准输出关闭)ls -l无法将结果显示在标准输出
http://www.cnblogs.com/mickole/p/3187409.html