1.IO开篇
2.文件与文件夹
3.四大抽象类
4.标准步骤
5.文件字节流 FileInputStream FileOutputStream
6.文件字符流 FileReader FileWriter
7.字节数组流ByteArrayInputStream ByteArrayOutputStream
8.装饰器设计模式
9.字节缓冲流BufferedInputStream BufferedOutputStream
10.字符缓冲流BufferedReader BufferedWriter
11.转换流
12.数据流
13.对象流
14.打印流
15.序列流
16.随机流 RandomAccessFile
17.CommonsIO
1.IO开篇
分类
- 按处理对象分
- 字节流(是给计算机看的)
- 字符流(是给人看的)
- 按流向分(输入输出是相对于程序的,以程序为中心)
- 输入流(从音视频,txt,word等文件读到程序中)
- 输出流(冲程序写出到文件)
- 按功能分
- 节点流(始终位于数据处理的一线)
- 处理流(使用了装饰器设计模式的流)
常见流
FileInputStream FileOutputStream
ByteArrayInputStream ByteArrayOutputStream
FileReader FileWriter
BufferedInputStream BufferedOutputStream
InputStreamReader OutputStreamWriter
DataOutputStream DataInputStream
ObjectInputStream ObjectOutputStream
PrintStream PrintWriter
RandomAccessFile
SequenceInputStream
编码与解码
编码:由字符到字节
解码:由字节到字符
public class EncodeAndDecode {
public static void main(String[] args) throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
String msg = "性命生命使命";
//编码:默认使用工程的字符集
byte[] datas = msg.getBytes("gbk");
System.out.println(datas.length);
//解码
String newmsg = new String(datas,0,datas.length,"gbk");
System.out.println(newmsg);
}
}
常见乱码原因
- 字节数不够
- 字符集不同
2.文件与文件夹
构造一个文件对象
String path = "IO.png";
//构造一个文件对象的方法
//1.该文件的路径
File f1 = new File(path);
System.out.println("f1:" + f1.length());
//2.父路径 + 子路径
String parent_path = "D:/";
String chile_path = "IO.png";
File f2 = new File(parent_path,chile_path);
System.out.println("f2:" + f2.length());
//3.父对象 + 子路径
File f3 = new File(new File(parent_path), chile_path);
System.out.println("f3:" + f3.length());
System.out.println("项目路径:" + System.getProperty("user.dir"));
测试文件对象相关的功能
public class TestFileFunction {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String pathname = "IO.png";
File f = new File(pathname);
System.out.println("文件名称:" + f.getName());
System.out.println("文件路径:" + f.getPath());
//getPath返回文件路径,构造文件对象时使用的是绝对路径,就返回绝对路径,构造时使用的是相对路径,则返回相对路径
System.out.println("绝对路径:" + f.getAbsolutePath());
//返回file的绝对路径
System.out.println("父对象路径:" + f.getParent());
//返回构造file文件对象是使用的path中文件名之前的路径,存在则返回,不存在返回null
System.out.println("是否存在:" + f.exists());
System.out.println("是否是文件:" + f.isFile());
System.out.println("是否是文件夹:" + f.isDirectory());
//只要file对象存在时判断是文件还是文件夹才有意义
System.out.println("文件的大小:" + f.length());
//返回文件大小,若是文件夹或者不存在,返回0
File newfile = new File("text");
boolean flag = newfile.createNewFile();
System.out.println("新文件是否创建成功:" + flag);
//createNewFile函数用来创建新的文件,如果file对象不存在,则创建,如果存在,则返回false
//如果创建file对象是给的pathname参数是一个目录,那么该函数会创建一个没有后缀的文件(名称为pathname所给的字符串)
//注意:该函数不能创建一些与底层操作系统关键字相同的文件,如con,con3
flag = newfile.delete();
System.out.println("文件是否删除成功:" + flag);
}
}
3.四大抽象类
适用音视频,图片,word等文件
- InputStream 字节输入流
- OutputStream 字节输出流
适用纯文本文件
- Reader 字符输入流
- Writer 字符输出流
能用字符流处理的一定能用字节流处理
反之,用字节流处理的不一定能用字符流处理,如图片等
4.标准步骤
- 创建源
- 选择流
- 具体操作
- 释放资源
5.文件字节流
可以处理任何类型的文件
构造器参数可以是文件对象,也可以是文件路径String path
FileInputStream一个一个字符的读取
public class IOInputByOne {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String path = "src.txt";
//创建源
File file = new File(path);
//选择流
InputStream in = null;
try {
in = new FileInputStream(file);
int temp;
//具体操作 一个一个的读取,in.read()里面没有参数
while((temp = in.read()) != -1){
System.out.println((char)temp);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
try {
//释放资源
if(in!=null)
in.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
FileInputStream一卡车一卡车的读(为了提高读取速率,先设置一个容器,将内容读到容器内,当容器满时,再将容器中的内容写到文件中去)
为避免文件最后的一段内容(小于容器容量)滞留再内存中,要进行强制刷新操作out.flush()。
public class IOOutputByFlush {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String path = "dest.txt";
//创建源
File file = new File(path);
//选择流
OutputStream out = null;
try {
out = new FileOutputStream(file, true);
//append:是否追加
String msg = "this is a msg!
";
//编码
byte[] flush = msg.getBytes("utf8");
out.write(flush,0, flush.length);
out.flush();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if(out!=null)
{
out.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
FileOutputStream将数据写到文件中去
public class IOOutputByFlush {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String path = "dest.txt";
//创建源
File file = new File(path);
//选择流
OutputStream out = null;
try {
out = new FileOutputStream(file, true);
//append:是否追加
String msg = "this is a msg!
";
//编码
byte[] flush = msg.getBytes("utf8");
out.write(flush,0, flush.length);
out.flush();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if(out!=null)
{
out.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
6.文件字符流
用于处理文件,仅限纯文本类型
FileReader 测试
public class Test_File_Read {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String path = "src.txt";
File src = new File(path);
Reader reader = null;
try {
reader = new FileReader(src);
char[] flush = new char[1024];
int len = -1;
while((len=reader.read(flush))!=-1){
String msg = new String(flush);
System.out.println(msg);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if(reader!=null)
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
FileWriter测试
public class Test_File_Writer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String path = "dest.txt";
File dest = new File(path);
Writer writer = null;
try {
writer = new FileWriter(dest);
//写法一
String msg = "I'm destination!我是目的地!!!";
char[] flush = msg.toCharArray();
writer.write(flush);
writer.flush();
//写法二
String msg = "I'm destination!我是目的地!!!";
writer.write(msg,0,msg.length);
writer.flush();
//写法三
String msg = "I'm destination!我是目的地!!!";
writer.append(msg).append("追加内容!");
//append返回this对象,可以链式调用
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if(writer!=null)
writer.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
7.字节数组流
用于处理字节数组
该流直接操作电脑内存,由JVM进行GC操作,不需要通知OS关闭,不像文件流Java程序不能直接操作系统资源,需要与操作系统OS打交道,让OS去释放相关资源。
它的close函数是一个空方法
ByteArrayInputStream测试
//1.创建源
String msg = "这是一段文本!";
byte[] src = msg.getBytes();
//2.选择流
InputStream in = null;
in = new ByteArrayInputStream(src);//传入字节数组
byte[] flush = new byte[6];
int len = -1;
try{
while((len=in.read(flush))!=-1){
String str = new String(flush,0,len);
System.out.println(str);
}
}
catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
try {
if(in!=null)
in.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
ByteArrayOutputStream测试
//1.创建源
byte[] dest = null;
//2.选择流,不用关联源
ByteArrayOutputStream out = null;
try{
out = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
//构造器不需要参数,它会自动的指定相关的地址,如果手的指定的话,大小不易确定,不好控制
String msg = "show me the code!";
byte[] datas = msg.getBytes();
out.write(datas,0,datas.length);
out.flush();
//使用toByteArray函数获取字节数组流的相关数据
dest = out.toByteArray();
String dest_str = new String(dest,0,dest.length);
System.out.println(dest_str);
}catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if(out!=null)
out.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
8.装饰器设计模式
节点流永远在一线,但为了能够更加灵活方便且高效的处理数据,我们通过一个间接流去调用(装饰)节点流,这个间接流称之为处理流或者装饰流。采用了装饰器设计模式。
装饰器的四个部分:
- 抽象组件
- 具体组件
- 抽象装饰类
- 具体装饰类
装饰器设计模式的体验
public class TestDecorate {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Drink coffee = new Coffee();
Drink coffee_milk = new Milk(coffee);
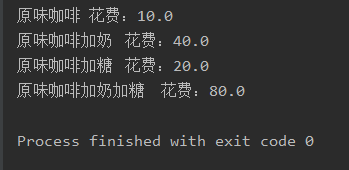
System.out.println(coffee_milk.info() + " 花费:" + coffee_milk.cost());
Drink coffee_suger = new Suger(coffee);
System.out.println(coffee_suger.info() + " 花费:" + coffee_suger.cost());
Drink coffee_milk_suger = new Suger(coffee_milk);
System.out.println(coffee_milk_suger.info() + " 花费:" + coffee_milk_suger.cost());
}
}
/**
* 抽象组件
*/
interface Drink{
double cost();
String info();
}
/**
* 具体组件
*/
class Coffee implements Drink{
String name = "原味咖啡";
@Override
public double cost() {
return 10;
}
@Override
public String info() {
return name;
}
}
/**
* 抽象装饰类
*/
abstract class Decorate implements Drink {
//对抽象组件的引用
private Drink drink;
public Decorate(Drink drink) {
this.drink = drink;
}
@Override
public double cost() {
return this.drink.cost();
}
@Override
public String info() {
return this.drink.info();
}
}
/**
* 具体装饰类Milk
*/
class Milk extends Decorate{
public Milk(Drink drink) {
super(drink);
}
@Override
public double cost() {
return super.cost()*4;
}
@Override
public String info() {
return super.info() + "加奶";
}
}
/**
* 具体装饰类Suger
*/
class Suger extends Decorate{
public Suger(Drink drink) {
super(drink);
}
@Override
public double cost() {
return super.cost() * 2;
}
@Override
public String info() {
return super.info() + "加糖";
}
}
9.字节缓冲流
BufferedInputStream,BufferedOutputStream
处理流,可以提高数据读写速度,但只能提高一次,无论嵌套几次,都只提高一次效率
File src = new File(srcPath);
File dest = new File(destPath);
InputStream in = null;
OutputStream out = null;
try {
in = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(src));
out = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(dest));
//处理流这么用就行了,先new一个处理流对象,里面参数传一个节点流对象
byte[] flush = new byte[1024];
int len = -1;
while ((len=in.read(flush)) != -1){
out.write(flush,0,flush.length);
out.flush();
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//释放资源遵循先打开后关闭的原则,也可以直接关闭外层的流
//再关闭外层流的时候,其底层也会先找到关闭内部流
try {
if(out!=null)
out.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if(in!=null)
in.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
10.字符缓冲流
BufferedReader,BufferedWriter
用于处理纯文本数据,如果是音视频等文件,则无法处理
JDK的try...with...resource功能,在try后面借一个括号,在括号里面声明流,多个流以分号";"分隔
这样写的好处是我们不再需要自己手动去关闭流,jdk会自动帮我们关闭
File src = new File(srcPath);
File dest = new File(destPath);
try(BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(src));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(dest))) {
String line = null;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null){
bw.write(line);
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
//readLine读取一行,返回值String
//newLine相当于"
",不用在字符串末尾加
了
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
11.转换流
BufferedReader,BufferedWriter
换流是字节流与字符流的桥梁,只有在处理纯文本的时候才能将字节流转换为字符流,在转换为字符流之后,我们又可以为了提高效率在外层加上一层BufferedReader或者BufferedWriter
try(BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
BufferedWriter writer = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out))) {
String msg = "";
while(!msg.equals("exit")) {
msg = reader.readLine();
writer.write(msg);
writer.newLine();
writer.flush();
}
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
12.数据流
DataOutputStream,DataInputStream
先写出后读取
1.读取顺序要和写出顺序保持一致,否则报错
2.使用了BufferedOutputStream来提高效率的话,切记要在写完后flush一下,否则也用可能报错 使用了缓冲区的任何流最后在写完数据之后flush一下,避免数据滞留在缓冲区,未完全写入,从而出现各种错误
public class TestDataIO {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(new BufferedOutputStream(baos));
dos.writeUTF("i'm string!"); //写字符串
dos.writeInt(18); //写int型
dos.writeBoolean(false); //写boolean型
dos.flush();
byte[] datas = baos.toByteArray();
System.out.println(datas.length);
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(new BufferedInputStream(new ByteArrayInputStream(datas)));
String msg = dis.readUTF();
int age = dis.readInt();
boolean flag = dis.readBoolean();
System.out.println("msg:" + msg + "
age:" + age + "
flag:" + flag);
}
}
13.对象流
ObjectOutputStream,ObjectInputStream
由对象到文件(txt,数据库文件等) 序列化(也称持久化)
由文件到对象 反序列化
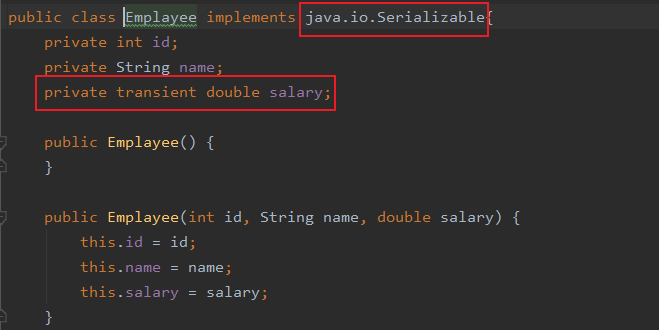
不是所有的对象都可以实现序列化,只有实现了java.io.Serializable接口的类才可以序列化
instanceof关键字,判断某对象是否是某个类的实例
transient关键字,透明,如果类中的某个属性比较敏感,不想再序列化的时候保存, 则可以加上此关键字,最后获取该属性的时候即变为透明,基本类型为默认值,对象为null
public class TestObject {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("obj.txt")));
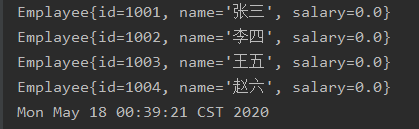
Emplayee e1 = new Emplayee(1001, "张三", 20000);
Emplayee e2 = new Emplayee(1002, "李四", 2000);
Emplayee e3 = new Emplayee(1003, "王五", 2000);
Emplayee e4 = new Emplayee(1004, "赵六", 2000);
oos.writeObject(e1);
oos.writeObject(e2);
oos.writeObject(e3);
oos.writeObject(e4);
Date d = new Date();
oos.writeObject(d);
oos.flush();
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("obj.txt")));
Object o1= ois.readObject();
Object o2 = ois.readObject();
Object o3 = ois.readObject();
Object o4 = ois.readObject();
Object date_obj = ois.readObject();
System.out.println(o1);
System.out.println(o2);
System.out.println(o3);
System.out.println(o4);
if(date_obj instanceof Date){
System.out.println((Date)date_obj);
}
ois.close();
oos.close();
}
}
14.打印流
PrintStream 对OutputStream处理
PrintWriter 增加对Writer out的处理
PrintStream
public class TestPrintStream {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
PrintStream ps = new PrintStream(new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("print.txt")),true);
ps.println(false);
ps.println("hello, future!");
//重定向输出端到文件里
System.setOut(ps);
System.out.println("change");//此时change会被写入到print.txt文件中
//重定向输出到控制台
System.setOut(new PrintStream(new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(FileDescriptor.out)), true));
System.out.println("i'm back");
ps.close();
}
}
PrintWriter
public class TestPrintWriter {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("printWriter.txt")));
pw.println("future");
pw.println(2022);
pw.close();
}
}
15.序列流
如果有多个流,将多个流放到一个容器中,再将容器丢入序列流,从而把对多个流的处理简化成对一个流的处理
public class TestSequence {
private String outPath;//输出文件
private String srcDirs;//输入文件夹
private List<String> srcPaths;
private File filesDir;
public TestSequence(String srcDirs, String outPath) {
this.outPath = outPath;
this.srcDirs = srcDirs;
this.filesDir = new File(srcDirs);
this.srcPaths = new ArrayList<>();
for(File temp: filesDir.listFiles()){
srcPaths.add(temp.getName());
}
}
public void meger() throws IOException {
OutputStream os = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(outPath));
Vector<InputStream> vi = new Vector<>();//容器
for(int i=0;i<srcPaths.size();i++){
vi.add(new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("dest/" + srcPaths.get(i))));
}
//序列流
SequenceInputStream sis = null;
sis = new SequenceInputStream(vi.elements());
//拷贝文件到一个文件里
byte[] flush = new byte[1024];
int len = -1;
while ((len=sis.read(flush))!=-1){
os.write(flush,0,len);
}
os.flush();
sis.close();
os.close();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
TestSequence ts = new TestSequence("dest","i'm.txt");
ts.meger();
}
}
16.随机流
RandomAccessFile 使用seek()函数设置起始位置偏移量
通过构造器的第二个参数mode为"r"还是"rw"区分读文件还是写文件
RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile(this.src,"r");
RandomAccessFile raf2 = new RandomAccessFile(this.destPaths.get(i) ,"rw");
//起始位置偏移
raf.seek(beginPos);
byte[] flush = new byte[1024];
int len = -1;
while ((len=raf.read(flush))!=-1){
if(realSize>len){
raf2.write(flush,0,len);
realSize -= len;
}else {
raf2.write(flush,0,realSize);
break;
}
}
17.CommonsIO
下载地址:https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/apache//commons/io/binaries/commons-io-2.6-bin.zip
导入:将下载下来的zip解压,把里面的commons.io.jar和sources.jar复制到项目中的lib文件夹,然后右键
idea:

eclipse:bulid path---->add to path
测试基本功能:
public class TestCIO {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//文件大小
long len = FileUtils.sizeOf(new File("IO.png"));
System.out.println(len);
//文件夹大小
len = FileUtils.sizeOf(new File("src"));
System.out.println(len);
//子孙文件
Collection<File> files = FileUtils.listFiles(new File("D:\IDEA_Workspace\Sxt_Java_Study\src\IO_Study_CLL"),
EmptyFileFilter.NOT_EMPTY,null);
for(File file: files){
System.out.println(file.getPath());
}
/**
* FileFilterUtils 文件过滤的工具,有or,and
* EmptyFileFilter 空文件过滤工具,有为空,不为空选项
* SuffixFileFilter 文件后缀过滤工具
* DirectoryFileFilter 目录过滤工具,.INSTANCE表示所有子孙集
*/
files = FileUtils.listFiles(new File("D:\IDEA_Workspace\Sxt_Java_Study\src\IO_Study_CLL"),
FileFilterUtils.and(new SuffixFileFilter("java"), EmptyFileFilter.NOT_EMPTY), DirectoryFileFilter.INSTANCE);
for(File file: files){
System.out.println(file.getPath());
}
}
}
测试文件拷贝
/**
* 复制文件
*
* 注意事项:
* copyDirectory仅仅是复制目录里面的内容
* copyDirectoryToDirectory是将源目录作为子目录复制到目的目录里面去
*/
public class testCIOCopy {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//复制文件
FileUtils.copyFile(new File("D:\IDEA_Workspace\Sxt_Java_Study\src\TestCommonsIO\IO.png"), new File("D:\IDEA_Workspace\Sxt_Java_Study\src\TestCommonsIO\IO-copy.png"));
//复制目录
FileUtils.copyDirectory(new File("random"), new File("random-copy"));
//复制文件到目录
FileUtils.copyFileToDirectory(new File("hello.txt"), new File("random"));
//复制目录到目录
FileUtils.copyDirectoryToDirectory(new File("random"), new File("random-parent"));
//拷贝URL内容
String url = "http://img.netbian.com/file/2019/1216/9cc8ee311939ec9bfcf9a30a7eb380bc.jpg";
FileUtils.copyURLToFile(new URL(url), new File("net.jpg"));
//拷贝url到String
String data = IOUtils.toString(new URL("http://www.baidu.com"), "utf8");
System.out.println(data);
}
}
测试读取文件
/**
* 测试读取文件
*/
public class testCIOread {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File file = new File("D:\IDEA_Workspace\Sxt_Java_Study\src\TestCommonsIO\shi.txt");
//读取到字符串中
String shi = FileUtils.readFileToString(file,"utf8");
System.out.println(shi);
//读取到字符数组中
byte[] shi2 = FileUtils.readFileToByteArray(file);
//逐行读取
List<String> shi3 = FileUtils.readLines(file,"utf8");
for(String temp: shi3){
System.out.println(temp);
}
//类似迭代器
LineIterator iter = FileUtils.lineIterator(file,"utf8");
while (iter.hasNext()){
System.out.println(iter.nextLine());
}
}
}
测试写入文件
/**
* 测试CIO写文件
*/
public class testCIOwrite {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String outPath = "D:/IDEA_Workspace/Sxt_Java_Study/src/TestCommonsIO/output.txt";
File outFile = new File(outPath);
String data = "学习是一件幸福的事情!
";
//写String数据
FileUtils.write(outFile,"学习是一件伟大的事业!
","utf8");
FileUtils.writeStringToFile(outFile,"学习是一件辛苦的事情!
","utf8",true);
//true->追加
//写byte数组
FileUtils.writeByteArrayToFile(outFile,data.getBytes("utf8"),0,data.getBytes().length,true);
//写list集合
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
list.add(i + " ");
}
FileUtils.writeLines(outFile,list,"
",true);
//第三个参数"
"是list元素与元素之间的间隔字符串
}
}