今天要介绍一个这样的数据结构:
- 单向链接
- 有序保存
- 支持添加、删除和检索操作
- 链表的元素查询接近线性时间
——跳跃表 Skip List
一、普通链表
对于普通链接来说,越靠前的节点检索的时间花费越低,反之则越高。而且,即使我们引入复杂算法,其检索的时间花费依然为O(n)。为了解决长链表结构的检索问题,一位名叫William Pugh的人于1990年提出了跳跃表结构。基本思想是——以空间换时间。
二、简单跳跃表(Integer结构)
跳跃表的结构是多层的,通过从最高维度的表进行检索再逐渐降低维度从而达到对任何元素的检索接近线性时间的目的O(logn)。
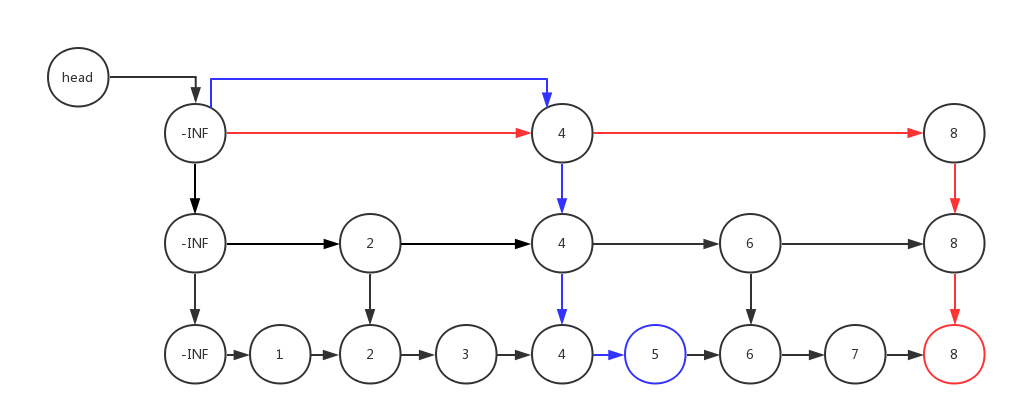
如图:对节点8的检索走红色标记的路线,需要4步。对节点5的检索走蓝色路线,需要4步。由此可见,跳跃表本质上是一种网络布局结构,通过增加检索的维度(层数)来减少链表检索中需要经过的节点数。理想跳跃表应该具备如下特点:包含有N个元素节点的跳跃表拥有log2N层,并且上层链表包含的节点数恰好等于下层链表节点数的1/2。但如此严苛的要求在算法上过于复杂。因此通常的做法是:每次向跳跃表中增加一个节点就有50%的随机概率向上层链表增加一个跳跃节点,并以此类推。
接下来,我们做如下规范说明:
- 跳跃表的层数,我们称其维度。自顶向下,我们称为降维,反之亦然。
- 表中,处于不同链表层的相同元素。我们称为“同位素”。
- 最底层的链表,即包含了所有元素节点的链表是L1层,或称基础层。除此以外的所有链表层都称为跳跃层。
以下是代码实现
#pragma once #ifndef SKIPLIST_INT_H_ #define SKIPLIST_INT_H_ #include <cstdlib> /* srand, rand */ #include <ctime> /* time */ #include <climits> /* INT_MIN */ /* 简单跳跃表,它允许简单的插入和删除元素,并提供O(logn)的查询时间复杂度。 */ /* SkipList_Int的性质 (1) 由很多层结构组成,level是通过一定的概率随机产生的,基本是50%的产生几率。 (2) 每一层都是一个有序的链表,默认是升序,每一层的链表头作为跳点。 (3) 最底层(Level 1)的链表包含所有元素。 (4) 如果一个元素出现在Level i 的链表中,则它在Level i 之下的链表也都会出现。 (5) 每个节点包含四个指针,但有可能为nullptr。 (6) 每一层链表横向为单向连接,纵向为双向连接。 */ // Simple SkipList_Int 表头始终是列表最小的节点 class SkipList_Int { private: /* 节点元素 */ struct node { node(int val = INT_MIN) :value(val), up(nullptr), down(nullptr), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} int value; // 设置4个方向上的指针 struct node* up; // 上 struct node* down; // 下 struct node* left; // 左 struct node* right; // 右 }; private: node* head; // 头节点,查询起始点 int lvl_num; // 当前链表层数 /* 随机判断 */ bool randomVal(); public: SkipList_Int(): lvl_num(1) { head = new node(); } /* 插入新元素 */ void insert(int val); /* 查询元素 */ bool search(int val); /* 删除元素 */ void remove(int val); }; #endif // !SKIPLIST_INT_H_
我们需要实现插入、查询和删除三种操作。为了保证所有插入的元素均处于链表头的右侧。我们使用INT_MIN作为头部节点。并且为了方便在不同维度的链表上转移,链表头节点包含up和down指针,普通整型节点之间的只存在down指针,水平方向上只存在right指针。
#include "SkipList_Int.h" static unsigned int seed = NULL; // 随机种子 bool SkipList_Int::randomVal() { if (seed == NULL) { seed = (unsigned)time(NULL); } ::srand(seed); int ret = ::rand() % 2; seed = ::rand(); if (ret == 0) { return true; } else { return false; } } void SkipList_Int::insert(int val) { /* 首先查找L1层 */ node* cursor = head; node* new_node = nullptr; while (cursor->down != nullptr) { cursor = cursor->down; } node* cur_head = cursor; // 当前层链表头 while (cursor->right != nullptr) { if (val < cursor->right->value && new_node == nullptr) { new_node = new node(val); new_node->right = cursor->right; cursor->right = new_node; } cursor = cursor->right; // 向右移动游标 } if (new_node == nullptr) { new_node = new node(val); cursor->right = new_node; } /* L1层插入完成 */ /* 上层操作 */ int cur_lvl = 1; // 当前所在层 while (randomVal()) { cur_lvl++; if (lvl_num < cur_lvl) { // 增加一层 lvl_num++; node* new_head = new node(); new_head->down = head; head->up = new_head; head = new_head; } cur_head = cur_head->up; // 当前链表头上移一层 cursor = cur_head; // 继续获取游标 node* skip_node = nullptr; // 非L1层的节点 while (cursor->right != nullptr) { if (val < cursor->right->value && skip_node == nullptr) { skip_node = new node(val); skip_node->right = cursor->right; } cursor = cursor->right; } if (skip_node == nullptr) { skip_node = new node(val); cursor->right = skip_node; } while (new_node->up != nullptr) { new_node = new_node->up; } /* 连接上下两个节点 */ skip_node->down = new_node; new_node->up = skip_node; } } bool SkipList_Int::search(int val) { node* cursor = nullptr; if (head == nullptr) { return false; } /* 初始化游标指针 */ cursor = head; while (cursor->down != nullptr) { // 第一层循环游标向下 while (cursor->right != nullptr) { // 第二层循环游标向右 if (val <= cursor->right->value) { // 定位元素:于当前链表发现可定位坐标则跳出循环... break; } cursor = cursor->right; } cursor = cursor->down; } while (cursor->right != nullptr) { // L1层循环开始具体查询 if (val > cursor->right->value) { cursor = cursor->right; // 如果查找的值大于右侧值则游标可以继续向右 } else if (val == cursor->right->value) { // 如果等于则表明已经找到节点 return true; } else if (val < cursor->right->value) { // 如果小于则表明不存在该节点 return false; } } return false; // 完成遍历返回false; } void SkipList_Int::remove(int val) { node* cursor = head; // 获得游标 node* pre_head = nullptr; // 上一行的头指针,删除行时使用 while (true) { node* cur_head = cursor; // 当前行头指针 if (pre_head != nullptr) { cur_head->up = nullptr; pre_head->down = nullptr; // 解除上下级的指针 delete pre_head; pre_head = nullptr; // 指针归0 lvl_num--; // 层数-1 head = cur_head; // 重新指定起始指针 } while (cursor != nullptr && cursor->right != nullptr) { // 在当前行中查询val if (val == cursor->right->value) { node* delptr = cursor->right; cursor->right = cursor->right->right; delete delptr; // 析构找到的节点 } cursor = cursor->right; } if (cur_head->right == nullptr) { // 判断当前行是否还存在其它元素,如果不存在则删除该行并将整个跳跃表降维 pre_head = cur_head; } if (cur_head->down == nullptr) { break; } else { cursor = cur_head->down; } } }
以上代码演示的是简单整型跳跃表的具体实现方法。它演示了一种最基本的跳跃,而它的问题也显而易见。如果非整型对象,我们如何设计链表头节点?普通对象如何实现排序?以及如何比较相等?为了解决这些问题,我们需要设计一种能够支持各种类型对象的跳跃表。我们的思路是:
- 跳跃表应该支持泛型结构
- 排序规则由使用者来确定
- 链表头节点必须是独立的
三、泛型跳跃表
首先设计一个可直接比较的节点对象,重载运算符是一个不错的选择:
template<typename T> class Entry { private: int key; // 排序值 T value; // 保存对象 Entry* pNext; Entry* pDown; public: // The Constructor Entry(int k, T v) :value(v), key(k), pNext(nullptr), pDown(nullptr) {} // The Copy-constructor Entry(const Entry& e) :value(e.value), key(e.key), pNext(nullptr), pDown(nullptr) {} public: /* 重载运算符 */ bool operator<(const Entry& right) { return key < right.key; } bool operator>(const Entry& right) { return key > right.key; } bool operator<=(const Entry& right) { return key <= right.key; } bool operator>=(const Entry& right) { return key >= right.key; } bool operator==(const Entry& right) { return key == right.key; } Entry*& next() { return pNext; } Entry*& down() { return pDown; } };
特别说明一下最后两个方法的返回值是指针的引用,它可以直接作为左值。(Java程序员表示一脸懵逼)
然后,还需要设计一个独立于检索节点的链表头对象:
struct Endpoint { Endpoint* up; Endpoint* down; Entry<T>* right; };
随机判断函数没有太大变化,只是将种子seed的保存位置从函数外放到了对象中。以下是完整代码:
#pragma once #ifndef SKIPLIST_ENTRY_H_ #define SKIPLIST_ENTRY_H_ /* 一个更具备代表性的泛型版本 */ #include <ctime> #include <cstdlib> template<typename T> class Entry { private: int key; // 排序值 T value; // 保存对象 Entry* pNext; Entry* pDown; public: // The Constructor Entry(int k, T v) :value(v), key(k), pNext(nullptr), pDown(nullptr) {} // The Copy-constructor Entry(const Entry& e) :value(e.value), key(e.key), pNext(nullptr), pDown(nullptr) {} public: /* 重载运算符 */ bool operator<(const Entry& right) { return key < right.key; } bool operator>(const Entry& right) { return key > right.key; } bool operator<=(const Entry& right) { return key <= right.key; } bool operator>=(const Entry& right) { return key >= right.key; } bool operator==(const Entry& right) { return key == right.key; } Entry*& next() { return pNext; } Entry*& down() { return pDown; } }; template<typename T> class SkipList_Entry { private: struct Endpoint { Endpoint* up; Endpoint* down; Entry<T>* right; }; struct Endpoint* header; int lvl_num; // level_number 已存在的层数 unsigned int seed; bool random() { srand(seed); int ret = rand() % 2; seed = rand(); return ret == 0; } public: SkipList_Entry() :lvl_num(1), seed(time(0)) { header = new Endpoint(); } /* 插入新元素 */ void insert(Entry<T>* entry) { // 插入是一系列自底向上的操作 struct Endpoint* cur_header = header; // 首先使用链表header到达L1 while (cur_header->down != nullptr) { cur_header = cur_header->down; } /* 这里的一个简单想法是L1必定需要插入元素,而在上面的各跳跃层是否插入则根据random确定 因此这是一个典型的do-while循环模式 */ int cur_lvl = 0; // current_level 当前层数 Entry<T>* temp_entry = nullptr; // 用来临时保存一个已经完成插入的节点指针 do { Entry<T>* cur_cp_entry = new Entry<T>(*entry); // 拷贝新对象 // 首先需要判断当前层是否已经存在,如果不存在增新增 cur_lvl++; if (lvl_num < cur_lvl) { lvl_num++; Endpoint *new_header = new Endpoint(); new_header->down = header; header->up = new_header; header = new_header; } // 使用cur_lvl作为判断标准,!=1表示cur_header需要上移并连接“同位素”指针 if (cur_lvl != 1) { cur_header = cur_header->up; cur_cp_entry->down() = temp_entry; } temp_entry = cur_cp_entry; // 再需要判断的情况是当前所在链表是否已经有元素节点存在,如果是空链表则直接对右侧指针赋值并跳出循环 if (cur_header->right == nullptr) { cur_header->right = cur_cp_entry; break; } else { Entry<T>* cursor = cur_header->right; // 创建一个游标指针 while (true) { // 于当前链表循环向右寻找可插入点,并在找到后跳出当前循环 if (*cur_cp_entry < *cursor) { // 元素小于当前链表所有元素,插入链表头 cur_header->right = cur_cp_entry; cur_cp_entry->next() = cursor; break; } else if (cursor->next() == nullptr) { // 元素大于当前链表所有元素,插入链表尾 cursor->next() = cur_cp_entry; break; } else if (*cur_cp_entry < *cursor->next()) { // 插入链表中间 cur_cp_entry->next() = cursor->next(); cursor->next() = cur_cp_entry; break; } cursor = cursor->next(); // 右移动游标 } } } while(random()); } /* 查询元素 */ bool search(Entry<T>* entry) const { if (header->right == nullptr) { // 判断链表头右侧空指针 return false; } Endpoint* cur_header = header; // 在lvl_num层中首先找到可以接入的点 for (int i = 0; i < lvl_num; i++) { if (*entry < *cur_header->right) { cur_header = cur_header->down; } else { Entry<T>* cursor = cur_header->right; while (cursor->down() != nullptr) { while (cursor->next() != nullptr) { if (*entry <= *cursor->next()) { break; } cursor = cursor->next(); } cursor = cursor->down(); } while (cursor->next() != nullptr) { if (*entry > *cursor->next()) { cursor = cursor->next(); } else if (*entry == *cursor->next()) { return true; } else { return false; } } return false; // 节点大于L1最后一个元素节点,返回false } } return false; // 找不到接入点,则直接返回false; } /* 删除元素 */ void remove(Entry<T>* entry) { if (header->right == nullptr) { return; } Endpoint* cur_header = header; Entry<T>* cursor = cur_header->right; int lvl_counter = lvl_num; // 因为在删除的过程中,跳跃表的层数会中途发生变化,因此应该在进入循环之前要获取它的值。 for (int i = 0; i < lvl_num; i++) { if (*entry == *cur_header->right) { Entry<T>* delptr = cur_header->right; cur_header->right = cur_header->right->next(); delete delptr; } else { Entry<T> *cursor = cur_header->right; while (cursor->next() != nullptr) { if (*entry == *cursor->next()) { // 找到节点->删除->跳出循环 Entry<T>* delptr = cursor->next(); cursor->next() = cursor->next()->next(); delete delptr; break; } cursor = cursor->next(); } } // 向下移动链表头指针的时候需要先判断当前链表中是否还存在Entry节点 if (cur_header->right == nullptr) { Endpoint* delheader = cur_header; cur_header = cur_header->down; header = cur_header; delete delheader; lvl_num--; } else { cur_header = cur_header->down; } } } }; #endif // !SKIPLIST_ENTRY_H_
后记:网上有不少别人提供的具体实现。不过感觉相互复制的居多。学习没有近路可言,抄小路取得的“成功”并不完全属于自己。作为一个或许入行有些晚的程序员,我时刻惊醒自己要想在这条路上走的更远更稳,必须依靠扎实的基本功。什么是基本功?无非“语言”,“数据结构与算法”,“设计模式”。但是这些东西往往对于企业或项目而言并不被看重。理由很简单,他们只关心你能否完成工作以及足够快速——代码质量或个人成长于客户于雇主皆为浮云。
但对于自己来说,试着接触那些“本源”性的知识是对未来的投资。如果你和我一样希望5年后的自己能够更加自由的生活。就请暂时忽略项目经理的催促和无理客户的抱怨,也请放下在领导面前所做出的表面文章。静下来,对于大家都好。