一、对象转型 Casting
//对象转型Casting class Animal{ public String name; Animal(String name){ this.name = name; } } class Cat extends Animal{ public String eyesColor; Cat(String n, String c){ super(n); eyesColor = c; } } class Dog extends Animal{ public String furColor; Dog(String n, String c){ super(n); furColor = c; } } public class Casting{ public static void main(String[]args){ Animal a = new Animal("name"); Cat c = new Cat("catname", "blue"); Dog d = new Dog("dogname", "black"); System.out.println(a instanceof Animal); System.out.println(c instanceof Animal); System.out.println(d instanceof Animal); System.out.println(a instanceof Cat); a = new Dog("bigyellow","yellow"); System.out.println(a.name); //System.out.println(a.furColor); wrong System.out.println(a instanceof Animal); System.out.println(a instanceof Dog); Dog d1 = (Dog)a; System.out.println(d1.furColor); } }

true true true false bigyellow true true yellow
1、对象转型:父类引用指向子类对象,如上述代码中,Animal a = new Dog("bigyellow" , "yellow"); Animal 的引用类型变量a 指向子类对象Dog。
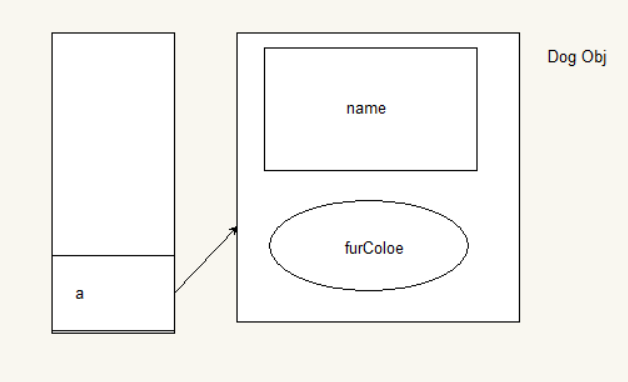
p.s.提及一下继承,子类继承父类时,子类对象中含有相应的父类对象 。如下图所示,但是 a 只能访问本身对象内的成员变量。(虽然引用指向Dog Obj ,但是只能看到Animal Obj的成员)不能访问furColor (图中打错。 = = )若要访问子类对象内的成员变量,进行强制类型转换。 Dog d1 = (Dog ) a ;
2、 Advantage : 对象转型的引入,使得可扩展性提高。如某方法中,只是参数的类型不同(且参数继承同一父类),其他一致。避免了重复写结构一样,只是传递参数不同的代码,而且加入新的子类的话,只需定义新子类的属性和方法,使父类对象指向子类。若需执行子类的内部内容,进行强制类型转换再调用。 Casting 是 Dynamic Binding 的前提和基础!
Disadvantage:只能访问父类的成员,子类的成员的访问需要强制类型转换。
二、动态绑定/多态 Dynamic Binding / Polymorph
abstract class Animal{ public String name; Animal(String name){ this.name = name; } /* public void enjoy(){ System.out.println("yelling..."); } */ public abstract void enjoy(); } class Cat extends Animal{ private String eyesColor; Cat(String n, String c){ super(n); eyesColor = c; } public void enjoy(){ System.out.println("meow..."); } } class Dog extends Animal{ private String furColor; Dog(String n, String c){ super(n); furColor = c; } public void enjoy(){ System.out.println("Dog barking..."); } } class Bird extends Animal{ Bird(){ super("bird"); } public void enjoy(){ System.out.println("bird screaming...."); } } class Lady{ private String name; private Animal pet; //define superclass reference Lady(String name, Animal pet){ this.name = name; this.pet = pet; } public void myPetEnjoy(){ pet.enjoy(); } } public class TestPolymorph{ public static void main(String [] args){ Cat c = new Cat("catname","blue"); Dog d = new Dog("dogname", "black"); Bird b = new Bird(); Lady L1 = new Lady("L1",c); Lady L2 = new Lady("L2",d); Lady L3 = new Lady("L3",b); L1.myPetEnjoy(); c.enjoy(); L2.myPetEnjoy(); L3.myPetEnjoy(); } }

meow...
meow...
Dog barking...
bird screaming....
1、动态绑定:根据实际传进来的对象调用其相应的方法。
Lady L1 = new Lady("L1" , c); Lady 类中形参为Animal , 但实际传入为 Cat (Casting的实现) 根据最终结果,调用的为传入的Cat c 的重写方法。
动态:java在执行过程中(java 指令),会识别实际传入的Obj 的类型。 绑定:将原来Animal Obj 的 内部方法指针(类似C++中函数指针,存放Animal中方法在Code Segment 的地址,通过该指针可以找到方法,执行方法),改成传入Obj(即Cat 类型中定义的方法) 导致最后呈现的结果为Cat 的方法的调用。即 enjoy() 由原本的Animal 中enjoy() 改为Cat 的 enjoy()

