在spark启动之后,worker和master注册通信之后,在进入用户提交app中,new SparkContext之后就会在worker上分配exectors了。
首先在sparkContext中,会先创建和启动TaskScheduler和DAGSchedule
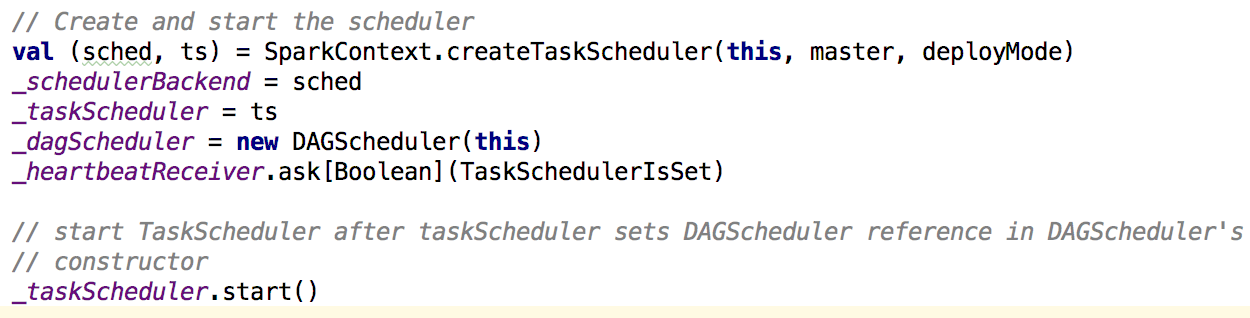
在创建TaskScheduler的时候也会创建schedulerBackend;下面看createTaskScheduler方法:
1 private def createTaskScheduler( 2 sc: SparkContext, 3 master: String, 4 deployMode: String): (SchedulerBackend, TaskScheduler) = { 5 import SparkMasterRegex._ 6 7 // When running locally, don't try to re-execute tasks on failure. 8 val MAX_LOCAL_TASK_FAILURES = 1 9 10 master match { 11 case "local" => 12 val scheduler = new TaskSchedulerImpl(sc, MAX_LOCAL_TASK_FAILURES, isLocal = true) 13 val backend = new LocalSchedulerBackend(sc.getConf, scheduler, 1) 14 scheduler.initialize(backend) 15 (backend, scheduler) 16 17 case LOCAL_N_REGEX(threads) => 18 def localCpuCount: Int = Runtime.getRuntime.availableProcessors() 19 // local[*] estimates the number of cores on the machine; local[N] uses exactly N threads. 20 val threadCount = if (threads == "*") localCpuCount else threads.toInt 21 if (threadCount <= 0) { 22 throw new SparkException(s"Asked to run locally with $threadCount threads") 23 } 24 val scheduler = new TaskSchedulerImpl(sc, MAX_LOCAL_TASK_FAILURES, isLocal = true) 25 val backend = new LocalSchedulerBackend(sc.getConf, scheduler, threadCount) 26 scheduler.initialize(backend) 27 (backend, scheduler) 28 29 case LOCAL_N_FAILURES_REGEX(threads, maxFailures) => 30 def localCpuCount: Int = Runtime.getRuntime.availableProcessors() 31 // local[*, M] means the number of cores on the computer with M failures 32 // local[N, M] means exactly N threads with M failures 33 val threadCount = if (threads == "*") localCpuCount else threads.toInt 34 val scheduler = new TaskSchedulerImpl(sc, maxFailures.toInt, isLocal = true) 35 val backend = new LocalSchedulerBackend(sc.getConf, scheduler, threadCount) 36 scheduler.initialize(backend) 37 (backend, scheduler) 38 39 case SPARK_REGEX(sparkUrl) => 40 val scheduler = new TaskSchedulerImpl(sc) 41 val masterUrls = sparkUrl.split(",").map("spark://" + _) 42 val backend = new StandaloneSchedulerBackend(scheduler, sc, masterUrls) 43 scheduler.initialize(backend) 44 (backend, scheduler) 45 46 case LOCAL_CLUSTER_REGEX(numSlaves, coresPerSlave, memoryPerSlave) => 47 // Check to make sure memory requested <= memoryPerSlave. Otherwise Spark will just hang. 48 val memoryPerSlaveInt = memoryPerSlave.toInt 49 if (sc.executorMemory > memoryPerSlaveInt) { 50 throw new SparkException( 51 "Asked to launch cluster with %d MB RAM / worker but requested %d MB/worker".format( 52 memoryPerSlaveInt, sc.executorMemory)) 53 } 54 55 val scheduler = new TaskSchedulerImpl(sc) 56 val localCluster = new LocalSparkCluster( 57 numSlaves.toInt, coresPerSlave.toInt, memoryPerSlaveInt, sc.conf) 58 val masterUrls = localCluster.start() 59 val backend = new StandaloneSchedulerBackend(scheduler, sc, masterUrls) 60 scheduler.initialize(backend) 61 backend.shutdownCallback = (backend: StandaloneSchedulerBackend) => { 62 localCluster.stop() 63 } 64 (backend, scheduler) 65 66 case masterUrl => 67 val cm = getClusterManager(masterUrl) match { 68 case Some(clusterMgr) => clusterMgr 69 case None => throw new SparkException("Could not parse Master URL: '" + master + "'") 70 } 71 try { 72 val scheduler = cm.createTaskScheduler(sc, masterUrl) 73 val backend = cm.createSchedulerBackend(sc, masterUrl, scheduler) 74 cm.initialize(scheduler, backend) 75 (backend, scheduler) 76 } catch { 77 case se: SparkException => throw se 78 case NonFatal(e) => 79 throw new SparkException("External scheduler cannot be instantiated", e) 80 } 81 } 82 }
在这个方法中会根据配置的master的url来创建相应的TaskScheduler和schedulerBackend,如果是local则创建TaskSchedulerImpl和LocalSchedulerBackend,如果是Standalone则创建TaskSchedulerImpl和StandaloneSchedulerBackend,如果是其他,例如yarn,则会在getClusterManager方法中从加载的类文件中获取ExternalClusterManager类型的类,并调用其canCreate查看是否可以创建,来创建其他的TaskScheduler和scheduler。
下面就以Standalone模式来分析接下来的操作:
扎起创建完TaskSchedulerImpl和StandaloneSchedulerBackend之后会接着创建DAGScheduler,创建的时候回用到上面创建的TaskSchedulerImpl作为参数,在其创建的过程中也会创建一个eventProcessLoop,它是DAGScheduler接收处理各类消息的时间循环体,其继承自EventLoop,它会启动一个线程来处理eventQueue中保存的信息。下面是具体的代码:
private[scheduler] val eventProcessLoop = new DAGSchedulerEventProcessLoop(this) taskScheduler.setDAGScheduler(this) ............. private[scheduler] class DAGSchedulerEventProcessLoop(dagScheduler: DAGScheduler) extends EventLoop[DAGSchedulerEvent]("dag-scheduler-event-loop") with Logging ............... private[spark] abstract class EventLoop[E](name: String) extends Logging { private val eventQueue: BlockingQueue[E] = new LinkedBlockingDeque[E]() private val stopped = new AtomicBoolean(false) private val eventThread = new Thread(name) { setDaemon(true) override def run(): Unit = { try { while (!stopped.get) { val event = eventQueue.take() try { onReceive(event) } catch { case NonFatal(e) => try { onError(e) } catch { case NonFatal(e) => logError("Unexpected error in " + name, e) } } } } catch { case ie: InterruptedException => // exit even if eventQueue is not empty case NonFatal(e) => logError("Unexpected error in " + name, e) } } } }
在OnReceive接收处理的事件信息在DAGScheduler中有定义:
private def doOnReceive(event: DAGSchedulerEvent): Unit = event match { case JobSubmitted(jobId, rdd, func, partitions, callSite, listener, properties) => dagScheduler.handleJobSubmitted(jobId, rdd, func, partitions, callSite, listener, properties) case MapStageSubmitted(jobId, dependency, callSite, listener, properties) => dagScheduler.handleMapStageSubmitted(jobId, dependency, callSite, listener, properties) case StageCancelled(stageId, reason) => dagScheduler.handleStageCancellation(stageId, reason) case JobCancelled(jobId, reason) => dagScheduler.handleJobCancellation(jobId, reason) case JobGroupCancelled(groupId) => dagScheduler.handleJobGroupCancelled(groupId) case AllJobsCancelled => dagScheduler.doCancelAllJobs() case ExecutorAdded(execId, host) => dagScheduler.handleExecutorAdded(execId, host) case ExecutorLost(execId, reason) => val workerLost = reason match { case SlaveLost(_, true) => true case _ => false } dagScheduler.handleExecutorLost(execId, workerLost) case WorkerRemoved(workerId, host, message) => dagScheduler.handleWorkerRemoved(workerId, host, message) case BeginEvent(task, taskInfo) => dagScheduler.handleBeginEvent(task, taskInfo) case SpeculativeTaskSubmitted(task) => dagScheduler.handleSpeculativeTaskSubmitted(task) case GettingResultEvent(taskInfo) => dagScheduler.handleGetTaskResult(taskInfo) case completion: CompletionEvent => dagScheduler.handleTaskCompletion(completion) case TaskSetFailed(taskSet, reason, exception) => dagScheduler.handleTaskSetFailed(taskSet, reason, exception) case ResubmitFailedStages => dagScheduler.resubmitFailedStages() }
关于eventloop在sparkStreaming中job生出和处理中也有用到,都是同样的原理;
在sparkContext创建完成TaskScheduler和DAGScheduler之后,会调用taskScheduler.start来启动TaskScheduler。这里指向的是TaskSchedulerImpl
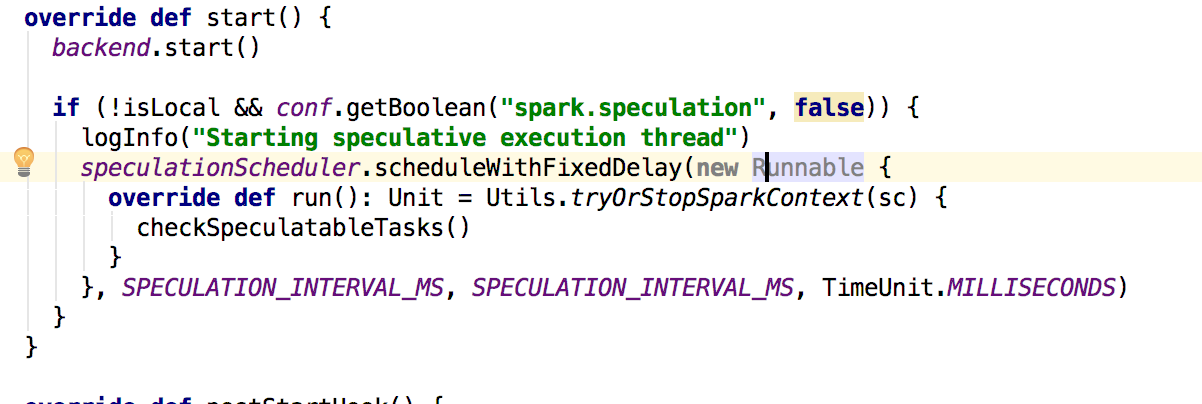
其首先会启动backend也就是StandaloneSchedulerBackend,然后在看是否开启了推测执行,如果开始则进行推测执行的相关操作,下面看看StandaloneSchedulerBackend的start方法
override def start() {
//调用父类的start方法,会根据配置参数创建DriverEndpointRef,这里的父类是CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend super.start() // SPARK-21159. The scheduler backend should only try to connect to the launcher when in client // mode. In cluster mode, the code that submits the application to the Master needs to connect // to the launcher instead. if (sc.deployMode == "client") { launcherBackend.connect() } // The endpoint for executors to talk to us val driverUrl = RpcEndpointAddress( sc.conf.get("spark.driver.host"), sc.conf.get("spark.driver.port").toInt, CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend.ENDPOINT_NAME).toString
//设置关于程序运行的参数变量 val args = Seq( "--driver-url", driverUrl, "--executor-id", "{{EXECUTOR_ID}}", "--hostname", "{{HOSTNAME}}", "--cores", "{{CORES}}", "--app-id", "{{APP_ID}}", "--worker-url", "{{WORKER_URL}}") val extraJavaOpts = sc.conf.getOption("spark.executor.extraJavaOptions") .map(Utils.splitCommandString).getOrElse(Seq.empty) val classPathEntries = sc.conf.getOption("spark.executor.extraClassPath") .map(_.split(java.io.File.pathSeparator).toSeq).getOrElse(Nil) val libraryPathEntries = sc.conf.getOption("spark.executor.extraLibraryPath") .map(_.split(java.io.File.pathSeparator).toSeq).getOrElse(Nil) // When testing, expose the parent class path to the child. This is processed by // compute-classpath.{cmd,sh} and makes all needed jars available to child processes // when the assembly is built with the "*-provided" profiles enabled. val testingClassPath = if (sys.props.contains("spark.testing")) { sys.props("java.class.path").split(java.io.File.pathSeparator).toSeq } else { Nil } // Start executors with a few necessary configs for registering with the scheduler val sparkJavaOpts = Utils.sparkJavaOpts(conf, SparkConf.isExecutorStartupConf) val javaOpts = sparkJavaOpts ++ extraJavaOpts
//这里的CoarseGraninedExecutorBackend最后会在exector启动相当与exector容器 val command = Command("org.apache.spark.executor.CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend", args, sc.executorEnvs, classPathEntries ++ testingClassPath, libraryPathEntries, javaOpts) val webUrl = sc.ui.map(_.webUrl).getOrElse("") val coresPerExecutor = conf.getOption("spark.executor.cores").map(_.toInt) // If we're using dynamic allocation, set our initial executor limit to 0 for now. // ExecutorAllocationManager will send the real initial limit to the Master later. val initialExecutorLimit = if (Utils.isDynamicAllocationEnabled(conf)) { Some(0) } else { None }
//这里包含了注册这个app的所有的信息 val appDesc = ApplicationDescription(sc.appName, maxCores, sc.executorMemory, command, webUrl, sc.eventLogDir, sc.eventLogCodec, coresPerExecutor, initialExecutorLimit)
//创建AppClient,然后启动 client = new StandaloneAppClient(sc.env.rpcEnv, masters, appDesc, this, conf) client.start() launcherBackend.setState(SparkAppHandle.State.SUBMITTED) waitForRegistration() launcherBackend.setState(SparkAppHandle.State.RUNNING) }
接下来看client的start方法,其主要是创建了一个ClientEndpoint;ClientEndpoint继承了ThreadSafeRpcEndpoint,在创建的过程中会调用他的onStart方法

在ClientEndpoint的方法中主要是调用了registerWithMaster(1)方法,最终调用的是tryRegisterAllMasters方法:
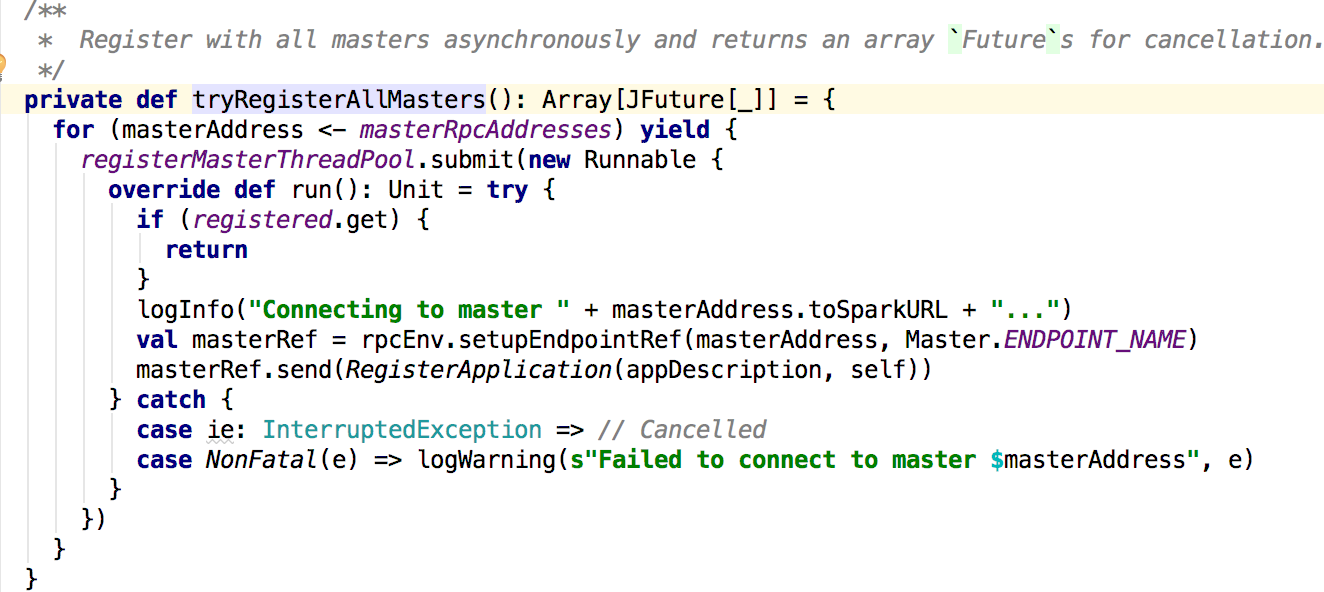
这里向master发送了一个 消息;接下来看看master对这个消息的处理:
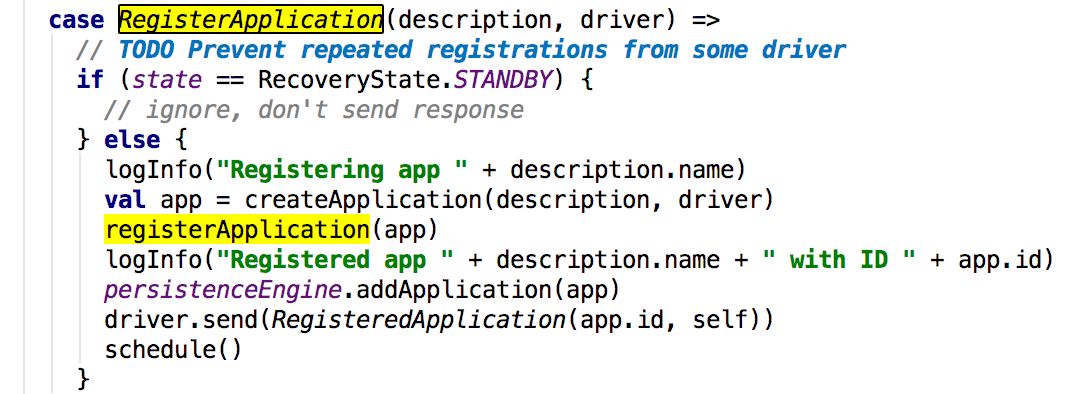
可以看到最后调用的是master的registerApplication方法,其主要就是获取传递到master关于app的数据,然后添加这个app倒Waitingapps中,其后给driver发送registeredApplication消息,
最后调用scheduler方法,其实scheduler在worker启动的时候已经调用过,因此exector,在worker启动完成之后就已经启动了,此处只是新的app过来,因此需要调用scheduler来为app分配资源:
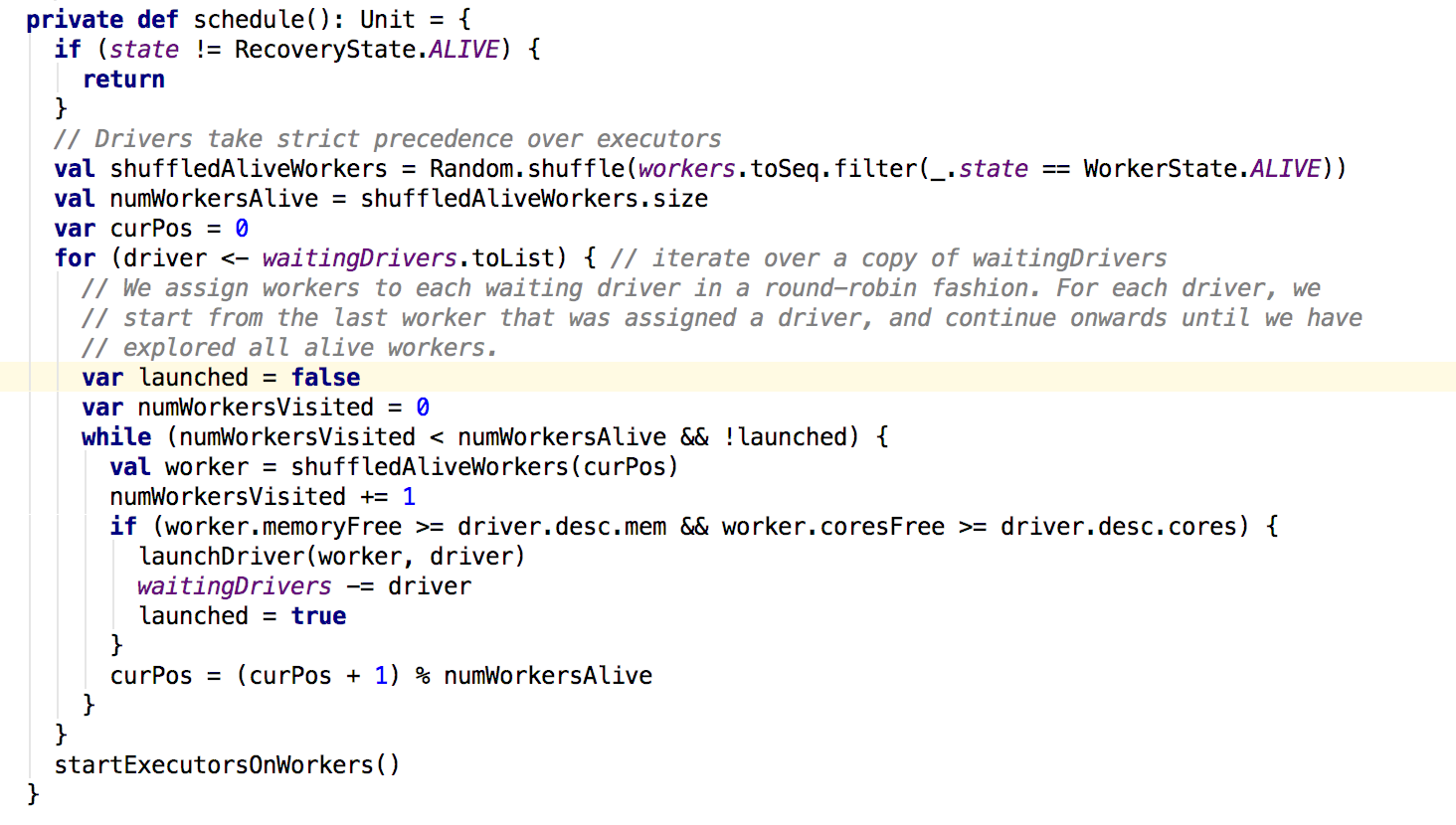
在schedule方法中,首先会进行shuffle操作,类似模拟随机选取操作,然后返回新的随机选取的集合并且过滤出来存活的worker,然后给等待调度的driver分配worker;利用while循环遍历每个woker,若满足申请的内存和core,则分配资源,并结束分配,获取下个等待调度的dirver。。。。在dirver分配到worker之后会调用launchDriver方法:
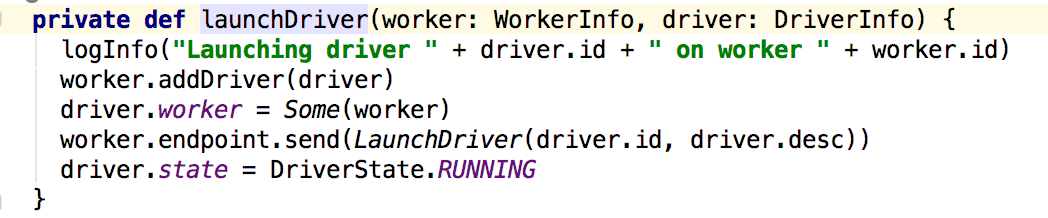
这个方法向worker发送了一个LaunchDriver消息:然后更新了driver的信息,接下来看看worker对消息的处理,
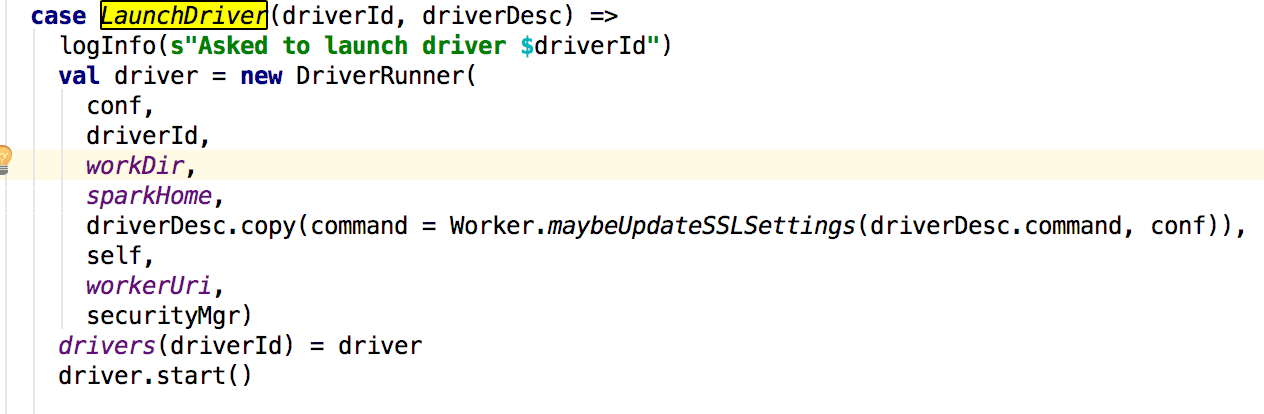
这里创建了一个DriverRunner并且进行了启动,接下来看start方法:
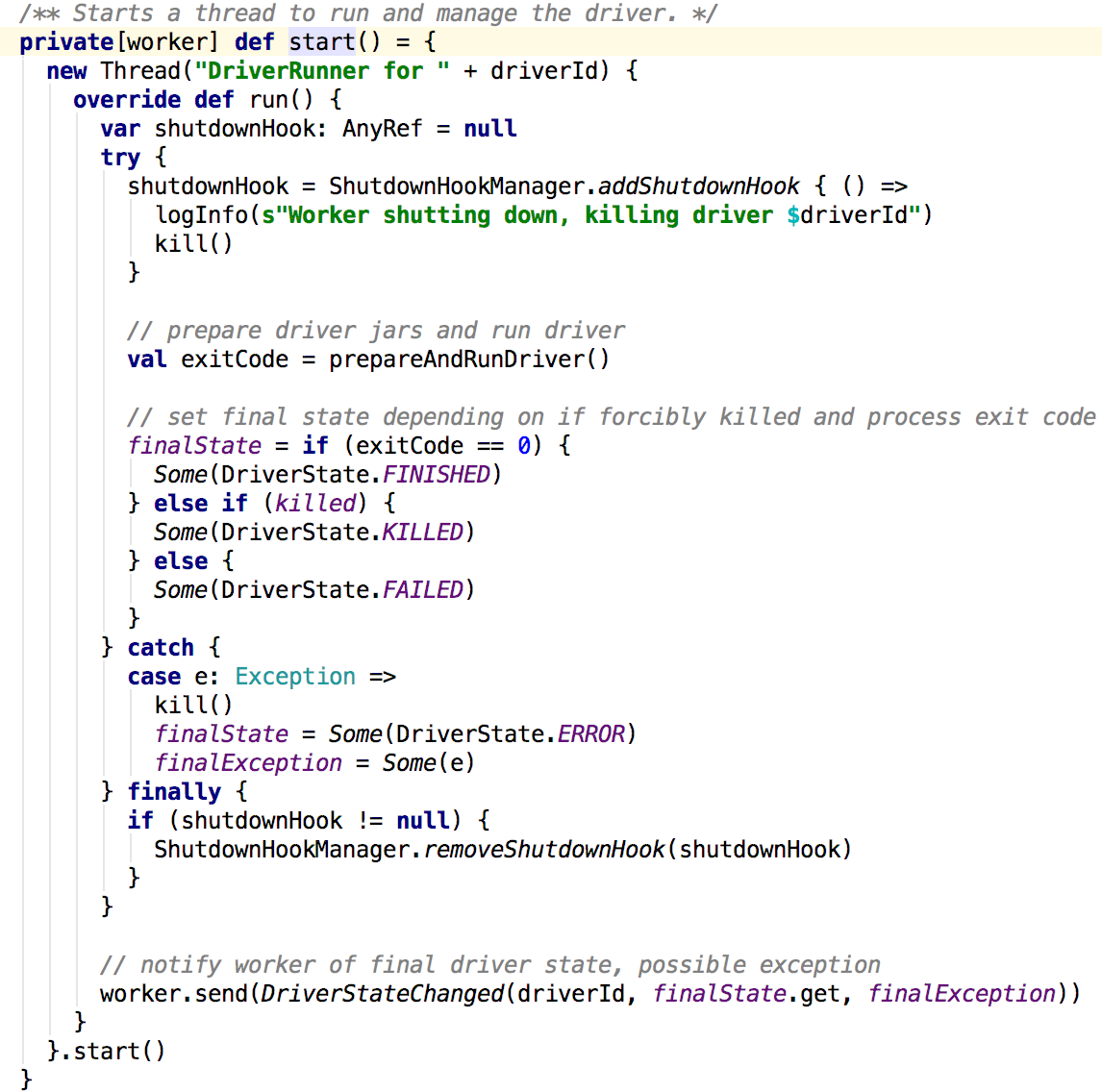
在prepareAndRunDriver中:

可以看到worker启动了一个线程来启动driver,driver利用command的参数builder而成,参数在sparkSubmit启动启动app的时候发送给master加入waitingDrivers中
接下来看startExecutorOnWorkers方法:
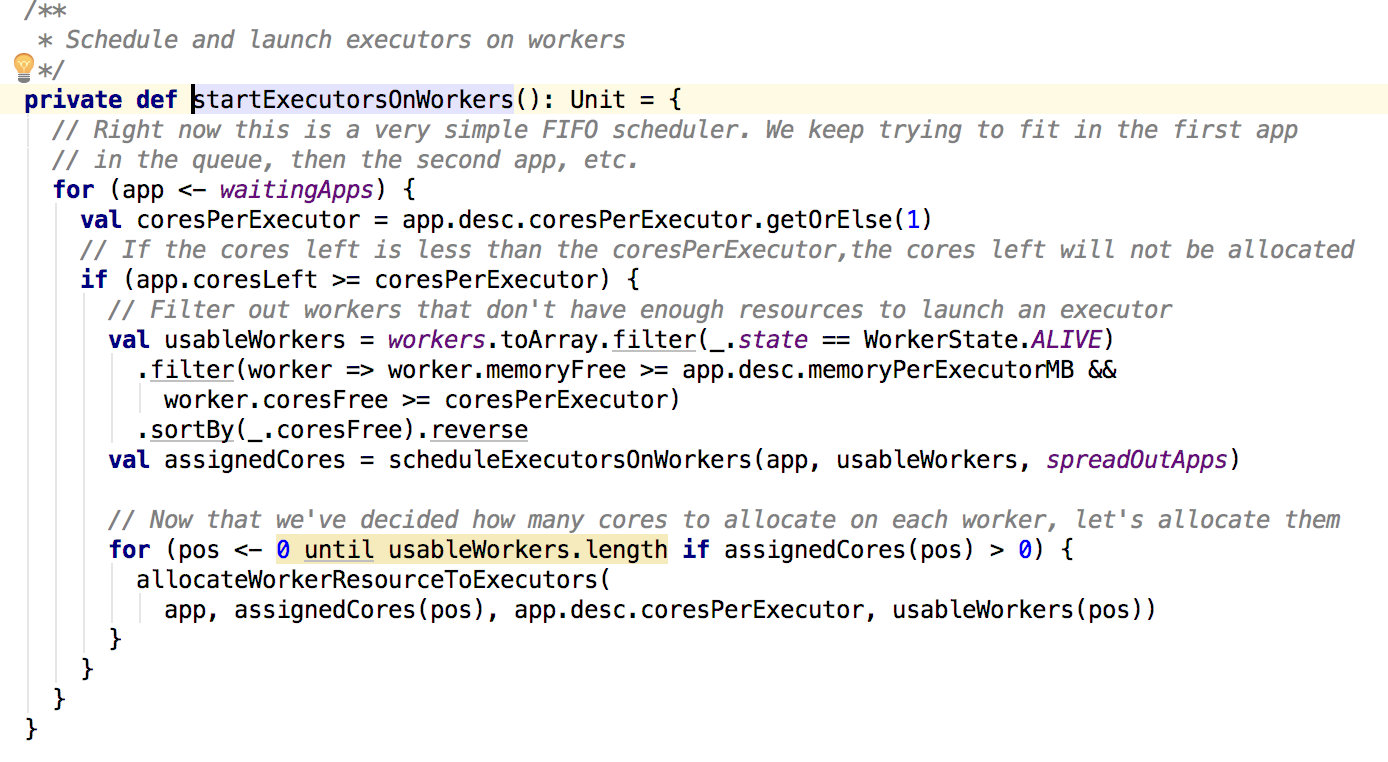
其中主要逻辑就是根据等待的app依次来分配资源,过滤满足需要的内存和core的worker来运行app,最后调用allocateWorkerResourseToExectors,然后在调用了launchExecutor方法:
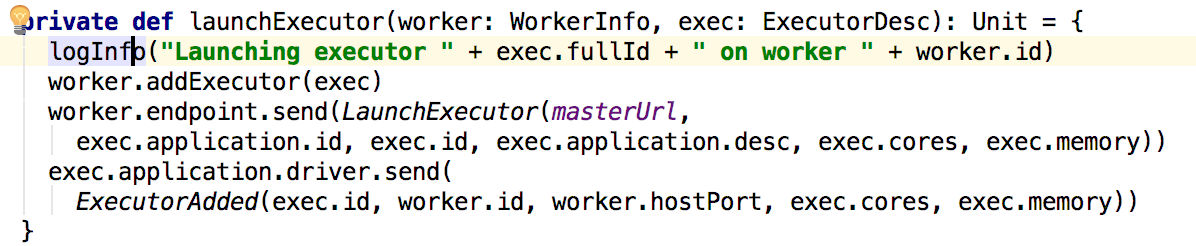
可以看到master向worker发送了启动execitor的信息,下面看worker对这个信息的处理即可:
case LaunchExecutor(masterUrl, appId, execId, appDesc, cores_, memory_) => if (masterUrl != activeMasterUrl) { logWarning("Invalid Master (" + masterUrl + ") attempted to launch executor.") } else { try { logInfo("Asked to launch executor %s/%d for %s".format(appId, execId, appDesc.name)) // 创建exector的工作目录 val executorDir = new File(workDir, appId + "/" + execId) if (!executorDir.mkdirs()) { throw new IOException("Failed to create directory " + executorDir) } // Create local dirs for the executor. These are passed to the executor via the // SPARK_EXECUTOR_DIRS environment variable, and deleted by the Worker when the // application finishes. val appLocalDirs = appDirectories.getOrElse(appId, { val localRootDirs = Utils.getOrCreateLocalRootDirs(conf) val dirs = localRootDirs.flatMap { dir => try { val appDir = Utils.createDirectory(dir, namePrefix = "executor") Utils.chmod700(appDir) Some(appDir.getAbsolutePath()) } catch { case e: IOException => logWarning(s"${e.getMessage}. Ignoring this directory.") None } }.toSeq if (dirs.isEmpty) { throw new IOException("No subfolder can be created in " + s"${localRootDirs.mkString(",")}.") } dirs }) appDirectories(appId) = appLocalDirs
//创建executorRunner来真正运行executor val manager = new ExecutorRunner( appId, execId, appDesc.copy(command = Worker.maybeUpdateSSLSettings(appDesc.command, conf)), cores_, memory_, self, workerId, host, webUi.boundPort, publicAddress, sparkHome, executorDir, workerUri, conf, appLocalDirs, ExecutorState.RUNNING) executors(appId + "/" + execId) = manager
//executorRunner启动 manager.start() coresUsed += cores_ memoryUsed += memory_
//通知masterexecitor状态 sendToMaster(ExecutorStateChanged(appId, execId, manager.state, None, None)) } catch { case e: Exception => logError(s"Failed to launch executor $appId/$execId for ${appDesc.name}.", e) if (executors.contains(appId + "/" + execId)) { executors(appId + "/" + execId).kill() executors -= appId + "/" + execId } sendToMaster(ExecutorStateChanged(appId, execId, ExecutorState.FAILED, Some(e.toString), None)) } }
在ExecutorRunner的run方法最后启动一个线程调用的是fetchAndRunExector方法
private def fetchAndRunExecutor() { try { // 通过应用程序的信息和环境配置创建构造器builder val builder = CommandUtils.buildProcessBuilder(appDesc.command, new SecurityManager(conf), memory, sparkHome.getAbsolutePath, substituteVariables) val CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend = builder.command() val formattedCommand = command.asScala.mkString(""", "" "", """) logInfo(s"Launch command: $formattedCommand") builder.directory(executorDir) builder.environment.put("SPARK_EXECUTOR_DIRS", appLocalDirs.mkString(File.pathSeparator)) // In case we are running this from within the Spark Shell, avoid creating a "scala" // parent process for the executor command builder.environment.put("SPARK_LAUNCH_WITH_SCALA", "0") // 添加webUi相关设置 val baseUrl = if (conf.getBoolean("spark.ui.reverseProxy", false)) { s"/proxy/$workerId/logPage/?appId=$appId&executorId=$execId&logType=" } else { s"http://$publicAddress:$webUiPort/logPage/?appId=$appId&executorId=$execId&logType=" } builder.environment.put("SPARK_LOG_URL_STDERR", s"${baseUrl}stderr") builder.environment.put("SPARK_LOG_URL_STDOUT", s"${baseUrl}stdout") //启动构造器,这里实际创建的CorarseGrainedExecutorBackend process = builder.start() val header = "Spark Executor Command: %s %s ".format( formattedCommand, "=" * 40) // Redirect its stdout and stderr to files val stdout = new File(executorDir, "stdout") stdoutAppender = FileAppender(process.getInputStream, stdout, conf) val stderr = new File(executorDir, "stderr") Files.write(header, stderr, StandardCharsets.UTF_8) stderrAppender = FileAppender(process.getErrorStream, stderr, conf) // Wait for it to exit; executor may exit with code 0 (when driver instructs it to shutdown) // or with nonzero exit code
//情启动executor的进程,并等待退出 val exitCode = process.waitFor() state = ExecutorState.EXITED val message = "Command exited with code " + exitCode
//通知worker关于executor的状态 worker.send(ExecutorStateChanged(appId, execId, state, Some(message), Some(exitCode))) } catch { case interrupted: InterruptedException => logInfo("Runner thread for executor " + fullId + " interrupted") state = ExecutorState.KILLED killProcess(None) case e: Exception => logError("Error running executor", e) state = ExecutorState.FAILED killProcess(Some(e.toString)) } }
到此work的executor已经启动就等taskScheduler调度的task来运行。