1.二叉树遍历
前序遍历
中序遍历
后续遍历
from collections import deque class BiTreeNode: def __init__(self, data): self.data = data self.lchild = None self.rchild = None a = BiTreeNode('A') b = BiTreeNode('B') c = BiTreeNode('C') d = BiTreeNode('D') e = BiTreeNode('E') f = BiTreeNode('F') g = BiTreeNode('G') e.lchild = a e.rchild = g a.rchild = c c.lchild = b c.rchild = d g.rchild = f root = e def pre_order(root): if root: print(root.data, end='') pre_order(root.lchild) pre_order(root.rchild) def in_order(root): if root: in_order(root.lchild) print(root.data, end='') in_order(root.rchild) def post_order(root): if root: post_order(root.lchild) post_order(root.rchild) print(root.data, end='') def level_order(root): queue = deque() queue.append(root) while len(queue) > 0: node = queue.popleft() print(node.data,end='') if node.lchild: queue.append(node.lchild) if node.rchild: queue.append(node.rchild) pre_order(root) print("") in_order(root) print("") post_order(root) print("") level_order(root)
2.B树的排序查询
class BiTreeNode: def __init__(self, data): self.data = data self.lchild = None self.rchild = None class BST: def __init__(self, li=None): self.root = None if li: self.root = self.insert(self.root, li[0]) for val in li[1:]: self.insert(self.root, val) def insert(self, root, val): if root is None: root = BiTreeNode(val) elif val < root.data: root.lchild = self.insert(root.lchild, val) else: root.rchild = self.insert(root.rchild, val) return root def insert_no_rec(self, val): p = self.root if not p: self.root = BiTreeNode(val) return while True: if val < p.data: if p.lchild: p = p.lchild else: p.lchild = BiTreeNode(val) break else: if p.rchild: p = p.rchild else: p.rchild = BiTreeNode(val) break def query(self, root, val): if not root: return False if root.data == val: return True elif root.data > val: return self.query(root.lchild, val) else: return self.query(root.rchild, val) def query_no_rec(self, val): p = self.root while p: if p.data == val: return True elif p.data > val: p = p.lchild else: p = p.rchild return False def in_order(self, root): if root: self.in_order(root.lchild) print(root.data, end=',') self.in_order(root.rchild) tree = BST() for i in [1,5,9,8,7,6,4,3,2]: tree.insert_no_rec(i) tree.in_order(tree.root) print(tree.query_no_rec(9))
3.栈的应用:迷宫问题
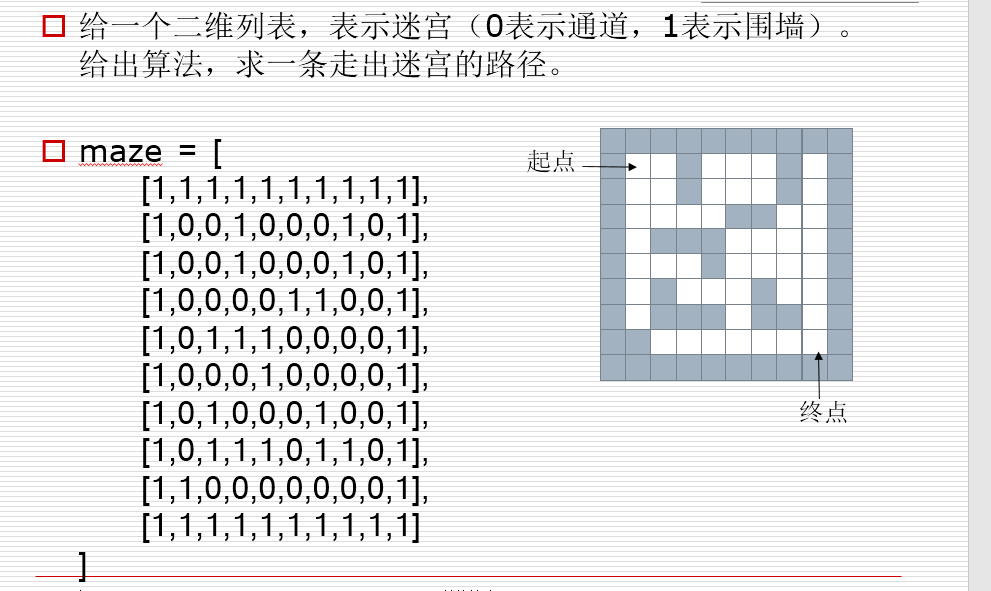
from collections import deque maze = [ [1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1], [1,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,1], [1,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,1], [1,0,0,0,0,1,1,0,0,1], [1,0,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,1], [1,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1], [1,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,1], [1,0,1,1,1,0,1,1,0,1], [1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1], [1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1] ] dirs = [ lambda x,y:(x-1,y), #上 lambda x,y:(x,y+1), #右 lambda x,y:(x+1,y), #下 lambda x,y:(x,y-1), #左 ] def solve_maze(x1, y1, x2, y2): stack = [] stack.append((x1,y1)) maze[x1][y1] = 2 while len(stack) > 0: # 当栈不空循环 cur_node = stack[-1] if cur_node == (x2,y2): #到达终点 for p in stack: print(p) return True for dir in dirs: next_node = dir(*cur_node) if maze[next_node[0]][next_node[1]] == 0: #找到一个能走的方向 stack.append(next_node) maze[next_node[0]][next_node[1]] = 2 # 2表示已经走过的点 break else: #如果一个方向也找不到 stack.pop() else: print("无路可走") return False def solve_maze2(x1,y1,x2,y2): queue = deque() path = [] # 记录出队之后的节点 queue.append((x1,y1,-1)) maze[x1][y1] = 2 while len(queue) > 0: cur_node = queue.popleft() path.append(cur_node) if cur_node[0] == x2 and cur_node[1] == y2: #到终点 real_path = [] x,y,i = path[-1] real_path.append((x,y)) while i >= 0: node = path[i] real_path.append(node[0:2]) i = node[2] real_path.reverse() for p in real_path: print(p) return True for dir in dirs: next_node = dir(cur_node[0], cur_node[1]) if maze[next_node[0]][next_node[1]] == 0: queue.append((next_node[0], next_node[1], len(path)-1)) maze[next_node[0]][next_node[1]] = 2 # 标记为已经走过 else: print("无路可走") return False solve_maze2(1,1,8,8)
4.栈的应用:括号匹配问题

def brace_match(s): stack = [] match = {')':'(', ']':'[', '}':'{'} match2 = {'(':')', '[':']', '{':'}'} for ch in s: if ch in {'(', '[', '{'}: stack.append(ch) elif len(stack) == 0: print("缺少%s" % match[ch]) return False elif stack[-1] == match[ch]: stack.pop() else: print("括号不匹配") return False if len(stack) > 0: print("缺少%s" % (match2[stack[-1]])) return False return True brace_match("[{()[]}{}{}")
5.链表操作
class Node: def __init__(self, data): self.data = data self.next = None def create_linklist(li): head = None for num in li: node = Node(num) node.next = head head = node return head def create_linklist_tail(li): head = None if not li: return head head = Node(li[0]) tail = head for num in li[1:]: node = Node(num) tail.next = node tail = node return head def print_linklist(head): node = head while node: print(node.data) node = node.next linklist = create_linklist_tail([1,2,3,4]) print_linklist(linklist)