参考 (http://www.cnblogs.com/rocedu/p/6371315.html#SECUNITTEST)
参考 (http://www.cnblogs.com/rocedu/p/6736847.html)
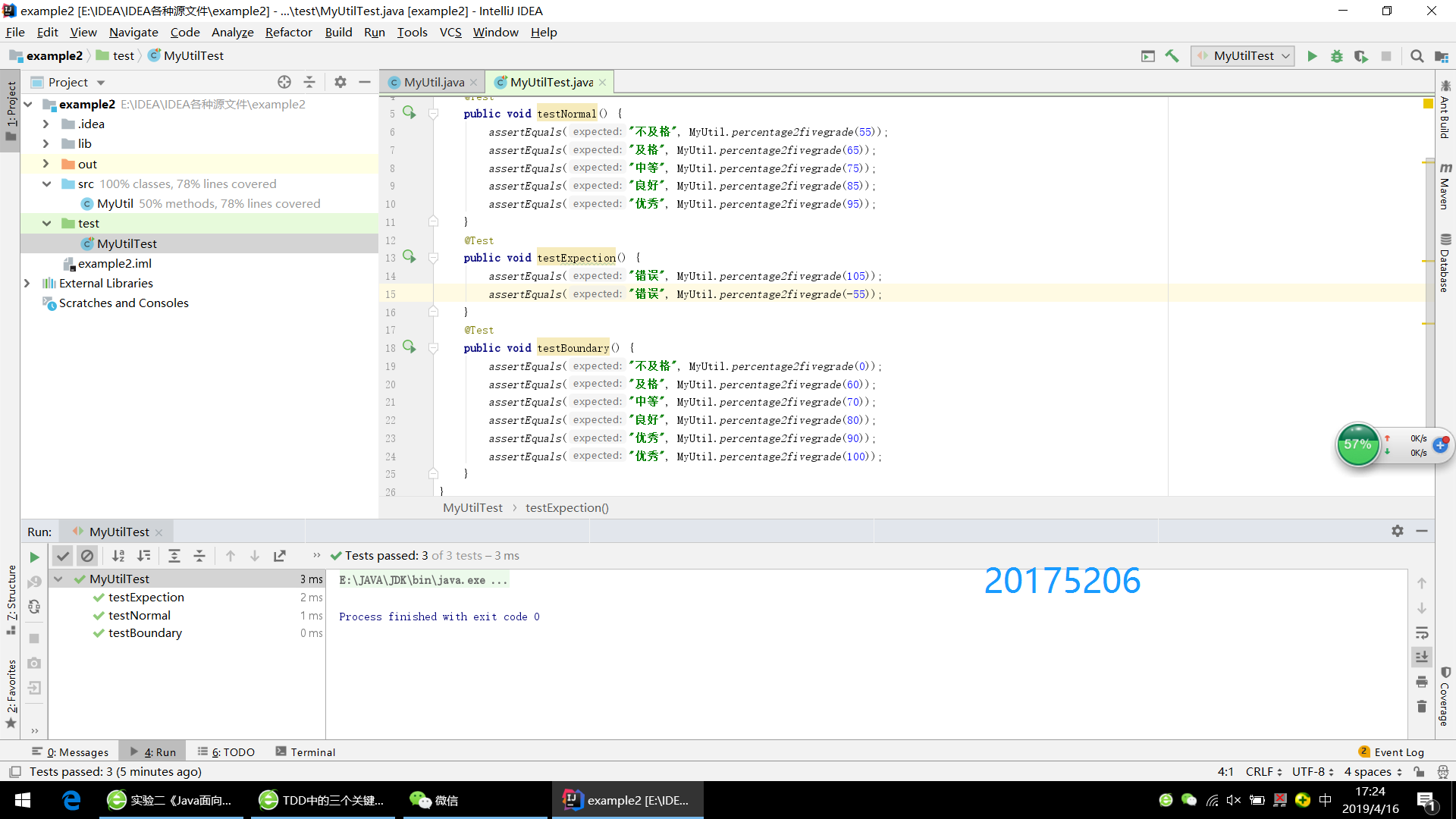
提交最后三个测试用例都通过的截图,截图上要有画图加水印,输入自己的学号。
单元测试(unit testing),是指对软件中的最小可测试单元进行检查和验证。对于单元测试中单元的含义,一般来说,要根据实际情况去判定其具体含义,如Java里单元指一个类。
(1)伪代码
百分制转五分制:
如果成绩小于60,转成“不及格”
如果成绩在60与70之间,转成“及格”
如果成绩在70与80之间,转成“中等”
如果成绩在80与90之间,转成“良好”
如果成绩在90与100之间,转成“优秀”
其他,转成“错误”
(2)产品代码
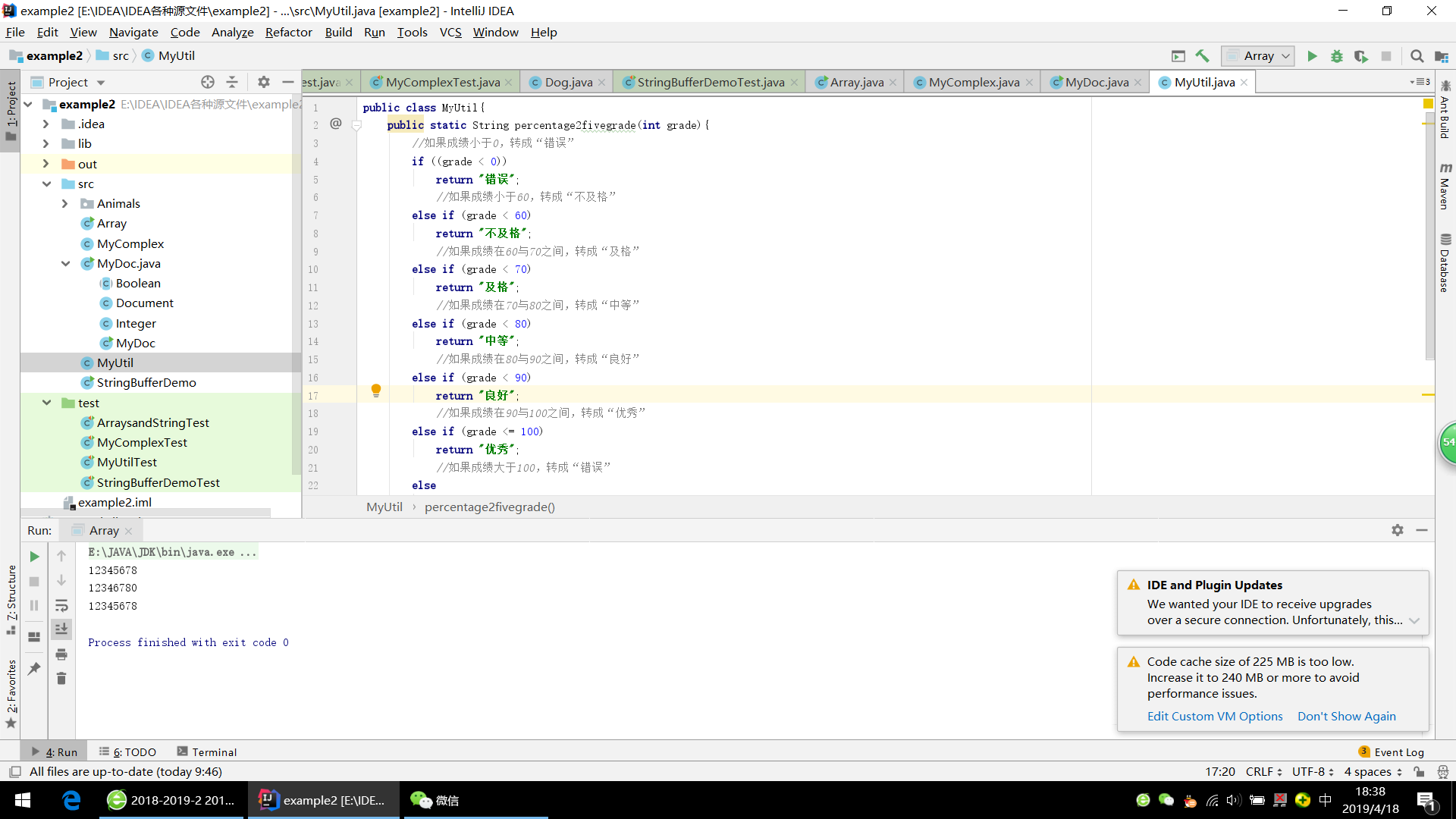
public class MyUtil{
public static String percentage2fivegrade(int grade){
//如果成绩小于0,转成“错误”
if ((grade < 0))
return "错误";
//如果成绩小于60,转成“不及格”
else if (grade < 60)
return "不及格";
//如果成绩在60与70之间,转成“及格”
else if (grade < 70)
return "及格";
//如果成绩在70与80之间,转成“中等”
else if (grade < 80)
return "中等";
//如果成绩在80与90之间,转成“良好”
else if (grade < 90)
return "良好";
//如果成绩在90与100之间,转成“优秀”
else if (grade <= 100)
return "优秀";
//如果成绩大于100,转成“错误”
else
return "错误";
}
public static String percentage2fivegrade() {
return "错误";}
}
(3)测试代码
import org.junit.Test;
import junit.framework.TestCase;
public class MyUtilTest extends TestCase {
@Test
public void testNormal() {
assertEquals("不及格", MyUtil.percentage2fivegrade(55));
assertEquals("及格", MyUtil.percentage2fivegrade(65));
assertEquals("中等", MyUtil.percentage2fivegrade(75));
assertEquals("良好", MyUtil.percentage2fivegrade(85));
assertEquals("优秀", MyUtil.percentage2fivegrade(95));
}
@Test
public void testExpection() {
assertEquals("错误", MyUtil.percentage2fivegrade(105));
assertEquals("错误", MyUtil.percentage2fivegrade(-55));
}
@Test
public void testBoundary() {
assertEquals("不及格", MyUtil.percentage2fivegrade(0));
assertEquals("及格", MyUtil.percentage2fivegrade(60));
assertEquals("中等", MyUtil.percentage2fivegrade(70));
assertEquals("良好", MyUtil.percentage2fivegrade(80));
assertEquals("优秀", MyUtil.percentage2fivegrade(90));
assertEquals("优秀", MyUtil.percentage2fivegrade(100));
}
}
(4)截图
实验二 面向对象程序设计-2
参考 积极主动敲代码,使用JUnit学习Java (http://www.cnblogs.com/rocedu/p/4837092.html)
参考(http://www.cnblogs.com/rocedu/p/6736847.html)
以 TDD的方式研究学习StringBuffer,提交你的单元测试用例和测试通过的截图,截图要加上学号水印。
(1)产品代码
public class StringBufferDemo {
public static void main(String [] args){
StringBuffer buffer = new StringBuffer();
buffer.append('S');
buffer.append("tringBuffer");
System.out.println(buffer.charAt(1));
System.out.println(buffer.capacity());
System.out.println(buffer.indexOf("tring"));
System.out.println("buffer = " + buffer.toString());
}
}
(2)测试代码
import junit.framework.TestCase;
import org.junit.Test;
public class StringBufferDemoTest extends TestCase {
StringBuffer str = new StringBuffer("StringBuffer");
@Test
public void testcharAt() {
assertEquals('S', str.charAt(0));
assertEquals('B', str.charAt(6));
}
@Test
public void testcapacity() {
assertEquals(28, str.capacity());
}
@Test
public void testindexOf() {
assertEquals(6, str.indexOf("Buffer"));
}
@Test
public void testtostring () {
assertEquals("str:StringBuffer", "str:" + str.toString());
}
}
(3)截图


实验二 面向对象程序设计-3
参考(http://www.cnblogs.com/rocedu/p/6736847.html)
对设计模式示例进行扩充,体会OCP原则和DIP原则的应用,初步理解设计模式
用自己的学号%6进行取余运算,根据结果进行代码扩充:
0: 让系统支持Byte类,并在MyDoc类中添加测试代码表明添加正确,提交测试代码和运行结的截图,加上学号水印
1: 让系统支持Short类,并在MyDoc类中添加测试代码表明添加正确,提交测试代码和运行结的截图,加上学号水印
2: 让系统支持Boolean类,并在MyDoc类中添加测试代码表明添加正确,提交测试代码和运行结的截图,加上学号水印
3: 让系统支持Long类,并在MyDoc类中添加测试代码表明添加正确,提交测试代码和运行结的截图,加上学号水印
4: 让系统支持Float类,并在MyDoc类中添加测试代码表明添加正确,提交测试代码和运行结的截图,加上学号水印
5: 让系统支持Double类,并在MyDoc类中添加测试代码表明添加正确,提交测试代码和运行结的截图,加上学号水印
(1)代码
abstract class Boolean {
public abstract void DisplayValue();
}
class Integer extends Boolean {
int value;
Integer(){
value=100;
}
public void DisplayValue(){
System.out.println(true);
}
}
class Document {
Boolean pd;
Document() {
pd=new Integer();
}
public void DisplayData(){
pd.DisplayValue();
}
}
public class MyDoc {
static Document d;
public static void main(String[] args) {
d = new Document();
d.DisplayData();
}
}
(2)截图

实验二 面向对象程序设计-4
提交:单元测试代码和运行成功截图及码云上代码链接,截图要加上学号水印
参考(http://www.cnblogs.com/rocedu/p/6736847.html)
任务:以TDD的方式开发一个复数类Complex,要求如下:
// 定义属性并生成getter,setter
double RealPart;
double ImagePart;
// 定义构造函数
public Complex()
public Complex(double R,double I)
//Override Object
public boolean equals(Object obj)
public String toString()
// 定义公有方法:加减乘除
Complex ComplexAdd(Complex a)
Complex ComplexSub(Complex a)
Complex ComplexMulti(Complex a)
Complex ComplexDiv(Complex a)
(1)产品代码
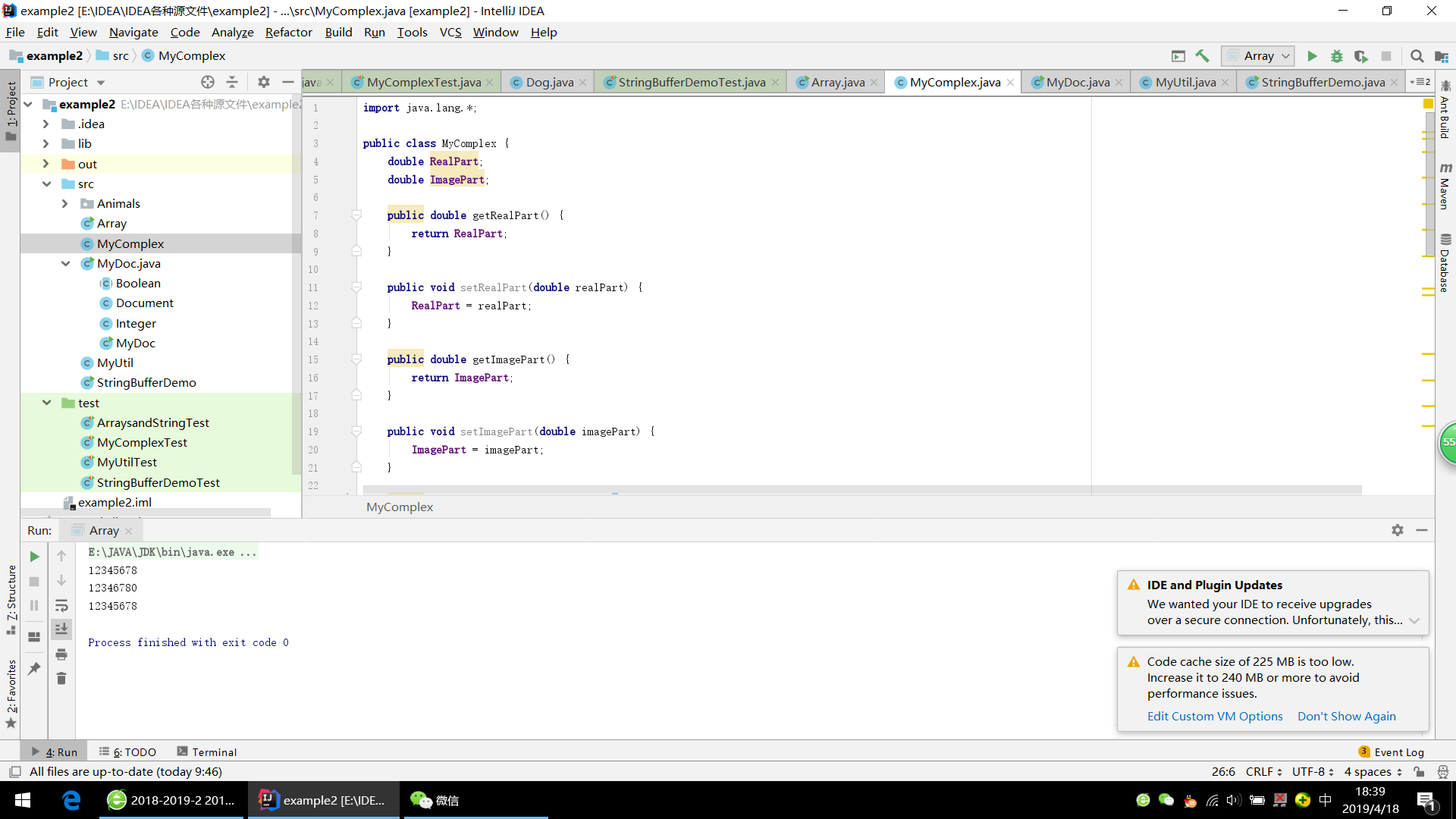
import java.lang.*;
public class MyComplex {
double RealPart;
double ImagePart;
public double getRealPart() {
return RealPart;
}
public void setRealPart(double realPart) {
RealPart = realPart;
}
public double getImagePart() {
return ImagePart;
}
public void setImagePart(double imagePart) {
ImagePart = imagePart;
}
public MyComplex(double R, double I) {
RealPart = R;
ImagePart = I;
}
public boolean equals(MyComplex in) {
if (this.getRealPart () == in.getRealPart () && this.getImagePart () == in.getImagePart ())
return true;
else return false;
}
public String toString() {
return RealPart + " + " + ImagePart + "i";
}
public MyComplex ComplexAdd(MyComplex result) {
return new MyComplex ( RealPart + result.getRealPart (), ImagePart + result.getImagePart () );
}
public MyComplex ComplexSub(MyComplex result) {
return new MyComplex ( RealPart - result.getRealPart (), ImagePart - result.getImagePart () );
}
public MyComplex ComplexMulti(MyComplex result) {
return new MyComplex ( RealPart * result.getRealPart () - ImagePart * result.getImagePart (), RealPart * result.getImagePart () + ImagePart * result.getRealPart () );
}
public MyComplex ComplexDiv(MyComplex result) {
return new MyComplex ( RealPart /result.getRealPart () - ImagePart / result.getImagePart (), RealPart / result.getImagePart () + ImagePart / result.getRealPart () );
}
}
(2)测试代码
import junit.framework.TestCase;
import org.junit.Test;
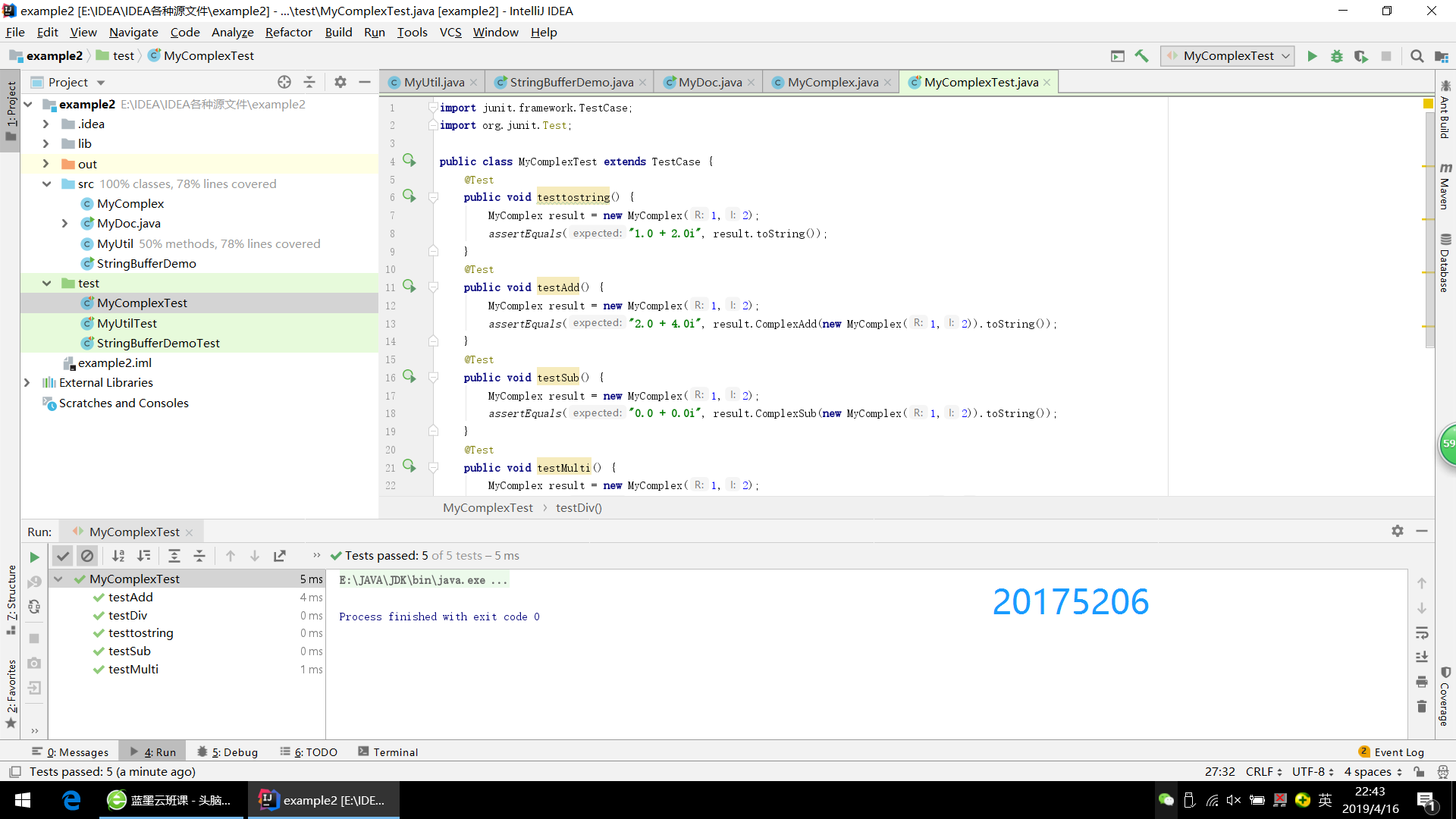
public class MyComplexTest extends TestCase {
@Test
public void testtostring() {
MyComplex result = new MyComplex(1,2);
assertEquals("1.0 + 2.0i", result.toString());
}
@Test
public void testAdd() {
MyComplex result = new MyComplex(1,2);
assertEquals("2.0 + 4.0i", result.ComplexAdd(new MyComplex(1,2)).toString());
}
@Test
public void testSub() {
MyComplex result = new MyComplex(1,2);
assertEquals("0.0 + 0.0i", result.ComplexSub(new MyComplex(1,2)).toString());
}
@Test
public void testMulti() {
MyComplex result = new MyComplex(1,2);
assertEquals("-3.0 + 4.0i", result.ComplexMulti(new MyComplex(1,2)).toString());
}
public void testDiv() {
MyComplex result = new MyComplex(1,2);
assertEquals("0.0 + 2.5i", result.ComplexDiv(new MyComplex(1,2)).toString());
}
}
(3)截图
实验二 面向对象程序设计-5
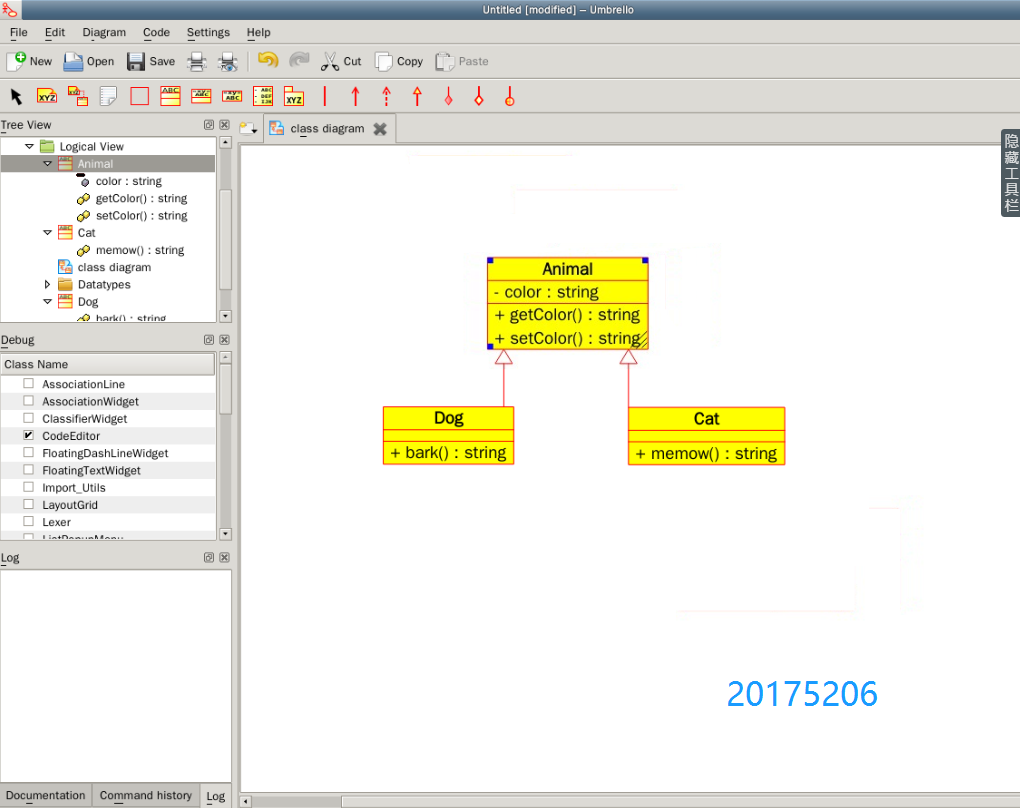
使用WhiteStarUML(http://whitestaruml.sourceforge.net/)对实验二中的代码进行建模,发类图的截图,加上学号水印。
参考(http://www.cnblogs.com/rocedu/p/6736847.html)
类图中只少两个类。
(1)产品代码
Animals类
package Animals;
public abstract class Animal {
private String color;
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
public abstract String shout();
}
Cat类
package Animals;
import Animals.Animal;
public class Cat extends Animal {
public String shout(){
return "喵喵";
}
public String toString(){
return "The Cat's color is " + this.getColor() +", and it shouts "+ this.shout() + "!";
}
}
Dog类
package Animals;
import Animals.Animal;
public class Dog extends Animal {
public String shout(){
return "汪汪";
}
public String toString(){
return "The Dog's color is " + this.getColor() +", and it shouts "+ this.shout() + "!";
}
}
(2)截图
实验总结
本次实验出现了如下问题:
(1)junit3在电脑程序中无法找到,出现not found in the module 的字样提示
(2)绿条并未出现,甚至连红条也没有出现
(3)产品代码无法运行
(4)JAVA API不适应该电脑
(5)API 中的命令有些理解错误。
解决方法:
(1)点击fix,在电脑中查找junit4,然后加载到文件中进行使用
(2)我上网了解了一下,junit3在使用时会出现警告红条和通过绿条,而junit4则不会出现,junit3无法寻找得到,所以用的junit4
(3)提供的产品代码的程序一般没有主类,所以无法运行
(4)暂未解决,我的做法是换一种软件进行使用
(5)这是知识面的问题,只能多看多思考来解决。
本次实验让我对JAVA在面向对象的设计有了更深入的了解,还有对产品代码的测试,UML图等能更好的学习,虽然其中遇到了一些难题,但是通过同学的帮助和自己上网学习,问题得以解决,我认为比较困难的是junit的应用,可能是我的电脑的问题不太适用,造成了很大的困扰,不过最后也解决了该难题,希望以后能够再接再厉,更深地投入到java的学习当中去。
总结分析
| 步骤 | 耗时 | 百分比 |
|---|---|---|
| 需求分析 | 10min | 12.5% |
| 设计 | 5min | 6.25% |
| 代码实现 | 30min | 37.5% |
| 测试 | 15min | 18.75% |
| 分析总结 | 20min | 25% |