实验目的
(1)进一步理解4个成员访问权限修饰符的用途;
(2)掌握Object类的常用API用法;
(3)掌握ArrayList类用法与常用API;
(4)掌握枚举类使用方法;
(5)结合本章知识,理解继承与多态性两个面向对象程序设计特征,并体会其优点;
(6)熟练掌握Java语言中基于类、继承技术构造程序的语法知识(ch1-ch5);
(7)利用已掌握Java语言程序设计知识,学习设计开发含有1个主类、2个以上用户自定义类的应用程序。
2、实验内容和步骤
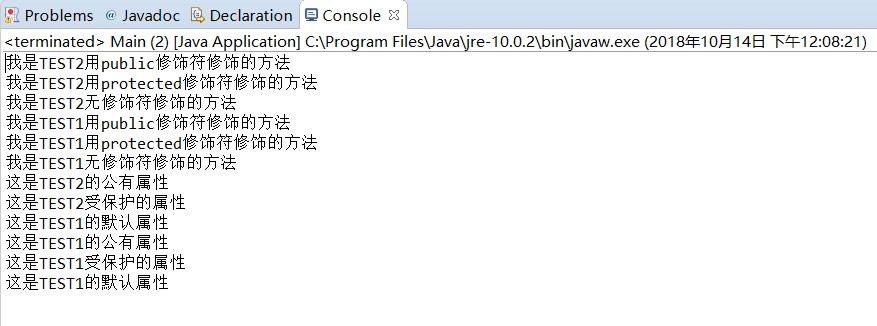
实验1 补充以下程序中主类内main方法体,以验证四种权限修饰符的用法。
|
public class TEST1 { private String t1 = "这是TEST1的私有属性"; public String t2 = "这是TEST1的公有属性"; protected String t3 = "这是TEST1受保护的属性"; String t4 = "这是TEST1的默认属性"; private void tese1() { System.out.println("我是TEST1用private修饰符修饰的方法"); } public void tese2() { System.out.println("我是TEST1用public修饰符修饰的方法"); } protected void tese3() { System.out.println("我是TEST1用protected修饰符修饰的方法"); } void tese4() { System.out.println("我是TEST1无修饰符修饰的方法"); } } public class TEST2 extends TEST1{ private String e1 = "这是TEST2的私有属性"; public String e2 = "这是TEST2的公有属性"; protected String e3 = "这是TEST2受保护的属性"; String e4 = "这是TEST2的默认属性"; public void demo1() { System.out.println("我是TEST2用public修饰符修饰的方法"); } private void demo2() { System.out.println("我是TEST2用private修饰符修饰的方法"); } protected void demo3() { System.out.println("我是TEST2用protected修饰符修饰的方法"); } void demo4() { System.out.println("我是TEST2无修饰符修饰的方法"); } } public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { TEST2 test2 = new TEST2(); /*以下设计代码分别调用 demo1 demo2 demo3 demo4 test1 test2 test3 test4方法和t1 t2 t3 t3 e1 e2 e3 e4属性,结合程序运行结果理解继承和权限修饰符的用法与区别*/ } } |
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { TEST2 test2 = new TEST2(); /*在下面分别调用 demo1 demo2 demo3 demo4 test1 test2 test3 test4方法 和t1 t2 t3 t3 e1 e2 e3 e4属性,好好理解继承和权限修饰符的用法与区别*/ TEST2 test21 = new TEST2(); test21.demo1(); test21.demo3(); test21.demo4(); test21.test2(); test21.test3(); test21.test4(); String e2=test21.e2; String e3=test21.e3; String e4=test21.e4; System.out.println(e2); System.out.println(e3); System.out.println(e4); System.out.println(test21.t2); System.out.println(test21.t3); System.out.println(test21.t4); } }
public class TEST1 { private String t1 = "这是TEST1的私有属性"; public String t2 = "这是TEST1的公有属性"; protected String t3 = "这是TEST1受保护的属性"; String t4 = "这是TEST1的默认属性"; private void test1() { System.out.println("我是TEST1用private修饰符修饰的方法"); } public void test2() { System.out.println("我是TEST1用public修饰符修饰的方法"); } protected void test3() { System.out.println("我是TEST1用protected修饰符修饰的方法"); } void test4() { System.out.println("我是TEST1无修饰符修饰的方法"); } }
public class TEST2 extends TEST1{ private String e1 = "这是TEST2的私有属性"; public String e2 = "这是TEST2的公有属性"; protected String e3 = "这是TEST2受保护的属性"; String e4 = "这是TEST1的默认属性"; public void demo1() { System.out.println("我是TEST2用public修饰符修饰的方法"); } private void demo2() { System.out.println("我是TEST2用private修饰符修饰的方法"); } protected void demo3() { System.out.println("我是TEST2用protected修饰符修饰的方法"); } void demo4() { System.out.println("我是TEST2无修饰符修饰的方法"); } }
实验2 第五章测试程序反思,继承知识总结。
测试程序1:
Ÿ 编辑、编译、调试运行教材程序5-8、5-9、5-10(教材174页-177页);
Ÿ 结合程序运行结果,理解程序代码,掌握Object类的定义及用法;
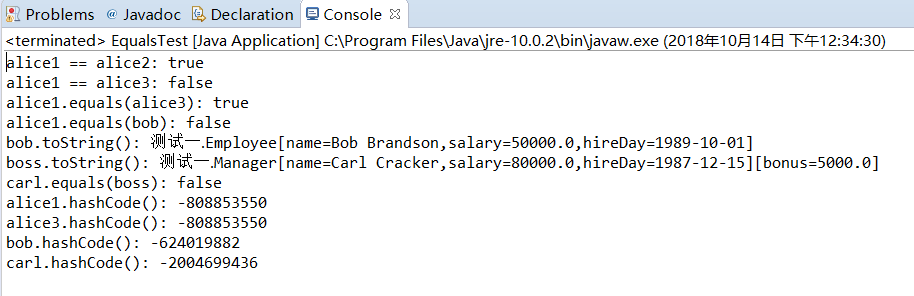
package 测试一; import java.time.*; import java.util.Objects; public class Employee { private String name; private double salary; private LocalDate hireDay; public Employee(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day) { this.name = name; this.salary = salary; hireDay = LocalDate.of(year, month, day); } public String getName() { return name; } public double getSalary() { return salary; } public LocalDate getHireDay() { return hireDay; } public void raiseSalary(double byPercent) { double raise = salary * byPercent / 100; salary += raise; } public boolean equals(Object otherObject) { // 快速测试,看看这些对象是否相同 if (this == otherObject) return true; // 如果显示参数为空,则必须显示false if (otherObject == null) return false; // 如果类不匹配,他们就不能相等 if (getClass() != otherObject.getClass()) return false; // 现在我知道另一个对象是非空雇员 Employee other = (Employee) otherObject; // 测试字段是否具有相同的值 return Objects.equals(name, other.name) && salary == other.salary && Objects.equals(hireDay, other.hireDay); } public int hashCode() { return Objects.hash(name, salary, hireDay); } public String toString() { return getClass().getName() + "[name=" + name + ",salary=" + salary + ",hireDay=" + hireDay + "]"; } }
package 测试一; /** * This program demonstrates the equals method. * @version 1.12 2012-01-26 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class EqualsTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Employee alice1 = new Employee("Alice Adams", 75000, 1987, 12, 15); Employee alice2 = alice1; Employee alice3 = new Employee("Alice Adams", 75000, 1987, 12, 15); Employee bob = new Employee("Bob Brandson", 50000, 1989, 10, 1); System.out.println("alice1 == alice2: " + (alice1 == alice2)); System.out.println("alice1 == alice3: " + (alice1 == alice3)); System.out.println("alice1.equals(alice3): " + alice1.equals(alice3)); System.out.println("alice1.equals(bob): " + alice1.equals(bob)); System.out.println("bob.toString(): " + bob); Manager carl = new Manager("Carl Cracker", 80000, 1987, 12, 15); Manager boss = new Manager("Carl Cracker", 80000, 1987, 12, 15); boss.setBonus(5000); System.out.println("boss.toString(): " + boss); System.out.println("carl.equals(boss): " + carl.equals(boss)); System.out.println("alice1.hashCode(): " + alice1.hashCode()); System.out.println("alice3.hashCode(): " + alice3.hashCode()); System.out.println("bob.hashCode(): " + bob.hashCode()); System.out.println("carl.hashCode(): " + carl.hashCode()); } }
package 测试一; public class Manager extends Employee { private double bonus; public Manager(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day) { super(name, salary, year, month, day); bonus = 0; } public double getSalary() { double baseSalary = super.getSalary(); return baseSalary + bonus; } public void setBonus(double bonus) { this.bonus = bonus; } public boolean equals(Object otherObject) { if (!super.equals(otherObject)) return false; Manager other = (Manager) otherObject; // 检查这个和其他属于同一个类 return bonus == other.bonus; } public int hashCode() { return java.util.Objects.hash(super.hashCode(), bonus); } public String toString() { return super.toString() + "[bonus=" + bonus + "]"; } }
测试程序2:
Ÿ 编辑、编译、调试运行教材程序5-11(教材182页);
Ÿ 结合程序运行结果,理解程序代码,掌握ArrayList类的定义及用法;
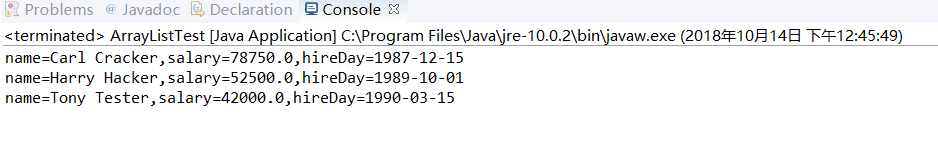
import java.util.*; /** * This program demonstrates the ArrayList class. * @version 1.11 2012-01-26 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class ArrayListTest { public static void main(String[] args) { // 用三个Employee对象填充staff数组列表 ArrayList<Employee> staff = new ArrayList<>(); staff.add(new Employee("Carl Cracker", 75000, 1987, 12, 15)); staff.add(new Employee("Harry Hacker", 50000, 1989, 10, 1)); staff.add(new Employee("Tony Tester", 40000, 1990, 3, 15)); // 把每个人的薪水提高5% for (Employee e : staff) e.raiseSalary(5); // 打印所有Employee对象的信息 for (Employee e : staff) System.out.println("name=" + e.getName() + ",salary=" + e.getSalary() + ",hireDay=" + e.getHireDay()); } }
import java.time.*; public class Employee { private String name; private double salary; private LocalDate hireDay; public Employee(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day) { this.name = name; this.salary = salary; hireDay = LocalDate.of(year, month, day); } public String getName() { return name; } public double getSalary() { return salary; } public LocalDate getHireDay() { return hireDay; } public void raiseSalary(double byPercent) { double raise = salary * byPercent / 100; salary += raise; } }
测试程序3:
Ÿ 编辑、编译、调试运行程序5-12(教材189页);
Ÿ 结合运行结果,理解程序代码,掌握枚举类的定义及用法;
import java.util.*; /** * This program demonstrates enumerated types. * @version 1.0 2004-05-24 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class EnumTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("Enter a size: (SMALL, MEDIUM, LARGE, EXTRA_LARGE) "); String input = in.next().toUpperCase(); Size size = Enum.valueOf(Size.class, input); System.out.println("size=" + size); System.out.println("abbreviation=" + size.getAbbreviation()); if (size == Size.EXTRA_LARGE)//判断语句 System.out.println("Good job--you paid attention to the _."); } } enum Size { SMALL("S"), MEDIUM("M"), LARGE("L"), EXTRA_LARGE("XL"); private Size(String abbreviation) { this.abbreviation = abbreviation; } public String getAbbreviation() { return abbreviation; } private String abbreviation; }

实验3:采用个人账号登录https://pintia.cn/,完成《2018秋季西北师范大学面向对象程序设计(Java)(ch1-ch5)测试题2》,测试时间60分钟;
实验4: 课后完成实验3未完成的测试内容。
实验总结:
通过本次实验,我理解了四个权限修饰符,同时发现我对于继承的知识点掌握还太浅显。在接下来的学习中,我会努力弥补之前缺失,掌握不牢靠的知识点。