I - Beautiful Spacing
Time Limit:8000MS Memory Limit:65536KB 64bit IO Format:%lld
& %llu
Description
Text is a sequence of words, and a word consists of characters. Your task is to put words into a grid with W columns and sufficiently many lines. For the beauty of the layout, the following conditions have to be satisfied.
- The words in the text must be placed keeping their original order. The following figures show correct and incorrect layout examples for a 4 word text "This is a pen" into 11 columns.
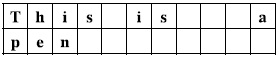 |
 |
|
Figure I.1: A good layout.
|
Figure I.2: BAD | Do not reorder words.
|
- Between two words adjacent in the same line, you must place at least one space character. You sometimes have to put more than one space in order to meet other conditions.

Figure I.3: BAD | Words must be separated by spaces.
- A word must occupy the same number of consecutive columns as the number of characters in it. You cannot break a single word into two or more by breaking it into lines or by inserting spaces.
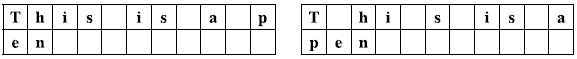
Figure I.4: BAD | Characters in a single word must be contiguous.
- The text must be justified to the both sides. That is, the first word of a line must startfrom the first column of the line, and except the last line, the last word of a line must end at the last column.
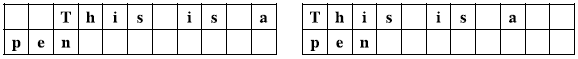
Figure I.5: BAD | Lines must be justi ed to both the left and the right sides.
The text is the most beautifully laid out when there is no unnecessarily long spaces. For instance, the layout in Figure I.6 has at most 2 contiguous spaces, which is more beautiful than that in Figure I.1, having 3 contiguous spaces. Given an input text
and the number of columns, please find a layout such that the length of the longest contiguous spaces between words is minimum.

Figure I.6: A good and the most beautiful layout.
Input
The input consists of multiple datasets, each in the following format.
W N
x1x2 ... xN
W, N, and xi are all integers. W is the number of columns (3 ≤ W ≤ 80,000). N is the number of words (2 ≤ N ≤ 50,000). xi is the number of characters in the i-th
word (1 ≤ xi ≤ (W−1)/2 ). Note that the upper bound on xi assures that there always exists a layout satisfying the conditions.
The last dataset is followed by a line containing two zeros.
Output
For each dataset, print the smallest possible number of the longest contiguous spaces between words.
Sample Input
11 4
4 2 1 3
5 7
1 1 1 2 2 1 2
11 7
3 1 3 1 3 3 4
100 3
30 30 39
30 3
2 5 3
0 0
Output for the Sample Input
2
1
2
40
1
题意:给你一个含n个单词的文本。依照一些规则放入宽度为w的矩形中,如何使最大的空格最小。
思路:答案是单调的,二分答案,然后用dp来检验,dp[i]表示第i个单词是否能结尾,easy想到的是n^2检验,可是肯定会TLE的,须要优化。能够发现假设i-j能够放在一行,可是最大空格会超过mid,那么i+1-j也不行,假设用i来推的时候能够推到[s,t]能够,那么下次就能够直接从t+1開始了。
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <string>
#include <map>
#include <stack>
#include <vector>
#include <set>
#include <queue>
#define maxn 50005
#define MAXN 200005
#define mod 1000000007
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define eps 1e-6
const double pi=acos(-1.0);
typedef long long ll;
using namespace std;
int n,w;
int len[maxn],sum[maxn];
bool dp[maxn];
bool isok(int mid)
{
int i,j,last=0;
memset(dp,0,sizeof(dp));
dp[0]=1;
if(sum[n]+n-1<=w) return true ;
for(i=0; i<n-1; i++)
{
if(!dp[i]) continue ;
for(j=max(i+2,last+1); j<=n; j++)
{
if(w<sum[j]-sum[i]+j-i-1) break ;
if(w>sum[j]-sum[i]+ll(j-i-1)*mid) continue ;
last=j;
dp[j]=1;
if(sum[n]-sum[j]+n-j-1<=w) return true ;
}
}
return false ;
}
void solve()
{
int i,j,le=1,ri=w,mid,ans;
while(le<=ri)
{
mid=(le+ri)>>1;
if(isok(mid))
{
ans=mid;
ri=mid-1;
}
else le=mid+1;
}
printf("%d
",ans);
}
int main()
{
int i,j;
while(~scanf("%d%d",&w,&n))
{
if(w==0&&n==0) break ;
sum[0]=0;
for(i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
scanf("%d",&len[i]);
sum[i]=sum[i-1]+len[i];
}
solve();
}
return 0;
}
版权声明:本文博主原创文章,博客,未经同意不得转载。





