整体设计
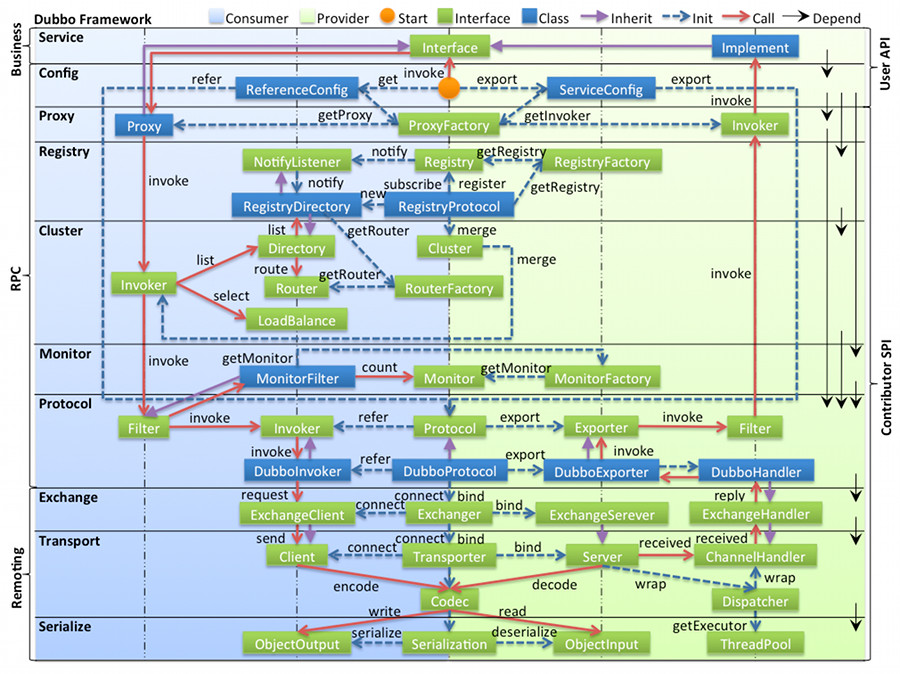
图中从下至上分为十层,各层均为单向依赖,右边的黑色箭头代表层之间的依赖关系,每一层都可以剥离上层被复用,其中,Service 和 Config 层为 API,其它各层均为 SPI。
Service 业务层:业务代码的接口与实现。我们实际使用 Dubbo
==================== RPC ====================
config 配置层:对外配置接口,以 ServiceConfig, ReferenceConfig 为中心,可以直接初始化配置类,也可以通过 Spring 解析配置生成配置类。
dubbo-config模块实现。proxy 服务代理层:服务接口透明代理,生成服务的客户端 Stub 和服务器端 Skeleton,扩展接口为 ProxyFactory 。
dubbo-rpc-rpc模块实现。
com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.proxy包 +com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.ProxyFactory接口 。registry 注册中心层:封装服务地址的注册与发现,以服务 URL 为中心,扩展接口为 RegistryFactory, Registry, RegistryService 。
dubbo-registry模块实现。cluster 路由层:封装多个提供者的路由及负载均衡,并桥接注册中心,以 Invoker 为中心,扩展接口为 Cluster, Directory, Router, LoadBalance 。
dubbo-cluster模块实现。这层的代码,
monitor 监控层:RPC 调用次数和调用时间监控,以 Statistics 为中心,扩展接口为 MonitorFactory, Monitor, MonitorService 。
dubbo-monitor模块实现。==================== Remoting ====================
protocol 远程调用层:封将 RPC 调用,以 Invocation, Result 为中心,扩展接口为 Protocol, Invoker, Exporter 。
dubbo-rpc-rpc模块实现。
com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.protocol包 +com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Protocol接口 。exchange 信息交换层:封装请求响应模式,同步转异步,以 Request, Response 为中心,扩展接口为 Exchanger, ExchangeChannel, ExchangeClient, ExchangeServer 。
dubbo-remoting-api模块定义接口。
com.alibaba.dubbo.remoting.exchange包。transport 网络传输层:抽象 mina 和 netty 为统一接口,以 Message 为中心,扩展接口为 Channel, Transporter, Client, Server, Codec 。
dubbo-remoting-api模块定义接口。
com.alibaba.dubbo.remoting.transport包。serialize 数据序列化层:可复用的一些工具,扩展接口为 Serialization, ObjectInput, ObjectOutput, ThreadPool 。
dubbo-common模块实现。
在 RPC 中,Protocol 是核心层,也就是只要有 Protocol + Invoker + Exporter 就可以完成非透明的 RPC 调用,然后在 Invoker 的主过程上 Filter 拦截点。
- 解说:
dubbo-rpc-rpc模块即可独立完成该功能。
Cluster 是外围概念,所以 Cluster 的目的是将多个 Invoker 伪装成一个 Invoker,这样其它人只要关注 Protocol 层 Invoker 即可,加上 Cluster 或者去掉 Cluster 对其它层都不会造成影响,因为只有一个提供者时,是不需要 Cluster 的。
- 解说:
dubbo-cluster模块提供的是非必须的功能。移除该模块,RPC 亦可正常运行。
Proxy 层封装了所有接口的透明化代理,而在其它层都以 Invoker 为中心,只有到了暴露给用户使用时,才用 Proxy 将 Invoker 转成接口,或将接口实现转成 Invoker,也就是去掉 Proxy 层 RPC 是可以 Run 的,只是不那么透明,不那么看起来像调本地服务一样调远程服务。
- 解说:简单粗暴的说,Proxy 会拦截
service.doSomething(args)的调用,“转发”给该 Service 对应的 Invoker ,从而实现透明化的代理。
而 Remoting 实现是 Dubbo 协议的实现,如果你选择 RMI 协议,整个 Remoting 都不会用上。Remoting 内部再划为 Transport 传输层和 Exchange 信息交换层,Transport 层只负责单向消息传输,是对 Mina, Netty, Grizzly 的抽象,它也可以扩展 UDP 传输;而 Exchange 层是在传输层之上封装了 Request-Response 语义。
核心流程
调用链
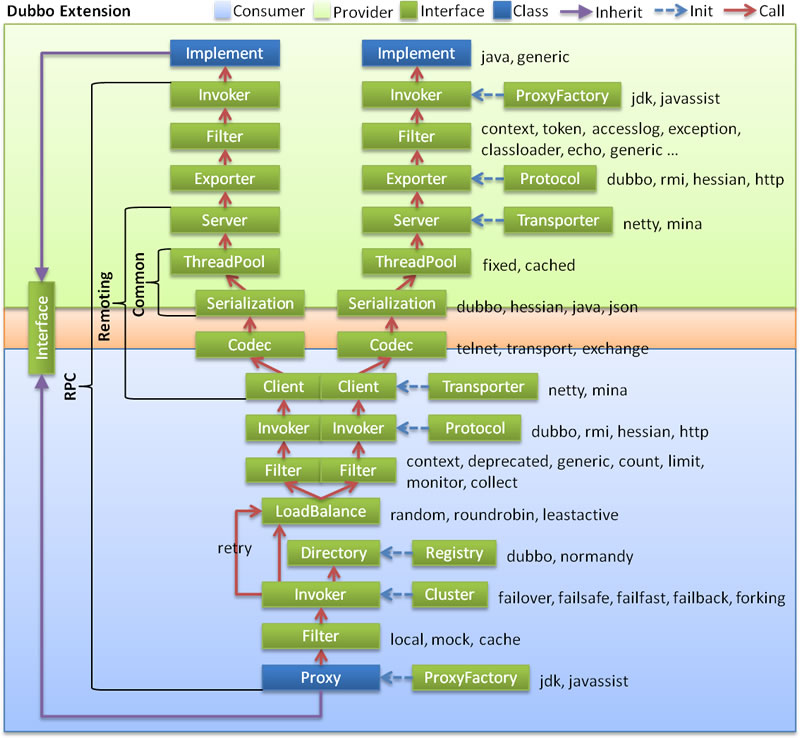
- 垂直分层如下:
- 下方 淡蓝背景( Consumer ):服务消费方使用的接口
- 上方 淡绿色背景( Provider ):服务提供方使用的接口
- 中间 粉色背景( Remoting ):通信部分的接口
- 自 LoadBalance 向上,每一行分成了多个相同的 Interface ,指的是负载均衡后,向 Provider 发起调用。
- 左边 括号 部分,代表了垂直部分更细化的分层,依次是:Common、Remoting、RPC、Interface 。
- 右边 蓝色虚线( Init ) 为初始化过程,通过对应的组件进行初始化。例如,ProxyFactory 初始化出 Proxy 。
领域模型
在 Dubbo 的核心领域模型中:
- Protocol 是服务域,它是 Invoker 暴露和引用的主功能入口,它负责 Invoker 的生命周期管理。
- Invoker 是实体域,它是 Dubbo 的核心模型,其它模型都向它靠扰,或转换成它,它代表一个可执行体,可向它发起 invoke 调用,它有可能是一个本地的实现,也可能是一个远程的实现,也可能一个集群实现。
- Invocation 是会话域,它持有调用过程中的变量,比如方法名,参数等。
Invoker
代码如下:
public interface Invoker<T> extends Node { /** * get service interface. * * @return service interface. */ Class<T> getInterface(); /** * invoke. * * @param invocation * @return result * @throws RpcException */ Result invoke(Invocation invocation) throws RpcException; }
#getInterface()方法,获得 Service 接口。#invoke(Invocation)方法,调用方法。
最重要的两种 Invoker:服务提供 Invoker 和服务消费 Invoker:
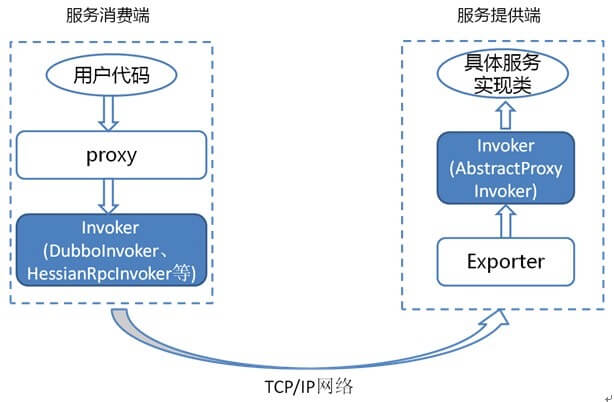
结合服务消费和提供者的代码示例来进行说明
- 服务消费者代码
public class DemoClientAction { private DemoService demoService; public void setDemoService(DemoService demoService) { this.demoService = demoService; } public void start() { String hello = demoService.sayHello("world" + i); } }
- 上面代码中的 DemoService 就是上图中服务消费端的 Proxy,用户代码通过这个 Proxy 调用其对应的 Invoker,而该 Invoker 实现了真正的远程服务调用。
- 服务提供者代码:
public class DemoServiceImpl implements DemoService { public String sayHello(String name) throws RemoteException { return "Hello " + name; } }
- 上面这个类会被封装成为一个 AbstractProxyInvoker 实例,并新生成一个 Exporter 实例。这样当网络通讯层收到一个请求后,会找到对应的 Exporter 实例,并调用它所对应的 AbstractProxyInvoker 实例,从而真正调用了服务提供者的代码。
Invocation
Invocation 是会话域,它持有调用过程中的变量,比如方法名,参数等。
代码如下:
public interface Invocation { /** * get method name. * * @return method name. * @serial */ String getMethodName(); /** * get parameter types. * * @return parameter types. * @serial */ Class<?>[] getParameterTypes(); /** * get arguments. * * @return arguments. * @serial */ Object[] getArguments(); /** * get attachments. * * @return attachments. * @serial */ Map<String, String> getAttachments(); /** * get attachment by key. * * @return attachment value. * @serial */ String getAttachment(String key); /** * get attachment by key with default value. * * @return attachment value. * @serial */ String getAttachment(String key, String defaultValue); /** * get the invoker in current context. * * @return invoker. * @transient */ Invoker<?> getInvoker(); }
#getMethodName()方法,获得方法名。#getParameterTypes()方法,获得方法参数类型数组。#getArguments()方法,获得方法参数数组。#getAttachments()等方法,获得隐式参数相关。#getInvoker()方法,获得对应的 Invoker 对象。
ProxyFactory
代码如下:
@SPI("javassist")
public interface ProxyFactory {
/**
* create proxy.
*
* 创建 Proxy ,在引用服务调用。
*
* @param invoker
* @return proxy
*/
@Adaptive({Constants.PROXY_KEY})
<T> T getProxy(Invoker<T> invoker) throws RpcException;
/**
* create invoker.
*
* 创建 Invoker ,在暴露服务时调用。
*
* @param <T>
* @param proxy
* @param type
* @param url
* @return invoker
*/
@Adaptive({Constants.PROXY_KEY})
<T> Invoker<T> getInvoker(T proxy, Class<T> type, URL url) throws RpcException;
}
#getProxy(invoker) 方法,创建 Proxy ,在引用服务时调用。
- 方法参数如下:
invoker参数,Consumer 对 Provider 调用的 Invoker 。
-
服务消费着引用服务的 主过程 如下图:
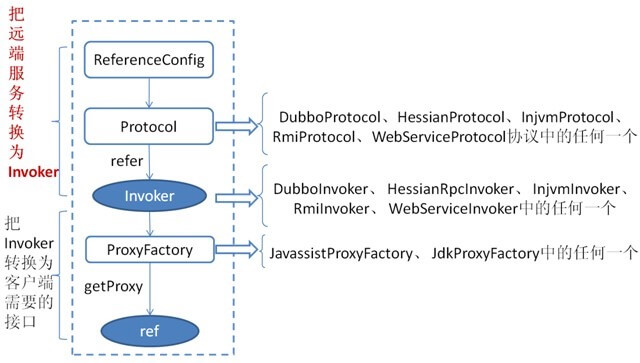
- 从图中我们可以看出,方法的
invoker参数,通过 Protocol 将 Service接口 创建出 Invoker 。 - 通过创建 Service 的 Proxy ,实现我们在业务代理调用 Service 的方法时,透明的内部转换成调用 Invoker 的
#invoke(Invocation)方法。
服务提供者暴露服务的 主过程 如下图:

- 从图中我们可以看出,该方法创建的 Invoker ,下一步会提交给 Protocol ,从 Invoker 转换到 Exporter 。
- Dubbo 支持 Javassist 和 JDK Proxy 两种方式生成代理。
Protocol
Protocol 是服务域,它是 Invoker 暴露和引用的主功能入口。
它负责 Invoker 的生命周期管理。
代码如下:
@SPI("dubbo")
public interface Protocol {
/**
* Get default port when user doesn't config the port.
*
* @return default port
*/
int getDefaultPort();
/**
* Export service for remote invocation: <br>
* 1. Protocol should record request source address after receive a request:
* RpcContext.getContext().setRemoteAddress();<br>
* 2. export() must be idempotent, that is, there's no difference between invoking once and invoking twice when
* export the same URL<br>
* 3. Invoker instance is passed in by the framework, protocol needs not to care <br>
*
* @param <T> Service type
* @param invoker Service invoker
* @return exporter reference for exported service, useful for unexport the service later
* @throws RpcException thrown when error occurs during export the service, for example: port is occupied
*/
/**
* 暴露远程服务:<br>
* 1. 协议在接收请求时,应记录请求来源方地址信息:RpcContext.getContext().setRemoteAddress();<br>
* 2. export() 必须是幂等的,也就是暴露同一个 URL 的 Invoker 两次,和暴露一次没有区别。<br>
* 3. export() 传入的 Invoker 由框架实现并传入,协议不需要关心。<br>
*
* @param <T> 服务的类型
* @param invoker 服务的执行体
* @return exporter 暴露服务的引用,用于取消暴露
* @throws RpcException 当暴露服务出错时抛出,比如端口已占用
*/
@Adaptive
<T> Exporter<T> export(Invoker<T> invoker) throws RpcException;
/**
* Refer a remote service: <br>
* 1. When user calls `invoke()` method of `Invoker` object which's returned from `refer()` call, the protocol
* needs to correspondingly execute `invoke()` method of `Invoker` object <br>
* 2. It's protocol's responsibility to implement `Invoker` which's returned from `refer()`. Generally speaking,
* protocol sends remote request in the `Invoker` implementation. <br>
* 3. When there's check=false set in URL, the implementation must not throw exception but try to recover when
* connection fails.
*
* @param <T> Service type
* @param type Service class
* @param url URL address for the remote service
* @return invoker service's local proxy
* @throws RpcException when there's any error while connecting to the service provider
*/
/**
* 引用远程服务:<br>
* 1. 当用户调用 refer() 所返回的 Invoker 对象的 invoke() 方法时,协议需相应执行同 URL 远端 export() 传入的 Invoker 对象的 invoke() 方法。<br>
* 2. refer() 返回的 Invoker 由协议实现,协议通常需要在此 Invoker 中发送远程请求。<br>
* 3. 当 url 中有设置 check=false 时,连接失败不能抛出异常,并内部自动恢复。<br>
*
* @param <T> 服务的类型
* @param type 服务的类型
* @param url 远程服务的URL地址
* @return invoker 服务的本地代理
* @throws RpcException 当连接服务提供方失败时抛出
*/
@Adaptive
<T> Invoker<T> refer(Class<T> type, URL url) throws RpcException;
/**
* Destroy protocol: <br>
* 1. Cancel all services this protocol exports and refers <br>
* 2. Release all occupied resources, for example: connection, port, etc. <br>
* 3. Protocol can continue to export and refer new service even after it's destroyed.
*/
/**
* 释放协议:<br>
* 1. 取消该协议所有已经暴露和引用的服务。<br>
* 2. 释放协议所占用的所有资源,比如连接和端口。<br>
* 3. 协议在释放后,依然能暴露和引用新的服务。<br>
*/
void destroy();
}
Dubbo 处理服务暴露的关键就在 Invoker 转换到 Exporter 的过程。
- Dubbo 的实现
Dubbo 协议的 Invoker 转为 Exporter 发生在 DubboProtocol 类的 export 方法,它主要是打开 socket 侦听服务,并接收客户端发来的各种请求,通讯细节由 Dubbo 自己实现。
- RMI 的实现
RMI 协议的 Invoker 转为 Exporter 发生在 RmiProtocol 类的 export 方法,它通过 Spring 或 Dubbo 或 JDK 来实现 RMI 服务,通讯细节这一块由 JDK 底层来实现,这就省了不少工作量。