1 打开流的函数
FIEL * fopen(const char * restrict pathname,const char* restrict type)
FILE *fdopen(int filedes,const char *type)
注意:函数1:第一个参数打开文件的路径 第二参数打开的方式
函数2:第一个参数为已经打开的文件描述符
2 打开方式理解
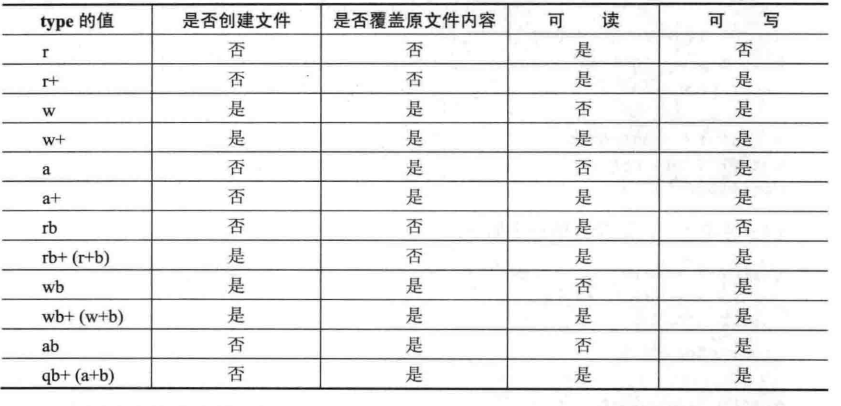
特点:type中开头为a的一般为“追加写,也就是说文件的读写位置在文件的末尾。
type中开头为b的一般是按照二进制文件的形式打开,其他则是按照文本形式打开。
3 返回值
成功返回file指针,失败将错误的值放入error中
4 关闭流 fclose(FILE *FP)成功返回0 失败返回eof
注意:fclose()函数在关闭文件的时候将缓冲区中的内容回写到磁盘上,实际上就是进行了一个文件的操作。在网络的环境中,文件的内容是要通过网路传输到达目的主机并写入磁盘。那么如果网络出了问题 这个时候就会导致写入失败。
5 例子1:打开关闭流
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <fcntl.h> 4 int main(void) 5 { 6 FILE *fp; 7 int fd; 8 if( (fp = fopen("test.txt", "w+")) == NULL){ /* 以读写方式打开流 */ 9 perror("fail to open"); 10 exit(1); 11 } 12 fprintf(fp, "hello world "); /* 向该流输出一段信息,这段信息会反馈到文件上 */ 13 fclose(fp); /* 关闭流 */ 14 if( (fd = open("test.txt", O_RDWR)) == -1){ /* 以读写的方式打开文件 */ 15 perror("fail to open"); 16 exit(1); 17 } 18 if((fp = fdopen(fd, "a")) == NULL){ /* 在打开的文件上打开一个流 */ 19 perror("fail to open stream"); 20 exit(1); 21 } 22 fprintf(fp,"hello world again "); 23 fclose(fp); /* 关闭流,文件也被关闭 */ 24 return 0; 25 }
6 截图
打开test.txt
