一、Spring Security
1、什么是 Spring Security?
(1)基本认识
Spring Security 是基于 Spring 框架,用于解决 Web 应用安全性的 一种方案,是一款优秀的权限管理框架。
Web 应用的安全一般关注 用户认证(authentication) 以及 用户授权(authorization) 这两个部分。简单的理解就是 Web 应用 如何确定 你是谁 以及 你能干什么。
【官网地址:】 https://spring.io/projects/spring-security
(2)用户认证(authentication)
用户认证就是 验证某个用户是否为系统中的合法主体,也即该用户是否能登陆系统,通常根据用户名以及密码进行确认。
简单的理解就是 使 Web 应用确定 你是谁。
(3)用户授权(authorization)
用户授权就是 验证某个用户是否有执行某个操作的权限。
简单的理解就是 使 Web 应用确定 你能干什么。
(4)记住几个点
【@EnableWebSecurity】
用于开启 WebSecurity 模式。有时不需要也可以实现相应的功能。
【@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity】
用于开启注解。常见参数为:prePostEnabled、securedEnabled。
【WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter】
用于自定义 Security 策略。
【AuthenticationManagerBuilder】
用于自定义 认证策略。
2、Spring Security 与 Shiro 简单比较一下?
(1)Spring Security
基于 Spring 框架开发,可以与 Spring 无缝整合。
属于重量级的权限控制框架(依赖其他组件、引入各种依赖),提供了全面的权限控制。
(2)Shiro
Apache 的轻量级权限控制框架,不与任何框架捆绑。
使用起来比 Spring Security 简单。
(3)使用
一般来说,使用 Shiro 可以解决大部分项目的问题,且容易操作。
而 SpringBoot 提供了自动化配置方案,通过较少的配置就可以使用 Spring Security。
所以常见组合通常为: SSM + Shiro 或者 SpringBoot / SpringCloud + Spring Security。
3、Spring Security 初体验(SpringBoot + Spring Security)
(1)步骤
【步骤:】
Step1:新建一个 SpringBoot 项目。
Step2:引入 Web 依赖、Spring Security 依赖。
Step3:新建一个 controller 进行测试。
注:
此处仅导入依赖,未进行任何配置,所以显示的都是默认效果。
【效果:】
当 Spring Security 依赖存在时,访问 controller 时会默认跳转到登陆页面。
默认用户名为:user
密码在控制台上可以看到(随机生成)。
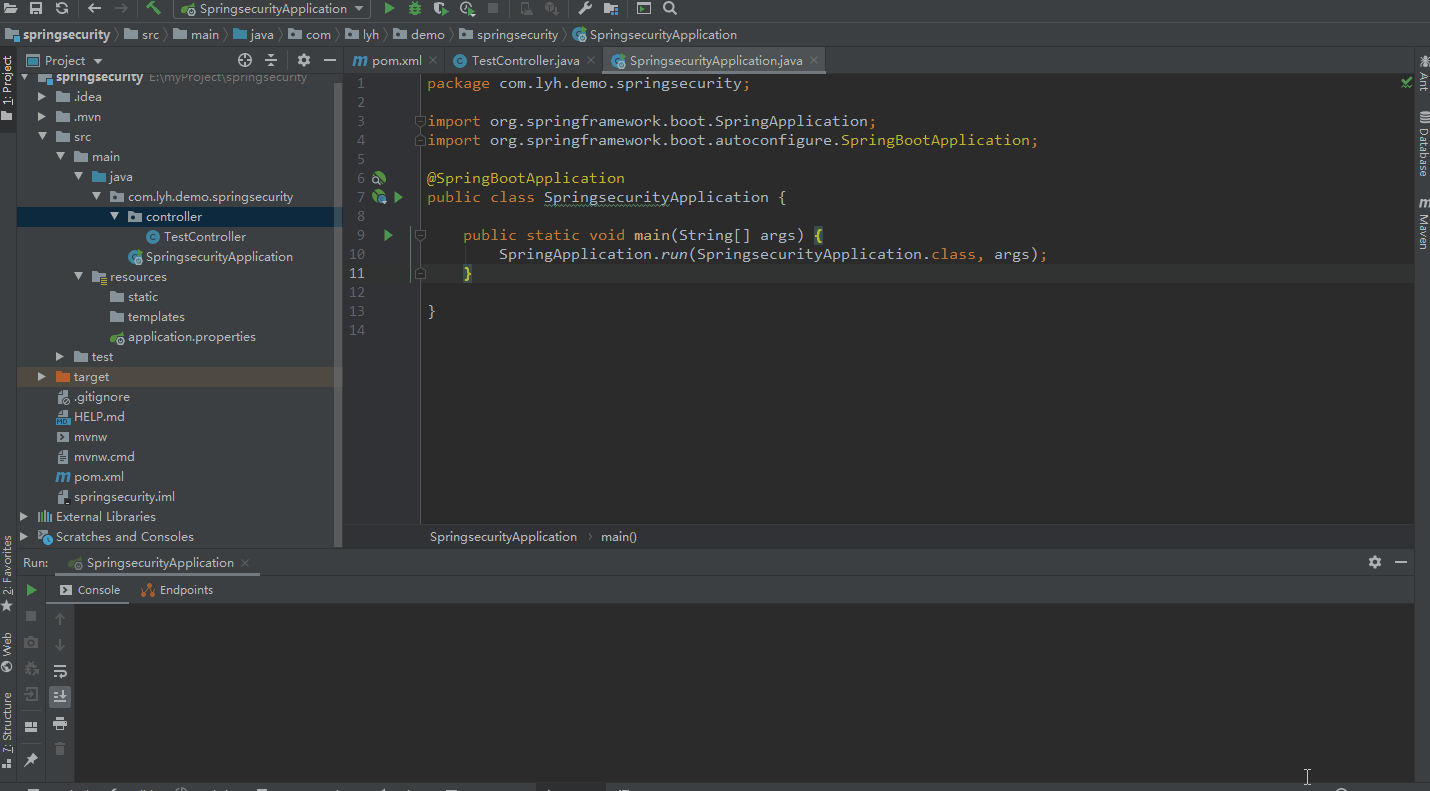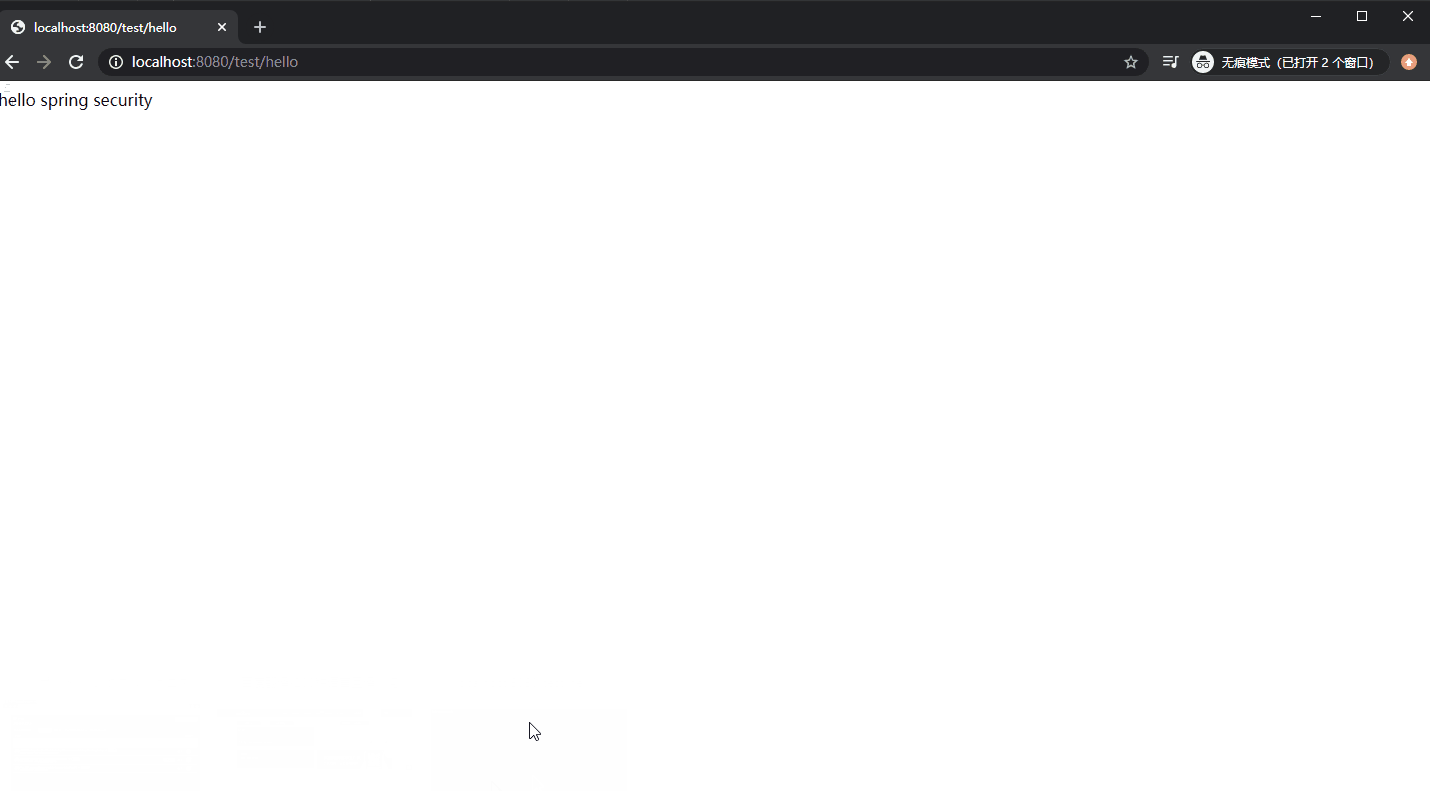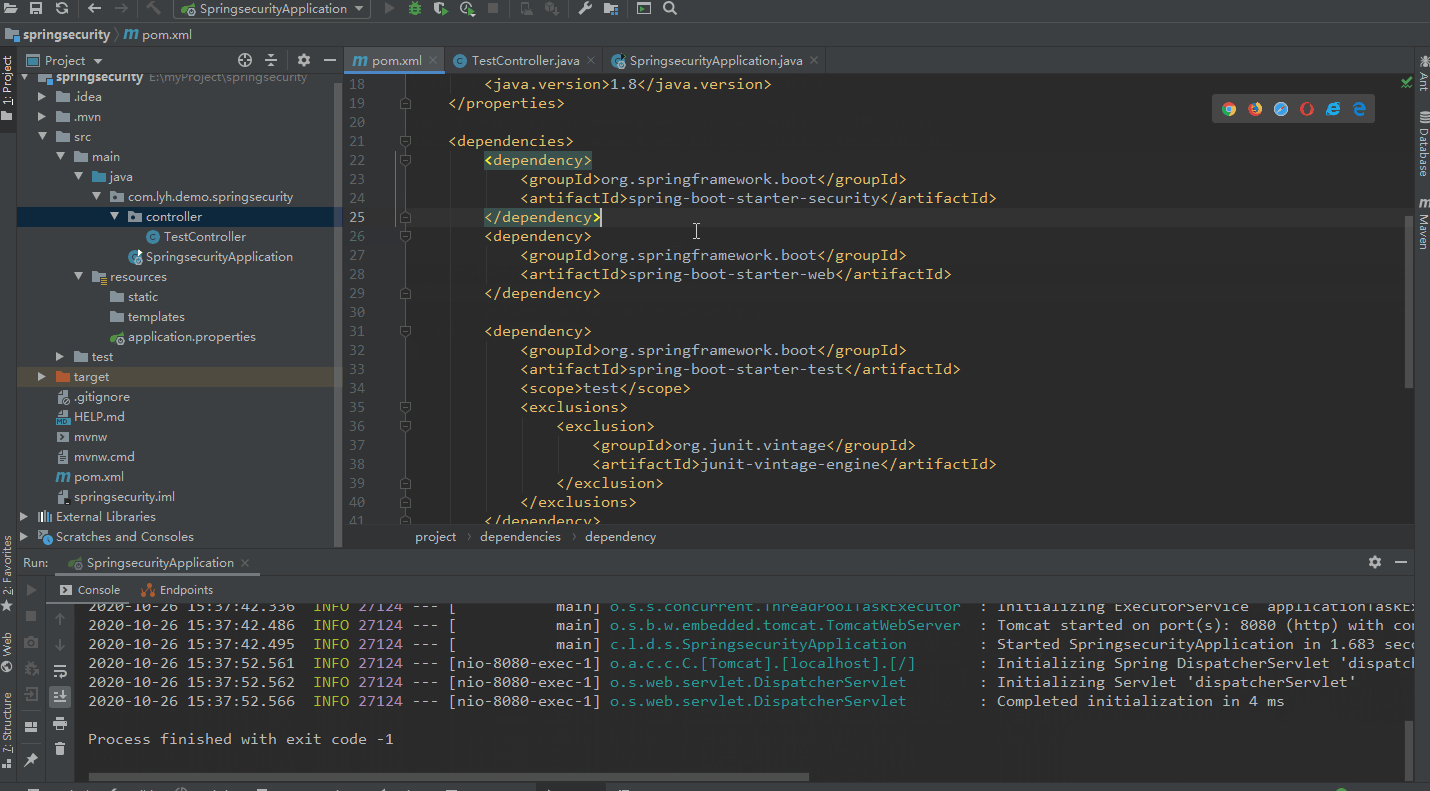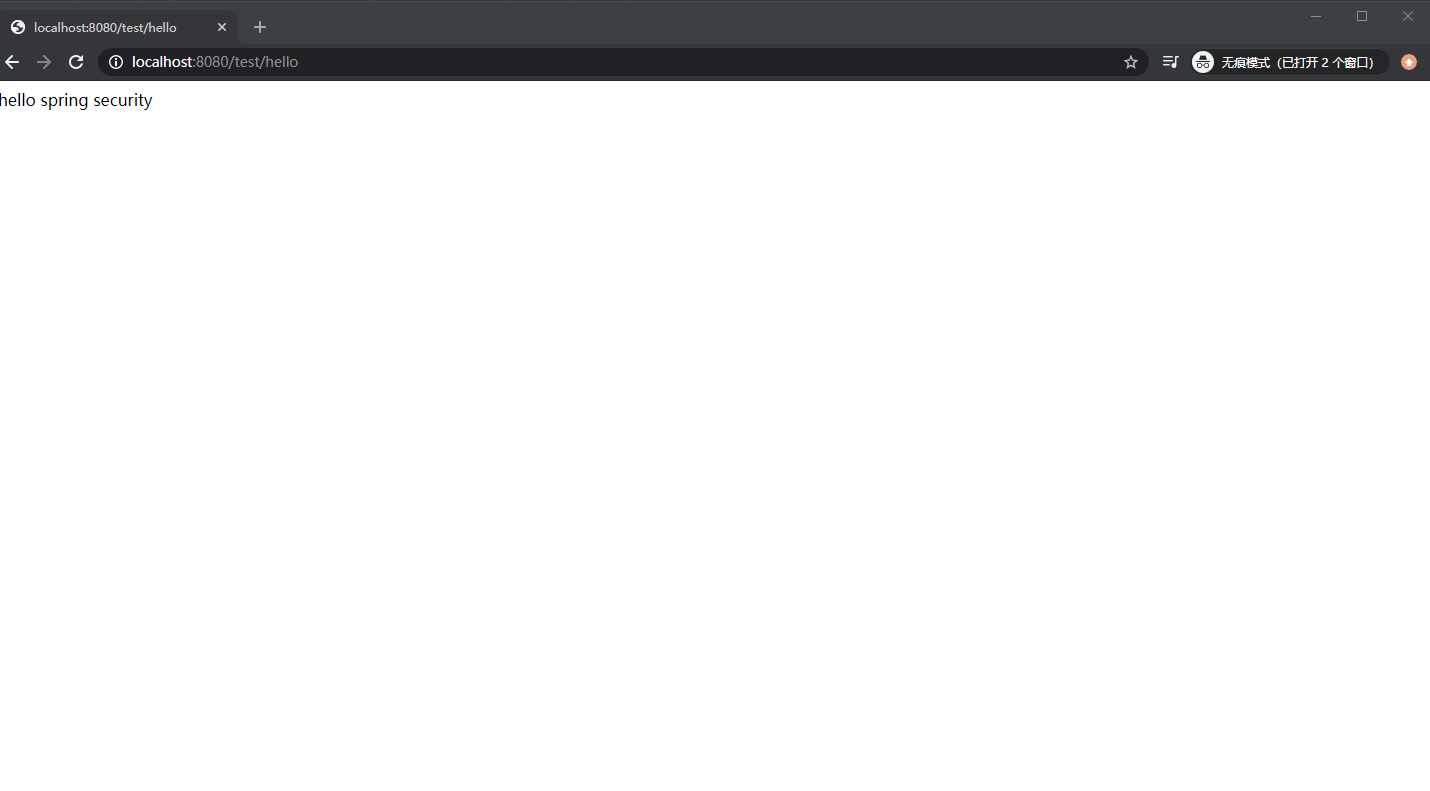
(2)新建一个 SpringBoot 项目,并添加 Web、Spring Security 等依赖。
【依赖:】
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
(3)新建一个 controller,并简单测试一下 Spring Security。
【controller:】 package com.lyh.demo.springsecurity.controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @RequestMapping("test") @RestController public class TestController { @GetMapping("/hello") public String hello() { return "hello spring security"; } }
如下图所示,未添加 SpringSecurity 依赖时,访问 controller 没有限制。
而 添加上依赖后,访问 controller 会首先跳转到登录页面,成功登录后才允许访问。
4、Spring Security 再次体验(SSM + Spring Security)
(1)步骤
使用 SSM 时,需要进行一些繁琐的配置,没有 SpringBoot 用起来舒服,
此处简单配置一下,后面介绍仍然以 SpringBoot 为主。
【步骤:】 Step1:创建一个 maven 工程 或者 web 工程(能使用 SpringMVC 即可),可参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/l-y-h/p/12030104.html Step2:配置 SpringSecurity,并测试。
(2)新建 maven 工程,导入相关依赖
此处使用 tomcat 8 版本启动项目,tomcat 7 启动后在登录时可能会报错。
【依赖】 <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId> <artifactId>spring-security-core</artifactId> <version>5.3.4.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId> <artifactId>spring-security-web</artifactId> <version>5.3.4.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId> <artifactId>spring-security-config</artifactId> <version>5.3.4.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId> <version>5.2.8.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.11</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> 【注意:(tomcat7 版本可能会报如下的错误,更换 tomcat 8 以上版本即可)】 java.lang.NoSuchMethodError: javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest.changeSessionId()Ljava/lang/String;
(3)配置基本的 web 环境(Spring 以及 SpringMVC)
【web.xml】 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_1.xsd" version="3.1"> <!-- step1: 配置全局的参数,启动Spring容器 --> <context-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <!-- 若没有提供值,默认会去找/WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml。 --> <param-value>classpath:applicationContext.xml</param-value> </context-param> <listener> <listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class> </listener> <!-- step2: 配置SpringMVC的前端控制器,用于拦截所有的请求 --> <servlet> <servlet-name>springmvcDispatcherServlet</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> <init-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <!-- 若没有提供值,默认会去找WEB-INF/*-servlet.xml。 --> <param-value>classpath:dispatcher-servlet.xml</param-value> </init-param> <!-- 启动优先级,数值越小优先级越大 --> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>springmvcDispatcherServlet</servlet-name> <!-- 将DispatcherServlet请求映射配置为"/",则Spring MVC将捕获Web容器所有的请求,包括静态资源的请求 --> <url-pattern>/</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> <!-- step3: characterEncodingFilter字符编码过滤器,放在所有过滤器的前面 --> <filter> <filter-name>characterEncodingFilter</filter-name> <filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class> <init-param> <!--要使用的字符集,一般我们使用UTF-8(保险起见UTF-8最好)--> <param-name>encoding</param-name> <param-value>UTF-8</param-value> </init-param> <init-param> <!--是否强制设置request的编码为encoding,默认false,不建议更改--> <param-name>forceRequestEncoding</param-name> <param-value>false</param-value> </init-param> <init-param> <!--是否强制设置response的编码为encoding,建议设置为true--> <param-name>forceResponseEncoding</param-name> <param-value>true</param-value> </init-param> </filter> <filter-mapping> <filter-name>characterEncodingFilter</filter-name> <!--这里不能留空或者直接写 ' / ' ,否则可能不起作用--> <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> </filter-mapping> <!-- step4: 配置过滤器,将post请求转为delete,put --> <filter> <filter-name>HiddenHttpMethodFilter</filter-name> <filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.HiddenHttpMethodFilter</filter-class> </filter> <filter-mapping> <filter-name>HiddenHttpMethodFilter</filter-name> <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> </filter-mapping> </web-app> 【applicationContext.xml】 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util-4.0.xsd"> <!-- step1: 配置包扫描方式。扫描所有包,但是排除Controller层 --> <context:component-scan base-package="com.lyh.demo"> <context:exclude-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/> </context:component-scan> </beans> 【dispatcher-servlet.xml】 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd"> <!-- step1: 配置Controller扫描方式 --> <!-- 使用组件扫描的方式可以一次扫描多个Controller,只需指定包路径即可 --> <context:component-scan base-package="com.lyh.demo" use-default-filters="false"> <!-- 一般在SpringMVC的配置里,只扫描Controller层,Spring配置中扫描所有包,但是排除Controller层。 context:include-filter要注意,如果base-package扫描的不是最终包,那么其他包还是会扫描、加载,如果在SpringMVC的配置中这么做,会导致Spring不能处理事务, 所以此时需要在<context:component-scan>标签上,增加use-default-filters="false",就是真的只扫描context:include-filter包括的内容--> <context:include-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller" /> </context:component-scan> <!-- step2: 配置视图解析器 --> <bean id="defaultViewResolver" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver"> <property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/"/><!--设置JSP文件的目录位置--> <property name="suffix" value=".jsp"/> </bean> <!-- step3: 标准配置 --> <!-- 将springmvc不能处理的请求交给 spring 容器处理 --> <mvc:default-servlet-handler/> <!-- 简化注解配置,并提供更高级的功能 --> <mvc:annotation-driven /> </beans>
(4)配置 SpringSecurity,并新建一个 controller 进行测试
【web.xml 中配置核心过滤器链 springSecurityFilterChain】 <filter> <filter-name>springSecurityFilterChain</filter-name> <filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.DelegatingFilterProxy</filter-class> </filter> <filter-mapping> <filter-name>springSecurityFilterChain</filter-name> <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> </filter-mapping> 【新建一个 spring-security.xml 用于进行 Spring Security 相关配置】 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:security="http://www.springframework.org/schema/security" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/security http://www.springframework.org/schema/security/spring-security.xsd"> <!-- 配置 Spring-Security. auto-config="true" 表示使用框架默认提供的登录界面 use-expressions="true" 表示使用 Spring 的 EL 表达式 --> <security:http auto-config="true" use-expressions="true"> <!-- 配置拦截请求。 pattern="/**" 表示拦截所有请求 access="hasAnyRole('ROLE_USER')" 表示只有角色为 ROLE_USER 的用户才能访问并登陆系统 --> <security:intercept-url pattern="/**" access="hasAnyRole('ROLE_USER')"/> </security:http> <!-- 配置用户信息(用户管理) 密码默认是加密的,若不想密码加密,则可以在 密码前面添加 {noop} --> <security:authentication-manager> <security:authentication-provider> <security:user-service> <security:user name="tom" password="{noop}123456" authorities="ROLE_USER" /> <security:user name="jarry" password="{noop}123456" authorities="ROLE_ADMIN" /> <security:user name="jack" password="123456" authorities="ROLE_USER" /> </security:user-service> </security:authentication-provider> </security:authentication-manager> </beans> 【在 web.xml 中导入 spring-security.xml 文件(与导入 applicationContext.xml 类似,也可以在 applicationContext.xml 中通过 <import> 标签引入 spring-security.xml)】 <context-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <!-- 若没有提供值,默认会去找/WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml。 --> <param-value> classpath:applicationContext.xml classpath:spring-security.xml </param-value> </context-param> 【完整 web.xml 如下:】 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_1.xsd" version="3.1"> <!-- step1: 配置全局的参数,启动Spring容器 --> <context-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <!-- 若没有提供值,默认会去找/WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml。 --> <param-value> classpath:applicationContext.xml classpath:spring-security.xml </param-value> </context-param> <listener> <listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class> </listener> <!-- step2: 配置SpringMVC的前端控制器,用于拦截所有的请求 --> <servlet> <servlet-name>springmvcDispatcherServlet</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> <init-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <!-- 若没有提供值,默认会去找WEB-INF/*-servlet.xml。 --> <param-value>classpath:dispatcher-servlet.xml</param-value> </init-param> <!-- 启动优先级,数值越小优先级越大 --> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>springmvcDispatcherServlet</servlet-name> <!-- 将DispatcherServlet请求映射配置为"/",则Spring MVC将捕获Web容器所有的请求,包括静态资源的请求 --> <url-pattern>/</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> <!-- step3: characterEncodingFilter字符编码过滤器,放在所有过滤器的前面 --> <filter> <filter-name>characterEncodingFilter</filter-name> <filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class> <init-param> <!--要使用的字符集,一般我们使用UTF-8(保险起见UTF-8最好)--> <param-name>encoding</param-name> <param-value>UTF-8</param-value> </init-param> <init-param> <!--是否强制设置request的编码为encoding,默认false,不建议更改--> <param-name>forceRequestEncoding</param-name> <param-value>false</param-value> </init-param> <init-param> <!--是否强制设置response的编码为encoding,建议设置为true--> <param-name>forceResponseEncoding</param-name> <param-value>true</param-value> </init-param> </filter> <filter-mapping> <filter-name>characterEncodingFilter</filter-name> <!--这里不能留空或者直接写 ' / ' ,否则可能不起作用--> <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> </filter-mapping> <!-- step4: 配置过滤器,将post请求转为delete,put --> <filter> <filter-name>HiddenHttpMethodFilter</filter-name> <filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.HiddenHttpMethodFilter</filter-class> </filter> <filter-mapping> <filter-name>HiddenHttpMethodFilter</filter-name> <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> </filter-mapping> <!-- Step5:配置 SpringSecurity 核心过滤器链 --> <filter> <filter-name>springSecurityFilterChain</filter-name> <filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.DelegatingFilterProxy</filter-class> </filter> <filter-mapping> <filter-name>springSecurityFilterChain</filter-name> <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> </filter-mapping> </web-app> 【新建一个 TestController.java 进行测试】 package com.lyh.demo.controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @RequestMapping("test") @RestController public class TestController { @GetMapping("/hello") public String hello() { return "hello spring security"; } }
如下图所示,未配置 springSecurityFilterChain 时,等同于普通的系统登录。
配置 springSecurityFilterChain 后,在 spring-security.xml 中可以看到,
配置了如下内容:
拦截所有请求,并只允许拥有 ROLE_USER 这个角色的用户才可以登录。
设置了三个用户,tom 为 ROLE_USER 角色,且密码未加密,所以可以正常登陆。
jarry 为 ROLE_ADMIN 角色,没有权限,所以不能正常登陆。
jack 为 ROLE_USER 角色,但密码被加密,所以不能正常登陆。
5、Spring Security 过滤器链
(1)本质
Spring Security 基于 Servlet 过滤器实现的。
默认由 15 个过滤器组成过滤器链(可以通过配置添加、移除过滤器),通过过滤器拦截请求并进行相关操作。

(2)简单了解几个过滤器
【org.springframework.security.web.context.SecurityContextPersistenceFilter】 此过滤器主要是在 SecurityContextRepository 中 保存或者更新 SecurityContext,并交给后续的过滤器操作。 而 SecurityContext 中保存了当前用户认证、权限等信息。 【org.springframework.security.web.csrf.CsrfFilter】 此过滤器用于防止 CSRF 攻击。Spring Security 4.0 开始,默认开启 CSRF 防护,针对 PUT、POST、DELETE 等请求进行防护。 注: CSRF 指的是 Cross Site Request Forgery,即 跨站请求伪造。 简单理解为:攻击者冒用用户身份去执行操作。 举例: 用户打开浏览器并成功登陆某个网站 A, 此时用户 未登出网站 A,且在同一浏览器中新增一个 Tab 页并访问 网站 B, 而浏览器接收到网站 B 返回的恶意代码后,在用户不知情的情况下携带 cookie 等用户信息向 A 网站发送请求。 网站 A 处理该请求,从而导致网站 B 的恶意代码被执行。 简单理解就是:用户登录一个网站 A,并打开了另一个网站 B,B 网站携带恶意代码 且使用用户身份去访问 网站 A。 XSS 指的是 Cross Site Scripting,即 跨站脚本。 简单理解:攻击者将恶意代码嵌入网站,当用户访问网站时导致 恶意代码被执行。 【org.springframework.security.web.authentication.logout.LogoutFilter】 匹配 URL(默认为 /logout),用于实现用户退出并清除认证信息。 【org.springframework.security.web.authentication.UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter】 匹配 URL(默认为 /login),用于实现用户登录认证操作(必须为 POST 请求)。 【org.springframework.security.web.authentication.ui.DefaultLoginPageGeneratingFilter】 若没有指定登录认证界面,此过滤器会提供一个默认的界面。 【org.springframework.security.web.authentication.ui.DefaultLogoutPageGeneratingFilter】 若没有指定登出界面,此过滤器会提供一个默认的界面。 【org.springframework.security.web.authentication.AnonymousAuthenticationFilter】 创建一个匿名身份,用于系统的访问。(兼容游客登录模式) 【org.springframework.security.web.access.ExceptionTranslationFilter】 位于整个 springSecurityFilterChain 过滤链后方,用于处理链路中的异常(跳转到指定页面或者返回错误信息)。 【org.springframework.security.web.access.intercept.FilterSecurityInterceptor】 获取资源访问的授权信息,根据 SecurityContext 中存储的用户信息来决定操作是否有权限。
(3)这些过滤器是如何加载进来的?
通过前面 SSM + Spring Security 可以看到,在 web.xml 中配置了名为 springSecurityFilterChain 的过滤器,可以 Debug 看下 DelegatingFilterProxy 加载的流程。
【基本流程:】
Step1:
通过 DelegatingFilterProxy 过滤器的 doFilter() 获取到 FilterChainProxy 过滤器并执行。
Step2:
通过 FilterChainProxy 过滤器的 doFilter() 调用 doFilterInternal() 加载到 过滤器链。
Step3:
doFilterInternal() 内部通过 SecurityFilterChain 接口获取到 过滤器链。
Step4:
SecurityFilterChain 接口实现类为 DefaultSecurityFilterChain。
二、SpringBoot + SpringSecurity 相关操作
1、三种认证方式(设置用户名、密码)
不进行任何 SpringSecurity 配置时,系统默认提供用户名以及密码,但是这种情况肯定不适用于工作场景。那么如何进行 认证呢?
(1)方式一:
通过配置文件 application.properties 或者 application.yml 中直接定义。
不太适用于实际工作场景。
【在 application.properties 中直接定义 用户名、密码】 spring.security.user.name=tom spring.security.user.password=123456
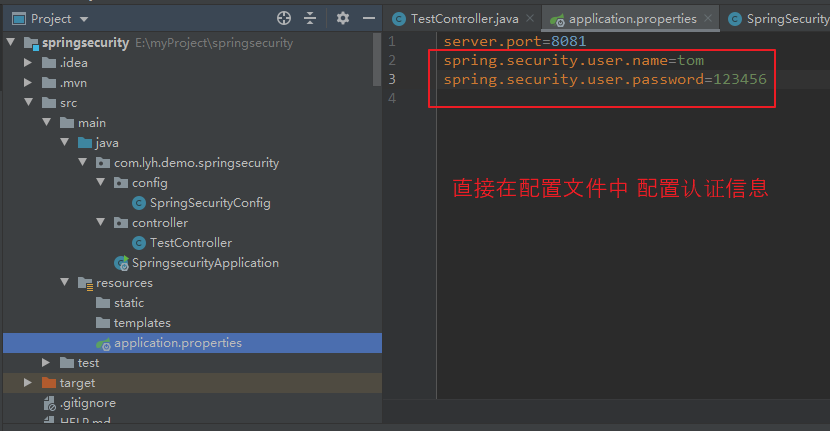
(2)方式二:
通过配置类的形式。(需要继承 WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter 抽象类)
不太适用于实际工作场景。
【通过配置类的形式:】 package com.lyh.demo.springsecurity.config; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.authentication.builders.AuthenticationManagerBuilder; import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter; import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder; import org.springframework.security.crypto.password.PasswordEncoder; /** * 配置 Spring Security */ @Configuration public class SpringSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter { @Override protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception { BCryptPasswordEncoder bCryptPasswordEncoder = new BCryptPasswordEncoder(); auth.inMemoryAuthentication() .withUser("jack") // .password("{noop}" + "123456") // 未配置 PasswordEncoder 时,可以在 密码前拼接上 {noop},防止出错 .password(bCryptPasswordEncoder.encode("123456")) .roles("admin"); } /** * 配置加密类,若不配置,则 bCryptPasswordEncoder.encode() 进行加密时会出错。 * java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: There is no PasswordEncoder mapped for the id "null" * * 若不想配置,可以在 设置 password 时,在密码前添加上 {noop} * @return 加密类 */ @Bean PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() { return new BCryptPasswordEncoder(); } }

(3)方式三
通过配置类 以及 自定义实现类(实现 UserDetailsService 接口)实现。
适用于工作场景(从数据库中查询出用户信息并认证)。
【步骤一:在配置类中 指定使用 UserDetailsService 接口,并注入其 实现类】 package com.lyh.demo.springsecurity.config; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.authentication.builders.AuthenticationManagerBuilder; import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter; import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService; import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder; import org.springframework.security.crypto.password.PasswordEncoder; /** * 配置 Spring Security */ @Configuration public class SpringSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter { @Autowired private UserDetailsService userDetailsService; @Override protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception { auth.userDetailsService(userDetailsService).passwordEncoder(passwordEncoder()); } @Bean PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() { return new BCryptPasswordEncoder(); } }
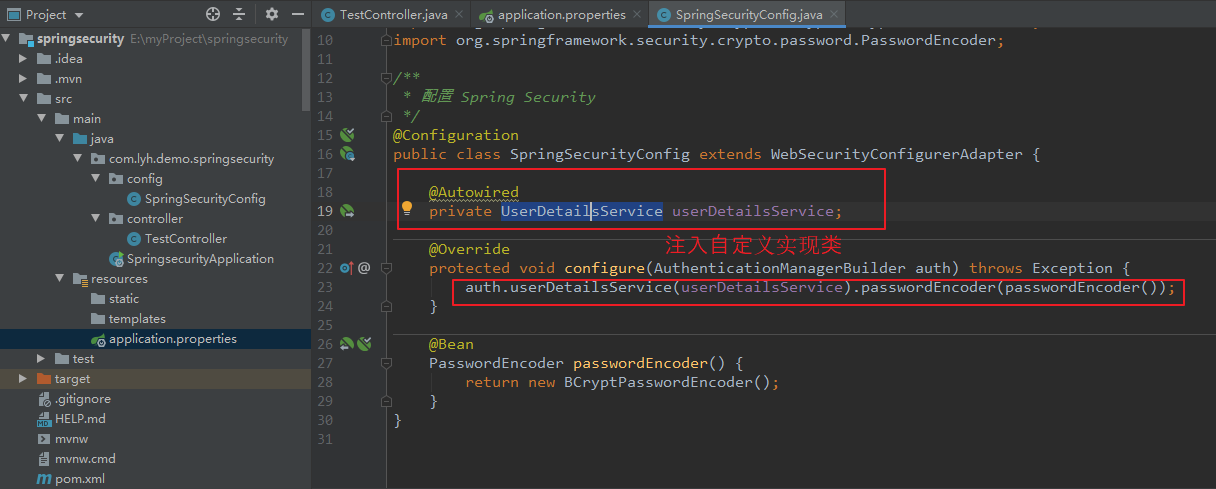
【步骤二:编写自定义实现类(实现 UserDetailsService 接口)】 package com.lyh.demo.springsecurity.service; import org.springframework.security.core.GrantedAuthority; import org.springframework.security.core.authority.AuthorityUtils; import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User; import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails; import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService; import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UsernameNotFoundException; import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import java.util.List; @Service("userDetailsService") public class MyUserDetailsService implements UserDetailsService { @Override public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String s) throws UsernameNotFoundException { // 设置用户权限,若有多个权限可以使用 逗号分隔 List<GrantedAuthority> auths = AuthorityUtils.commaSeparatedStringToAuthorityList("admin"); return new User("jarry", new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode("123456"), auths); } }
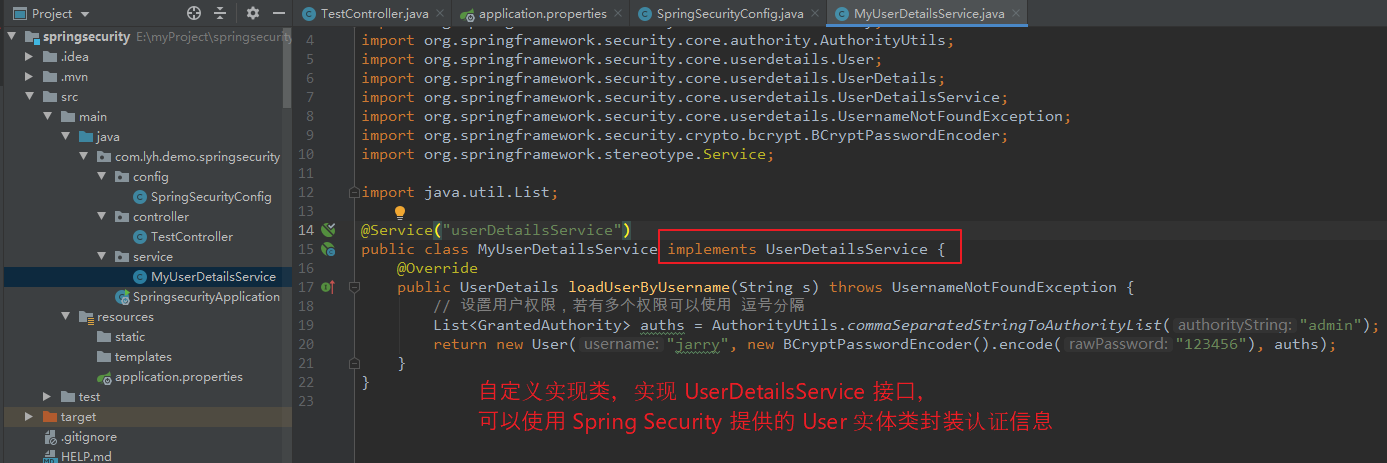
2、SpringSecurity 中登录认证过程中 的密码加密(BCryptPasswordEncoder)
(1)为什么要了解密码加密?
Spring Security 5.0 以上版本 对于密码处理需要特别注意一下,前面也介绍了,Spring Security 认证时会对密码进行加密,采用 {encodingId}password 的形式设置加密方式。
如果不想密码加密,可以在配置密码时在 密码前拼接上 {noop}, 即 ({noop}password)。
而实际场景中,数据库存储的密码都是非明文存储(即存储的都是加密后的密码),所以有必要了解一下 SpringSecurity 加密相关内容。
【相关的 encodingId 与其 对应的 实体类 如下:】 public static PasswordEncoder createDelegatingPasswordEncoder() { String encodingId = "bcrypt"; Map<String, PasswordEncoder> encoders = new HashMap(); encoders.put(encodingId, new BCryptPasswordEncoder()); encoders.put("ldap", new LdapShaPasswordEncoder()); encoders.put("MD4", new Md4PasswordEncoder()); encoders.put("MD5", new MessageDigestPasswordEncoder("MD5")); encoders.put("noop", NoOpPasswordEncoder.getInstance()); encoders.put("pbkdf2", new Pbkdf2PasswordEncoder()); encoders.put("scrypt", new SCryptPasswordEncoder()); encoders.put("SHA-1", new MessageDigestPasswordEncoder("SHA-1")); encoders.put("SHA-256", new MessageDigestPasswordEncoder("SHA-256")); encoders.put("sha256", new StandardPasswordEncoder()); encoders.put("argon2", new Argon2PasswordEncoder()); return new DelegatingPasswordEncoder(encodingId, encoders); }
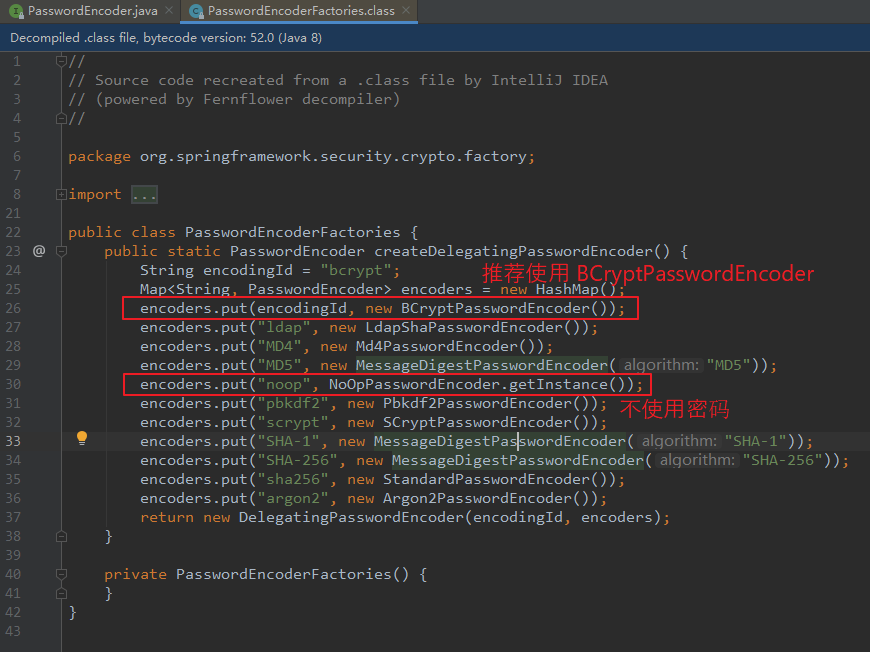
(2)PasswordEncoder
SpringSecurity 默认需要在容器中存在 PasswordEncoder 实例对象,用于进行密码加密。所以配置 SpringSecurity 时,需要在容器中配置一个 PasswordEncoder Bean 对象(一般使用 BCryptPasswordEncoder 实例对象)。
【在配置类中通过 @Bean 配置一个 PasswordEncoder 的 Bean 对象:】 @Bean PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() { return new BCryptPasswordEncoder(); } 【PasswordEncoder 常用方法:】 String encode(CharSequence rawPassword); // 用于密码加密 boolean matches(CharSequence rawPassword, String encodedPassword); // 用于密码解密,rawPassword 表示待匹配的密码,encodedPassword 表示加密后的密码。
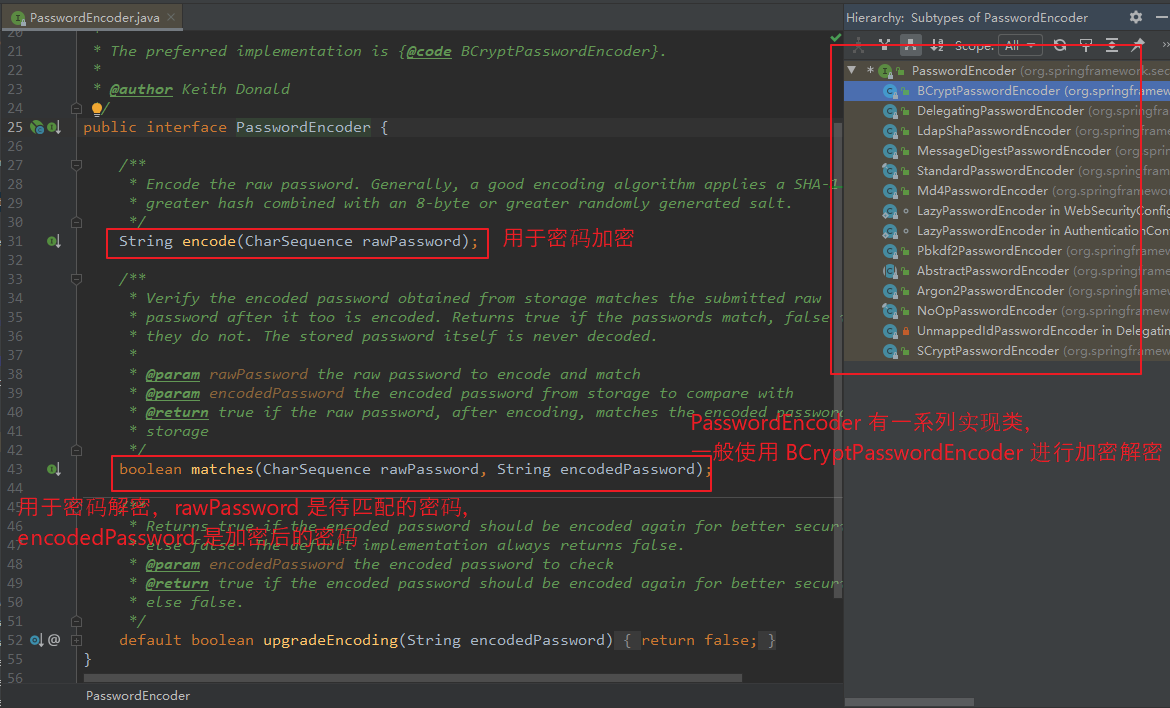
(3)BCryptPasswordEncoder
是最常用的一种密码解析器,其通过 哈希算法 并加上 随机盐(salt)的方式进行密码加密。
密码解密时,根据加密后的数据 A 得到盐值(salt),将待比较数据根据盐值进行一次加密得到 B,如果 B 与 A 是相同的结果,则说明密码是正确的。
密码加密、解密的关键点在于 盐值的计算。
密码加密相关代码如下所示:
【 encode() 加密:】 加密代码如下所示,首先调用 BCrypt.gensalt() 方法计算出 盐值(salt), 然后调用 BCrypt.hashpw() 方法,根据 盐值(salt)进行密码(password)加密。 而在 BCrypt 中的 hashpw() 中,会通过 salt.substring() 截取并得到真实的盐值(real_salt), 通过 B.crypt_raw() 求得一个哈希数组(hashed),通过 encode_base64() 进行加密。 public String encode(CharSequence rawPassword) { if (rawPassword == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("rawPassword cannot be null"); } String salt; if (random != null) { salt = BCrypt.gensalt(version.getVersion(), strength, random); } else { salt = BCrypt.gensalt(version.getVersion(), strength); } return BCrypt.hashpw(rawPassword.toString(), salt); } 【BCrypt】 public static String hashpw(String password, String salt) { byte passwordb[]; passwordb = password.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8); return hashpw(passwordb, salt); } public static String hashpw(byte passwordb[], String salt) { BCrypt B; String real_salt; byte saltb[], hashed[]; char minor = (char) 0; int rounds, off; StringBuilder rs = new StringBuilder(); if (salt == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("salt cannot be null"); } int saltLength = salt.length(); if (saltLength < 28) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid salt"); } if (salt.charAt(0) != '$' || salt.charAt(1) != '2') throw new IllegalArgumentException ("Invalid salt version"); if (salt.charAt(2) == '$') off = 3; else { minor = salt.charAt(2); if ((minor != 'a' && minor != 'x' && minor != 'y' && minor != 'b') || salt.charAt(3) != '$') throw new IllegalArgumentException ("Invalid salt revision"); off = 4; } // Extract number of rounds if (salt.charAt(off + 2) > '$') throw new IllegalArgumentException ("Missing salt rounds"); if (off == 4 && saltLength < 29) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid salt"); } rounds = Integer.parseInt(salt.substring(off, off + 2)); real_salt = salt.substring(off + 3, off + 25); saltb = decode_base64(real_salt, BCRYPT_SALT_LEN); if (minor >= 'a') // add null terminator passwordb = Arrays.copyOf(passwordb, passwordb.length + 1); B = new BCrypt(); hashed = B.crypt_raw(passwordb, saltb, rounds, minor == 'x', minor == 'a' ? 0x10000 : 0); rs.append("$2"); if (minor >= 'a') rs.append(minor); rs.append("$"); if (rounds < 10) rs.append("0"); rs.append(rounds); rs.append("$"); encode_base64(saltb, saltb.length, rs); encode_base64(hashed, bf_crypt_ciphertext.length * 4 - 1, rs); return rs.toString(); }
密码解密相关代码如下所示:
【matches() 解密:】 解密代码如下所示,首先确保 encodedPassword 是加密后的代码。 然后调用 BCrypt.checkpw() 进行密码匹配。 而 BCrypt 的 checkpw() 中,可以看到其会将待比较的密码 重新进行一次 hashpw() 密码加密。 而此时传入的盐值是 加密的代码,在 hashpw() 方法中会截取出相应的 盐值(real_salt)并用于加密。 加密完成后,再去比较新加密的密码 与 原来加密的密码 是否相同即可。 所以如果待比较的密码 与 加密的密码是相同的,也即相当于 根据相同的 盐值 再加密了一次,加密结果是相同的。 public boolean matches(CharSequence rawPassword, String encodedPassword) { if (rawPassword == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("rawPassword cannot be null"); } if (encodedPassword == null || encodedPassword.length() == 0) { logger.warn("Empty encoded password"); return false; } if (!BCRYPT_PATTERN.matcher(encodedPassword).matches()) { logger.warn("Encoded password does not look like BCrypt"); return false; } return BCrypt.checkpw(rawPassword.toString(), encodedPassword); } 【BCrypt】 public static boolean checkpw(String plaintext, String hashed) { return equalsNoEarlyReturn(hashed, hashpw(plaintext, hashed)); } static boolean equalsNoEarlyReturn(String a, String b) { return MessageDigest.isEqual(a.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8), b.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)); }
3、从数据库中查询用户信息并认证(MyBatis-Plus + MySQL 8 )
(1)建表(SQL)
MyBatis-Plus 使用可以参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/l-y-h/p/12859477.html
配置 SpringSecurity 时需要配置 使用密码加密,
若不使用加密,则需在设置密码时在密码前拼接上 {noop}。
若使用加密,则使用 BCryptPasswordEncoder 的 encode() 方法对其进行加密。
若数据库存储的已经是 BCryptPasswordEncoder 加密后的数据,不用再次加密。
此处为了方便理解,存储密码时均使用 明文存储。
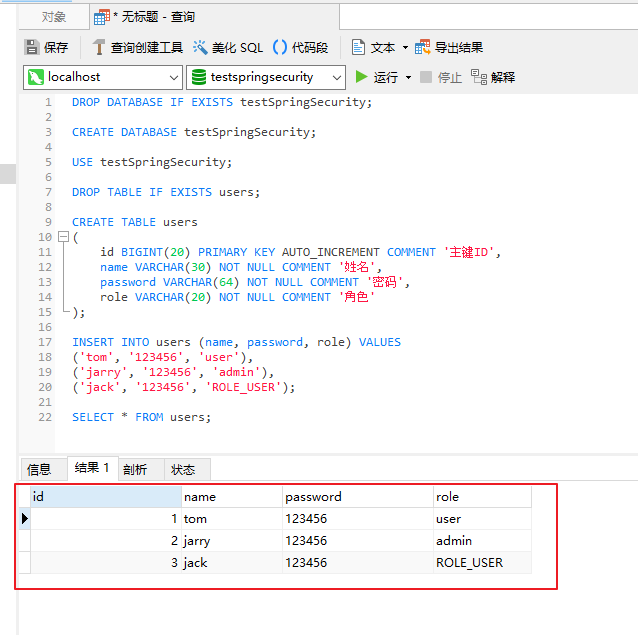
【建表 SQL :】 DROP DATABASE IF EXISTS testSpringSecurity; CREATE DATABASE testSpringSecurity; USE testSpringSecurity; DROP TABLE IF EXISTS users; CREATE TABLE users ( id BIGINT(20) PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '主键ID', name VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL COMMENT '姓名', password VARCHAR(64) NOT NULL COMMENT '密码', role VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '角色' ); INSERT INTO users (name, password, role) VALUES ('tom', '123456', 'user'), ('jarry', '123456', 'admin'), ('jack', '123456', 'ROLE_USER');
(2)引入 MyBatis-Plus 与 MySQL 相关依赖
【依赖:】
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.3.1.tmp</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.18</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.10</version>
</dependency>
(3)配置 MyBatis-Plus 以及 MySQL 数据源信息
【数据源信息】 spring: datasource: driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver username: root password: 123456 url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/testSpringSecurity?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8
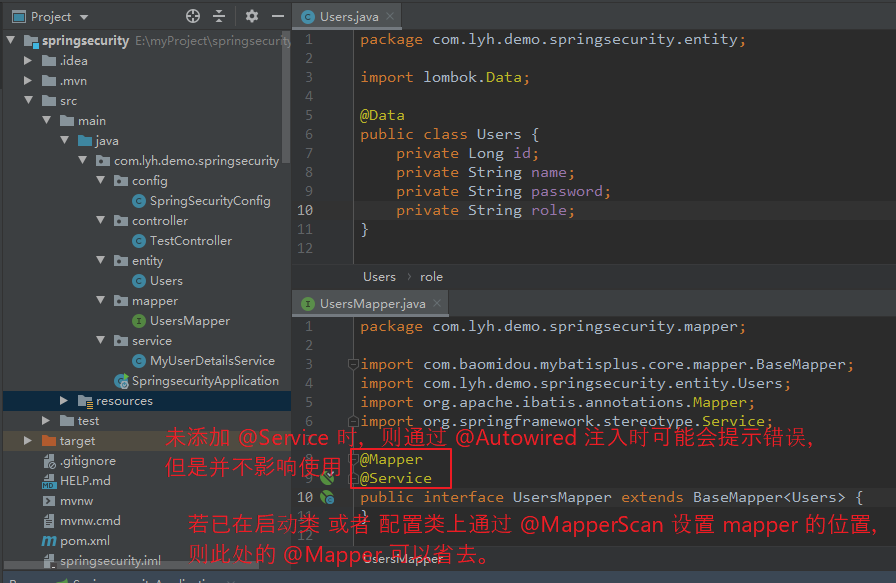
(4)编写 数据表对应的 实体类,以及相应的 mapper 或者 service(用于操作数据库)
【实体类:】 package com.lyh.demo.springsecurity.entity; import lombok.Data; @Data public class Users { private Long id; private String name; private String password; private String role; } 【Mapper:】 package com.lyh.demo.springsecurity.mapper; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.mapper.BaseMapper; import com.lyh.demo.springsecurity.entity.Users; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; @Mapper @Service public interface UsersMapper extends BaseMapper<Users> { }
(5)结合 SpringSecurity 进行安全验证。
通过前面分析,添加上 SpirngSecurity 配置类后,会执行 loadUserByUsername() 方法将需要认证的用户信息加载到当前认证系统中,所以在此添加 查询数据库的逻辑即可。
首先根据用户名 在数据库中 查询出相应的 用户、密码 并封装到 实体类中,并将此时的用户、密码、角色等加入到 当前认证系统中。然后再根据 输入的用户名、密码 进行验证。
【修改 MyUserDetailsService 中 loadUserByUsername() 代码:(改为从数据库中获取用户)】 package com.lyh.demo.springsecurity.service; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.conditions.query.QueryWrapper; import com.lyh.demo.springsecurity.entity.Users; import com.lyh.demo.springsecurity.mapper.UsersMapper; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.security.core.GrantedAuthority; import org.springframework.security.core.authority.AuthorityUtils; import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User; import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails; import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService; import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UsernameNotFoundException; import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import java.util.List; @Service("userDetailsService") public class MyUserDetailsService implements UserDetailsService { @Autowired private UsersMapper usersMapper; @Override public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String name) throws UsernameNotFoundException { // 定义查询条件,根据用户名 从数据库查询 对应的 用户、密码、角色 QueryWrapper<Users> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>(); queryWrapper.eq("name", name); Users user = usersMapper.selectOne(queryWrapper); // 用户不存在时,直接抛异常 if (user == null) { throw new UsernameNotFoundException("用户不存在"); } // 用户存在时,把 用户、密码、角色 加入到当前认证系统中 List<GrantedAuthority> auths = AuthorityUtils.commaSeparatedStringToAuthorityList(user.getRole()); // 将数据库中的密码进行 加密 return new User(user.getName(), new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode(user.getPassword()), auths); // return new User(user.getName(), user.getPassword(), auths); // 若数据库密码已经加密过,直接使用即可 } }

4、自定义页面(不使用默认页面)以及 页面跳转、页面访问权限控制
(1)自定义页面
在前面与 数据库 交互的基础上,添加如下代码。
【登录页面:(login.html)】 <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Login</title> </head> <body> <div> <form method="post" action="/login"> <h2>Please sign in</h2> <p> <label for="username">Username</label> <input type="text" id="username" name="username" placeholder="Username" required="" autofocus=""> </p> <p> <label for="password" class="sr-only">Password</label> <input type="password" id="password" name="password" placeholder="Password" required=""> </p> <button type="submit">Sign in</button> </form> </div> </body> </html> 【403 页面:】 <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>403</title> </head> <body> <h1>403</h1> </body> </html> 【在 TestController 中添加一个 处理错误的逻辑:】 package com.lyh.demo.springsecurity.controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @RequestMapping("test") @RestController public class TestController { @GetMapping("/hello") public String hello() { return "hello spring security"; } @PostMapping("/error") public String error() { return "login error"; } }
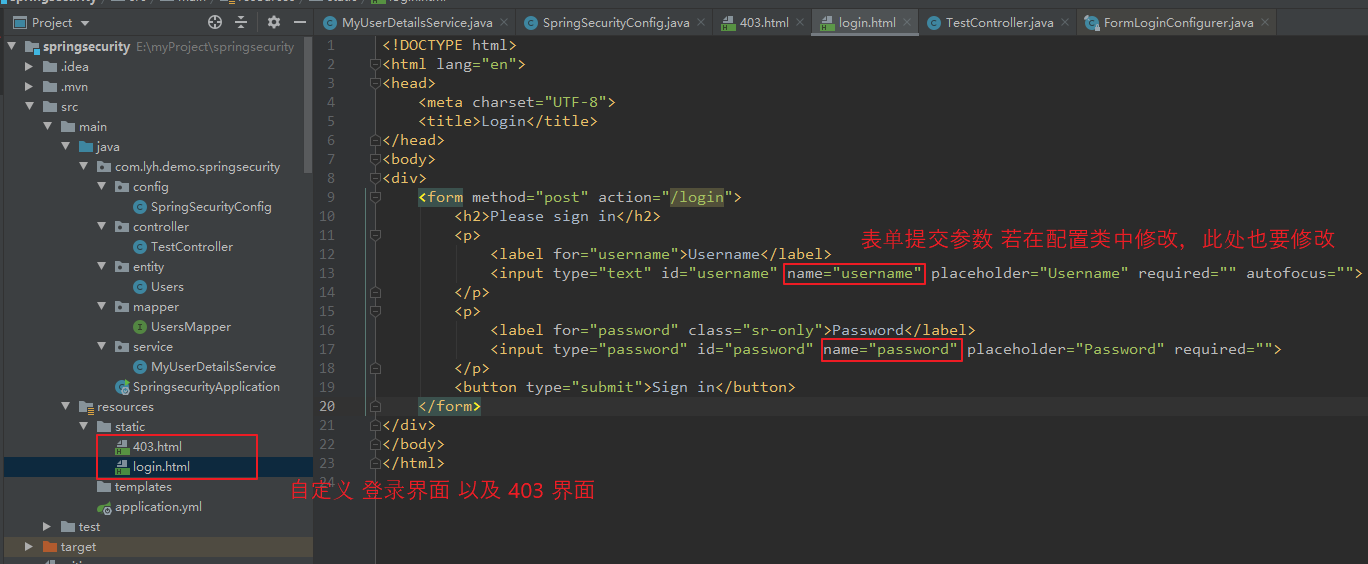
(2)编写配置类,配置页面跳转规则
在配置类中,重写 configure() 方法,并通过 formLogin() 方法设置相关页面。
【配置类中重写 configure() 方法:】 package com.lyh.demo.springsecurity.config; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.authentication.builders.AuthenticationManagerBuilder; import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity; import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter; import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService; import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder; import org.springframework.security.crypto.password.PasswordEncoder; /** * 配置 Spring Security */ @Configuration public class SpringSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter { @Autowired private UserDetailsService userDetailsService; @Override protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception { auth.userDetailsService(userDetailsService).passwordEncoder(passwordEncoder()); } @Override protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { /** * csrf() 表示开启 csrf 防护。 * disable() 表示关闭 csrf 防护。 */ http.csrf().disable(); /** * formLogin() 用于自定义表单登录。 * loginPage() 用于自定义登录页面。 * defaultSuccessUrl() 登录成功后 跳转的路径。 * loginProcessingUrl() 表单提交的 action 地址(默认为 /login,修改后,对应的表单 action 也要修改),由系统提供 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 过滤器拦截并处理。 * usernameParameter() 用于自定义表单提交的用户参数名,默认为 username,修改后,对应的表单参数也要修改。 * passwordParameter() 用于自定义表单提交的用户密码名,默认为 password,修改后,对应的表单参数也要修改。 * failureForwardUrl() 用于自定义表单提交失败后 重定向地址,可用于前后端分离中,指向某个 controller,注意使用 POST 处理。 */ http.formLogin() .loginPage("/login.html") .loginProcessingUrl("/login") .defaultSuccessUrl("/test/hello") //.usernameParameter("name") //.passwordParameter("pwd") .failureForwardUrl("/test/error") ; /** * authorizeRequests() 用于 开启认证,基于 HttpServletRequest 对 url 进行身份控制并授权访问。 * antMatchers() 用于匹配 url。 * permitAll() 用于允许任何人访问该 url。 * hasAuthority() 用于指定 具有某种权限的 人才能访问 url。 * hasAnyAuthority() 用于指定 多个权限 进行访问,多个权限间使用逗号分隔。 * * hasRole() 写法与 hasAuthority() 类似,但是其会在 角色前 拼接上 ROLE_,使用时需要注意。 * hasAnyRole() 写法与 hasAnyAuthority() 类似,同样会在 角色前 拼接上 ROLE_。 * * 使用时 hasAuthority()、hasAnyAuthority() 或者 hasAnyRole()、hasAnyAuthority() 任选一对即可,同时使用四种可能会出现问题。 */ http.authorizeRequests() .antMatchers("/test/hello").hasAuthority("user") //.antMatchers("/test/hello").hasAnyRole("USER,GOD") //.antMatchers("/test/hello").hasRole("GOD") .antMatchers("/test/hello").hasAnyAuthority("user,admin") .antMatchers("/login", "/test/error").permitAll(); /** * 自定义 403 页面 */ http.exceptionHandling().accessDeniedPage("/403.html"); } @Bean PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() { return new BCryptPasswordEncoder(); } }
如下图所示,tom 的角色为 user、jarry 的角色为 admin,jack 的角色为 ROLE_USER。
只允许 user、admin 角色能够访问 /test/hello,即 tom、jarry 可以成功访问系统,而 jack 访问时会跳转到 403 页面,若 用户名 或者 密码输入错误时,将会跳转到 /test/error 画面。
5、了解几个注解
为了简化开发,可以使用注解进行相关操作(操作不太灵活,慎用)。
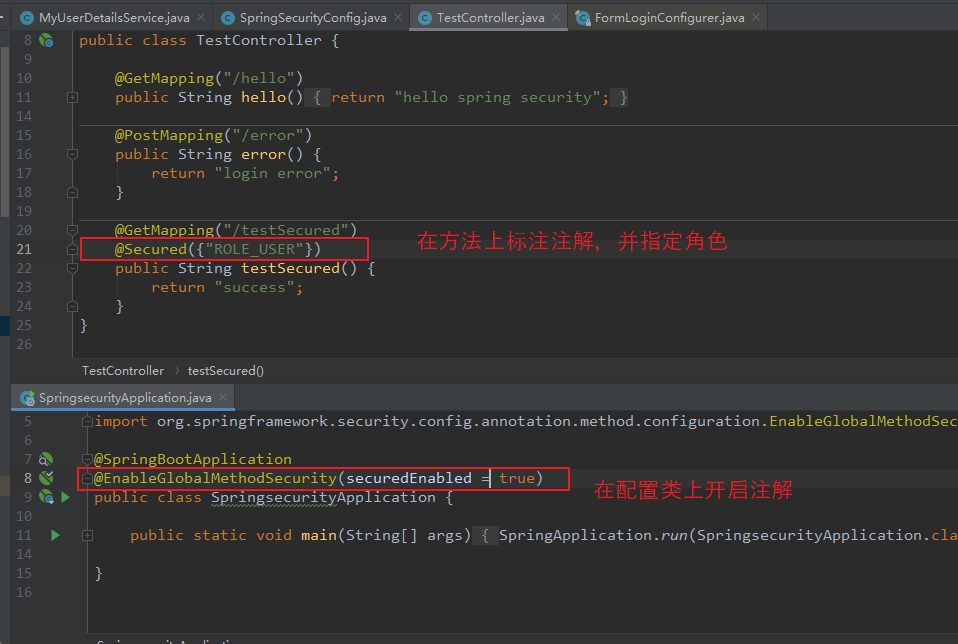
(1)@Secured
添加在 方法上,并可以指定用户角色,作用是只允许指定的用户角色去访问 该方法。
【使用步骤一:】 在配置类上,通过 @EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(securedEnabled = true) 开启注解。 【使用步骤二:】 在方法上添加注解 @Secured,并指定 角色,角色前缀要为 ROLE_。 @GetMapping("/testSecured") @Secured({"ROLE_USER"}) public String testSecured() { return "success"; } 注: 由于 角色需要使用 ROLE_ 为前缀,所以数据库存储的 角色需要以 ROLE_ 为前缀 或者 设置权限时手动加上 ROLE_。
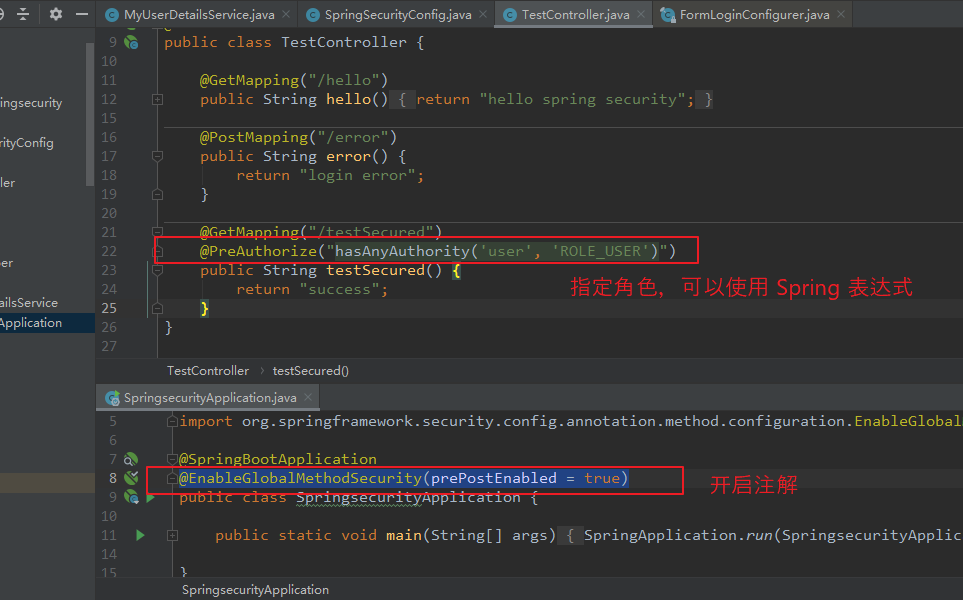
(2)@PreAuthorize
添加在 方法上,并可以指定用户角色,作用是只允许指定的用户角色去访问 该方法。
在进入方法之前 会进行 校验,校验通过后才能执行方法。
【使用步骤一:】 在配置类上,通过 @EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true) 开启注解。 【使用步骤二:】 在方法上添加 @PreAuthorize 注解,并指定角色,角色的指定可以使用 Spring 表达式。 @GetMapping("/testSecured") @PreAuthorize("hasAnyAuthority('user', 'ROLE_USER')") public String testSecured() { return "success"; }
(3)@PostAuthorize
添加在 方法上,并可以指定用户角色,作用是只允许指定的用户角色去访问 该方法。
在进入方法之后 会进行 校验。不管有没有权限,都会执行方法,适合带有返回值的校验。
【使用步骤一:】 在配置类上,通过 @EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true) 开启注解。 【使用步骤二:】 在方法上添加 @PostAuthorize 注解,并指定角色,角色的指定可以使用 Spring 表达式。 @GetMapping("/testSecured") @PostAuthorize("hasAuthority('user')") public String testSecured() { System.out.println("不管有没有权限,我都会执行"); return "success"; }
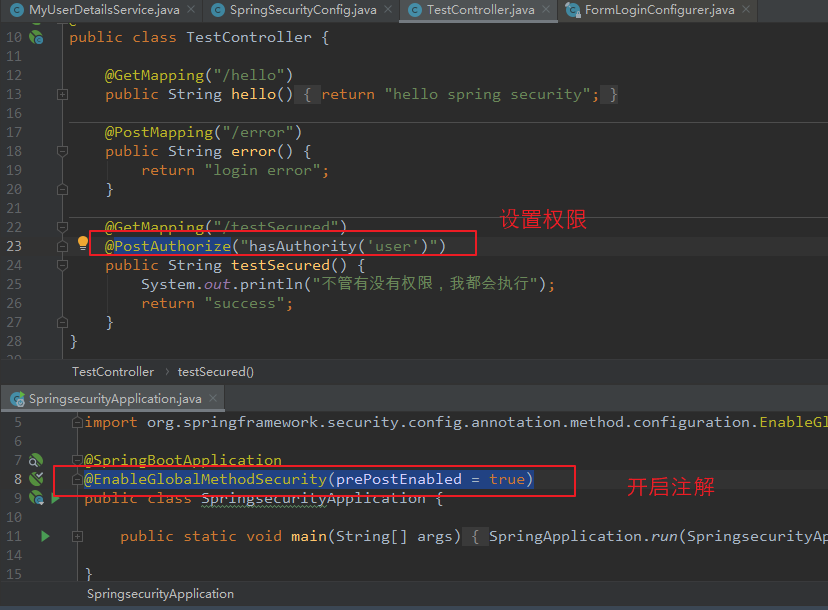
6、用户注销操作
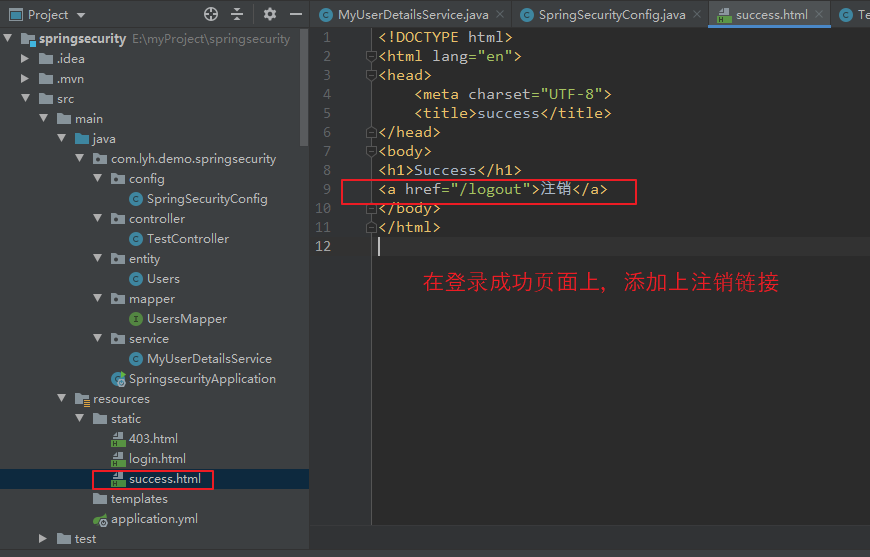
(1)自定义一个登录成功页面,并添加一个 退出链接。
【登录成功页面 success.html】
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>success</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Success</h1>
<a href="/logout">注销</a>
</body>
</html>
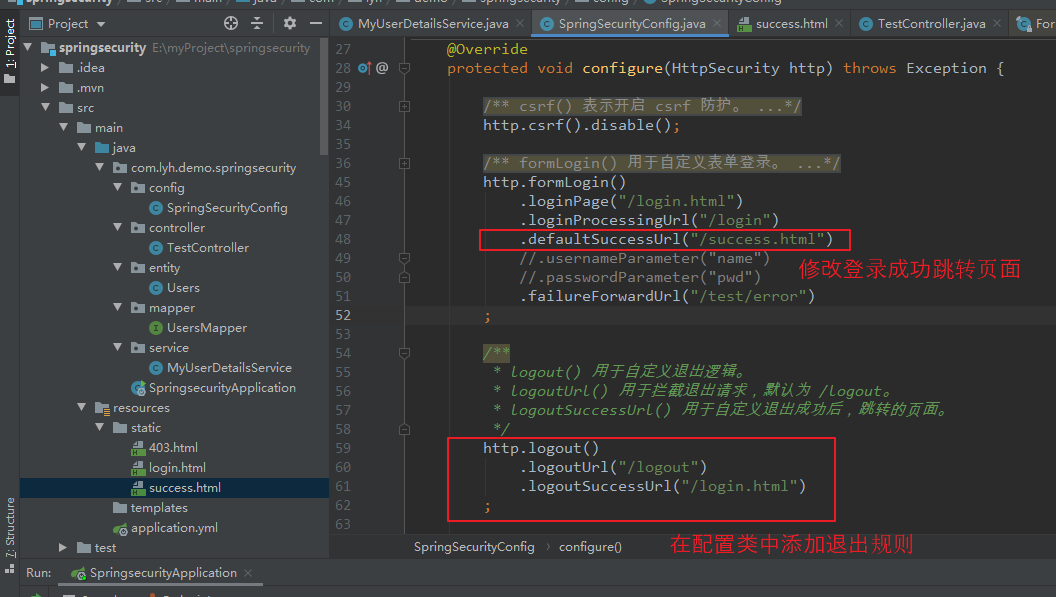
(2)编写配置类,修改页面退出规则。
此处为了跳转到 success.html 页面,还需要 通过 http.formLogin().defaultSuccessUrl() 去指定页面。
【添加退出规则:】 http.formLogin() .loginPage("/login.html") .loginProcessingUrl("/login") .defaultSuccessUrl("/success.html") //.usernameParameter("name") //.passwordParameter("pwd") .failureForwardUrl("/test/error") ; /** * logout() 用于自定义退出逻辑。 * logoutUrl() 用于拦截退出请求,默认为 /logout。 * logoutSuccessUrl() 用于自定义退出成功后,跳转的页面。 */ http.logout() .logoutUrl("/logout") .logoutSuccessUrl("/login.html") ;
如下图所示,tom、jarry 可以访问 /test/hello,jack 不可以访问,所以当使用 tom、jarry 登录时可以成功登陆,jack 会显示 403,一旦点击注销后,需要再次进行登录才能继续访问 /test/hello。

7、记住我
(1)工作流程
记住我 功能上指的是 用户通过浏览器登录一次网站后,关闭浏览器并再次访问网站时,可以不用再次登录而直接进行相关操作。
【工作流程:】
第一次通过浏览器登录系统时:
首先 用户名、密码 会被 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 过滤器拦截,并进行认证。
认证通过后,会调用 RememberMeServices 生成 token,并将 token 写入数据库 以及 浏览器 cookie 中。
第二次通过浏览器登录系统时:
直接携带 cookie 访问,会被 RememberMeAuthenticationFilter 过滤器拦截,根据 cookie 读取出 token 信息。
从数据库中查找出 对应的 token 并比较,若相同,则可以登录系统,否则跳转到登录页面。
工作流程见下图(图片来源于网络):

(2)基本实现:
由于 token 需要存储在 数据库中,所以需要配置数据源信息,并操作,而 SpringSecurity 中已经提供了相关操作类,只需在配置类中配置即可。
【配置如下:(注入 DataSource,并配置 PersistentTokenRepository 交给 Spring 管理)】 @Autowired private DataSource dataSource; @Bean public PersistentTokenRepository persistentTokenRepository() { JdbcTokenRepositoryImpl jdbcTokenRepository = new JdbcTokenRepositoryImpl(); // 设置数据源 jdbcTokenRepository.setDataSource(dataSource); // 自动建表 // jdbcTokenRepository.setCreateTableOnStartup(true); return jdbcTokenRepository; } 【完整配置类:(通过 http.rememberMe() 配置)】 package com.lyh.demo.springsecurity.config; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.authentication.builders.AuthenticationManagerBuilder; import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity; import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity; import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter; import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService; import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder; import org.springframework.security.crypto.password.PasswordEncoder; import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.rememberme.JdbcTokenRepositoryImpl; import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.rememberme.PersistentTokenRepository; import javax.sql.DataSource; /** * 配置 Spring Security */ @Configuration @EnableWebSecurity public class SpringSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter { @Autowired private UserDetailsService userDetailsService; @Override protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception { auth.userDetailsService(userDetailsService).passwordEncoder(passwordEncoder()); } @Autowired private DataSource dataSource; /** * 默认使用 PersistentTokenRepository 的子类 InMemoryTokenRepositoryImpl 将 token 放在内存中, * 可以使用子类 JdbcTokenRepositoryImpl 将 token 持久化到 数据库中。 * 注: * * jdbcTokenRepository.setCreateTableOnStartup(true); 等同于下面 SQL, * 若不手动创建,可以使用代码自动创建,但是执行一次后需要将其注释掉。 * * create table persistent_logins ( * username varchar(64) not null, * series varchar(64) primary key, * token varchar(64) not null, * last_used timestamp not null * ) */ @Bean public PersistentTokenRepository persistentTokenRepository() { JdbcTokenRepositoryImpl jdbcTokenRepository = new JdbcTokenRepositoryImpl(); // 设置数据源 jdbcTokenRepository.setDataSource(dataSource); // 自动建表 // jdbcTokenRepository.setCreateTableOnStartup(true); return jdbcTokenRepository; } @Override protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { /** * rememberMe() 用于实现记住我功能。 * tokenRepository() 设置数据访问层。 * userDetailsService() 设置 userDetailsService。 * tokenValiditySeconds() 设置过期时间。 * rememberMeParameter() 自定义参数名,默认为 remember-me */ http.rememberMe() .tokenRepository(persistentTokenRepository()) .userDetailsService(userDetailsService) //.rememberMeParameter("remember") .tokenValiditySeconds(24 * 60 * 60); /** * csrf() 表示开启 csrf 防护。 * disable() 表示关闭 csrf 防护。 */ http.csrf().disable(); /** * formLogin() 用于自定义表单登录。 * loginPage() 用于自定义登录页面。 * defaultSuccessUrl() 登录成功后 跳转的路径。 * loginProcessingUrl() 表单提交的 action 地址(默认为 /login,修改后,对应的表单 action 也要修改),由系统提供 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 过滤器拦截并处理。 * usernameParameter() 用于自定义表单提交的用户参数名,默认为 username,修改后,对应的表单参数也要修改。 * passwordParameter() 用于自定义表单提交的用户密码名,默认为 password,修改后,对应的表单参数也要修改。 * failureForwardUrl() 用于自定义表单提交失败后 重定向地址,可用于前后端分离中,指向某个 controller。 */ http.formLogin() .loginPage("/login.html") .loginProcessingUrl("/login") .defaultSuccessUrl("/success.html") //.usernameParameter("name") //.passwordParameter("pwd") .failureForwardUrl("/test/error") ; /** * logout() 用于自定义退出逻辑。 * logoutUrl() 用于拦截退出请求,默认为 /logout。 * logoutSuccessUrl() 用于自定义退出成功后,跳转的页面。 */ http.logout() .logoutUrl("/logout") .logoutSuccessUrl("/login.html") ; /** * authorizeRequests() 用于 开启认证,基于 HttpServletRequest 对 url 进行身份控制并授权访问。 * antMatchers() 用于匹配 url。 * permitAll() 用于允许任何人访问该 url。 * hasAuthority() 用于指定 具有某种权限的 人才能访问 url。 * hasAnyAuthority() 用于指定 多个权限 进行访问,多个权限间使用逗号分隔。 * * hasRole() 写法与 hasAuthority() 类似,但是其会在 角色前 拼接上 ROLE_,使用时需要注意。 * hasAnyRole() 写法与 hasAnyAuthority() 类似,同样会在 角色前 拼接上 ROLE_。 * * 使用时 hasAuthority()、hasAnyAuthority() 或者 hasAnyRole()、hasAnyAuthority() 任选一对即可,同时使用四种可能会出现问题。 */ http.authorizeRequests() .antMatchers("/test/hello").hasAuthority("user") //.antMatchers("/test/hello").hasAnyRole("USER,GOD") //.antMatchers("/test/hello").hasRole("GOD") .antMatchers("/test/hello").hasAnyAuthority("user,admin") .antMatchers("/login", "/test/error").permitAll(); /** * 自定义 403 页面 */ http.exceptionHandling().accessDeniedPage("/403.html"); } @Bean PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() { return new BCryptPasswordEncoder(); } }
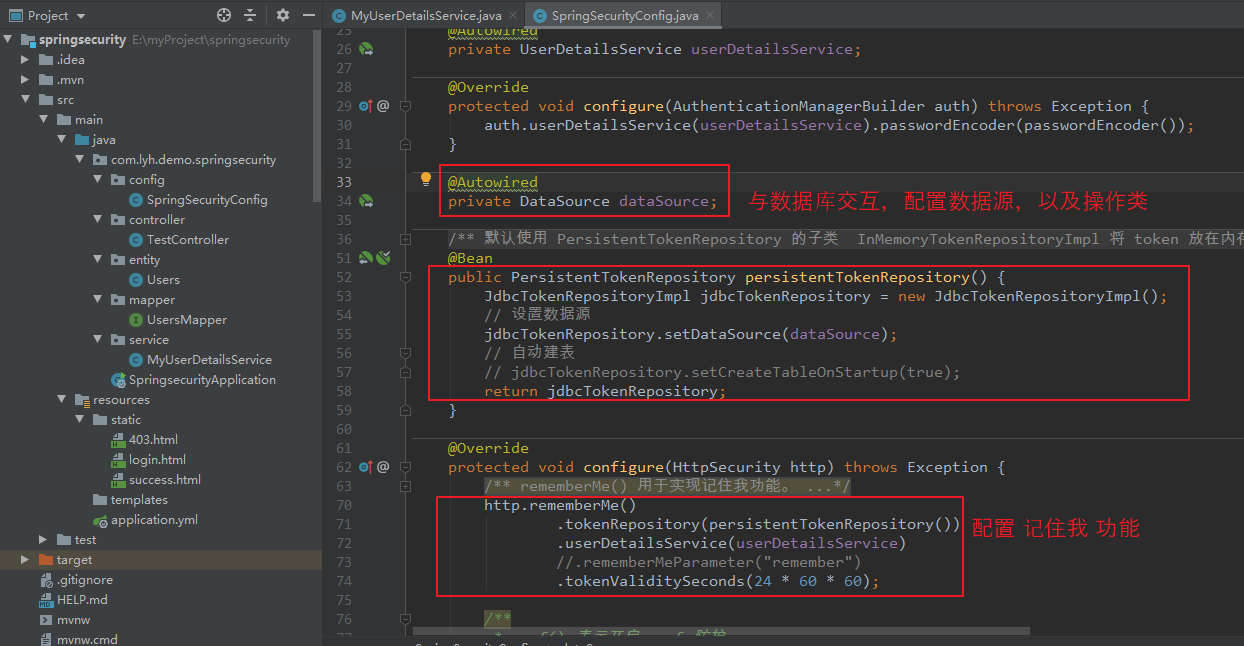
如下图所示,点击 记住我,并登陆后,会在浏览器 cookie 以及 数据库中 各存放一份 token,关闭浏览器并再次登录时,无需重新登录,会自动检测 cookie 中的 token 值是否正确,若相同则可以正常登陆。注销时,浏览器 token 以及 数据库的 token 会一起注销。
(3)源码分析:
Step1:
第一次通过浏览器登录系统时,首先会被 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 过滤器拦截,认证通过后,会在 AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter 抽象类的 successfulAuthentication() 方法中 进行 token 的处理。
【UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 继承 AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter:】 public class UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter extends AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter {} 【AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter 的 doFilter() 中 调用了 successfulAuthentication() 方法:】 public abstract class AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter extends GenericFilterBean implements ApplicationEventPublisherAware, MessageSourceAware { public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException { ... successfulAuthentication(request, response, chain, authResult); } }

Step2:
AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter 中定义了 RememberMeServices 接口,在 successfulAuthentication() 方法中 会调用 RememberMeServices 接口的 loginSuccess() 方法。
【调用 RememberMeServices 的 loginSuccess() 方法:】 private RememberMeServices rememberMeServices = new NullRememberMeServices(); protected void successfulAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain, Authentication authResult) throws IOException, ServletException { ... rememberMeServices.loginSuccess(request, response, authResult); }
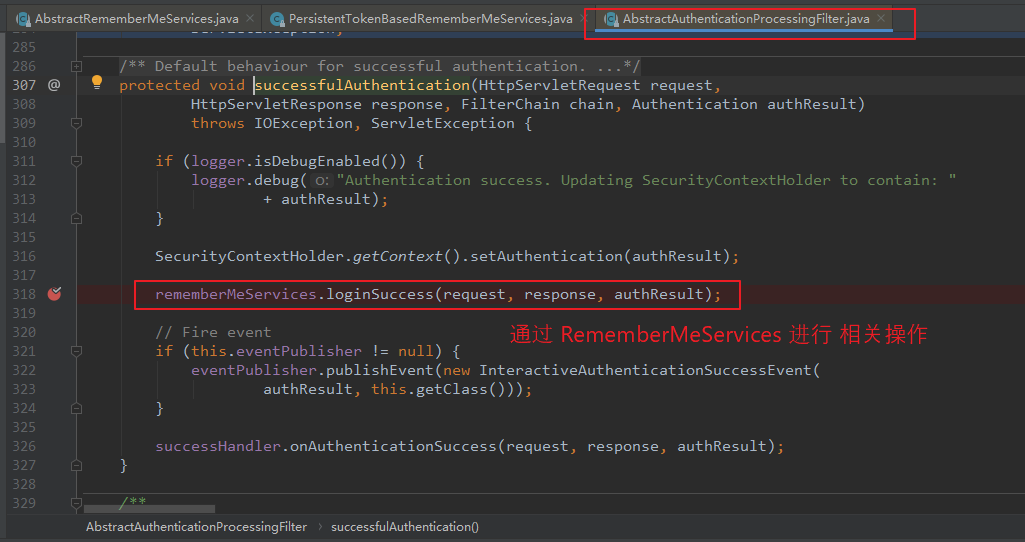
Step3:
RememberMeServices 接口的 loginSuccess() 方法 由子类 AbstractRememberMeServices 实现,loginSuccess() 会先检测是否存在 记住我 的功能,默认参数名为 remember-me,若表单中不存在 或者 为 false 时,会直接返回。为 true 时,会执行 onLoginSuccess() 方法。
【调用 AbstractRememberMeServices 的 loginSuccess() 方法:】 public final void loginSuccess(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Authentication successfulAuthentication) { if (!rememberMeRequested(request, parameter)) { logger.debug("Remember-me login not requested."); return; } onLoginSuccess(request, response, successfulAuthentication); }
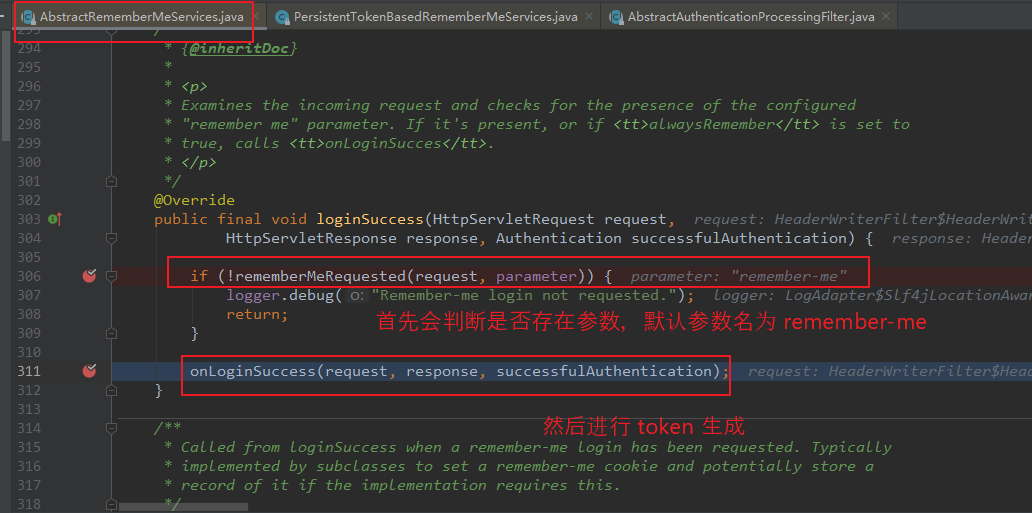
Step4:
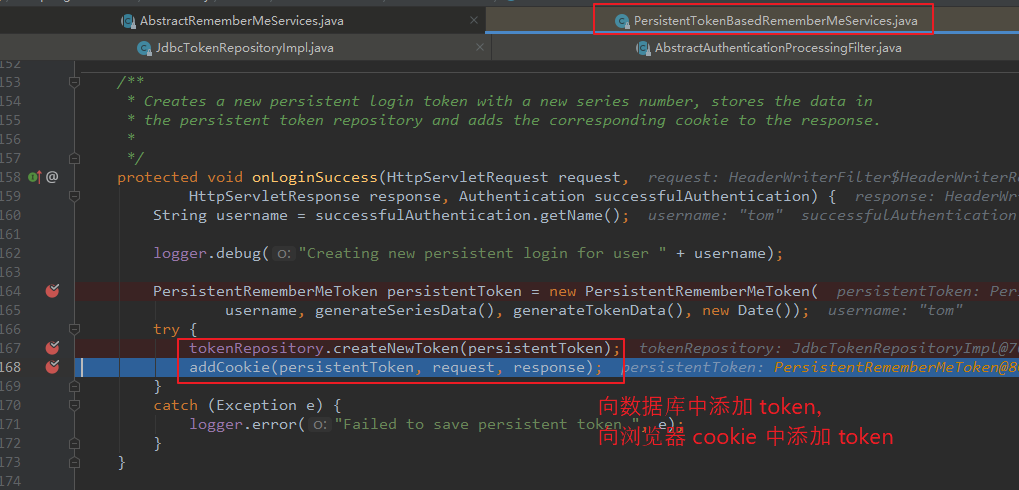
onLoginSuccess() 方法由 AbstractRememberMeServices 的子类 PersistentTokenBasedRememberMeServices 去实现。向数据库中 添加 token 以及 向 cookie 中添加 token。
【调用 PersistentTokenBasedRememberMeServices 的 onLoginSuccess() 方法:】 protected void onLoginSuccess(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Authentication successfulAuthentication) { String username = successfulAuthentication.getName(); logger.debug("Creating new persistent login for user " + username); PersistentRememberMeToken persistentToken = new PersistentRememberMeToken( username, generateSeriesData(), generateTokenData(), new Date()); try { tokenRepository.createNewToken(persistentToken); addCookie(persistentToken, request, response); } catch (Exception e) { logger.error("Failed to save persistent token ", e); } }
Step5:
关闭浏览器,再次登录时,由 RememberMeAuthenticationFilter 过滤器拦截请求,在其 doFilter() 方法中 调用 RememberMeServices 接口的 autoLogin() 方法进行处理。
【RememberMeAuthenticationFilter 的 】 public class RememberMeAuthenticationFilter extends GenericFilterBean implements ApplicationEventPublisherAware { private RememberMeServices rememberMeServices; public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException { ... Authentication rememberMeAuth = rememberMeServices.autoLogin(request,response); ... } }
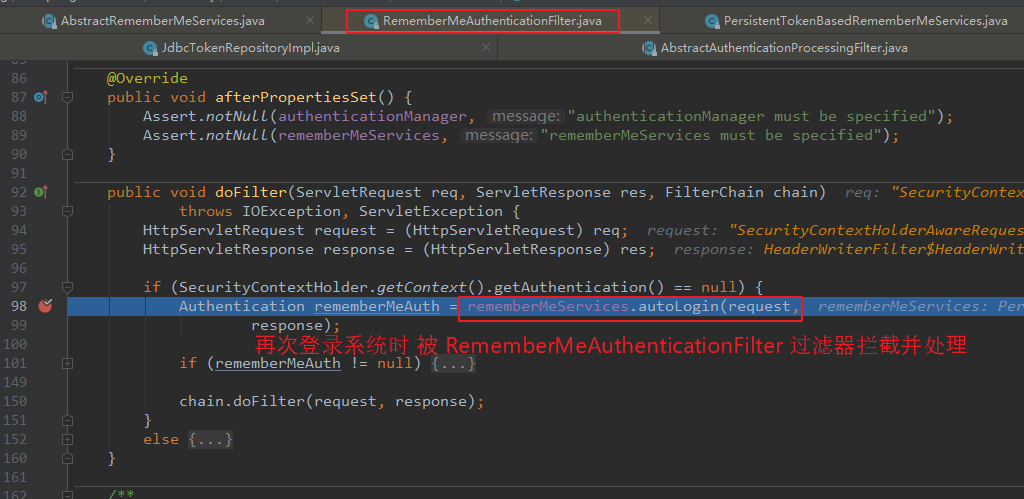
Step6:
RememberMeServices 接口的 autoLogin() 方法由 AbstractRememberMeServices 子类实现,其根据 cookie 值解析出相应的 token。并根据 token 从数据库中查询用户,并验证用户是否合法。
public final Authentication autoLogin(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) { String rememberMeCookie = extractRememberMeCookie(request); ... String[] cookieTokens = decodeCookie(rememberMeCookie); user = processAutoLoginCookie(cookieTokens, request, response); userDetailsChecker.check(user); }
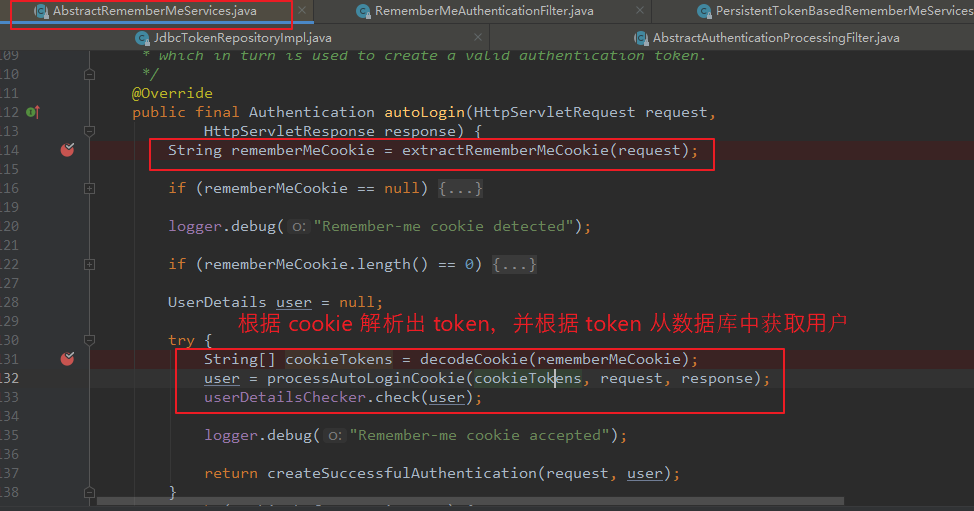
Step7:
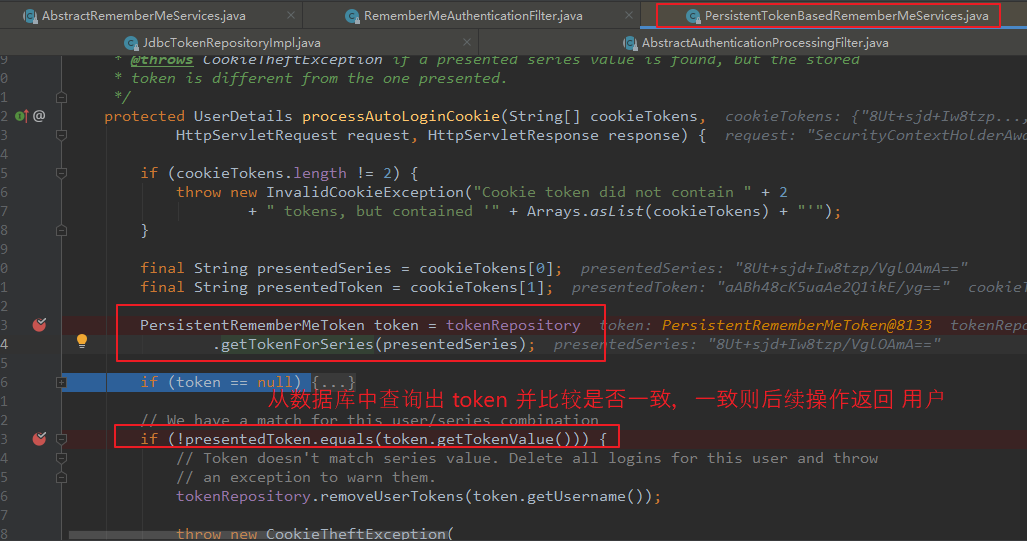
调用 processAutoLoginCookie() 方法根据 token 从数据库中查询出用户。
protected UserDetails processAutoLoginCookie(String[] cookieTokens, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) { final String presentedSeries = cookieTokens[0]; final String presentedToken = cookieTokens[1]; PersistentRememberMeToken token = tokenRepository.getTokenForSeries(presentedSeries); if (!presentedToken.equals(token.getTokenValue())) { } ... return getUserDetailsService().loadUserByUsername(token.getUsername()); }