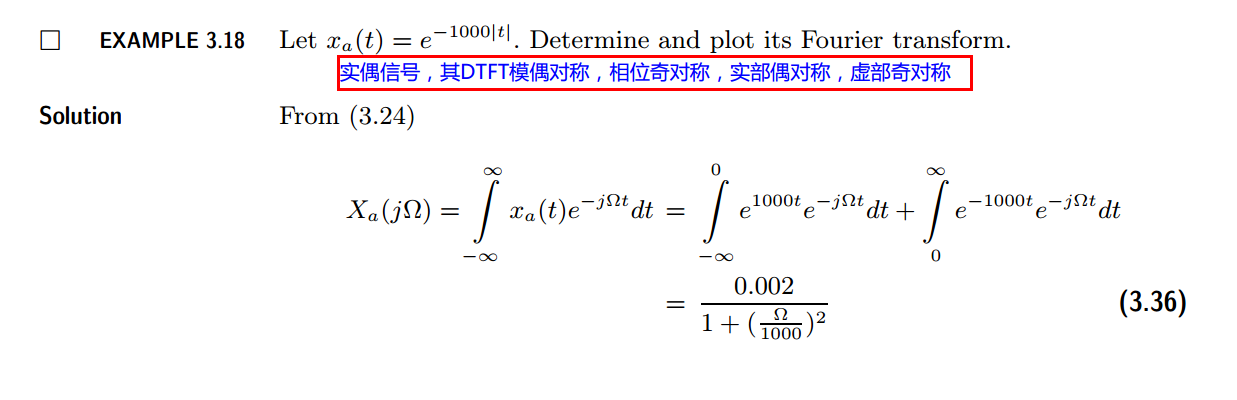
代码:
% Analog Signal
Dt = 0.00005; t = -0.005:Dt:0.005; xa = exp(-1000*abs(t));
% Continuous-time Fourier Transform
Wmax = 2*pi*2000;
K = 500; k = 0:1:K; % index array k for frequencies
W = k*Wmax/K; % freqency between 0 and +pi, [0,pi] axis divided into 501 points.
Xa = xa * exp(-j*t'*W) * Dt;
magXa = abs(Xa); angXa = angle(Xa); realXa = real(Xa); imagXa = imag(Xa);
%% --------------------------------------------------------------------
%% START Xa's mag ang real imag
%% --------------------------------------------------------------------
figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Example3.18 Xa its mag ang real imag');
set(gcf,'Color','white');
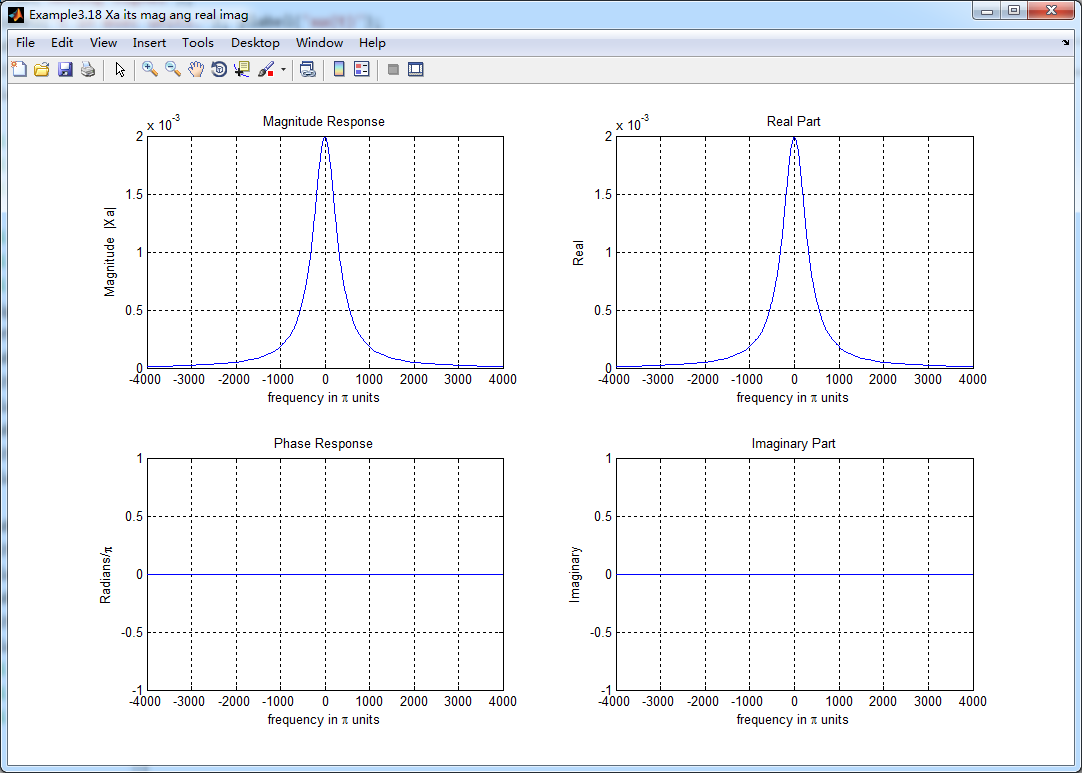
subplot(2,2,1); plot(W/pi,magXa); grid on; %axis([0,1,0,1.5]);
title('Magnitude Response');
xlabel('frequency in pi units'); ylabel('Magnitude |Xa|');
subplot(2,2,3); plot(W/pi, angXa/pi); grid on; axis([-1,1,-1,1]);
title('Phase Response');
xlabel('frequency in pi units'); ylabel('Radians/pi');
subplot('2,2,2'); plot(W/pi, realXa); grid on;
title('Real Part');
xlabel('frequency in pi units'); ylabel('Real');
subplot('2,2,4'); plot(W/pi, imagXa); grid on;
title('Imaginary Part');
xlabel('frequency in pi units'); ylabel('Imaginary');
%% -------------------------------------------------------------------
%% END Xa's mag ang real imag
%% -------------------------------------------------------------------
Xa = real(Xa);
W = [-fliplr(W), W(2:501)]; % Omega from -Wmax to Wmax
Xa = [fliplr(Xa), Xa(2:501)]; % Xa over -Wmax to Wmax interval
%% --------------------------------------------------------------------
%%
%% --------------------------------------------------------------------
figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'DSP MATLAB Example3.18');
set(gcf,'Color','white');
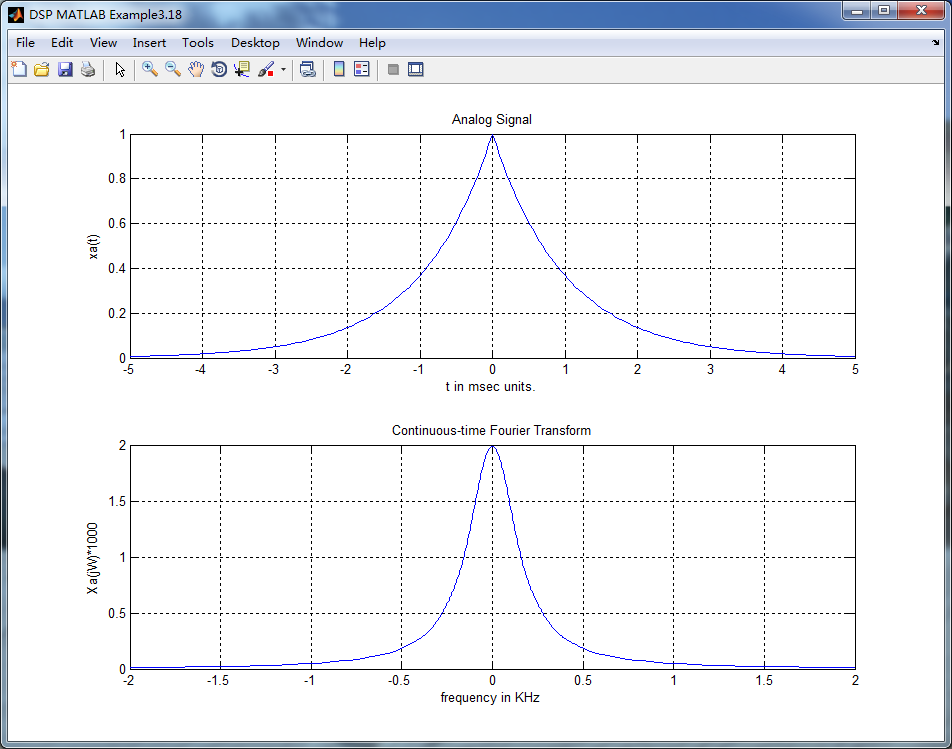
subplot(2,1,1); plot(t*1000,xa); grid on; %axis([0,1,0,1.5]);
title('Analog Signal');
xlabel('t in msec units.'); ylabel('xa(t)');
subplot(2,1,2); plot(W/(2*pi*1000), Xa*1000); grid on; % axis([-1,1,-1,1]);
title('Continuous-time Fourier Transform');
xlabel('frequency in KHz'); ylabel('Xa(jW)*1000');
%% -------------------------------------------------------------------
%%
%% -------------------------------------------------------------------
运行结果: