K近邻算法
给定一个训练数据集,对新的输入实例,在训练数据集中找到跟它最近的k个实例,根据这k个实例的类判断它自己的类(一般采用多数表决的方法)。
算法详解:
输入:训练数据集
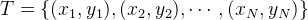
其中,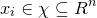 为实例的特征向量,
为实例的特征向量,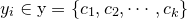 为实例的类别,
为实例的类别,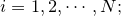 实例特征向量
实例特征向量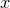 ;
;
输出:实例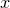 所属的类
所属的类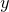 ;
;
(1)根据给定的距离度量,在训练集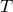 中找出与
中找出与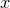 最邻近的
最邻近的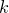 个点,涵盖这
个点,涵盖这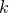 个点的
个点的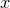 的邻域记作
的邻域记作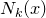 ;
;
(2)在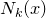 中根据分类决策规则(如多数表决)决定
中根据分类决策规则(如多数表决)决定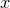 的类别
的类别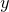 :
:

注: 为指示函数,即当
为指示函数,即当 时
时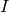 为1,否则
为1,否则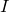 为0
为0
K近邻模型
模型三要素:距离度量方法、k值的选择和分类决策规则
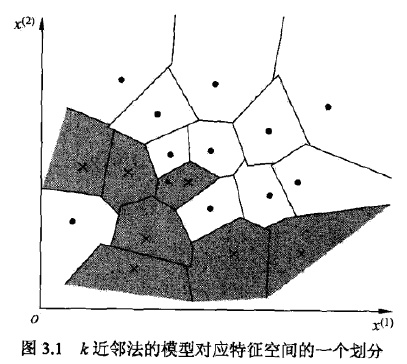
当三要素确定的时候,对任何实例(训练或输入),它所属的类都是确定的,相当于将特征空间分为一些子空间。
距离度量
对n维实数向量空间Rn,经常用Lp距离或曼哈顿Minkowski距离。
Lp距离定义如下:
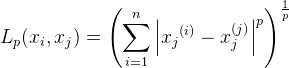
当p=2时,称为欧氏距离:

当p=1时,称为曼哈顿距离:
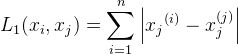
当p=∞,它是各个坐标距离的最大值,即:

用图表示如下:

k值的选择
k较小,容易被噪声影响,发生过拟合。
k较大,较远的训练实例也会对预测起作用,容易发生错误。
分类决策规则
使用0-1损失函数衡量,那么误分类率是:
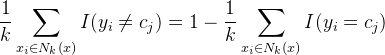
 是近邻集合,要使左边最小,右边的
是近邻集合,要使左边最小,右边的![]() 必须最大,所以多数表决=经验最小化 。
必须最大,所以多数表决=经验最小化 。
k近邻法的实现:kd树
算法核心在于怎么快速搜索k个近邻出来,朴素做法是线性扫描,不可取,这里介绍的方法是kd树。
构造kd树
对数据集T中的子集S初始化S=T,取当前节点node=root取维数的序数i=0,对S递归执行:找出S的第i维的中位数对应的点,通过该点,且垂直于第i维坐标轴做一个超平面。该点加入node的子节点。该超平面将空间分为两个部分,对这两个部分分别重复此操作(S=S',++i,node=current),直到不可再分。
例子:给定一个二维空间的数据集
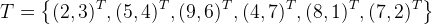
构造一个平衡kd树 。
Python代码实现:

# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- import copy import itertools from matplotlib import pyplot as plt from matplotlib.patches import Rectangle from matplotlib import animation T = [[2, 3], [5, 4], [9, 6], [4, 7], [8, 1], [7, 2]] def draw_point(data): X, Y = [], [] for p in data: X.append(p[0]) Y.append(p[1]) plt.plot(X, Y, 'bo') def draw_line(xy_list): for xy in xy_list: x, y = xy plt.plot(x, y, 'g', lw=2) def draw_square(square_list): currentAxis = plt.gca() colors = itertools.cycle(["r", "b", "g", "c", "m", "y", '#EB70AA', '#0099FF']) for square in square_list: currentAxis.add_patch( Rectangle((square[0][0], square[0][1]), square[1][0] - square[0][0], square[1][1] - square[0][1], color=next(colors))) def median(lst): m = len(lst) / 2 return lst[m], m history_quare = [] def build_kdtree(data, d, square): history_quare.append(square) data = sorted(data, key=lambda x: x[d]) p, m = median(data) del data[m] print data, p if m >= 0: sub_square = copy.deepcopy(square) if d == 0: sub_square[1][0] = p[0] else: sub_square[1][1] = p[1] history_quare.append(sub_square) if m > 0: build_kdtree(data[:m], not d, sub_square) if len(data) > 1: sub_square = copy.deepcopy(square) if d == 0: sub_square[0][0] = p[0] else: sub_square[0][1] = p[1] build_kdtree(data[m:], not d, sub_square) build_kdtree(T, 0, [[0, 0], [10, 10]]) print history_quare # draw an animation to show how it works, the data comes from history # first set up the figure, the axis, and the plot element we want to animate fig = plt.figure() ax = plt.axes(xlim=(0, 2), ylim=(-2, 2)) line, = ax.plot([], [], 'g', lw=2) label = ax.text([], [], '') # initialization function: plot the background of each frame def init(): plt.axis([0, 10, 0, 10]) plt.grid(True) plt.xlabel('x_1') plt.ylabel('x_2') plt.title('build kd tree (www.hankcs.com)') draw_point(T) currentAxis = plt.gca() colors = itertools.cycle(["#FF6633", "g", "#3366FF", "c", "m", "y", '#EB70AA', '#0099FF', '#66FFFF']) # animation function. this is called sequentially def animate(i): square = history_quare[i] currentAxis.add_patch( Rectangle((square[0][0], square[0][1]), square[1][0] - square[0][0], square[1][1] - square[0][1], color=next(colors))) return # call the animator. blit=true means only re-draw the parts that have changed. anim = animation.FuncAnimation(fig, animate, init_func=init, frames=len(history_quare), interval=1000, repeat=False, blit=False) plt.show() anim.save('kdtree_build.gif', fps=2, writer='imagemagick')

搜索kd树
上面的代码其实并没有搜索kd树,现在来实现搜索。
搜索跟二叉树一样来,是一个递归的过程。先找到目标点的插入位置,然后往上走,逐步用自己到目标点的距离画个超球体,用超球体圈住的点来更新最近邻(或k最近邻)。以最近邻为例,实现如下(本实现由于测试数据简单,没有做超球体与超立体相交的逻辑):

# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- T = [[2, 3], [5, 4], [9, 6], [4, 7], [8, 1], [7, 2]] class node: def __init__(self, point): self.left = None self.right = None self.point = point self.parent = None pass def set_left(self, left): if left == None: pass left.parent = self self.left = left def set_right(self, right): if right == None: pass right.parent = self self.right = right def median(lst): m = len(lst) / 2 return lst[m], m def build_kdtree(data, d): data = sorted(data, key=lambda x: x[d]) p, m = median(data) tree = node(p) del data[m] if m > 0: tree.set_left(build_kdtree(data[:m], not d)) if len(data) > 1: tree.set_right(build_kdtree(data[m:], not d)) return tree def distance(a, b): print a, b return ((a[0] - b[0]) ** 2 + (a[1] - b[1]) ** 2) ** 0.5 def search_kdtree(tree, d, target): if target[d] < tree.point[d]: if tree.left != None: return search_kdtree(tree.left, not d, target) else: if tree.right != None: return search_kdtree(tree.right, not d, target) def update_best(t, best): if t == None: return t = t.point d = distance(t, target) if d < best[1]: best[1] = d best[0] = t best = [tree.point, 100000.0] while (tree.parent != None): update_best(tree.parent.left, best) update_best(tree.parent.right, best) tree = tree.parent return best[0] kd_tree = build_kdtree(T, 0) print search_kdtree(kd_tree, 0, [9, 4])
输出:
[8, 1] [9, 4] [5, 4] [9, 4] [9, 6] [9, 4] [9, 6]
可见对于点[9, 4],在n=6的数据集中,kdtree算法一共只进行了3次计算。
K-近邻算法实现手写数字识别

1 #-*- coding: utf-8 -*- 2 3 from numpy import * 4 from os import listdir 5 import operator 6 7 # 读取数据到矩阵 8 def img2vector(filename): 9 # 创建向量 10 returnVect = zeros((1,1024)) 11 12 # 打开数据文件,读取每行内容 13 fr = open(filename) 14 15 for i in range(32): 16 # 读取每一行 17 lineStr = fr.readline() 18 19 # 将每行前32字符转成int存入向量 20 for j in range(32): 21 returnVect[0,32*i+j] = int(lineStr[j]) 22 23 return returnVect 24 25 # kNN算法实现 26 def classify0(inX, dataSet, labels, k): 27 # 获取样本数据数量 28 dataSetSize = dataSet.shape[0] 29 30 # 矩阵运算,计算测试数据与每个样本数据对应数据项的差值 31 diffMat = tile(inX, (dataSetSize,1)) - dataSet 32 33 # sqDistances 上一步骤结果平方和 34 sqDiffMat = diffMat**2 35 sqDistances = sqDiffMat.sum(axis=1) 36 37 # 取平方根,得到距离向量 38 distances = sqDistances**0.5 39 40 # 按照距离从低到高排序 41 sortedDistIndicies = distances.argsort() 42 classCount={} 43 44 # 依次取出最近的样本数据 45 for i in range(k): 46 # 记录该样本数据所属的类别 47 voteIlabel = labels[sortedDistIndicies[i]] 48 classCount[voteIlabel] = classCount.get(voteIlabel,0) + 1 49 50 # 对类别出现的频次进行排序,从高到低 51 sortedClassCount = sorted(classCount.iteritems(), key=operator.itemgetter(1), reverse=True) 52 53 # 返回出现频次最高的类别 54 return sortedClassCount[0][0] 55 56 # 算法测试 57 def handwritingClassTest(): 58 # 样本数据的类标签列表 59 hwLabels = [] 60 61 # 样本数据文件列表 62 trainingFileList = listdir('digits/trainingDigits') 63 m = len(trainingFileList) 64 65 # 初始化样本数据矩阵(M*1024) 66 trainingMat = zeros((m,1024)) 67 68 # 依次读取所有样本数据到数据矩阵 69 for i in range(m): 70 # 提取文件名中的数字 71 fileNameStr = trainingFileList[i] 72 fileStr = fileNameStr.split('.')[0] 73 classNumStr = int(fileStr.split('_')[0]) 74 hwLabels.append(classNumStr) 75 76 # 将样本数据存入矩阵 77 trainingMat[i,:] = img2vector('digits/trainingDigits/%s' % fileNameStr) 78 79 # 循环读取测试数据 80 testFileList = listdir('digits/testDigits') 81 82 # 初始化错误率 83 errorCount = 0.0 84 mTest = len(testFileList) 85 86 # 循环测试每个测试数据文件 87 for i in range(mTest): 88 # 提取文件名中的数字 89 fileNameStr = testFileList[i] 90 fileStr = fileNameStr.split('.')[0] 91 classNumStr = int(fileStr.split('_')[0]) 92 93 # 提取数据向量 94 vectorUnderTest = img2vector('digits/testDigits/%s' % fileNameStr) 95 96 # 对数据文件进行分类 97 classifierResult = classify0(vectorUnderTest, trainingMat, hwLabels, 3) 98 99 # 打印KNN算法分类结果和真实的分类 100 print "the classifier came back with: %d, the real answer is: %d" % (classifierResult, classNumStr) 101 102 # 判断KNN算法结果是否准确 103 if (classifierResult != classNumStr): errorCount += 1.0 104 105 # 打印错误率 106 print " the total number of errors is: %d" % errorCount 107 print " the total error rate is: %f" % (errorCount/float(mTest)) 108 109 # 执行算法测试 110 handwritingClassTest()

