学习视频参考链接:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1V4411p7EF?p=27
这篇写的实在有点乱,线程池后面会再专门写一篇补充,有问题评论区提啊^_^!!!
1、线程简介
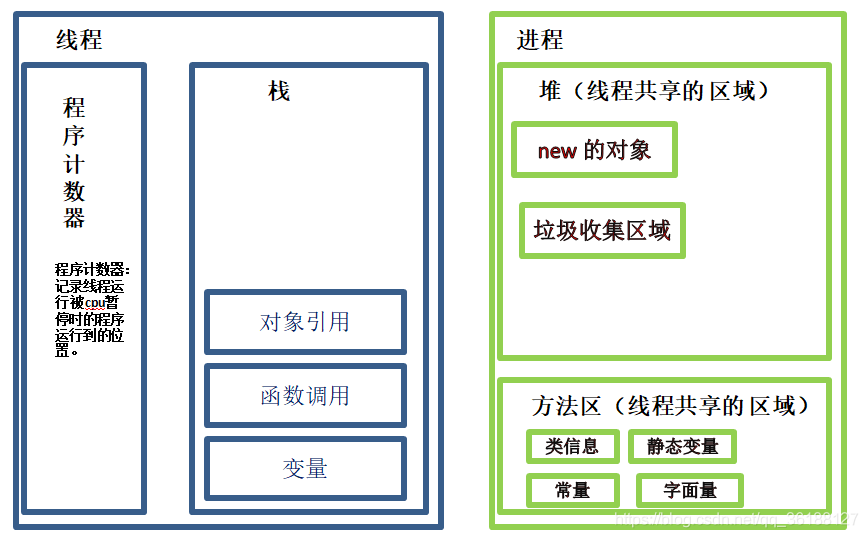
栈空间操作起来最快但是栈很小,通常大量的对象都是放在堆空间,栈和堆的大小都可以通过 JVM 的启动参数来进行调整,栈空间用光了会引发 StackOverflowError,而堆和常量池空间不足则会引发 OutOfMemoryError。
1 String str = new String("hello");
上面的语句中变量 str 放在栈上,用 new 创建出来的字符串对象放在堆上,而 “hello” 这个字面量是放在方法区的。
例子:
开车 + 打电话
吃饭 + 玩手机
这些动作都可以抽象为任务,虽然看起来一心二用,但人只有一个大脑,在一个时间片刻只能处理一个任务。
CPU 也是一样,面对多个任务,只能在一个时间片刻处理一个任务。
主线程调用 run 方法和调用 start 方法开启子线程的区别如下图所示。
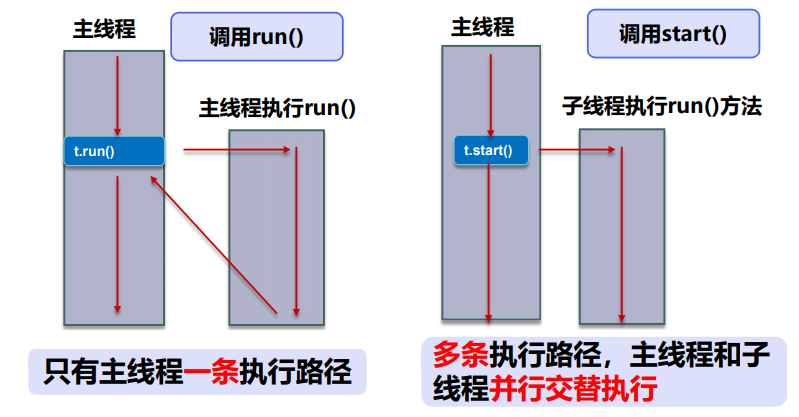
线程就是独立的执行路径;
在程序运行时,即使没有自己创建线程,后台也会有多个线程,如主线程,GC 线程;
main()称之为主线程,为系统的入口,用于执行整个程序;
在一个进程中,如果开辟了多个线程,线程的运行由调度器安排调度,调度器是与操作系统紧密相关的,先后顺序是不能人为干预。
对同一份资源操作时,会存在资源抢夺的问题,需要加入并发控制;
线程会带来额外的开销,如 CPU 调度时间,并发控制开销。
每个线程在自己的工作内存交互,内存控制不当会造成数据不一致
2、线程实现
线程的三种实现方式:
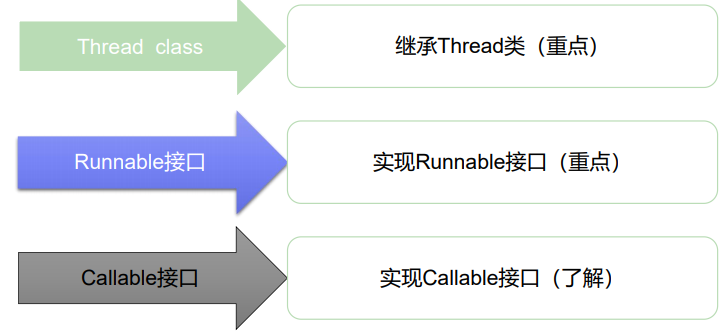
2.1继承Thread类,重写run()方法
继承Thread类,重写run()。创建这个类的对象,再调用start()即可。
1 //创建线程方式一:继承Thread类,重写run()方法,调用start开启线程 2 public class TestThread1 extends Thread{ 3 4 @Override 5 public void run() { 6 //run方法线程体 7 for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { 8 System.out.println("thread"); 9 } 10 } 11 12 public static void main(String[] args) { 13 //main线程,主线程 14 15 TestThread1 testThread1 = new TestThread1(); 16 testThread1.start(); 17 18 for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { 19 System.out.println("main"); 20 } 21 22 } 23 }
下面做一个小例子:
1 package com.gzq.java.demo01; 2 3 import org.apache.commons.io.FileUtils; 4 5 import java.io.File; 6 import java.io.IOException; 7 import java.net.URL; 8 9 /** 10 * @author GaoZQ 11 * @date 2021/3/9 22:09 12 */ 13 //联系Thread,实现多线程同步下载图片 14 public class TestThread2 extends Thread{ 15 16 //图片的链接地址 17 private String url; 18 //保存的文件名称 19 private String fileName; 20 21 public TestThread2(String url,String fileName){ 22 this.url = url; 23 this.fileName = fileName; 24 } 25 26 @Override 27 public void run() { 28 WebDownLoader webDownLoader = new WebDownLoader(); 29 webDownLoader.downLoader(url,fileName); 30 System.out.println("下载了文件名为:" + fileName); 31 } 32 33 public static void main(String[] args) { 34 TestThread2 testThread2 = new TestThread2( 35 "https://images.cnblogs.com/cnblogs_com/koss/1938745/o_2103010229312000683.jpg", 36 "tupian.jpg"); 37 testThread2.start(); 38 } 39 } 40 41 //下载器 42 class WebDownLoader{ 43 //下载方法 44 public void downLoader(String url,String fileName){ 45 try { 46 FileUtils.copyURLToFile(new URL(url),new File(fileName)); 47 } catch (IOException e) { 48 System.out.println("downLoader方法出现问题"); 49 e.printStackTrace(); 50 } 51 } 52 }
2.2继承Runnable接口,创建Thread对象
1 //创建线程方式2:实现runnable接口 2 public class TestThread3 implements Runnable{ 3 @Override 4 public void run() { 5 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { 6 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "===" + i); 7 } 8 } 9 10 public static void main(String[] args) { 11 TestThread3 t = new TestThread3(); 12 Thread thread1 = new Thread(t); 13 Thread thread2 = new Thread(t); 14 15 thread1.start(); 16 thread2.start(); 17 18 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { 19 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "===" + i); 20 } 21 22 } 23 }
以上两种方式的比较:
继承Thread类:
子类继承Thread类具备多线程能力(本质上还是实现了Runnable接口,感兴趣的可以去看看源码,稍微看看就明白了)
启动线程:子类对象.start()
不建议使用:避免OOP单继承局限性
实现Runnable接口:
实现接口Runnable具有多线程能力
启动线程:传入目标对象+Thread对象.start()
推荐使用:避免单继承局限性,方便同一个对象被多个线程使用
火车抢票示例:
Runnable实现多线程,创造一个实例ticketRunnable,可共享给多个线程
1 package com.sjmp.demo01; 2 3 /** 4 * @author: sjmp1573 5 * @date: 2020/11/15 21:45 6 * @description: 7 */ 8 9 // 多个线程同时操作同一个对象 10 // 买火车票的例子 11 // 发现问题:多个线程操作同一个资源,线程不安全,数据紊乱! 12 13 public class TicketRunnable implements Runnable{ 14 15 private int ticketNums = 10; 16 17 @Override 18 public void run() { 19 while (true){ 20 if (ticketNums<=0){ 21 break; 22 } 23 // 模拟延时 24 /* 25 IllegalArgumentException 26 if the value of {@code millis} is negative, or the value of 27 {@code nanos} is not in the range {@code 0-999999} 28 InterruptedException 29 if any thread has interrupted the current thread. The 30 <i>interrupted status</i> of the current thread is 31 cleared when this exception is thrown. 32 */ 33 34 try { 35 Thread.sleep(200); 36 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 37 e.printStackTrace(); 38 } 39 ticketNums--; 40 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"-->拿到了第"+ticketNums+"票"); 41 42 } 43 } 44 45 public static void main(String[] args) { 46 // 实现了 Runnable 接口的类,创建其实例 47 TicketRunnable ticketRunnable = new TicketRunnable(); 48 // ticketRunnable 实例可用于多个线程,其中的资源被共享。 49 new Thread(ticketRunnable,"01小明+++++").start(); 50 new Thread(ticketRunnable,"02老师-----").start(); 51 new Thread(ticketRunnable,"03黄牛=====").start(); 52 53 } 54 }
2.3实现Callable接口(了解)
实现 Callable 接口,需要返回值类型
重写 call 方法,需要抛出异常
创建目标对象
创建执行服务:ExecutorService = Executor.newFixedThreadPool(1);
提交执行:Future result1 = ser.submit(1);
获取结果:boolean r1 = result.get()
关闭服务:ser.shutdownNow():
1 package com.gzq.java.demo02; 2 3 import com.gzq.java.demo01.TestThread2; 4 import org.apache.commons.io.FileUtils; 5 6 import java.io.File; 7 import java.io.IOException; 8 import java.net.URL; 9 import java.util.concurrent.*; 10 11 /** 12 * @author GaoZQ 13 * @date 2021/3/14 18:58 14 * 线程创建方式三:实现callable接口 15 * 实现一个接口 16 */ 17 public class TestCallable implements Callable { 18 //图片的链接地址 19 private String url; 20 //保存的文件名称 21 private String fileName; 22 23 public TestCallable(String url, String fileName) { 24 this.url = url; 25 this.fileName = fileName; 26 } 27 28 @Override 29 public Object call() throws Exception { 30 WebDownLoader webDownLoader = new WebDownLoader(); 31 webDownLoader.downLoader(url,fileName); 32 System.out.println("下载了文件名为:" + fileName); 33 return true; 34 } 35 36 public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { 37 TestCallable testCallable = new TestCallable( 38 "https://images.cnblogs.com/cnblogs_com/koss/1938745/o_2103010229312000683.jpg", 39 "tupian.jpg"); 40 //创建提交服务 41 ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1); 42 //提交执行 43 Future result = executorService.submit(testCallable); 44 //获取结果 45 Object o = result.get(); 46 System.out.println(o); 47 //关闭服务 48 executorService.shutdownNow(); 49 } 50 } 51 52 //下载器 53 class WebDownLoader{ 54 //下载方法 55 public void downLoader(String url,String fileName){ 56 try { 57 FileUtils.copyURLToFile(new URL(url),new File(fileName)); 58 } catch (IOException e) { 59 System.out.println("downLoader方法出现问题"); 60 e.printStackTrace(); 61 } 62 } 63 }
2.5静态代理模式
这个还是挺简单的,我直接上代码了,代码里有注释
1 package com.gzq.proxyStatic; 2 3 /** 4 * @author GaoZQ 5 * @date 2021/3/14 19:14 6 * 模拟静态代理 7 * 8 * 静态代理模式总结: 9 * 真实对象和代理对象都要实现同一个接口 10 * 代理对象要代理真实角色 11 * 12 * 好处: 13 * 代理对象可以做很多真是对象做不了的事情 14 * 真实对象专注做自己的事情就行了 15 */ 16 public class StaticProxy { 17 public static void main(String[] args) { 18 AgentRole agentRole = new AgentRole(new RealCharacter()); 19 agentRole.doSomething(); 20 } 21 } 22 23 interface DoSomething{ 24 25 void doSomething(); 26 } 27 28 //真实角色 29 class RealCharacter implements DoSomething{ 30 31 @Override 32 public void doSomething() { 33 System.out.println("doSomething..."); 34 } 35 } 36 37 //代理角色 38 class AgentRole implements DoSomething{ 39 40 //目标对象 41 private DoSomething target; 42 43 public AgentRole(DoSomething target) { 44 this.target = target; 45 } 46 47 @Override 48 public void doSomething() { 49 before(); 50 this.target.doSomething(); 51 after(); 52 } 53 54 private void before(){ 55 System.out.println("before..."); 56 } 57 58 private void after(){ 59 System.out.println("after..."); 60 } 61 }
3、线程的5种状态
- 创建
- 就绪
- 阻塞
- 运行
- 死亡


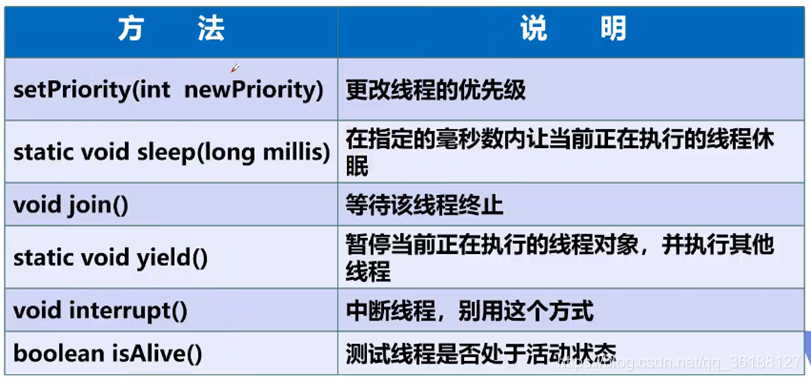
3.1线程的一些常用方法:
线程的一些方法如下图所示:
sleep():
1 package com.sjmp.method; 2 3 import java.awt.*; 4 import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; 5 import java.util.Date; 6 7 import static java.lang.Thread.*; 8 9 public class TestSleep { 10 11 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { 12 // Thread.sleep() 用于倒计时 13 14 // tenStop(); 15 16 17 // 打印当前系统时间 18 Date date = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()); 19 20 boolean flag = true; 21 int i = 5; 22 while(flag){ 23 if(--i<=0){ 24 flag = false; 25 } 26 try { 27 sleep(1000); 28 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 29 e.printStackTrace(); 30 } 31 System.out.println(new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss").format(date)); 32 date = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis());//更新时间 33 34 } 35 } 36 37 // 写一个倒计时的方式 38 public static void tenStop() throws InterruptedException { 39 int num = 10; 40 while(true){ 41 try{ 42 sleep(1000); 43 }catch ( InterruptedException e){ 44 e.printStackTrace(); 45 } 46 if (num<=0){ 47 break; 48 } 49 System.out.println(num--); 50 } 51 } 52 }
yield()
1 package com.gzq.java.state; 2 3 /** 4 * @author GaoZQ 5 * @date 2021/3/14 19:57 6 * 测试礼让线程 7 * 礼让不一定成功,看CPU心情 8 */ 9 public class TestYield { 10 11 public static void main(String[] args) { 12 MyYield myYield = new MyYield(); 13 new Thread(myYield,"a").start(); 14 new Thread(myYield,"b").start(); 15 } 16 } 17 18 class MyYield implements Runnable{ 19 20 @Override 21 public void run() { 22 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "线程开始执行"); 23 Thread.yield();//礼让 24 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "线程停止执行"); 25 } 26 }
join
1 package com.gzq.java.state; 2 3 /** 4 * @author GaoZQ 5 * @date 2021/3/14 20:02 6 * 测试join---方法 7 * join合并线程,待此线程执行完成后,再执行其他线程,其他线程阻塞 8 */ 9 public class TestJoin implements Runnable { 10 @Override 11 public void run() { 12 for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) { 13 System.out.println("线程vip来了" + i); 14 } 15 } 16 17 public static void main(String[] args) { 18 TestJoin testJoin = new TestJoin(); 19 Thread thread = new Thread(testJoin); 20 thread.start(); 21 22 //主线程 23 for (int i = 0; i < 500; i++) { 24 if (i == 200){ 25 try { 26 //插队 27 thread.join(); 28 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 29 e.printStackTrace(); 30 } 31 } 32 System.out.println("main" + i); 33 } 34 } 35 }
停止线程的方式:
- 不推荐使用 JDK 提供的 stop ()、destroy()方法。【已弃用】
- 推荐线程自己停止下来
- 建议使用一个标志位进行终止变量 , 当 flag == false,则终止线程运行
1 package com.gzq.java.state; 2 3 /** 4 * @author GaoZQ 5 * @date 2021/3/14 19:38 6 * 测试停止线程 7 * 1.建议线程正常停止---利用次数,不建议死循环 8 * 2.建议使用标志位---设置一个标志位 9 * 3.不要使用stop或者destory等过时或者JDK不建议使用的方法 10 */ 11 public class TestStop implements Runnable{ 12 13 //1.设置一个标识位 14 private boolean flag = true; 15 16 @Override 17 public void run() { 18 int i = 1; 19 while (flag){ 20 System.out.println("run...Thread" + i); 21 i++; 22 } 23 } 24 25 //2.设置一个公开的方法停止线程,转换标志位 26 public void stop(){ 27 this.flag = false; 28 } 29 30 public static void main(String[] args) { 31 TestStop testStop = new TestStop(); 32 new Thread(testStop).start(); 33 34 for (int i = 0; i < 1000000000; i++) { 35 if (i == 900){ 36 testStop.stop(); 37 System.out.println("stop"); 38 } 39 } 40 } 41 }
线程状态观测
Thread.State
线程状态。线程可以处于以下状态之一:
NEW
尚未启动的线程处于此状态。
RUNNABLE
在 Java 虚拟机中执行的线程处于此状态。
BLOCKED
被阻塞等待监视器锁定的线程处于此状态。
WAITING
正在等待另一个线程执行特定动作的线程处于此状态。
TERMINATED
已退出的线程处于此状态。
一个线程可以在给定时间点处于一个状态。
1 package com.gzq.java.state; 2 3 /** 4 * @author GaoZQ 5 * @date 2021/3/14 20:10 6 * 管擦测试线程的状态 7 */ 8 public class TestState { 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 Thread thread = new Thread(()->{ 11 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { 12 try { 13 Thread.sleep(1000); 14 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 15 e.printStackTrace(); 16 } 17 } 18 System.out.println("....."); 19 }); 20 21 //观察状态 22 Thread.State state = thread.getState(); 23 System.out.println(state); 24 25 thread.start(); 26 state = thread.getState(); 27 System.out.println(state); 28 29 while(state != Thread.State.TERMINATED){ 30 try { 31 Thread.sleep(200); 32 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 33 e.printStackTrace(); 34 } 35 state = thread.getState(); 36 System.out.println(state); 37 } 38 39 } 40 }
线程优先级
Java 提供一个线程调度器来监控程序中启动后进入就绪状态的所有线程,线程调度器按照优先级决定应该调度哪个线程来执行。
线程的优先级用数字表示,范围从1~10.
Thread.MIN_PRIORITY=1;
Thread.MAX_PRIORITY=10;
Thread.NORM_PRIORITY=5;
使用以下方式改变或获取优先级
getPriority().setPriority(int xxx)
优先级的设定建议在 start() 调度前
1 public class TestPriority implements Runnable { 2 @Override 3 public void run() { 4 System.out.println("当前线程:"+Thread.currentThread().getName()); 5 6 } 7 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 10 TestPriority runnable = new TestPriority(); 11 12 Thread thread01 = new Thread(runnable,"01"); 13 Thread thread02 = new Thread(runnable,"02"); 14 Thread thread03 = new Thread(runnable,"03"); 15 Thread thread04 = new Thread(runnable,"04"); 16 Thread thread05 = new Thread(runnable,"05"); 17 18 thread01.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY); 19 thread02.setPriority(7); 20 thread03.setPriority(6); 21 thread04.setPriority(5); 22 thread05.setPriority(4); 23 24 thread01.start(); 25 thread02.start(); 26 thread03.start(); 27 thread04.start(); 28 thread05.start(); 29 } 30 }
守护(daemon)线程
- 线程分为用户线程和守护线程
- 虚拟机必须确保用户线程执行完毕
- 虚拟机不用等待守护线程执行完毕
- 如,后台记录操作日志,监控内存垃圾回收等待…
1 public class TestsetDaemon { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 God god = new God(); 4 You you = new You(); 5 6 Thread thread = new Thread(god); 7 thread.setDaemon(true); 8 9 thread.start(); 10 new Thread(you).start(); 11 } 12 } 13 class God implements Runnable{ 14 @Override 15 public void run() { 16 while (true){ 17 System.out.println("Daemoning..."); 18 } 19 } 20 } 21 22 class You implements Runnable{ 23 @Override 24 public void run() { 25 for (int i = 0; i < 365; i++) { 26 System.out.println("living..."); 27 } 28 System.out.println("game over---------------------"); 29 } 30 }
并发
同一个对象被多个线程同时操作
现实生活中,我们会遇到”同一个资源,多个人都想使用”的问题,比如,食堂排队打饭,每个人都想吃饭,最天然的解决办法就是,排队一个个来。
处理多线程问题时,多个线程访问同一个对象,并且某些线程还想修改这个对象.这时候我们就需要线程同步.线程同步其实就是一种等待机制,多个需要同时访问!此对象的线程进入这个对象的等待池形成队列,等待前面线程使用完毕,下一个线程再使用。
形成线程安全的条件:
队列和锁
4、线程同步
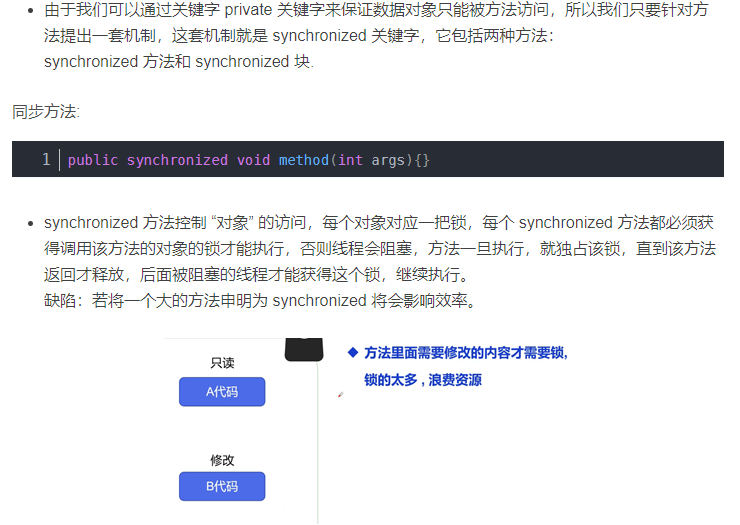
由于同一进程的多个线程共享同一块存储空间,在带来方便的同时,也带来了访问冲突问题,为了保证数据在方法中被访问时的正确性,在访问时加入锁机制synchronized,当一个线程获得对象的排它锁,独占资源,其他线程必须等待,使用后释放锁即可.存在以下问题:
一个线程持有锁会导致其他所有需要此锁的线程挂起;
在多线程竞争下,加锁,释放锁会导致比较多的上下文切换和调度延时,引起性能问题;
如果一个优先级高的线程等待一个优先级低的线程释放锁会导致优先级倒置,引起性能问题.
4.1 线程不安全举例
举例:不安全的售票
1 public class UnsafeBuyTicket { 2 3 } 4 5 class BuyTicket implements Runnable{ 6 private int ticketNum = 10; 7 boolean flag = true; 8 @Override 9 public void run() { 10 while (flag){ 11 buy(); 12 } 13 System.out.println("售罄"); 14 } 15 //加关键字 synchronized 就可以变成线程安全的 16 public void buy(){ 17 if (ticketNum<=0){ 18 flag = false; 19 return; 20 } 21 try { 22 // 模拟买票延时 23 Thread.sleep(100); 24 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 25 e.printStackTrace(); 26 } 27 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" get ticket:"+ticketNum); 28 ticketNum--; 29 } 30 31 public static void main(String[] args) { 32 BuyTicket buyTicket = new BuyTicket(); 33 34 Thread thread01 = new Thread(buyTicket,"01"); 35 Thread thread02 = new Thread(buyTicket,"02"); 36 Thread thread03 = new Thread(buyTicket,"03"); 37 38 thread01.start(); 39 thread02.start(); 40 thread03.start(); 41 } 42 }
4.2 同步方法



1 import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; 2 3 4 public class TestLock { 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 7 Ticket ticket = new Ticket(); 8 9 new Thread(ticket).start(); 10 new Thread(ticket).start(); 11 new Thread(ticket).start(); 12 13 } 14 15 } 16 17 18 class Ticket extends Thread{ 19 private int ticketNums = 10; 20 // 定义 lock 锁 21 private final ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); 22 23 @Override 24 public void run() { 25 while(true){ 26 try{ 27 lock.lock(); 28 if (ticketNums>0){ 29 try { 30 Thread.sleep(1000); 31 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 32 e.printStackTrace(); 33 } 34 System.out.println(ticketNums--); 35 36 }else{ 37 break; 38 } 39 }finally { 40 lock.unlock(); 41 } 42 } 43 } 44 }
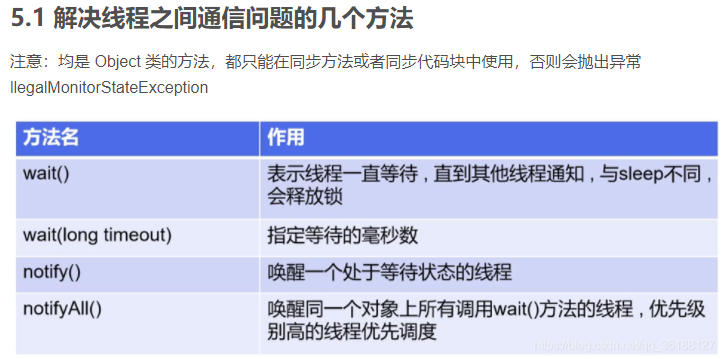
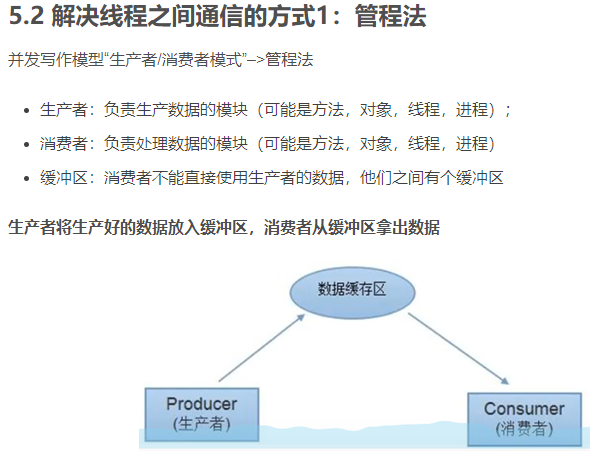
5.线程通信

1 package com.gzq.java; 2 3 /** 4 * @author: sjmp1573 5 * @date: 2020/11/18 20:52 6 * @description: 7 */ 8 9 // 生产者,消费者,产品,缓冲区 10 public class TestPC { 11 public static void main(String[] args) { 12 SynContainer container = new SynContainer(); 13 14 new Productor(container).start(); 15 new Consumer(container).start(); 16 } 17 18 } 19 20 // 生产者 21 class Productor extends Thread{ 22 SynContainer container; 23 public Productor(SynContainer container){ 24 this.container = container; 25 } 26 27 @Override 28 public void run() { 29 for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { 30 System.out.println("生产了"+i+"只鸡"); 31 container.push(new Chicken(i)); 32 } 33 } 34 } 35 36 37 class SynContainer{ 38 // 需要一个容器的大小 39 Chicken[] chickens = new Chicken[10]; 40 // 容器计数器 41 int count = 0; 42 43 44 // 生产者放入产品 45 public synchronized void push(Chicken chicken){ 46 // 如果容器满了,就需要等待消费者消费 47 if (count == chickens.length){ 48 // 通知消费者消费,生产等待 49 try { 50 this.wait(); 51 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 52 e.printStackTrace(); 53 } 54 } 55 chickens[count] = chicken; 56 count++; 57 this.notifyAll(); 58 } 59 60 61 // 消费者消费产品 62 public synchronized Chicken pop(){ 63 // 判断能否消费 64 if(count==0){ 65 // 等待生产者生产,消费者等待 66 try { 67 this.wait(); 68 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 69 e.printStackTrace(); 70 } 71 } 72 // 如果可以消费 73 count--; 74 Chicken chicken = chickens[count]; 75 // 可以通知消费了 76 this.notifyAll(); 77 78 return chicken; 79 } 80 } 81 82 83 84 class Consumer extends Thread{ 85 SynContainer container; 86 public Consumer(SynContainer container){ 87 this.container = container; 88 } 89 90 @Override 91 public void run() { 92 for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { 93 System.out.println("消费了-->"+container.pop().id+"只鸡"); 94 } 95 } 96 } 97 98 99 100 // 产品 101 class Chicken{ 102 int id; //产品编号 103 public Chicken(int id){ 104 this.id = id; 105 } 106 }
1 package com.gzq.java; 2 3 /** 4 * @author: sjmp1573 5 * @date: 2020/11/18 21:34 6 * @description: 7 */ 8 9 public class TestPC2 { 10 public static void main(String[] args) { 11 TV tv = new TV(); 12 new Player(tv).start(); 13 new Wathcher(tv).start(); 14 } 15 } 16 17 //生产者--演员 18 class Player extends Thread{ 19 TV tv; 20 public Player(TV tv){ 21 this.tv = tv; 22 } 23 24 @Override 25 public void run() { 26 for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { 27 if(i%2==0){ 28 this.tv.play("快乐大本营"); 29 }else{ 30 this.tv.play("天天向上"); 31 } 32 } 33 } 34 } 35 36 //观众 37 class Wathcher extends Thread{ 38 TV tv; 39 public Wathcher(TV tv){ 40 this.tv = tv; 41 } 42 43 @Override 44 public void run() { 45 for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { 46 tv.watch(); 47 } 48 } 49 } 50 51 //产品--节目 52 class TV{ 53 // 演员表演,观众等待 T 54 // 观众观看,演员等待 F 55 String voice; // 表演节目 56 boolean flag = true; 57 58 // 表演 59 public synchronized void play(String voice){ 60 if(!flag){ 61 try { 62 this.wait(); 63 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 64 e.printStackTrace(); 65 } 66 } 67 System.out.println("演员表演了: "+voice); 68 // 通知观众观看 69 this.notifyAll();// 通知唤醒 70 this.voice = voice; 71 this.flag = !flag; 72 } 73 74 // 观看 75 public synchronized void watch(){ 76 if (flag){ 77 try { 78 this.wait(); 79 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 80 e.printStackTrace(); 81 } 82 } 83 System.out.println("观看了: "+voice); 84 // 通知演员表演 85 this.notifyAll(); 86 this.flag = !this.flag; 87 } 88 }

1 package com.gzq.java; 2 3 import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; 4 import java.util.concurrent.Executors; 5 6 /** 7 * @author GaoZQ 8 * @date 2021/3/15 22:34 9 */ 10 public class TestPool { 11 public static void main(String[] args) { 12 // 1.创建服务,创建线程池 13 ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10); 14 // newFixedThreadPool 参数为线程池大小 15 // 执行 16 service.execute(new MyThread()); 17 service.execute(new MyThread()); 18 service.execute(new MyThread()); 19 service.execute(new MyThread()); 20 21 // 2.关闭连接 22 service.shutdown(); 23 24 } 25 } 26 class MyThread implements Runnable{ 27 28 @Override 29 public void run() { 30 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()); 31 } 32 }