总结来源于官方文档:https://www.crummy.com/software/BeautifulSoup/bs4/doc/index.zh.html#find-all
示例代码段
html_doc = """
<html>
<head><title>The Dormouse's story <!--Hey, buddy. Want to buy a used parser?-->
<a><!--Hey, buddy. Want to buy a used parser?--></a></title>
</head>
<body>
<p class="title">
<b>The Dormouse's story</b>
<a><!--Hey, buddy. Want to buy a used parser?--></a>
</p>
<p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1 link4">Elsie</a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.
</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
"""
1、快速操作:
soup.title == soup.find('title') # <title>The Dormouse's story</title> soup.title.name # u'title' soup.title.string == soup.title.text == soup.title.get_text() # u'The Dormouse's story' soup.title.parent.name # u'head' soup.p == soup.find('p') # . 点属性,只能获取当前标签下的第一个标签 # <p class="title"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p> soup.p['class'] # u'title' soup.a == soup.find('a') # <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">Elsie</a> soup.find_all('a') # [<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">Elsie</a>, # <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>, # <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>]
soup.find_all(['a','b']) # 查找所有的a标签和b标签
soup.find_all(id=["link1","link2"]) # 查找所有id=link1 和id=link2的标签
soup.find(id="link3") # <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>
2、Beautiful Soup对象有四种类型:
1、BeautifulSoup
2、tag:标签
3、NavigableString : 标签中的文本,可包含注释内容
4、Comment :标签中的注释,纯注释,没有正文内容
标签属性的操做跟字典是一样一样的
html多值属性(xml不适合):
意思为一个属性名称,它是多值的,即包含多个属性值,即使属性中只有一个值也返回值为list,
如:class,rel , rev , accept-charset , headers , accesskey
其它属性为单值属性,即使属性值中有多个空格隔开的值,也是反回一个字符串
soup.a['class'] #['sister'] id_soup = BeautifulSoup('<p id="my id"></p>') id_soup.p['id'] #'my id'
3、html中tag内容输出:
string:输出单一子标签文本内容或注释内容(选其一,标签中包含两种内容则输出为None)
strings: 返回所有子孙标签的文本内容的生成器(不包含注释)
stripped_strings:返回所有子孙标签的文本内容的生成器(不包含注释,并且在去掉了strings中的空行和空格)
text:只输出文本内容,可同时输出多个子标签内容
get_text():只输出文本内容,可同时输出多个子标签内容
string:
markup = "<b><!--Hey, buddy. Want to buy a used parser?--></b>" soup = BeautifulSoup(markup, 'html.parser') comm = soup.b.string print(comm) # Hey, buddy. Want to buy a used parser? print(type(comm)) #<class 'bs4.element.Comment'>
strings:
head_tag = soup.body for s in head_tag.strings: print(repr(s)) 结果: ' ' "The Dormouse's story" ' ' 'Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were ' 'Elsie' ', ' 'Lacie' ' and ' 'Tillie' '; and they lived at the bottom of a well. ' ' ' '...' ' '
stripped_strings:
head_tag = soup.body for s in head_tag.stripped_strings: print(repr(s)) 结果: "The Dormouse's story" 'Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were' 'Elsie' ',' 'Lacie' 'and' 'Tillie' '; and they lived at the bottom of a well.' '...'
text:
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc, 'html.parser') head_tag = soup.body print(head_tag.text) 结果: The Dormouse's story Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were Elsie, Lacie and Tillie; and they lived at the bottom of a well. ...
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc, 'html.parser') head_tag = soup.body print(repr(head_tag.text)) 结果: " The Dormouse's story Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were Elsie, Lacie and Tillie; and they lived at the bottom of a well. ... "
4、返回子节点列表:
.contents: 以列表的方式返回节点下的直接子节点
.children:以生成器的方式反回节点下的直接子节点
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc, 'html.parser') head_tag = soup.head print(head_tag) print(head_tag.contents) print(head_tag.contents[0]) print(head_tag.contents[0].contents) for ch in head_tag.children: print(ch) 结果: <head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head> [<title>The Dormouse's story</title>] <title>The Dormouse's story</title> ["The Dormouse's story"] <title>The Dormouse's story</title>
5、返回子孙节点的生成器:
.descendants: 以列表的方式返回标签下的子孙节点
for ch in head_tag.descendants: print(ch) 结果: <title>The Dormouse's story</title> The Dormouse's story
6、父标签(parent):如果是bs4对象,不管本来是标签还是文本都可以找到其父标签,但是文本对象不能找到父标签
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc, 'html.parser') tag_title = soup.b # b标签 print(tag_title.parent) # b标签的父标签 p print(type(tag_title.string)) # b标签中的文本的类型,文本中有注释时结果为None <class 'bs4.element.NavigableString'> print(tag_title.string.parent) # b标签中文本的父标签 b print(type(tag_title.text)) # b 标签中的文本类型为str,无bs4属性找到父标签
7、递归父标签(parents):递归得到元素的所有父辈节点
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc, 'html.parser') link = soup.a for parent in link.parents: print(parent.name)
结果:
p
body
html
[document]
8、前后节点查询(不是前后标签哦,文本也是节点之一):previous_sibling,next_sibling
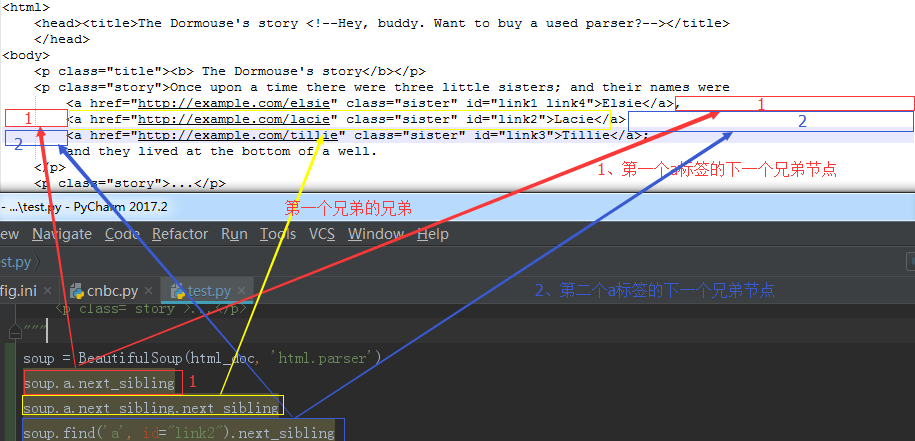
9、以生成器的方式迭代返回所有兄弟节点
for sib in soup.a.next_siblings: print(sib) print("---------") 结果: ------------- , --------- <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a> --------- --------- <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a> --------- ; and they lived at the bottom of a well. ---------
10、搜索文档树
过滤器:
1、字符串
2、正则表达式
3、列表
4、True
5、方法
html_doc = """<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head> <body> <p class="title"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p> <p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were</p> <a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>, <a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and <a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>; and they lived at the bottom of a well. <p class="story">...</p> </body> """ from bs4 import BeautifulSoup import re soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc, 'html.parser') soup.find_all("a") # 字符串参数 soup.find_all(re.compile("^b")) # 正则参数 soup.find_all(re.compile("a")) # 正则参数 soup.find_all(re.compile("l$")) # 正则参数 soup.find_all(["a", "b"]) # 标签的列表参数 soup.find_all(True) # 返回所有标签 def has_class_no_id(tag): return tag.has_attr("class") and not tag.has_attr("id") soup.find_all(has_class_no_id) # 方法参数
11、find选择器:
语法 :
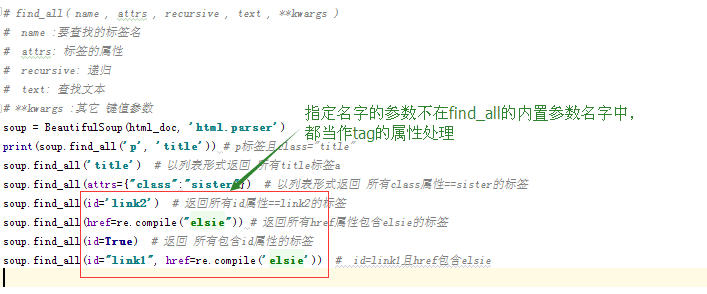
# find_all( name , attrs , recursive , text , **kwargs ) # name :要查找的标签名 # attrs: 标签的属性 # recursive: 递归 # text: 查找文本 # **kwargs :其它 键值参数
特殊情况:
data-foo="value",因中横杠不识别的原因,只能写成attrs={"data-foo":"value"},
class="value",因class是关键字,所以要写成class_="value"或attrs={"class":"value"}
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup import re html_doc = """ <html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head> <p class="title"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p> <p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were <a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>, <a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and <a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>; and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p> <p class="story">...</p> """ # find_all( name , attrs , recursive , text , **kwargs ) # name :要查找的标签名(字符串、正则、方法、True) # attrs: 标签的属性 # recursive: 递归 # text: 查找文本 # **kwargs :其它 键值参数 soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc, 'html.parser') print(soup.find_all('p', 'title')) # p标签且class="title" soup.find_all('title') # 以列表形式返回 所有title标签a soup.find_all(attrs={"class":"sister"}) # 以列表形式返回 所有class属性==sister的标签 soup.find_all(id='link2') # 返回所有id属性==link2的标签 soup.find_all(href=re.compile("elsie")) # 返回所有href属性包含elsie的标签 soup.find_all(id=True) # 返回 所有包含id属性的标签 soup.find_all(id="link1", href=re.compile('elsie')) # id=link1且href包含elsie
关于class的搜索
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc, 'html.parser') css_soup = BeautifulSoup('<p class="body strikeout"></p>', 'html.parser') css_soup.find_all("p", class_="body") # 多值class,指定其中一个即可 css_soup.find_all("p", class_="strikeout") css_soup.find_all("p", class_="body strikeout") # 精确匹配 # text 参数可以是字符串,列表、方法、True soup.find_all("a", text="Elsie") # text="Elsie"的a标签
12、父节点方法:
find_parents( name , attrs , recursive , text , **kwargs )
find_parent( name , attrs , recursive , text , **kwargs )
html_doc = """<html> <head> <title>The Dormouse's story</title> </head> <body> <p class="title"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p> <p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were</p> <a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>, <p> <a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and </p> <a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>; and they lived at the bottom of a well. <p class="story">...</p> </body> """ from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc, 'html.parser') a_string = soup.find(text="Lacie") # 文本为Lacie的节点 type(a_string), a_string # <class 'bs4.element.NavigableString'> Lacie a_parent = a_string.find_parent() # a_string的父节点中的第一个节点 a_parent = a_string.find_parent("p") # a_string的父节点中的第一个p节点 a_parents = a_string.find_parents() # a_string的父节点 a_parents = a_string.find_parents("a") # a_string的父点中所有a节点
13、后面的邻居节点:
find_next_siblings( name , attrs , recursive , text , **kwargs )
find_next_sibling( name , attrs , recursive , text , **kwargs )
html_doc = """<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head> <body> <p class="title"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p> <p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were</p> <a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>, <b href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</b>, <a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and <a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>; and they lived at the bottom of a well. <p class="story">...</p> </body> """ from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc, 'html.parser') first_link = soup.a # 第一个a标签 a_sibling = first_link.find_next_sibling() # 后面邻居的第一个 a_sibling = first_link.find_next_sibling("a") # 后面邻居的第一个a a_siblings = first_link.find_next_siblings() # 后面的所有邻居 a_siblings = first_link.find_next_siblings("a") # 后面邻居的所有a邻居
14、前面的邻居节点:
find_previous_siblings( name , attrs , recursive , text , **kwargs )
find_previous_sibling( name , attrs , recursive , text , **kwargs )
15、后面的节点:
find_all_next( name , attrs , recursive , text , **kwargs )
find_next( name , attrs , recursive , text , **kwargs )
html_doc = """<html> <head> <title>The Dormouse's story</title> </head> <body> <p class="title"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p> <p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were</p> <a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>, <p> <a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and </p> <p> <a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>; </p> and they lived at the bottom of a well. <p class="story">...</p> </body> """ from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc, 'html.parser') a_string = soup.find(text="Lacie") a_next = a_string.find_next() # 后面所有子孙标签的第一个 a_next = a_string.find_next('a') # 后面所有子孙标签的第一个a标签 a_nexts = a_string.find_all_next() # 后面的所有子孙标签 a_nexts = a_string.find_all_next('a') # 后面的所有子孙标签中的所有a标签
16、前面的节点:
find_all_previous( name , attrs , recursive , text , **kwargs )
find_previous( name , attrs , recursive , text , **kwargs )
17、解析部分文档:
如果仅仅因为想要查找文档中的<a>标签而将整片文档进行解析,实在是浪费内存和时间.最快的方法是从一开始就把<a>标签以外的东西都忽略掉. SoupStrainer 类可以定义文档的某段内容,这样搜索文档时就不必先解析整篇文档,只会解析在 SoupStrainer 中定义过的文档. 创建一个 SoupStrainer 对象并作为 parse_only 参数给 BeautifulSoup 的构造方法即可。
SoupStrainer 类参数:name , attrs , recursive , text , **kwargs
html_doc = """<html> <head> <title>The Dormouse's story</title> </head> <body> <p class="title"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p> <p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were <a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>, <a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and <a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>; </p> and they lived at the bottom of a well. <p class="story">...</p> </body> """ from bs4 import SoupStrainer a_tags = SoupStrainer('a') # 所有a标签 id_tags = SoupStrainer(id="link2") # id=link2的标签 def is_short_string(string): return len(string) < 10 # string长度小于10,返回True short_string = SoupStrainer(text=is_short_string) # 符合条件的文本 from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc, 'html.parser', parse_only=a_tags).prettify() soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc, 'html.parser', parse_only=id_tags).prettify() soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc, 'html.parser', parse_only=short_string).prettify()
最后一个方法:
patel = re.compile('(?<=(original_tel = ")).*(?=("))')