一、基本数据类型的包装类
基本类型4类8中:数值型、浮点型、字符型、布尔型
我们在日常工作中经常会用到集合框架:比如List、Map、Set
本身放值是没问题的,但是在Api里有一些基本的规定
源码:
例如:ArrayList
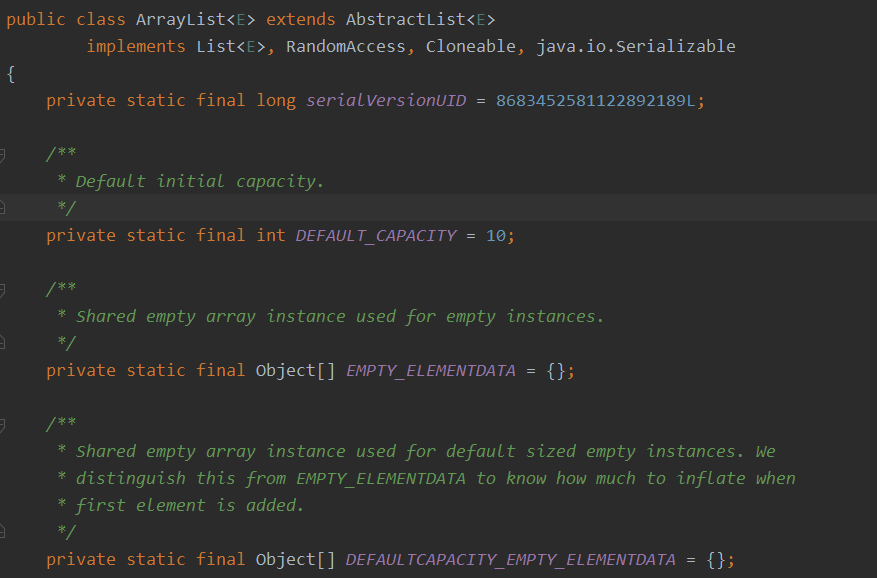
里面有一个重要的方法add
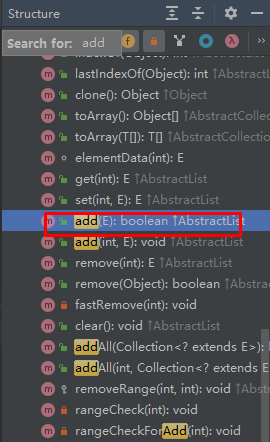
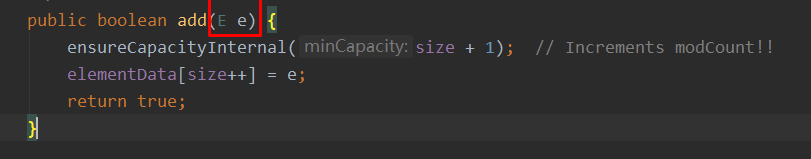
E e 表示什么意思
/** * Appends the specified element to the end of this list. * * @param e element to be appended to this list * @return <tt>true</tt> (as specified by {@link Collection#add}) */
看下继承关系,最上面



Collection有一个add
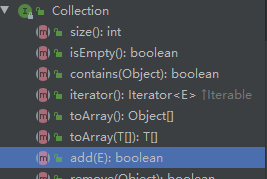
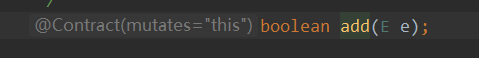
里面也有个E e
里面传入的值要是一个Object类型的一个对象
我们之前int、double、float都属于数值,而不是一个类,数值只表示一个单一的值,而类
表示有对应的属性和有对应的一个方法
所以如果没有包装类的话,放1、2、3这些值时可能会存在写问题
因此有了包装类
1、包装类
public class IntegerDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { int a = 10; Integer i = new Integer(10); System.out.println(a == i); } }
打印结果:
/* true Process finished with exit code 0 */
/* * 包装类与基本数据类型 * 包装类是将基本数据类型封装成一个类,包含属性和方法 * 使用: * 在使用过程中,会涉及到自动装箱和自动拆箱 * 装箱:将基本数据类型转换成包装类 * 拆箱:将包装类转换成基本数据类型 * * */
源码:
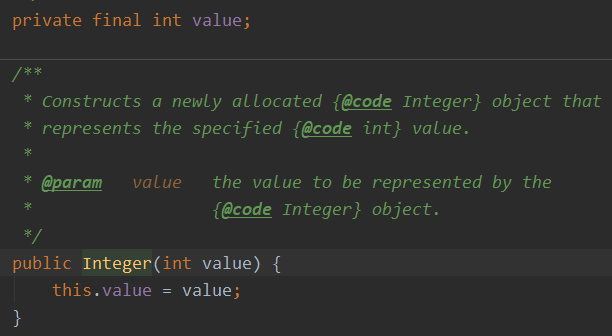
2、相互转换
public class IntegerDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { int a = 10; Integer i = new Integer(10); //通过方法进行类型的转换 Integer i2 = Integer.valueOf(a); int i3 = i.intValue(); System.out.println(a == i); } }
源码:
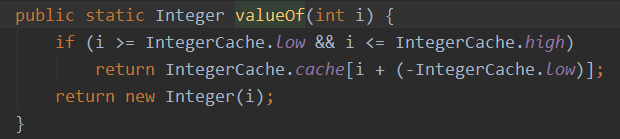
返回值是一个Integer对象
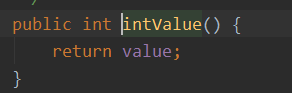
返回的是值
3、Float、Double等等
public class IntegerDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { Float f1 = new Float(3.14); Double d1 = new Double(3.14); } }
4、面试题:
4.1
public class IntegerDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { Integer i1 = 100; Integer i2 = 100; Integer i3 = 200; Integer i4 = 200; System.out.println(i1==i2); System.out.println(i3==i4); } }
打印结果:
/* true false Process finished with exit code 0 */
原因:
/* int i = 100; Integer i1 = 100; 这两个是完全不一样的 上面的是简单的赋值 下面的完成了两个步骤, 先定义100,再转换为Integer类型,Integer.vauleOf(100) */
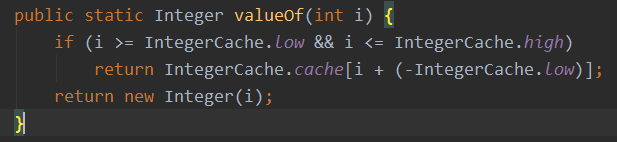
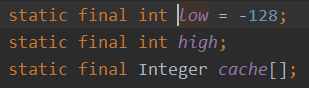
/* i是100,100>-128 && 100 <=127 返回的是Integer 对象, 只不过是cache规定好的数组 i2=100, 同样也返回的是数组里指定的 i3=200, 不在 i4=200, 不在 意味着每次都要new 一个Integer, 对象地址就不一样了 */
4.2
public class IntegerDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { Double d1 = 1.0; Double d2 = 1.0; Double d3 = 2.0; Double d4 = 2.0; System.out.println(d1==d2); System.out.println(d3==d4); } }
打印结果:
/* false false Process finished with exit code 0 */
原因:
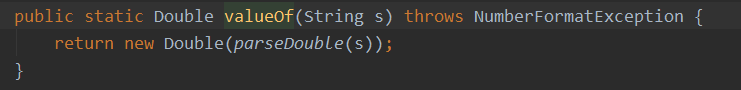
/* 每次都是一个新的new 所以为false */
4.3、
public class IntegerDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { Integer i = 10; int a = i; System.out.println(a==i); } }
打印结果:
/* true Process finished with exit code 0 */
原因:
/* 会自动拆箱 */
二、字符串相关类
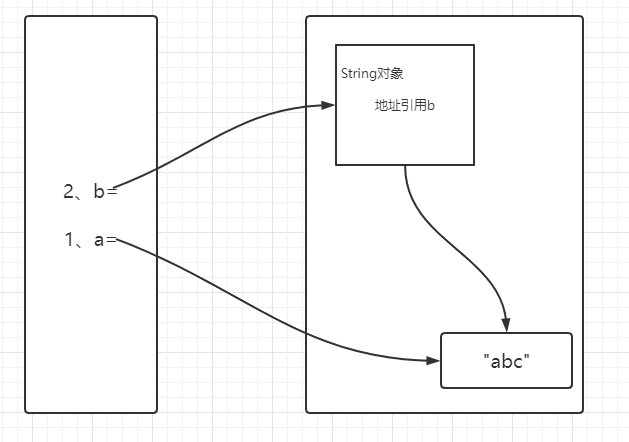
public class StringDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { String str = "abc"; String str2 = new String("abc"); } }
"abc"是放到什么地方的?
/* 常量池, 常量池在1.7之后放置在了堆空间之中,不是在方法区 */
public class StringDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { String str = "abc"; String str2 = new String("abc"); System.out.println(str==str2); System.out.println(str.equals(str2)); } }
结果为:
/* false
true Process finished with exit code 0 */
再看
public class StringDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { String str = "abc"; String str2 = new String("abc"); str2 = str2.intern(); System.out.println(str==str2); System.out.println(str.equals(str2)); } }
结果为:
/* true true Process finished with exit code 0 */
就变成true了
1、字符串的本质
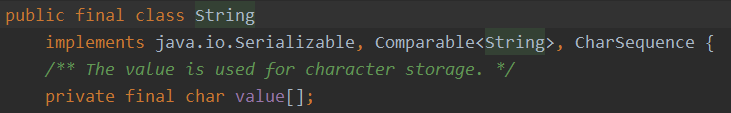
1.1、字符串的本质是字符数组或者叫做字符序列
1.2、String类使用final修饰,不可以被继承
1.3使用equals方法比较的是字符数组的每一个位置的值
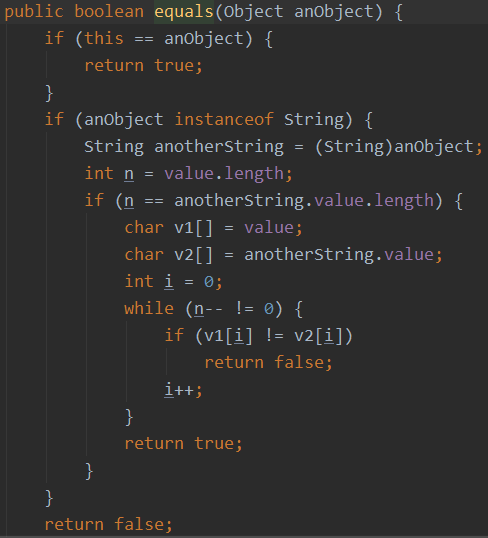
1.4、hashCode()
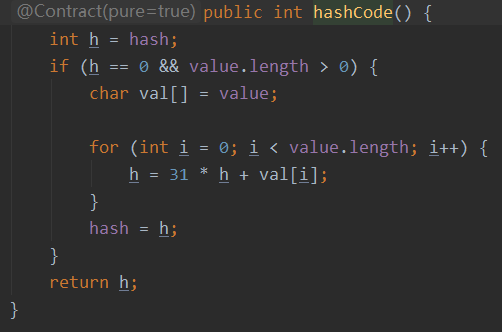
为什么用31乘
/* 31的二进制是 11111 16+8+4+2+1 移位运算速度是最快的 */
1.5、其他方法
public class StringDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { String str = "abc"; String str2 = new String("abc"); str2 = str2.intern(); System.out.println(str==str2); System.out.println(str.equals(str2)); //返回下标对应的值 System.out.println(str.charAt(0)); //数组的复制过程 拼接 System.out.println(str.concat("cde")); //返回指定下标的元素 System.out.println(str.indexOf("a")); String s = "abcdefghijklmn"; System.out.println(s.substring(3)); //在截取字符串的时候,需要注意是左闭右开区间 System.out.println(s.substring(3,5)); System.out.println(s.length()); } }
打印结果:
/* true true a abccde 0 defghijklmn de 14 */
常用方法总结:
char charAt(int index) //返回字符串中第index个字符。 boolean equals(String other) //如果字符串与other相等,返回true boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String other) //如果字符串与other相等(忽略大小写),则返回true int indexOf(String str) lastIndexOf(String str,int idx) int length() //返回字符串的长度。 String replace(char oldChar,char newChar) //返回一个新串,它是通过用 newChar 替换此字符串中出现的所有oldChar 而生成的 boolean startsWith(String prefix) //如果字符串以prefix开始,则返回true boolean endsWith(String prefix) //如果字符串以prefix结尾,则返回true String substring(int beginIndex)
String substring(int beginIndex,int endIndex) //返回一个新字符串,该串包含从原始字符串beginIndex到串尾戒endIndex-1的所有字符 String toLowerCase() //返回一个新字符串,该串将原始字符串中的所有大写字母改成小写字母 String toUpperCase() //返回一个新字符串,该串将原始字符串中的所有小写字母改成大写字母 String trim() //返回一个新字符串,该串删除了原始字符串头部和尾部的空格
回到上面的一个问题,调用intern()方法后,为什么a==b就是true了
public class StringDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { String a = "abc"; String b = new String("abc"); b = b.intern(); System.out.println(a==b); } }
打印结果为:
/* true Process finished with exit code 0 */
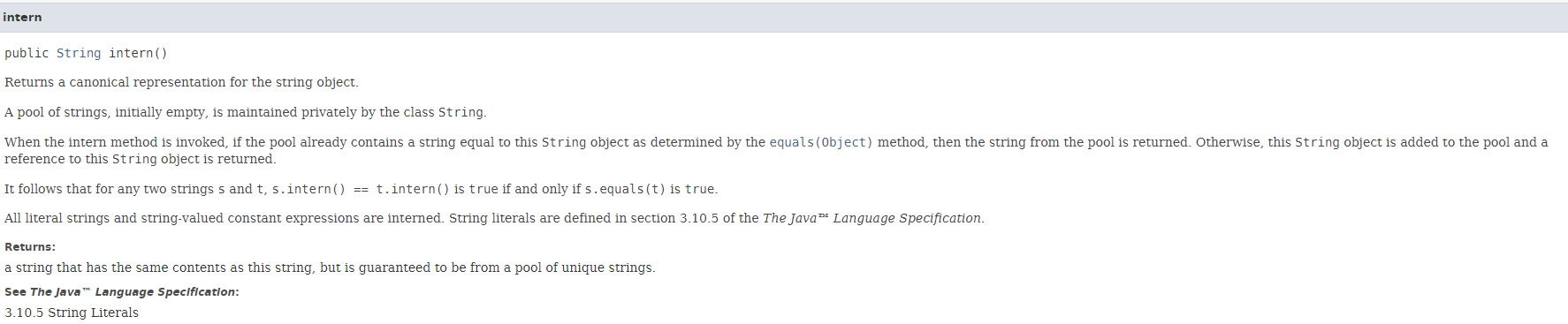
当方法被调用是, 如果常量池已经包含了一个string, 并且equal 等于这个string对象时,池子里面这个string将会被return
一个字符串池,最初是空的,由类私下维护String。 当调用 intern 方法时,如果池中已经包含一个与String该方法确定的对象相等equals(Object)的字符串,则返回池中的字符串。否则,将此String对象添加到池中并String返回对该对象的引用。 由此可见,对于任何两个字符串s和t, 当且 仅当s.intern() == t.intern()是。 trues.equals(t)true 所有文字字符串和字符串值的常量表达式都是实习的。字符串文字在 The Java™ Language Specification的第 3.10.5 节中定义。 回报: 与此字符串具有相同内容的字符串,但保证来自唯一字符串池。
对象地址和
地址比较肯定有问题的所以是false
当用intern方法后,
如果池中已经包含一个与String该方法确定的对象相等equals(Object)的字符串,则返回池中的字符串
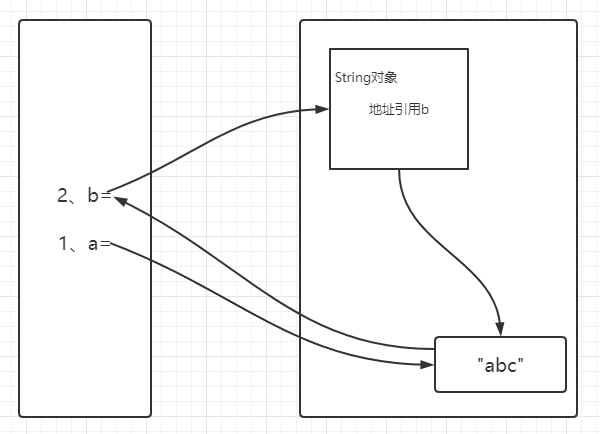
所以a==b 了,返回true
public class StringDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { String a = "abc"; String b = "def"; String c = "abcdef"; String d = a+b; String d1 = (a+b).intern(); String e = "abc"+"def"; System.out.println(c==d); System.out.println(c==d1); System.out.println(c==e); } }
打印结果为:
/* false true true Process finished with exit code 0 */
public class StringDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { String f = "a" + "b" +"c"; String a1 = "a"; String a2 = "b"; String a3 = "c"; String f1 = a1+a2+a3; } }
这个创建了几个对象?
f是 1 个对象
f1是 4 个对象
1.6、String是一个不可变对象
指的是数组的引用关系是不可以变的, 值是能改变的
2、可变字符序列:StringBuffer、StringBuilder
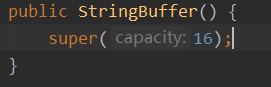
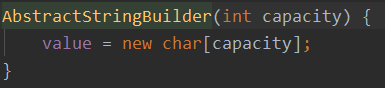
public class StringBufferDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer(); stringBuffer.append(1).append(1.234).append("abc").append(true); System.out.println(stringBuffer); System.out.println(stringBuffer.length()); System.out.println(stringBuffer.capacity());
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder(); stringBuilder.append("123").append(1).append(false); System.out.println(stringBuilder); } }
打印结果为:
11.234abctrue 13 // length() 表示 字符串放置在数组里占用数组的大小 16 // 初始化时的容量是16 1231false
线程安全
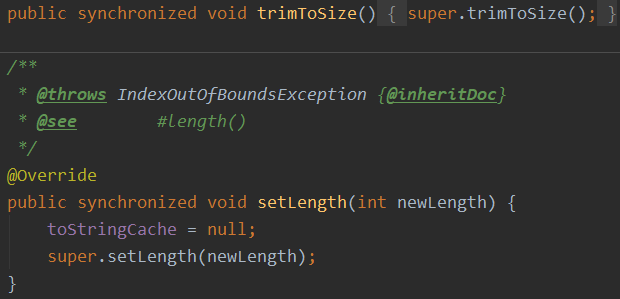
StringBuffer都是用synchronized修饰的(同步加锁), 是线程安全的
StringBuilder是线程不安全的
/* * 可变字符串 * StringBuffer:线程安全,效率低 * StringBuilder: 线程不安全,效率高 * */
三、时间处理相关类
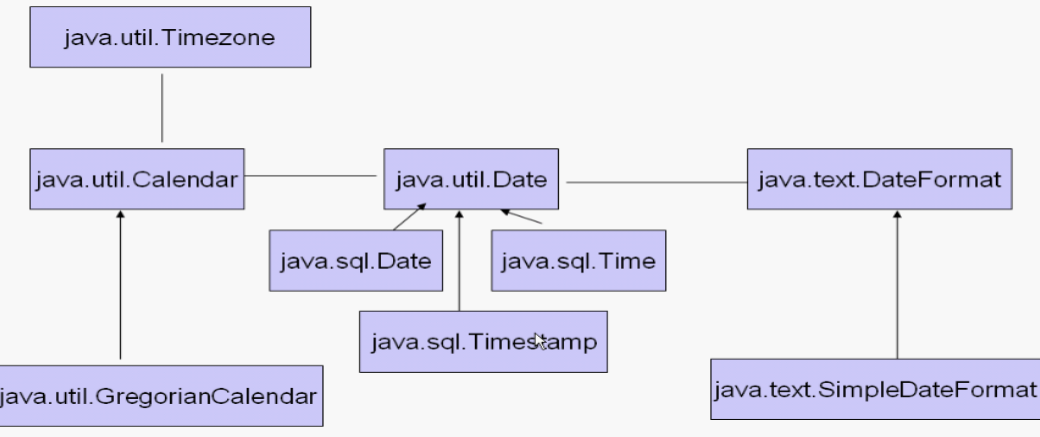
1、Date
DateFormat、SimpleDateFormat
Calender
import java.text.DateFormat; import java.text.ParseException; import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; import java.util.Calendar; import java.util.Date; public class DateDemo { public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException { Date date = new Date(); System.out.println(date); System.out.println(date.getTime()); DateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"); //将Date类按照规范转换为字符串格式 String str = dateFormat.format(date); System.out.println(str); //将字符串转换成对应的日期类 Date d1 = dateFormat.parse("2010-10-10 20:20:20"); System.out.println(d1); //获取的是当前系统的时间 Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance(); System.out.println(calendar); //设置指定时间的日历类 calendar.setTime(d1); System.out.println(calendar); System.out.println(calendar.get(Calendar.YEAR)); System.out.println(calendar.get(Calendar.MONTH)); System.out.println(calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH)); System.out.println(calendar.get(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY)); System.out.println(calendar.get(Calendar.MINUTE)); System.out.println(calendar.get(Calendar.SECOND)); } }
打印结果为:
/* Sun Apr 17 19:42:12 CST 2022 1650195732274 2022-04-17 19:42:12 Sun Oct 10 20:20:20 CST 2010 java.util.GregorianCalendar[time=1650195732403,areFieldsSet=true,areAllFieldsSet=true,lenient=true,zone=sun.util.calendar.ZoneInfo[id="Asia/Shanghai",offset=28800000,dstSavings=0,useDaylight=false,transitions=31,lastRule=null],firstDayOfWeek=1,minimalDaysInFirstWeek=1,ERA=1,YEAR=2022,MONTH=3,WEEK_OF_YEAR=17,WEEK_OF_MONTH=4,DAY_OF_MONTH=17,DAY_OF_YEAR=107,DAY_OF_WEEK=1,DAY_OF_WEEK_IN_MONTH=3,AM_PM=1,HOUR=7,HOUR_OF_DAY=19,MINUTE=42,SECOND=12,MILLISECOND=403,ZONE_OFFSET=28800000,DST_OFFSET=0] java.util.GregorianCalendar[time=1286713220000,areFieldsSet=true,areAllFieldsSet=true,lenient=true,zone=sun.util.calendar.ZoneInfo[id="Asia/Shanghai",offset=28800000,dstSavings=0,useDaylight=false,transitions=31,lastRule=null],firstDayOfWeek=1,minimalDaysInFirstWeek=1,ERA=1,YEAR=2010,MONTH=9,WEEK_OF_YEAR=42,WEEK_OF_MONTH=3,DAY_OF_MONTH=10,DAY_OF_YEAR=283,DAY_OF_WEEK=1,DAY_OF_WEEK_IN_MONTH=2,AM_PM=1,HOUR=8,HOUR_OF_DAY=20,MINUTE=20,SECOND=20,MILLISECOND=0,ZONE_OFFSET=28800000,DST_OFFSET=0] 2010 9 10 20 20 20 Process finished with exit code 0 */
四、Math类
public class MathDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(Math.abs(-1)); System.out.println(Math.sqrt(2)); System.out.println(Math.ceil(-3.14)); //向上取整 System.out.println(Math.floor(-3.14)); //向下取整 System.out.println(Math.pow(2,3)); } }
打印结果为:
/* 1 1.4142135623730951 -3.0 -4.0 8.0 */
五、枚举类:Jdk1.5
public enum Gender { 男,女 }
public class Test { Gender gender = Gender.女; Gender gender2 = Gender.男; } }
这种方式就太low了
定义一个Enum
public enum EventEnum { LAUNCH("launch"),PAGEVIEW("pageview"),EVENT("event"); EventEnum(String name){ this.name = name; } private String name; public void show(){ System.out.println(this.name); EventEnum[] ee = values(); for(int i = 0;i<ee.length;i++){ System.out.println(ee[i]); } } }
public class Test { Gender gender = Gender.女; Gender gender2 = Gender.男; public static void main(String[] args) { EventEnum ee = EventEnum.LAUNCH; ee.show(); String name = EventEnum.PAGEVIEW.name(); System.out.println(name); } }
打印结果为:
/* launch LAUNCH PAGEVIEW EVENT PAGEVIEW Process finished with exit code 0 */
- 1. 只能够取特定值中的一个
- 2. 使用enum关键字
- 3. 所有的枚举类型隐性地继承自 java.lang.Enum。(枚举实质上还是类!
- 而每个被枚举的成员实质就是一个枚举类型的实例,他们默认都是public static final的。
- 可以直接通过枚举类型名直接使用它们。)
- 4. 强烈建议当你需要定义一组常量时,使用枚举类型
六、File类
后面再说