1. 基本定义
- Think of a trait as a small object whose main purpose is to carry information used by another object or algorithm to determine “policy” or “implementation details”.
- In some cases the extra parameters are entirely determined by a few main paameters. 因此需要通过几个核心参数型别的定义,来设计不同的模板,满足不同需求。
2. Fixed Traits
- 主要是构造适应各种类型的函数
- Fixed主要指,一旦T在模板中被定义,则无法再调用中改变。
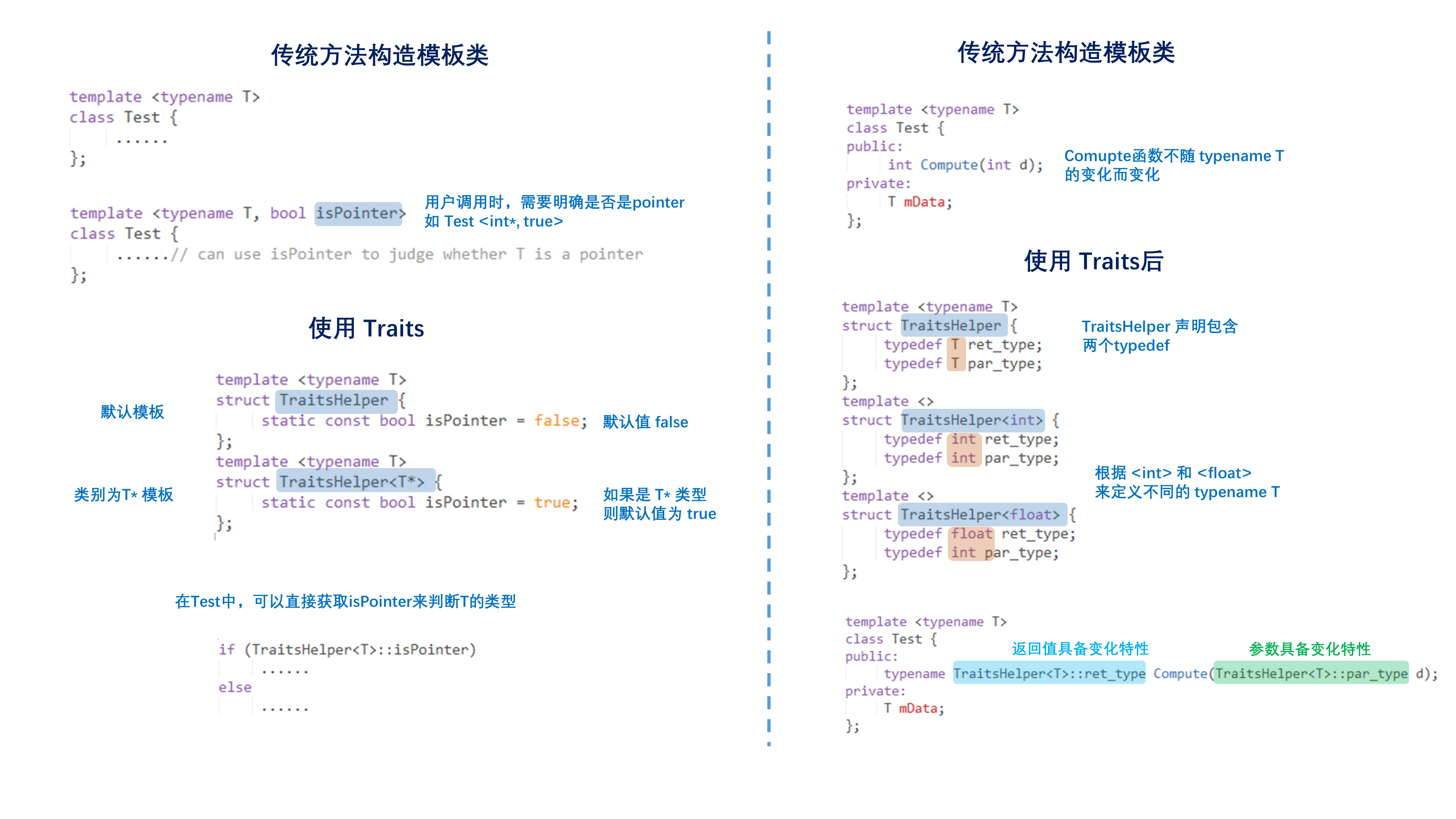
2.1 传统方法
- 传统方法定义的模板
#ifndef ACCUM_HPP#define ACCUM_HPPtemplate <typename T>inlineT accum (T const* beg, T const* end){T total = T(); // assume T() actually creates a zero valuewhile (beg != end) {total += *beg;++beg;}return total;}#endif // ACCUM_HPP
- 调用该模板
#include "accum1.hpp"#include <iostream>int main(){// create array of 5 integer valuesint num[]={1,2,3,4,5};// print average valuestd::cout << "the average value of the integer values is "<< accum(&num[0], &num[5]) / 5<< ' ';// create array of character valueschar name[] = "templates";int length = sizeof(name)-1;// (try to) print average character valuestd::cout << "the average value of the characters in ""<< name << "" is "<< accum(&name[0], &name[length]) / length<< ' ';}
存在问题,当调用的是
char时,模板自动将返回函数也定义为char,而不是期望的int。2.2 使用Traits方法
模板定义
template<typename T>class AccumulationTraits;template<>class AccumulationTraits<char> {public:typedef int AccT;};template<>class AccumulationTraits<short> {public:typedef int AccT;};template<>class AccumulationTraits<int> {public:typedef long AccT;};template<>class AccumulationTraits<unsigned int> {public:typedef unsigned long AccT;};template<>class AccumulationTraits<float> {public:typedef double AccT;};template <typename T>inlinetypename AccumulationTraits<T>::AccT accum (T const* beg,T const* end){// return type is traits of the element typetypedef typename AccumulationTraits<T>::AccT AccT;AccT total = AccT(); // assume T() actually creates a zero valuewhile (beg != end) {total += *beg;++beg;}return total;}
- 调用方法不变。
2.3 总结
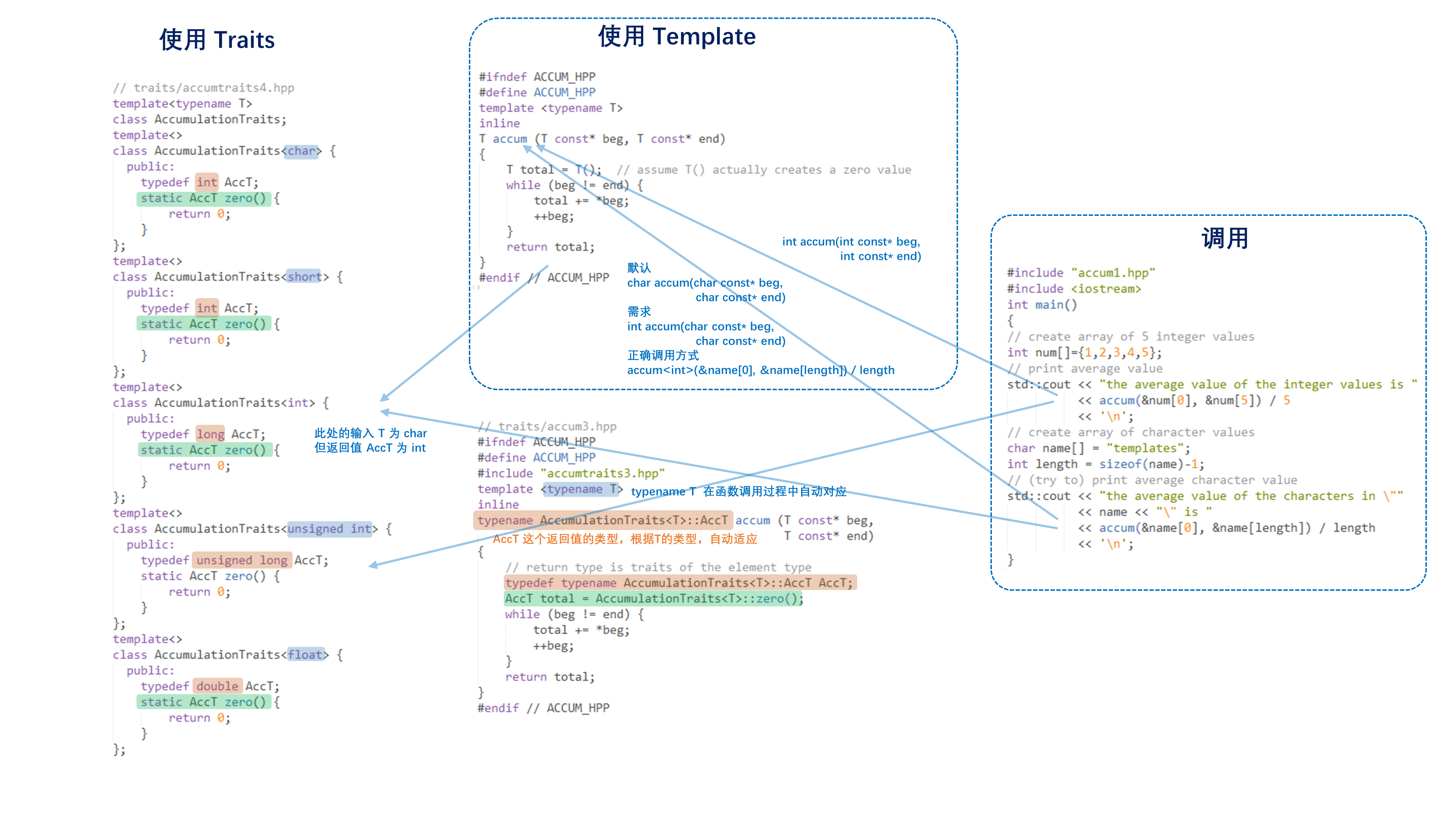
3. Value Traits
- 对模板中特定数值,特别是初始话时候的操作方法
- 模板的书写,引入
zero()
template<typename T>class AccumulationTraits;template<>class AccumulationTraits<char> {public:typedef int AccT;static AccT zero() {return 0;}};template<>class AccumulationTraits<short> {public:typedef int AccT;static AccT zero() {return 0;}};template<>class AccumulationTraits<int> {public:typedef long AccT;static AccT zero() {return 0;}};template<>class AccumulationTraits<unsigned int> {public:typedef unsigned long AccT;static AccT zero() {return 0;}};template<>class AccumulationTraits<float> {public:typedef double AccT;static AccT zero() {return 0;}};template <typename T>inlinetypename AccumulationTraits<T>::AccT accum (T const* beg,T const* end){// return type is traits of the element typetypedef typename AccumulationTraits<T>::AccT AccT;AccT total = AccumulationTraits<T>::zero();while (beg != end) {total += *beg;++beg;}return total;}
- 调用方法不变
- 总结
4. Parameterized Traits
- 为了增加灵活性,引入另一个参数(AT),使其来决定参数(T)的类型。
- 有两种方法,一种是基于
function traits的方法
template <typename T>inlinetypename AccumulationTraits<T>::AccT accum (T const* beg,T const* end){return Accum<T>::accum(beg, end);}template <typename Traits, typename T>inlinetypename Traits::AccT accum (T const* beg, T const* end){return Accum<T, Traits>::accum(beg, end);}
- 另一种是将
function traits方法引入Class
template <typename T,typename AT = AccumulationTraits<T> >class Accum {public:static typename AT::AccT accum (T const* beg, T const* end){typename AT::AccT total = AT::zero();while (beg != end) {total += *beg;++beg;}return total;}};
- 总结

Reference
- 项目中一次活用C++模板(traits)的经历
http://blog.csdn.net/my_business/article/details/8098417 - Traits的一个举例
http://www.cnblogs.com/hellogiser/p/cplusplus-traits.html - C++ Templates - The Complete Guide - Chp. 15