1.函数式接口
函数式接口(Functional Interface)就是一个有且仅有一个抽象方法,但是可以有多个非抽象方法的接口。
Functional Interface(功能接口)为lambda表达式和方法引用(用冒号::来进行方法的调用)提供目标类型。每个功能接口都有一个抽象方法,称为该功能接口的功能方法,lambda表达式的参数和返回类型与之匹配或适配。功能接口可以在多个上下文中提供目标类型,例如赋值上下文,方法调用或强制转换上下文:
// Assignment context
Predicate<String> p = String::isEmpty;
// Method invocation context
stream.filter(e -> e.getSize() > 10)...
// Cast context
stream.map((ToIntFunction) e -> e.getSize())...函数式接口可以使用lambda表达式,方法引用或构造函数引用创建功能接口的实例。
Java8为函数式接口引入了一个新注解@FunctionalInterface,主要用于编译级错误检查,加上该注解,当接口不符合函数式接口定义的时候,编译器会报错。
此注解不是编译器将接口识别为功能接口的必要条件,而仅是帮助捕获设计意图并获得编译器帮助识别意外违反设计意图的帮助。
正确例子,没有报错:
@FunctionalInterface
public interface HelloWorldService {
void sayHello(String msg);
}错误例子,接口中包含了两个抽象方法,违反了函数式接口的定义,提示在接口中找到多个非重写的抽象方法。
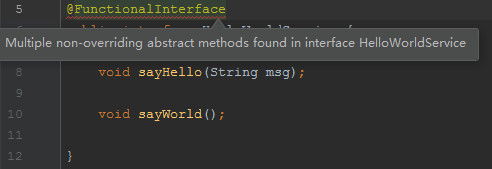
注意: 加不加 @FunctionalInterface对于接口是不是函数式接口没有影响,该注解只是提醒编译器去检查该接口是否仅包含一个抽象方法。
1.1允许定义默认方法
函数式接口里是可以包含默认方法,因为默认方法不是抽象方法,其有一个默认实现,所以是符合函数式接口的定义的。
如下代码不会报错:
@FunctionalInterface
public interface HelloWorldService {
void sayHello(String msg);
default void doSomeWork1() {
// Method body
}
default void doSomeWork2() {
// Method body
}
}1.2允许定义静态方法
函数式接口里是可以包含静态方法,因为静态方法不能是抽象方法,是一个已经实现了的方法,所以是符合函数式接口的定义的。
如下代码不会报错:
@FunctionalInterface
public interface HelloWorldService {
void sayHello(String msg);
static void printHello() {
System.out.println("Hello");
}
}1.3允许定义java.lang.Object的public方法
函数式接口里是可以包含Object里的public方法,这些方法对于函数式接口来说,不被当成是抽象方法(虽然它们是抽象方法);因为任何一个函数式接口的实现,默认都继承了Object类,包含了来自java.lang.Object里对这些抽象方法的实现;
如下代码不会报错:
@FunctionalInterface
public interface HelloWorldService {
void sayHello(String msg);
@Override
boolean equals(Object obj);
}1.4已有函数式接口
函数式接口可以对现有的函数友好地支持lambda。
JDK1.8之前已有的函数式接口:
- java.lang.Runnable
- java.util.concurrent.Callable
- java.security.PrivilegedAction
- java.util.Comparator
- java.io.FileFilter
- java.nio.file.PathMatcher
- java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler
- java.beans.PropertyChangeListener
- java.awt.event.ActionListener
- javax.swing.event.ChangeListener
JDK1.8新增加的函数接口:
- java.util.function
2.Function函数
| 序号 | 接口 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Function<T,R> | 接收一个参数并返回结果的函数 |
| 2 | BiFunction<T,U,R> | 接受两个参数并返回结果的函数 |
| 3 | DoubleFunction<R> |
接收一个double类型的参数并返回结果的函数 |
| 4 | DoubleToIntFunction | 接收一个double类型的参数并返回int结果的函数 |
| 5 | DoubleToLongFunction | 接收一个double类型的参数并返回long结果的函数 |
| 6 | IntFunction<R> |
接收一个int类型的参数并返回结果的函数 |
| 7 | IntToDoubleFunction | 接收一个int类型的参数并返回double结果的函数 |
| 8 | IntToLongFunction | 接收一个int类型的参数并返回long结果的函数 |
| 9 | LongFunction<R> |
接收一个long类型的参数并返回结果的函数 |
| 10 | LongToDoubleFunction | 接收一个long类型的参数并返回double结果的函数 |
| 11 | LongToIntFunction | 接收一个long类型的参数并返回int结果的函数 |
| 12 | ToDoubleBiFunction<T,U> | 接收两个参数并返回double结果的函数 |
| 13 | ToDoubleFunction<T> |
接收一个参数并返回double结果的函数 |
| 14 | ToIntBiFunction<T,U> | 接收两个参数并返回int结果的函数 |
| 15 | ToIntFunction<T> |
接收一个参数并返回int结果的函数 |
| 16 | ToLongBiFunction<T,U> | 接收两个参数并返回long结果的函数 |
| 17 | ToLongFunction<T> |
接收一个参数并返回long结果的函数 |
2.1Function<T, R>
| 接口方法 | 方法描述 |
|---|---|
| R apply(T t) | 将此参数应用到函数中 |
| Function<T, R> andThen(Function<? super R,? extends V> after) | 返回一个组合函数,该函数结果应用到after函数中 |
| Function<T, R> compose(Function<? super V,? extends T> before) | 返回一个组合函数,首先将入参应用到before函数,再将before函数结果应用到该函数中 |
①apply(T t)
Function<String, String> function = a -> a + " Jack!";
System.out.println(function.apply("Hello")); // Hello Jack!②andThen(Function<? super R,? extends V> after)
Function<String, String> function = a -> a + " Jack!";
Function<String, String> function1 = a -> a + " Bob!";
String greet = function.andThen(function1).apply("Hello");
System.out.println(greet); // Hello Jack! Bob!③compose(Function<? super V,? extends T> before)
Function<String, String> function = a -> a + " Jack!";
Function<String, String> function1 = a -> a + " Bob!";
String greet = function.compose(function1).apply("Hello");
System.out.println(greet); // Hello Bob! Jack!2.2BiFunction<T, U, R>
| 接口方法 | 方法描述 |
|---|---|
| R apply(T t, U u) | 将参数应用于函数执行 |
| BiFunction<T,U,V> andThen(Function<? super R,? extends V> after) | 返回一个组合函数,after函数应用于该函数之后 |
①apply(T t, U u)
BiFunction<String, String, String> biFunction = (a, b) -> a + b;
System.out.println(biFunction.apply("Hello ", "Jack!")); // Hello Jack!②andThen(Function<? super R,? extends V> after)
BiFunction<String, String, String> biFunction = (a, b) -> a + b;
Function<String, String> function = (a) -> a + "!!!";
System.out.println(biFunction.andThen(function).apply("Hello", " Jack")); // Hello Jack!!!2.3DoubleFunction
| 接口方法 | 方法描述 |
|---|---|
| R apply(double value) | 根据给定参数执行函数 |
①apply(double value)
DoubleFunction<String> doubleFunction = doub -> "结果:" + doub;
System.out.println(doubleFunction.apply(1.6)); // 结果:1.62.4DoubleToIntFunction
| 接口方法 | 方法描述 |
|---|---|
| int applyAsInt(double value) | 根据给定的参数执行函数 |
①applyAsInt(double value)
DoubleToIntFunction doubleToIntFunction = doub -> Double.valueOf(doub).intValue();
System.out.println(doubleToIntFunction.applyAsInt(1.2)); // 12.5ToDoubleBiFunction<T,U>
| 接口方法 | 方法描述 |
|---|---|
| double applyAsDouble(T t, U u) | 根据给定的参数执行函数 |
①applyAsDouble(T t, U u)
ToDoubleBiFunction<Long, Float> toDoubleBiFunction = (lon, floa) -> lon
.doubleValue() + floa.doubleValue();
System.out.println(toDoubleBiFunction.applyAsDouble(11L, 235.5f)); // 246.52.6ToDoubleFunction
| 接口方法 | 方法描述 |
|---|---|
| double applyAsDouble(T value) | 根据给定参数执行函数 |
①applyAsDouble(T value)
ToDoubleFunction<Float> toDoubleFunction = floa -> floa.doubleValue();
System.out.println(toDoubleFunction.applyAsDouble(12315f)); // 12315.03.Consumer消费者
| 序号 | 接口 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Consumer<T> |
提供一个T类型的输入参数,不返回执行结果 |
| 2 | BiConsumer<T,U> | 提供两个自定义类型的输入参数,不返回执行结果 |
| 3 | DoubleConsumer | 表示接受单个double值参数,但不返回结果的操作 |
| 4 | IntConsumer | 表示接受单个int值参数,但不返回结果的操作 |
| 5 | LongConsumer | 表示接受单个long值参数,但不返回结果的操作 |
| 6 | ObjDoubleConsumer<T> |
表示接受object值和double值,但是不返回任何操作结果 |
| 7 | ObjIntConsumer<T> |
表示接受object值和int值,但是不返回任何操作结果 |
| 8 | ObjLongConsumer<T> |
表示接受object值和long值,但是不返回任何操作结果 |
3.1Consumer<T>
| 接口方法 | 方法描述 |
|---|---|
| void accept(T t) | 对给定的参数执行操作 |
| default Consumer andThen(Consumer<? super T> after) | 返回一个组合函数,after将会在该函数执行之后应用 |
①accept(T t)
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("Hello ");
Consumer<StringBuilder> consumer = (str) -> str.append("Jack!");
consumer.accept(sb);
System.out.println(sb.toString()); // Hello Jack!②andThen(Consumer<? super T> after)
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("Hello ");
Consumer<StringBuilder> consumer = (str) -> str.append("Jack!");
Consumer<StringBuilder> consumer1 = (str) -> str.append(" Bob!");
consumer.andThen(consumer1).accept(sb);
System.out.println(sb.toString()); // Hello Jack! Bob!3.2BiConsumer<T,U>
| 接口方法 | 方法描述 |
|---|---|
| void accept(T t, U u) | 对给定的参数执行操作 |
| default BiConsumer<T,U> andThen(BiConsumer<? super T,? super U> after) | 返回一个组合函数,after将会在该函数执行之后应用 |
①accept(T t, U u)
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
BiConsumer<String, String> biConsumer = (a, b) -> {
sb.append(a);
sb.append(b);
};
biConsumer.accept("Hello ", "Jack!");
System.out.println(sb.toString()); // Hello Jack!②andThen(BiConsumer<? super T,? super U> after)
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
BiConsumer<String, String> biConsumer = (a, b) -> {
sb.append(a);
sb.append(b);
};
BiConsumer<String, String> biConsumer1 = (a, b) -> {
System.out.println(a + b);
};
biConsumer.andThen(biConsumer1).accept("Hello", " Jack!"); // Hello Jack!3.3DoubleConsumer
| 接口方法 | 方法描述 |
|---|---|
| void accept(double value) | 对给定的参数执行操作 |
| default DoubleConsumer andThen(DoubleConsumer after) | 返回一个组合函数,after在该函数执行之后应用 |
①accept(double value)
DoubleConsumer doubleConsumer = System.out::println;
doubleConsumer.accept(1.3); // 1.3②andThen(DoubleConsumer after)
DoubleConsumer doubleConsumer = System.out::println;
DoubleConsumer doubleConsumer1 = System.out::println;
doubleConsumer.andThen(doubleConsumer1).accept(1.3);
// 1.3
// 1.33.4ObjDoubleConsumer<T>
| 接口方法 | 方法描述 |
|---|---|
| void accept(T t, double value) | 对给定的参数执行操作 |
①accept(T t, double value)
ObjDoubleConsumer<String> doubleConsumer = (obj, doub)
-> System.out.println(obj + doub);
doubleConsumer.accept("金额:", 222.66); // 金额:222.664.Predicate谓语
| 序号 | 接口 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Predicate<T> |
对给定的输入参数执行操作,返回一个boolean类型的结果(布尔值函数) |
| 2 | BiPredicate<T,U> | 对给定的两个输入参数执行操作,返回一个boolean类型的结果(布尔值函数) |
| 3 | DoublePredicate | 对给定的double参数执行操作,返回一个boolean类型的结果(布尔值函数) |
| 4 | IntPredicate | 对给定的int输入参数执行操作,返回一个boolean类型的结果(布尔值函数) |
| 5 | LongPredicate | 对给定的long参数执行操作,返回一个boolean类型的结果(布尔值函数) |
4.1Predicate<T>
| 接口方法 | 方法描述 |
|---|---|
| boolean test(T t) | 根据给定的参数进行判断 |
| Predicate and(Predicate<? super T> other) | 返回一个组合判断,将other以短路与的方式加入到函数的判断中 |
| Predicate or(Predicate<? super T> other) | 返回一个组合判断,将other以短路或的方式加入到函数的判断中 |
| Predicate negate() | 将函数的判断取反 |
①test(T t)
Predicate<Integer> predicate = number -> number != 0;
System.out.println(predicate.test(10)); //true②and(Predicate<? super T> other)
Predicate<Integer> predicate = number -> number != 0;
predicate = predicate.and(number -> number >= 10);
System.out.println(predicate.test(10)); //true③or(Predicate<? super T> other)
Predicate<Integer> predicate = number -> number != 0;
predicate = predicate.or(number -> number != 10);
System.out.println(predicate.test(10)); //true④negate()
Predicate<Integer> predicate = number -> number != 0;
predicate = predicate.negate();
System.out.println(predicate.test(10)); //false4.2BiPredicate<T,U>
| 接口方法 | 方法描述 |
|---|---|
| boolean test(T t, U u) | 根据给定的两个输入参数进行判断 |
| BiPredicate<T,U> and(BiPredicate<? super T,? super U> other) | 返回一个组合判断,将other以短路与的方式加入到函数的判断中 |
| BiPredicate<T,U> or(BiPredicate<? super T,? super U> other) | 返回一个组合判断,将other以短路或的方式加入到函数的判断中 |
| BiPredicate<T,U> negate() | 将函数的判断取反 |
①test(T t, U u)
BiPredicate<Integer, Integer> biPredicate = (a, b) -> a != b;
System.out.println(biPredicate.test(1, 2)); // true②and(BiPredicate<? super T,? super U> other)
BiPredicate<Integer, Integer> biPredicate = (a, b) -> a != b;
biPredicate = biPredicate.and((a, b) -> a.equals(b));
System.out.println(biPredicate.test(1, 2)); // false③or(BiPredicate<? super T,? super U> other)
BiPredicate<Integer, Integer> biPredicate = (a, b) -> a != b;
biPredicate = biPredicate.or((a, b) -> a == b);
System.out.println(biPredicate.test(1, 1)); // true④negate()
BiPredicate<Integer, Integer> biPredicate = (a, b) -> a != b;
biPredicate = biPredicate.negate();
System.out.println(biPredicate.test(1, 2)); // false4.3DoublePredicate
| 接口方法 | 方法描述 |
|---|---|
| boolean test(double value) | 根据给定的参数进行判断 |
| DoublePredicate and(DoublePredicate other) | 返回一个组合判断,将other以短路与的方式加入到函数的判断中 |
| DoublePredicate or(DoublePredicate other) | 返回一个组合判断,将other以短路或的方式加入到函数的判断中 |
| default DoublePredicate negate() | 将函数的判断取反 |
①test(double value)
DoublePredicate doublePredicate = doub -> doub != 0;
System.out.println(doublePredicate.test(10)); // true②and(DoublePredicate other)
DoublePredicate doublePredicate = doub -> doub != 0;
doublePredicate = doublePredicate.and(doub -> doub < 2);
System.out.println(doublePredicate.test(1.7)); // true③or(DoublePredicate other)
DoublePredicate doublePredicate = doub -> doub != 0;
doublePredicate = doublePredicate.or(doub -> doub > 2);
System.out.println(doublePredicate.test(1.7)); // true④negate()
DoublePredicate doublePredicate = doub -> doub != 0;
doublePredicate = doublePredicate.negate();
System.out.println(doublePredicate.test(1.7)); // false5.Supplier供应商
| 序号 | 接口 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Supplier<T> |
不提供输入参数,但是返回结果的函数 |
| 2 | BooleanSupplier | 不提供输入参数,但是返回boolean结果的函数 |
| 3 | DoubleSupplier | 不提供输入参数,但是返回double结果的函数 |
| 4 | IntSupplier | 不提供输入参数,但是返回int结果的函数 |
| 5 | LongSupplier | 不提供输入参数,但是返回long结果的函数 |
5.1Supplier<T>
| 接口方法 | 方法描述 |
|---|---|
| T get() | 获取结果值 |
①get()
Supplier<String> supplier = () -> "Hello Jack!";
System.out.println(supplier.get()); // Hello Jack!5.2BooleanSupplier
| 接口方法 | 方法描述 |
|---|---|
| boolean getAsBoolean() | 获取函数的执行结果 |
①getAsBoolean()
BooleanSupplier booleanSupplier = () -> true;
System.out.println(booleanSupplier.getAsBoolean()); // true5.3DoubleSupplier
| 接口方法 | 方法描述 |
|---|---|
| double getAsDouble() | 获取函数的执行结果 |
①getAsDouble()
DoubleSupplier doubleSupplier = () -> 2.7;
System.out.println(doubleSupplier.getAsDouble()); // 2.76.Operator操作员
除了Function,Consumer,Predicate,Supplier这几个基本的函数形式,还有其它派生的函数形式,它们扩展了基本的函数形式,包括UnaryOperator (extends Function)和BinaryOperator (extends BiFunction)。
| 序号 | 接口 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | UnaryOperator<T> |
提供单个类型参数,并且返回一个与输入参数类型一致的结果 |
| 2 | BinaryOperator<T> |
提供两个相同类型参数,并且返回结果与输入参数类型一致的结果 |
| 3 | DoubleBinaryOperator | 提供两个double参数并且返回double结果 |
| 4 | DoubleUnaryOperator | 提供单个double参数并且返回double结果 |
| 5 | IntBinaryOperator | 提供两个int参数并且返回int结果 |
| 6 | IntUnaryOperator | 提供单个int参数并且返回int结果 |
| 7 | LongBinaryOperator | 提供两个long参数并且返回long结果 |
| 8 | LongUnaryOperator | 提供单个long参数并且返回long结果 |
6.1UnaryOperator<T>
| 接口方法 | 方法描述 |
|---|---|
| T apply(T t) | 将给定参数应用到函数中 |
| Function<T, R> andThen(Function<? super R,? extends V> after) | 返回一个组合函数,该函数结果应用到after函数中 |
| Function<T, R> compose(Function<? super V,? extends T> before) | 返回一个组合函数,首先将入参应用到before函数,再将before函数结果应用到该函数中 |
①apply(T t)
UnaryOperator<String> unaryOperator = greet -> greet + " Bob!";
System.out.println(unaryOperator.apply("Hello")); // Hello Bob!②andThen(Function<? super T,? extends T> after)
UnaryOperator<String> unaryOperator = greet -> greet + " Bob!";
UnaryOperator<String> unaryOperator1 = greet -> greet + " Jack!";
String greet = unaryOperator.andThen(unaryOperator1).apply("Hello");
System.out.println(greet); // Hello Bob! Jack!③compose(Function<? super T,? extends T> before)
UnaryOperator<String> unaryOperator = greet -> greet + " Bob!";
UnaryOperator<String> unaryOperator1 = greet -> greet + " Jack!";
String greet = unaryOperator.compose(unaryOperator1).apply("Hello");
System.out.println(greet); // Hello Jack! Bob!6.2BinaryOperator<T>
| 接口方法 | 方法描述 |
|---|---|
| T apply(T t, T u) | 根据给定参数执行函数 |
| BiFunction<T,T,T> andThen(Function<? super T,? extends T> after) | 返回一个组合函数,after应用于该函数之后 |
| BinaryOperator maxBy(Comparator<? super T> comparator) | 返回二元操作本身,通过特殊比较器返回最大的元素 |
| BinaryOperator minBy(Comparator<? super T> comparator) | 返回二元操作本身,通过特殊比较器返回最小的元素 |
①apply(T t, T u)
BinaryOperator<String> binaryOperator = (flag, flag1) -> flag + flag1;
System.out.println(binaryOperator.apply("Hello ", "Jack!")); // Hello Jack!②andThen(Function<? super T,? extends T> after)
BinaryOperator<String> binaryOperator = (flag, flag1) -> flag + flag1;
Function<String, String> function = a -> a + "!!!";
System.out.println(binaryOperator.andThen(function).apply("Hello", " Jack")); // Hello Jack!!!③maxBy(Comparator<? super T> comparator)
BinaryOperator<Integer> integerBinaryOperator = BinaryOperator.maxBy(Integer::compareTo);
Integer max = integerBinaryOperator.apply(12, 10);
System.out.println(max); // 12④minBy(Comparator<? super T> comparator)
BinaryOperator<Integer> integerBinaryOperator1 = BinaryOperator.minBy(Integer::compare);
Integer min = integerBinaryOperator1.apply(12, 10);
System.out.println(min); // 106.3DoubleBinaryOperator
| 接口方法 | 方法描述 |
|---|---|
| double applyAsDouble(double left, double right) | 根据给定的参数执行函数 |
①applyAsDouble(double left, double right)
DoubleBinaryOperator doubleBinaryOperator = (doub1, doub2) -> doub1
+ doub2;
System.out.println(doubleBinaryOperator.applyAsDouble(1.1, 2.3)); // 3.46.4DoubleUnaryOperator
| 接口方法 | 方法描述 |
|---|---|
| double applyAsDouble(double operand) | 根据给定参数执行函数 |
| DoubleUnaryOperator andThen(DoubleUnaryOperator after) | 返回一个组合函数,after应用于该函数之后 |
| DoubleUnaryOperator compose(DoubleUnaryOperator before) | 返回一个组合函数,before应用于该函数之前 |
①applyAsDouble(double operand)
DoubleUnaryOperator doubleUnaryOperator = doub -> doub + 2.5;
System.out.println(doubleUnaryOperator.applyAsDouble(2.6)); // 5.1②andThen(DoubleUnaryOperator after)
DoubleUnaryOperator doubleUnaryOperator = doub -> doub + 2.5;
DoubleUnaryOperator doubleUnaryOperator1 = doub -> doub * 3;
double result = doubleUnaryOperator.andThen(doubleUnaryOperator1)
.applyAsDouble(10);
System.out.println(result); // (10 + 2.5) * 3 = 37.5③compose(DoubleUnaryOperator before)
DoubleUnaryOperator doubleUnaryOperator = doub -> doub + 2.5;
DoubleUnaryOperator doubleUnaryOperator1 = doub -> doub * 3;
double result = doubleUnaryOperator.compose(doubleUnaryOperator1)
.applyAsDouble(10);
System.out.println(result); // 10 * 3 + 2.5 = 32.5本文参考:
Java 8 新特性-Function函数式接口
Java 8 函数式接口
https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/lang/FunctionalInterface.html
https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/function/package-summary.html#package.description