本文内容
- 如何声明通知
- 如何传递参数到通知方法中
- 多种通知多个切面的通知顺序
- 多个切面通知的顺序源码分析与图解
声明通知
Spring中有5种通知,通过对应的注解来声明:
@BeforeBefore 通知,用于方法执行前增强@AfterReturning:After Returning 通知,方法正常执行返回后增强@AfterThrowing:After Throwing 通知,方法执行通过抛出异常退出时@After:After (Finally) 通知,方法执行退出时执行增强,不管是正常返回,还是抛出异常退出,相当于try{}catch{}finally{}中的finally的语句。@Around:Around 通知,最强大的通知,环绕在目标方法前后执行。它有机会在方法运行之前和之后进行工作,并确定该方法何时、如何以及是否真正开始运行
始终使用满足您要求的最不强大的通知形式(也就是说,如果前置通知可以使用,请不要使用环绕通知)。
简单的使用通过一个综合实例来说明,具体的通知再详细说明。
综合案例
目标类,2个方法,一个正常执行,一个抛出异常。
package com.crab.spring.aop.demo03.advice;
/**
* @author zfd
* @version v1.0
* @date 2022/2/7 11:31
* @关于我 请关注公众号 螃蟹的Java笔记 获取更多技术系列
*/
public class Service1 {
/**
* 正常执行的方法
*/
public String hello(String name) {
System.out.println("hello " + name);
return "hello " + name + "!";
}
/**
* 执行抛出异常的方法
*/
public void throwException() {
System.out.println("throws a runtime exception");
throw new RuntimeException("方法执行异常了");
}
}
切面中的通知
@Aspect // 切面
public class CommonCaseAspect {
/**
* 公共切点
* 匹配Service1的所有方法
*/
@Pointcut("execution(* com.crab.spring.aop.demo03.advice.Service1.*(..))")
public void pc(){
}
/**
* 前置通知
*/
@Before("pc()")
public void before(JoinPoint joinpoint){
System.out.println("Before: " + joinpoint);
}
/**
* 返回通知
*/
@AfterReturning("pc()")
public void afterReturning(JoinPoint joinpoint){
System.out.println("AfterReturning: " + joinpoint);
}
/**
* 抛出异常通知
*/
@AfterThrowing("pc()")
public void afterThrowing(JoinPoint joinpoint){
System.out.println("AfterThrowing: " + joinpoint);
}
/**
* 最终通知
*/
@After("pc()")
public void after(JoinPoint joinpoint){
System.out.println("After: " + joinpoint);
}
/**
* 最终通知
*/
@Around("pc()")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint pdj) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("Around start: " + pdj);
Object ret = pdj.proceed();
System.out.println("Around end: " + pdj);
return ret;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Service1 target = new Service1();
AspectJProxyFactory proxyFactory = new AspectJProxyFactory();
proxyFactory.setTarget(target);
// 添加切面
proxyFactory.addAspect(CommonCaseAspect.class);
Service1 proxy = proxyFactory.getProxy();
// 方法调用
proxy.hello("xx");
System.out.println("\n执行异常的结果:");
proxy.throwException();
}
}
正常执行方法的结果,不会触发 @AfterThrowing 通知
Around start: execution(void com.crab.spring.aop.demo03.advice.Service1.hello(String))
Before: execution(void com.crab.spring.aop.demo03.advice.Service1.hello(String))
hello xx
AfterReturning: execution(void com.crab.spring.aop.demo03.advice.Service1.hello(String))
After: execution(void com.crab.spring.aop.demo03.advice.Service1.hello(String))
Around end: execution(void com.crab.spring.aop.demo03.advice.Service1.hello(String)
方法执行异常的结果,不会触发@AfterReturning通知
执行异常的结果:
Around start: execution(void com.crab.spring.aop.demo03.advice.Service1.throwException())
Before: execution(void com.crab.spring.aop.demo03.advice.Service1.throwException())
throws a runtime exception
AfterThrowing: execution(void com.crab.spring.aop.demo03.advice.Service1.throwException())
After: execution(void com.crab.spring.aop.demo03.advice.Service1.throwException())
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.RuntimeException: 方法执行异常了
@Before
前置通知比较简单,不深入讲解。
@After
最终通知比较简单,不深入讲解。
@AfterReturning
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
public @interface AfterReturning {
String pointcut() default "";
// 返回值名称
String returning() default "";
}
可以通过returning指定注入的返回值的名称,需要注意的是通知方法中的返回值类型,只有返回类型和指定的类型或其子类型一致时,通知方法才会执行。使用Object可接收所有返回类型。
案例说明
定义目标对象3个方法,返回值类型分别是String、Long、void。
public class Service2 {
public String getString() {
System.out.println("Service2 getString");
return "xxx";
}
public Long getLong() {
System.out.println("Service2 getLong");
return 100L;
}
public void m() {
System.out.println("Service2 m");
}
}
通知和测试方法
@Aspect
public class AfterReturningAdvice {
/**
*
*/
@Pointcut("execution(* com.crab.spring.aop.demo03.advice.Service2.*(..))")
public void pc(){
}
/**
* 返回通知通过获取returning返回值名称,
* 注意方法中的第二个参数的类型,仅返回指定类型的值的方法才会增强
*/
@AfterReturning(pointcut = "pc()", returning = "retVal")
public void afterReturning1(JoinPoint joinpoint, Object retVal) {
System.out.println("AfterReturning 返回 Object : " + retVal);
}
/**
* 返回通知通过获取returning返回值名称,
* 注意方法中的第二个参数的类型,仅返回指定类型String的值的方法才会增强
*/
@AfterReturning(pointcut = "pc()", returning = "retVal")
public void afterReturning1(JoinPoint joinpoint, String retVal) {
System.out.println("AfterReturning 返回 String :" + retVal);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Service2 target = new Service2();
AspectJProxyFactory proxyFactory = new AspectJProxyFactory();
proxyFactory.setTarget(target);
proxyFactory.addAspect(AfterReturningAdvice.class);
Service2 service2 = proxyFactory.getProxy();
service2.getString();
service2.getLong();
service2.m();
}
}
观察下测试结果
Service2 getString
AfterReturning 返回 Object : xxx
AfterReturning 返回 String :xxx
Service2 getLong
AfterReturning 返回 Object : 100
Service2 m
AfterReturning 返回 Object : null
afterReturning1 只拦截返回值为String的方法getString()的执行。
`afterReturning2 拦截所有方法的执行。
@AfterThrowing
public @interface AfterThrowing {
String pointcut() default "";
// 指定抛出的异常参数名称
String throwing() default "";
throwing可以指定注入到通知方法中的异常参数的名称,同时异常参数的类型会限制方法匹配,只有返回指定异常类型或是其子类型才会执行增强方法。java.lang.Throwable匹配所有异常类型。
直接看下案例
public class Service3 {
public void m(){
throw new IllegalStateException("自定义抛出IllegalStateException");
}
public void m2(){
throw new RuntimeException("自定义抛出RuntimeException");
}
}
@Aspect
public class AfterThrowingAdvice {
/**
*
*/
@Pointcut("execution(* com.crab.spring.aop.demo03.advice.Service3.*(..))")
public void pc(){
}
/**
* throwing指定异常参数名称
* 匹配 IllegalStateException
* @param joinpoint
* @param ex
*/
@AfterThrowing(pointcut = "pc()", throwing = "ex")
public void afterThrowing1(JoinPoint joinpoint, IllegalStateException ex) {
System.out.println("AfterThrowing 异常类型 : " + ex);
}
@AfterThrowing(pointcut = "pc()", throwing = "ex")
public void afterThrowing2(JoinPoint joinpoint, Throwable ex) {
System.out.println("AfterThrowing 异常类型 : " + ex);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Service3 target = new Service3();
AspectJProxyFactory proxyFactory = new AspectJProxyFactory();
proxyFactory.setTarget(target);
proxyFactory.addAspect(AfterThrowingAdvice.class);
Service3 service3 = proxyFactory.getProxy();
// service3.m();
service3.m2();
}
}
观察下 service3.m()的输出结果,2个拦截通知都执行了。
AfterThrowing 异常类型 : java.lang.IllegalStateException: 自定义抛出IllegalStateException
AfterThrowing 异常类型 : java.lang.IllegalStateException: 自定义抛出IllegalStateException
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.IllegalStateException: 自定义抛出IllegalStateException
at com.crab.spring.aop.demo03.advice.Service3.m(Service3.java:11)
观察下service3.m2();输出结果,只有afterThrowing1没有匹配到故不执行通知。
AfterThrowing 异常类型 : java.lang.RuntimeException: 自定义抛出RuntimeException
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.RuntimeException: 自定义抛出RuntimeException
@Around
使用 @Around 注释声明环绕通知。通知方法的第一个参数必须是 ProceedingJoinPoint 类型。在通知方法体中,对 ProceedingJoinPoint 调用proceed() 会导致底层目标方法运行。
常用的场景是方法的统计耗时,或是缓存层拦截方法的执行,直接返回缓存的数据,而不执行目标方法。
案例 统计耗时
@Aspect
public class AroundAdvice {
static class MyService {
public String getVal(String name) {
System.out.println("MyService getVal");
return UUID.randomUUID().toString();
}
}
/**
*
*/
@Pointcut("execution(* com.crab.spring.aop.demo03.advice.AroundAdvice.MyService.*(..))")
public void pc() {
}
@Around("pc()")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("统计耗时开始");
long start = System.nanoTime(); //统计耗时开始
Object retVal = joinPoint.proceed();
long end = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println("统计耗时结束");
System.out.println("方法执行耗时纳秒:" + (end - start));
return retVal;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyService target = new MyService();
AspectJProxyFactory proxyFactory = new AspectJProxyFactory();
proxyFactory.setTarget(target);
proxyFactory.addAspect(AroundAdvice.class);
MyService service2 = proxyFactory.getProxy();
service2.getVal("xx");
}
}
观察下输出结果
统计耗时开始
MyService getVal
统计耗时结束
方法执行耗时纳秒:87827000
通知参数
JoinPoint 接口获取信息
上面的例子中,任何通知方法都可以声明 org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint 类型的参数作为其第一个参数,当然环绕通知第一个参数类型是ProceedingJoinPoint,它是 JoinPoint 的子类。
JoinPoint 提供了一些方法来提供对连接点可用状态和关于连接点的静态信息的反射访问,其主要源码如下。
public interface JoinPoint {
// 打印所有通知方法的有用描述
String toString();
// 获取代理对象
Object getThis();
// 获取目标对象
Object getTarget();
// 获取所有的方法参数
Object[] getArgs();
// 返回被增强的方法的描述
Signature getSignature();
}
args传参
之前@AfterReturning可通过retVal将方法结果当做参数传递给通知方法,@AfterThrowing可通过throwing将抛出的异常当做参数传递给通知方法。切点表达式args也可以传递参数给通知方法。如果在 args 表达式中使用参数名称代替类型名称,则在调用通知时,相应参数的值将作为参数值传递。来看一个案例来理解。
定义一个参数对象
public class Account {
private String name;
private String password;
// ...
}
使用args指定参数名
@Aspect
public class UseArgs {
static class MyAccountService {
public void validateAccount(Account account) {
System.out.println("校验Account :" + account);
}
}
/**
*
*/
@Pointcut("execution(* com.crab.spring.aop.demo03.advice.parameter.UseArgs.MyAccountService.*(..))")
public void pc(){
}
/**
* args表达式不再指定参数类型,而是指定了传递到通知方法中的参数名称,参数类型在通知方法中定义了
* 此处指定了Account类型参数为account
* @param account
*/
@Before("pc() && args(account,..)")
public void validateAccountBefore(JoinPoint joinPoint, Account account) {
System.out.println("前置通知,传递的account参数: " + account);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyAccountService target = new MyAccountService();
AspectJProxyFactory proxyFactory = new AspectJProxyFactory();
proxyFactory.setTarget(target);
proxyFactory.addAspect(UseArgs.class);
MyAccountService proxy = proxyFactory.getProxy();
proxy.validateAccount(new Account("xx", "oo"));
}
}
观察下结果
前置通知,传递的account参数: Account{name='xx', password='oo'}
校验Account :Account{name='xx', password='oo'}
在前置通知方法中,已经可以获取到通过args传递的参数了。
@annotaion 传参
类似args表达式进行类型匹配可传递参数,@annotaion匹配模板方法的的注解类型也可以以同样的的方式进行传参。通过案例了解下。
自定义注解
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@interface Auditable {
int value();
}
@annotation不指定注解类型,而是指定参数名称
@Aspect
public class UseAnnotation {
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@interface Auditable {
int value();
}
static class MyAccountService {
@Auditable(100)
public void validateAccount(Account account) {
System.out.println("校验Account :" + account);
}
}
/**
*
*/
@Pointcut("execution(* com.crab.spring.aop.demo03.advice.parameter.UseAnnotation.MyAccountService.*(..))")
public void pc() {
}
/**
* @annotation表达式不再指定目标方法包含的注解类型,而是指定了传递到通知方法中的参数名称,参数类型在通知方法中定义了
* 此处指定了auditable参数,类型是注解 Auditable
*
* @param auditable
*/
@Before("pc() && @annotation(auditable)")
public void validateAccountBefore(JoinPoint joinPoint, Auditable auditable) {
System.out.println("前置通知,@annotation传递的auditable参数: " + auditable);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyAccountService target = new MyAccountService();
AspectJProxyFactory proxyFactory = new AspectJProxyFactory();
proxyFactory.setTarget(target);
proxyFactory.addAspect(UseAnnotation.class);
MyAccountService proxy = proxyFactory.getProxy();
proxy.validateAccount(new Account("xx", "oo"));
}
}
观察下输出结果,通知方法可以获取到作为参数传递的注解了。
前置通知,@annotation传递的auditable参数: @com.crab.spring.aop.demo03.advice.parameter.UseAnnotation$Auditable(value=100)
校验Account :Account{name='xx', password='oo'}
扩展一下:其它的匹配类型的切点表达式都可以通过类似的方法进行传递参数:
this代理对象target目标对象@within@target@args
传递泛型参数
支持传递泛型参数,单值指定具体类型生效,泛型集合传递无效。看下案例
定义一个泛型接口
public interface Sample<T> {
void sampleGenericMethod(T param);
void sampleGenericCollectionMethod(Collection<T> params);
}
来一个Account的具体类型的实现类
static class MyAccountService implements Sample<Account> {
public void validateAccount(Account account) {
System.out.println("校验Account :" + account);
}
@Override
public void sampleGenericMethod(Account param) {
System.out.println("MyAccountService sampleGenericMethod :" + param);
}
@Override
public void sampleGenericCollectionMethod(Collection<Account> params) {
System.out.println("sampleGenericCollectionMethod: ");
params.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
通过args传递泛型参数和泛型集合参数
@Aspect
public class UseArgsGeneric {
static class MyAccountService implements Sample<Account> {
public void validateAccount(Account account) {
System.out.println("校验Account :" + account);
}
@Override
public void sampleGenericMethod(Account param) {
System.out.println("MyAccountService sampleGenericMethod :" + param);
}
@Override
public void sampleGenericCollectionMethod(Collection<Account> params) {
System.out.println("sampleGenericCollectionMethod: ");
}
}
/**
* 匹配 Sample接口及其子类的sampleGenericMethod方法执行
*/
@Pointcut("execution(* com.crab.spring.aop.demo03.advice.parameter.Sample+.sampleGenericMethod(..))")
public void pc() {
}
/**
* 匹配 Sample接口及其子类的 sampleGenericCollectionMethod 方法执行
*/
@Pointcut("execution(* com.crab.spring.aop.demo03.advice.parameter.Sample+.sampleGenericCollectionMethod(..))")
public void pc2() {
}
/**
* args 传递泛型参数,参数类型指定具体的类型Account
*
*
* @param account
*/
@Before("pc() && args(account,..)")
public void before1(JoinPoint joinPoint, Account account) {
System.out.println("前置通知,传递的account参数: " + account);
}
/**
* args 传递泛型参数,参数类型指定具体的类型String
*
* @param account
*/
@Before("pc() && args(account,..)")
public void before2(JoinPoint joinPoint, String account) {
System.out.println("前置通知,传递的account参数: " + account);
}
/**
* 泛型集合无效
* @param col
*/
@Before("pc() && args(col,..)")
public void before3(JoinPoint joinPoint, Collection<?> col) {
System.out.println("前置通知,传递的集合参数: " + col);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyAccountService target = new MyAccountService();
AspectJProxyFactory proxyFactory = new AspectJProxyFactory();
proxyFactory.setTarget(target);
proxyFactory.addAspect(UseArgsGeneric.class);
MyAccountService proxy = proxyFactory.getProxy();
proxy.sampleGenericMethod(new Account("xx", "oo"));
// before1将拦截
// 观察下集合形式
List<Account> accountList = Arrays.asList(new Account("xx1", "00x"), new Account("00", "xx"), null);
proxy.sampleGenericCollectionMethod(accountList);
}
}
结果如下
前置通知,传递的account参数: Account{name='xx', password='oo'}
MyAccountService sampleGenericMethod :Account{name='xx', password='oo'}
sampleGenericCollectionMethod:
单值的具体类型参数成功传递,而泛型集合无效。
通知顺序
采用结论先上,验证程序后行,最后源码分析收尾顺序来说明。
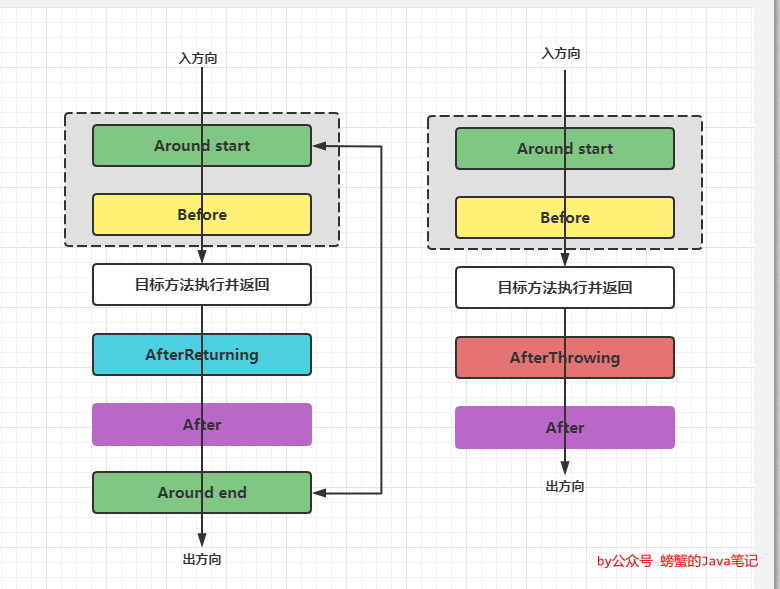
同一个切面内不同通知类型的顺序
-
方法正常执行通知顺序
Around前操作 Before: 目标方法执行 AfterReturning After -
方法抛出异常退出通知顺序
Around前操作 Before 目标方法执行 AfterThrowing After
测试程序如下,含5种通知
package com.crab.spring.aop.demo03.advice.ordering;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.aop.aspectj.annotation.AspectJProxyFactory;
/**
* 同一个切面内不同通知类型的顺序
* @author zfd
* @version v1.0
* @date 2022/2/7 11:34
* @关于我 请关注公众号 螃蟹的Java笔记 获取更多技术系列
*/
@Aspect // 切面
public class CommonAspect {
/**
* 公共切点
* 匹配Service1的所有方法
*/
@Pointcut("execution(* com.crab.spring.aop.demo03.advice.ordering.Service1.*(..))")
public void pc(){
}
/**
* 前置通知
*/
@Before("pc()")
public void before(JoinPoint joinpoint){
System.out.println("Before: " + joinpoint);
}
/**
* 返回通知
*/
@AfterReturning("pc()")
public void afterReturning(JoinPoint joinpoint){
System.out.println("AfterReturning: " + joinpoint);
}
/**
* 抛出异常通知
*/
@AfterThrowing("pc()")
public void afterThrowing(JoinPoint joinpoint){
System.out.println("AfterThrowing: " + joinpoint);
}
/**
* 最终通知
*/
@After("pc()")
public void after(JoinPoint joinpoint){
System.out.println("After: " + joinpoint);
}
/**
* 最终通知
*/
@Around("pc()")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint pdj) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("Around start: " + pdj);
Object ret = pdj.proceed();
System.out.println("Around end: " + pdj);
return ret;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Service1 target = new Service1();
AspectJProxyFactory proxyFactory = new AspectJProxyFactory();
proxyFactory.setTarget(target);
// 添加切面
proxyFactory.addAspect(CommonAspect.class);
Service1 proxy = proxyFactory.getProxy();
// 方法调用
proxy.hello("xx");
System.out.println("\n执行异常的结果:");
proxy.throwException();
}
}
观察下输出结果,符合结论
Around start: execution(String com.crab.spring.aop.demo03.advice.ordering.Service1.hello(String))
Before: execution(String com.crab.spring.aop.demo03.advice.ordering.Service1.hello(String))
hello xx
AfterReturning: execution(String com.crab.spring.aop.demo03.advice.ordering.Service1.hello(String))
After: execution(String com.crab.spring.aop.demo03.advice.ordering.Service1.hello(String))
Around end: execution(String com.crab.spring.aop.demo03.advice.ordering.Service1.hello(String))
执行异常的结果:
Around start: execution(void com.crab.spring.aop.demo03.advice.ordering.Service1.throwException())
Before: execution(void com.crab.spring.aop.demo03.advice.ordering.Service1.throwException())
throws a runtime exception
AfterThrowing: execution(void com.crab.spring.aop.demo03.advice.ordering.Service1.throwException())
After: execution(void com.crab.spring.aop.demo03.advice.ordering.Service1.throwException())
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.RuntimeException: 方法执行异常了
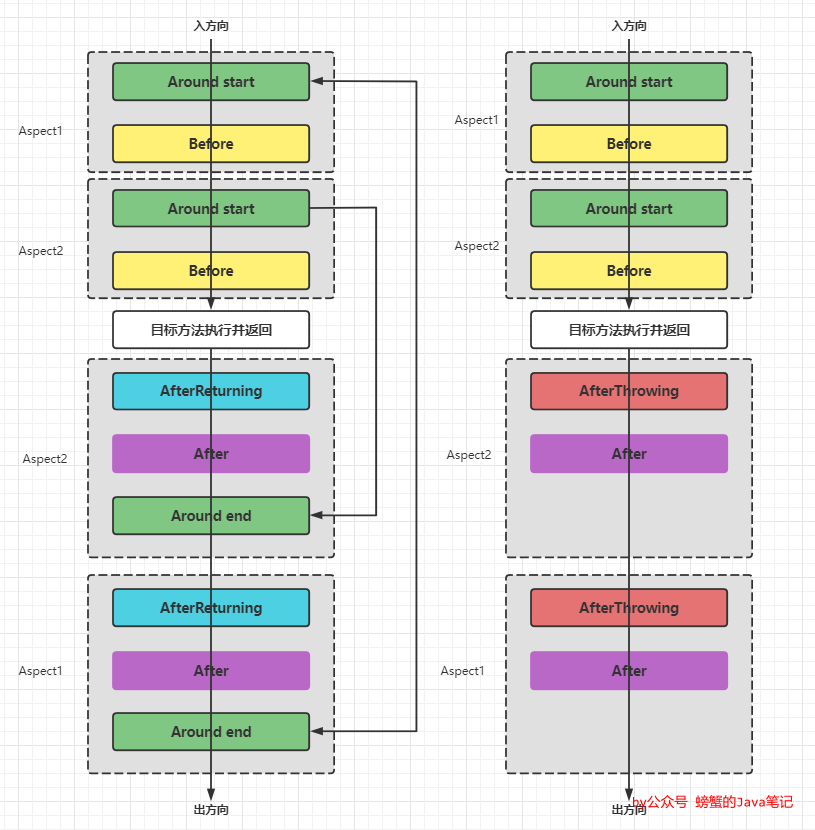
多个切面之间的通知顺序
- 切面级别的优先级可以通过注解
@Order或是实现接口org.springframework.core.Ordered,数值越小优先级越高。 - 类似洋葱圈,前置方向的优先级越高,后置方向的优先级越低。

结论如下(以2个切面为例)
-
方法正常执行
Around1 start Before1 Around2 start Before2 目标方法执行 AfterReturning2 After2 Around2 end AfterReturning Afte Around end -
方法异常退出
执行异常的结果: Around start Before Around2 start Before2 目标方法执行并抛出异常 AfterThrowing2 After2 AfterThrowing After
通知顺序源码分析
之前的2篇源码分析从对象生成和代理方法执行流程分析得比较清晰了,一篇是使用编程式的AOP代理,另外一篇是使用@Aspect声明式AOP代理。所以这里的源码分析着重点是在第二篇的基础上看下注解式的通知方法是如何转换成有序的Advios链,再到有序的MethodInterceptor链,如何执行的。
BeanPostProcessor触发代理对象的生成
之前的分析说过Spring中AOP代理的对象的通过AbstractAutoProxyCreator这个BeanPostProcessor生成的,就已这个为切入点,看一下关键方法。
AbstractAutoProxyCreator#postProcessAfterInitialization方法
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(@Nullable Object bean, String beanName) {
if (bean != null) {
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName);
if (this.earlyProxyReferences.remove(cacheKey) != bean) {
// bean初始化后为需要代理的bean的创建代理对象。
return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);
}
}
return bean;
}
``AbstractAutoProxyCreator#wrapIfNecessary`方法
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) {
// 1、 前面是判断是否需要新创建代理对象
if (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) && this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) {
return bean;
}
if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(this.advisedBeans.get(cacheKey))) {
return bean;
}
if (isInfrastructureClass(bean.getClass()) || shouldSkip(bean.getClass(), beanName)) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
// Create proxy if we have advice.
// 2、获取所有用于增强当前bean的Advisor链
Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null);
if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE);
// 3、创建AOP代理对象
Object proxy = createProxy(
bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean));
this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());
return proxy;
}
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
保持耐心,继续往下看下Advisor链的获取。
获取所有用于增强当前bean的Advisor链
子类AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator#getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean方法获取所有用于增强当前bean的Advisor链
protected Object[] getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(
Class<?> beanClass, String beanName, @Nullable TargetSource targetSource) {
// 1、查找符合的Advisor链
List<Advisor> advisors = findEligibleAdvisors(beanClass, beanName);
if (advisors.isEmpty()) {
return DO_NOT_PROXY;
}
return advisors.toArray();
}
AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator#findEligibleAdvisors方法查找符合的Advisor链
protected List<Advisor> findEligibleAdvisors(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {
// 1、获取候选的Advisos,实际调用其子类的方法实现,InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl对象列表
List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors = findCandidateAdvisors();
// 2、进行筛选Advisor
List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass, beanName);
// 3、添加特殊的 ExposeInvocationInterceptor.ADVISOR 是DefaultPointcutAdvisor对象
extendAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);
if (!eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty()) {
// 4、关键的对Advisor进行排序
eligibleAdvisors = sortAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);
}
return eligibleAdvisors;
}
候选的Advisors主要是子类AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator#findCandidateAdvisors方法实现。
@Override
protected List<Advisor> findCandidateAdvisors() {
// 父类查找Advisor
List<Advisor> advisors = super.findCandidateAdvisors();
// Build Advisors for all AspectJ aspects in the bean factory.
// 从容器中生成 Advisors
if (this.aspectJAdvisorsBuilder != null) {
advisors.addAll(this.aspectJAdvisorsBuilder.buildAspectJAdvisors());
}
return advisors;
}
往下看如何从从容器中生成 Advisors。
容器中切面类中的通知如何生成Advisor
BeanFactoryAspectJAdvisorsBuilder#buildAspectJAdvisors()从切面生成Advisor
public List<Advisor> buildAspectJAdvisors() {
//1、 保存已经找到的切面bean名称,防止每一次都循环一遍所有bean
List<String> aspectNames = this.aspectBeanNames;
// PS: 是否想起了单例模式的双重检查?
// 解析切面beanName并缓存,同时生成Adivsor
if (aspectNames == null) {
synchronized (this) {
aspectNames = this.aspectBeanNames;
if (aspectNames == null) {
List<Advisor> advisors = new ArrayList<>();
aspectNames = new ArrayList<>();
String[] beanNames = BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(
this.beanFactory, Object.class, true, false);
// 2、 循环容器中的beanNames列表
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
if (!isEligibleBean(beanName)) {
continue;
}
Class<?> beanType = this.beanFactory.getType(beanName, false);
if (beanType == null) {
continue;
}
// 3、 bean上面有Aspect就是切面
if (this.advisorFactory.isAspect(beanType)) {
// 添加切面bean缓存
aspectNames.add(beanName);
AspectMetadata amd = new AspectMetadata(beanType, beanName);
if (amd.getAjType().getPerClause().getKind() == PerClauseKind.SINGLETON) {
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory =
new BeanFactoryAspectInstanceFactory(this.beanFactory, beanName); // 4、关键的单个切面的所有通知转换成Advisor链
List<Advisor> classAdvisors = this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory);
if (this.beanFactory.isSingleton(beanName)) {
this.advisorsCache.put(beanName, classAdvisors);
}
else {
this.aspectFactoryCache.put(beanName, factory);
}
advisors.addAll(classAdvisors);
}
else {
// Per target or per this.
if (this.beanFactory.isSingleton(beanName)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Bean with name '" + beanName +
"' is a singleton, but aspect instantiation model is not singleton");
}
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory =
new PrototypeAspectInstanceFactory(this.beanFactory, beanName);
this.aspectFactoryCache.put(beanName, factory);
// 4、关键的单个切面的所有通知转换成Advisor链
advisors.addAll(this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory));
}
}
}
this.aspectBeanNames = aspectNames;
return advisors;
}
}
}
if (aspectNames.isEmpty()) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
// 缓存过切面beanName 直接生成Advisor
List<Advisor> advisors = new ArrayList<>();
for (String aspectName : aspectNames) {
List<Advisor> cachedAdvisors = this.advisorsCache.get(aspectName);
if (cachedAdvisors != null) {
advisors.addAll(cachedAdvisors);
}
else {
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory = this.aspectFactoryCache.get(aspectName);
advisors.addAll(this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory));
}
}
return advisors;
}
单个切面的通知方法是转换成有序的Advisor链的?接着往下看。
单个切面类内的通知如何转成有序的Advisor链
ReflectiveAspectJAdvisorFactory#getAdvisors方法获取Advisor链
@Override
public List<Advisor> getAdvisors(MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory) {
Class<?> aspectClass = aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass();
String aspectName = aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectName();
validate(aspectClass);
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory =
new LazySingletonAspectInstanceFactoryDecorator(aspectInstanceFactory);
List<Advisor> advisors = new ArrayList<>();
// 1、getAdvisorMethods 获取@Aspect切面中所有通知方法
for (Method method : getAdvisorMethods(aspectClass)) {
// 2、getAdvisor转换成Advisor对象,InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl
Advisor advisor = getAdvisor(method, lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory, 0, aspectName);
if (advisor != null) {
// 3、添加到 Advisor链
advisors.add(advisor);
}
}
// ...
return advisors;
}
ReflectiveAspectJAdvisorFactory#getAdvisorMethods方法,获取所有通知方法
private List<Method> getAdvisorMethods(Class<?> aspectClass) {
final List<Method> methods = new ArrayList<>();
// 1、获取所有通知方法
ReflectionUtils.doWithMethods(aspectClass, method -> {
// Exclude pointcuts
if (AnnotationUtils.getAnnotation(method, Pointcut.class) == null) {
methods.add(method);
}
}, ReflectionUtils.USER_DECLARED_METHODS);
if (methods.size() > 1) {
// 2、关键将通知方法排序的排序器
methods.sort(METHOD_COMPARATOR);
}
return methods;
}
通知方法是如何包装成MethodInterceptor的再到Advisor?
ReflectiveAspectJAdvisorFactory#getAdvisor()方法
public Advisor getAdvisor(Method candidateAdviceMethod, MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory,
int declarationOrderInAspect, String aspectName) {
validate(aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass());
AspectJExpressionPointcut expressionPointcut = getPointcut(
candidateAdviceMethod, aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass());
if (expressionPointcut == null) {
return null;
}
// 此处转换成 InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl,里面将通知方法转换成具体通知
return new InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl(expressionPointcut, candidateAdviceMethod,
this, aspectInstanceFactory, declarationOrderInAspect, aspectName);
}
InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl实现了Advisor接口
public InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl(AspectJExpressionPointcut declaredPointcut,
Method aspectJAdviceMethod, AspectJAdvisorFactory aspectJAdvisorFactory,
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory, int declarationOrder, String aspectName) {
// 省略...
else {
// A singleton aspect.
this.pointcut = this.declaredPointcut;
this.lazy = false;
// 将通知方法实例化为通知拦截器MethodInterceptor类
this.instantiatedAdvice = instantiateAdvice(this.declaredPointcut);
}
}
看下InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl#instantiateAdvice方法
private Advice instantiateAdvice(AspectJExpressionPointcut pointcut) {
// 干活的是AspectJAdvisorFactory
Advice advice = this.aspectJAdvisorFactory.getAdvice(this.aspectJAdviceMethod, pointcut,
this.aspectInstanceFactory, this.declarationOrder, this.aspectName);
return (advice != null ? advice : EMPTY_ADVICE);
}
看下干活的ReflectiveAspectJAdvisorFactory#getAdvice()方法是如何将通知方法实例化为通知拦截器MethodInterceptor类的。
public Advice getAdvice(Method candidateAdviceMethod, AspectJExpressionPointcut expressionPointcut,
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory, int declarationOrder, String aspectName) {
Class<?> candidateAspectClass = aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass();
validate(candidateAspectClass);
AspectJAnnotation<?> aspectJAnnotation =
AbstractAspectJAdvisorFactory.findAspectJAnnotationOnMethod(candidateAdviceMethod);
if (aspectJAnnotation == null) {
return null;
}
AbstractAspectJAdvice springAdvice;
// 1、获取注解
switch (aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotationType()) {
case AtPointcut:
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Processing pointcut '" + candidateAdviceMethod.getName() + "'");
}
return null;
// @Around -> AspectJAroundAdvice
case AtAround:
springAdvice = new AspectJAroundAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
break;
// @Before -> AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice
case AtBefore:
springAdvice = new AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
break;
// @After -> AspectJAfterAdvice
case AtAfter:
springAdvice = new AspectJAfterAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
break;
// @AfterReturning -> AspectJAfterReturningAdvice
case AtAfterReturning:
springAdvice = new AspectJAfterReturningAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
AfterReturning afterReturningAnnotation = (AfterReturning) aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotation();
if (StringUtils.hasText(afterReturningAnnotation.returning())) {
springAdvice.setReturningName(afterReturningAnnotation.returning());
}
break;
// @AfterThrowing -> AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice
case AtAfterThrowing:
springAdvice = new AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
AfterThrowing afterThrowingAnnotation = (AfterThrowing) aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotation();
if (StringUtils.hasText(afterThrowingAnnotation.throwing())) {
springAdvice.setThrowingName(afterThrowingAnnotation.throwing());
}
break;
default:
throw new UnsupportedOperationException(
"Unsupported advice type on method: " + candidateAdviceMethod);
}
// Now to configure the advice...
springAdvice.setAspectName(aspectName);
springAdvice.setDeclarationOrder(declarationOrder);
String[] argNames = this.parameterNameDiscoverer.getParameterNames(candidateAdviceMethod);
if (argNames != null) {
springAdvice.setArgumentNamesFromStringArray(argNames);
}
springAdvice.calculateArgumentBindings();
return springAdvice;
}
所以注解通知方法会转成对应的通知类,对应关系如下:
@Around -> AspectJAroundAdvice
@Before -> AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice
@After -> AspectJAfterAdvice
@AfterReturning -> AspectJAfterReturningAdvice
@AfterThrowing -> AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice
接下是切面内的Advisor对应的方法的排序,关键的METHOD_COMPARATOR通知排序器
private static final Comparator<Method> METHOD_COMPARATOR;
static {
// Note: although @After is ordered before @AfterReturning and @AfterThrowing,
// an @After advice method will actually be invoked after @AfterReturning and
// @AfterThrowing methods due to the fact that AspectJAfterAdvice.invoke(MethodInvocation)
// invokes proceed() in a `try` block and only invokes the @After advice method
// in a corresponding `finally` block.
Comparator<Method> adviceKindComparator = new ConvertingComparator<>(
new InstanceComparator<>(
// 此处是通知方法的排序
Around.class, Before.class, After.class, AfterReturning.class, AfterThrowing.class),
(Converter<Method, Annotation>) method -> {
AspectJAnnotation<?> ann = AbstractAspectJAdvisorFactory.findAspectJAnnotationOnMethod(method);
return (ann != null ? ann.getAnnotation() : null);
});
Comparator<Method> methodNameComparator = new ConvertingComparator<>(Method::getName);
METHOD_COMPARATOR = adviceKindComparator.thenComparing(methodNameComparator);
}
单个切面的通知转换成有序的Advisors了,循环多个切面添加到统一的Adivisors链中。
此时是会发现:局部单个切面的Advisor有序,整体多个切面的所有Advisor是无序的,需要再来一次排序。
多个切面生成的Advisor链是如何排序的
回到AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator#findEligibleAdvisors方法
protected List<Advisor> findEligibleAdvisors(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {
// 1、获取候选的Advisos,实际调用其子类的方法实现
List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors = findCandidateAdvisors();
// 局部单个切面的Advisor有序,整体多个切面的所有Advisor是无序的,需要再来一次排序!
// 2、进行筛选Advisor
List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass, beanName);
// 3、添加特殊的 ExposeInvocationInterceptor.ADVISOR 是DefaultPointcutAdvisor对象
extendAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);
if (!eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty()) {
// 4、关键的对Advisor进行排序
eligibleAdvisors = sortAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);
}
return eligibleAdvisors;
}
整体的Advisor链排序的职责是由其子类AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator#sortAdvisors方法实现的
protected List<Advisor> sortAdvisors(List<Advisor> advisors) {
// 用holder包装一下
List<PartiallyComparableAdvisorHolder> partiallyComparableAdvisors = new ArrayList<>(advisors.size());
for (Advisor advisor : advisors) {
partiallyComparableAdvisors.add(
new PartiallyComparableAdvisorHolder(advisor, DEFAULT_PRECEDENCE_COMPARATOR)); // 1 此处添加了一个排序器
}
// 2 使用排序器进行排序
List<PartiallyComparableAdvisorHolder> sorted = PartialOrder.sort(partiallyComparableAdvisors);
if (sorted != null) {
List<Advisor> result = new ArrayList<>(advisors.size());
for (PartiallyComparableAdvisorHolder pcAdvisor : sorted) {
//3 将排序的后的advisor返回
result.add(pcAdvisor.getAdvisor());
}
return result;
}
else {
return super.sortAdvisors(advisors);
}
}
排序器DEFAULT_PRECEDENCE_COMPARATOR 是AnnotationAwareOrderComparator对象
private static final Comparator<Advisor> DEFAULT_PRECEDENCE_COMPARATOR = new AspectJPrecedenceComparator();
/**
* Create a default {@code AspectJPrecedenceComparator}.
*/
public AspectJPrecedenceComparator() {
this.advisorComparator = AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.INSTANCE;
}
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator是Spring提供的一个排序器,用处非常广泛。AnnotationAwareOrderComparator是OrderComparator的扩展,它支持Spring的org.springframework.core.Ordered接口以及@Order和@Priority注解。
package org.springframework.core.annotation;
public class AnnotationAwareOrderComparator extends OrderComparator {
// 实例
public static final AnnotationAwareOrderComparator INSTANCE = new AnnotationAwareOrderComparator();
/**
* 除了超类中的org.springframework.core.Ordered检查外,
* 这个实现还检查各种类型的元素的@Order或@Priority
*/
@Override
@Nullable
protected Integer findOrder(Object obj) {
Integer order = super.findOrder(obj);
if (order != null) {
return order;
}
return findOrderFromAnnotation(obj);
}
// 从 @Order或@Priority 获取排序数值
@Nullable
private Integer findOrderFromAnnotation(Object obj) {
AnnotatedElement element = (obj instanceof AnnotatedElement ? (AnnotatedElement) obj : obj.getClass());
MergedAnnotations annotations = MergedAnnotations.from(element, SearchStrategy.TYPE_HIERARCHY);
Integer order = OrderUtils.getOrderFromAnnotations(element, annotations);
if (order == null && obj instanceof DecoratingProxy) {
return findOrderFromAnnotation(((DecoratingProxy) obj).getDecoratedClass());
}
return order;
}
@Override
@Nullable
public Integer getPriority(Object obj) {
if (obj instanceof Class) {
return OrderUtils.getPriority((Class<?>) obj);
}
Integer priority = OrderUtils.getPriority(obj.getClass());
if (priority == null && obj instanceof DecoratingProxy) {
return getPriority(((DecoratingProxy) obj).getDecoratedClass());
}
return priority;
}
public static void sort(List<?> list) {
if (list.size() > 1) {
list.sort(INSTANCE);
}
}
public static void sort(Object[] array) {
if (array.length > 1) {
Arrays.sort(array, INSTANCE);
}
}
public static void sortIfNecessary(Object value) {
if (value instanceof Object[]) {
sort((Object[]) value);
}
else if (value instanceof List) {
sort((List<?>) value);
}
}
}
通过获取切面类上的的org.springframework.core.Ordered接口或是@Order和@Priority注解对应的排序值,排序后就可以得到整体优先级由高到低的有序的Advisor链。
举个例子,假设Aspect1的优先级是1,Aspect2的优先级是2,那么最终的Advisor链如下。
ExposeInvocationInterceptor.ADVISOR(DefaultPointcutAdvisor)
Aspect1的:
(AspectJAroundAdvice) InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl
(AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice) InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl
(AspectJAfterAdvice) InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl
(AspectJAfterReturningAdvice) InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl
(AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice) InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl
Aspect2的:
(AspectJAroundAdvice) InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl
(AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice) InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl
(AspectJAfterAdvice) InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl
(AspectJAfterReturningAdvice) InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl
(AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice) InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl
MethodInterceptor链执行过程
此处的代理对象是通过CGLIB 方式创建的代理,所以从CglibAopProxy#getProxy()方法入手。
@Override
public Object getProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
try {
// ... 省略非关注的代码
// Configure CGLIB Enhancer...
Enhancer enhancer = createEnhancer();
enhancer.setSuperclass(proxySuperClass);
enhancer.setInterfaces(AopProxyUtils.completeProxiedInterfaces(this.advised));
enhancer.setNamingPolicy(SpringNamingPolicy.INSTANCE);
enhancer.setStrategy(new ClassLoaderAwareGeneratorStrategy(classLoader));
// GGLIB的关键是回调的设置
Callback[] callbacks = getCallbacks(rootClass);
Class<?>[] types = new Class<?>[callbacks.length];
for (int x = 0; x < types.length; x++) {
types[x] = callbacks[x].getClass();
}
// fixedInterceptorMap only populated at this point, after getCallbacks call above
enhancer.setCallbackFilter(new ProxyCallbackFilter(
this.advised.getConfigurationOnlyCopy(), this.fixedInterceptorMap, this.fixedInterceptorOffset));
enhancer.setCallbackTypes(types);
// Generate the proxy class and create a proxy instance.
return createProxyClassAndInstance(enhancer, callbacks);
}
}
关键方法是回调的设置
CglibAopProxy#getProxy()方法,关注关键的拦截器设置,删除了部分不关注代码
private Callback[] getCallbacks(Class<?> rootClass) throws Exception {
// Choose an "aop" interceptor (used for AOP calls).
// AOP相关的拦截器设置 advised 就是AdvisedSupport对象,熟悉的代理配置类
Callback aopInterceptor = new DynamicAdvisedInterceptor(this.advised);
Callback[] mainCallbacks = new Callback[] {
aopInterceptor, // for normal advice
targetInterceptor, // invoke target without considering advice, if optimized
new SerializableNoOp(), // no override for methods mapped to this
targetDispatcher, this.advisedDispatcher,
new EqualsInterceptor(this.advised),
new HashCodeInterceptor(this.advised)
};
Callback[] callbacks;
callbacks = mainCallbacks;
return callbacks;
}
上面将就是AdvisedSupport对象传递给了DynamicAdvisedInterceptor对象。DynamicAdvisedInterceptor应该不陌生,CGLIB的通用的AOP拦截器,代理方法的调用会触发该拦截器的intercept方法。
DynamicAdvisedInterceptor#intercept方法
@Override
@Nullable
public Object intercept(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {
Object oldProxy = null;
boolean setProxyContext = false;
Object target = null;
TargetSource targetSource = this.advised.getTargetSource();
try {
if (this.advised.exposeProxy) {
// Make invocation available if necessary.
oldProxy = AopContext.setCurrentProxy(proxy);
setProxyContext = true;
}
// Get as late as possible to minimize the time we "own" the target, in case it comes from a pool...
target = targetSource.getTarget();
Class<?> targetClass = (target != null ? target.getClass() : null);
// 1、关键的从AdvisedSupport中的Advisor链获取MethodInterceptor链
List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);
Object retVal;
// Check whether we only have one InvokerInterceptor: that is,
// no real advice, but just reflective invocation of the target.
if (chain.isEmpty() && CglibMethodInvocation.isMethodProxyCompatible(method)) {
Object[] argsToUse = AopProxyUtils.adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(method, args);
try {
retVal = methodProxy.invoke(target, argsToUse);
}
catch (CodeGenerationException ex) {
CglibMethodInvocation.logFastClassGenerationFailure(method);
retVal = AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(target, method, argsToUse);
}
}
else {
// We need to create a method invocation...
// 2、包装成 CglibMethodInvocation并执行proceed()
retVal = new CglibMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain, methodProxy).proceed();
}
retVal = processReturnType(proxy, target, method, retVal);
return retVal;
}
finally {
if (target != null && !targetSource.isStatic()) {
targetSource.releaseTarget(target);
}
if (setProxyContext) {
// Restore old proxy.
AopContext.setCurrentProxy(oldProxy);
}
}
}
上面的关键是方法:
-
关键的从AdvisedSupport中的Advisor链获取MethodInterceptor链
主要逻辑是之前分析过的使用适配DefaultAdvisorAdapterRegistry将Advisor中通知包装成对应的
MethodInterceptor类。不过此处注意的是Advisor中的部分通知在前面已经包装成MehtodIntertor的子类对象了,此处就不需要适配转换了,否则需要适配转换如下@Around -> AspectJAroundAdvice @Before -> AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice-> MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor @After -> AspectJAfterAdvice @AfterReturning -> AspectJAfterReturningAdvice->AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor @AfterThrowing -> AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice -
包装成 CglibMethodInvocation并执行proceed(),其实最终执行就是我们分析中的
ReflectiveMethodInvocation.procced,将MehtodIntertor拦截器链有序地执行@Override @Nullable public Object proceed() throws Throwable { // We start with an index of -1 and increment early. if (this.currentInterceptorIndex == this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.size() - 1) { return invokeJoinpoint(); } // 1 获取拦截器链 Object interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice = this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.get(++this.currentInterceptorIndex); // 省略 else { // 2 依次执行拦截器链 return ((MethodInterceptor) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice).invoke(this); } }
5个通知类解析
以单个切面内的通知顺序开始着手调试,直接将断点打到org.springframework.aop.framework.ReflectiveMethodInvocation.proceed()
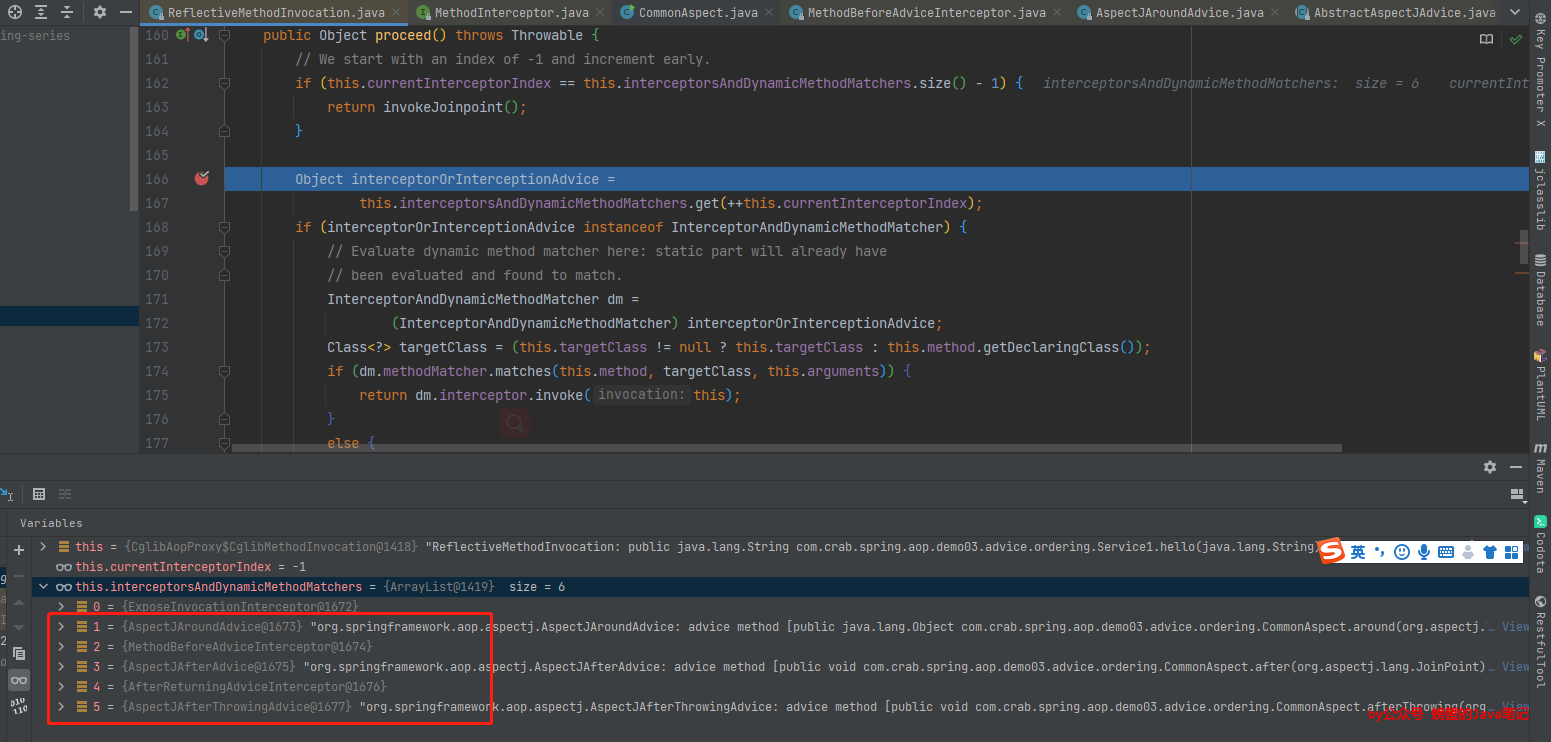
可以看到将执行的拦截器依次如下:
ExposeInvocationInterceptor
ApectJAroundAdvice
MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor
ApectJAfterAdvice
AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor
ApectJAfterThrowingAdvice
第一个之前说过是附加的特殊的拦截器,可以先忽略,来看下其它5个拦截器的类图和对应的通知。
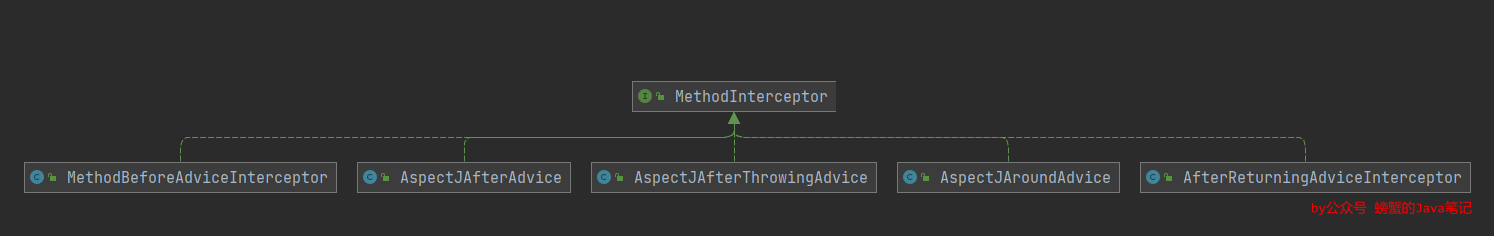
AspectJAroundAdvice 类
注意观察执行过程,后面的类类似
public class AspectJAroundAdvice extends AbstractAspectJAdvice implements MethodInterceptor, Serializable {
public AspectJAroundAdvice(
Method aspectJAroundAdviceMethod, AspectJExpressionPointcut pointcut, AspectInstanceFactory aif) {
super(aspectJAroundAdviceMethod, pointcut, aif);
}
@Override
public boolean isBeforeAdvice() {
return false;
}
@Override
public boolean isAfterAdvice() {
return false;
}
@Override
protected boolean supportsProceedingJoinPoint() {
return true;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {
if (!(mi instanceof ProxyMethodInvocation)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("MethodInvocation is not a Spring ProxyMethodInvocation: " + mi);
}
ProxyMethodInvocation pmi = (ProxyMethodInvocation) mi;
ProceedingJoinPoint pjp = lazyGetProceedingJoinPoint(pmi);
JoinPointMatch jpm = getJoinPointMatch(pmi);
// 1 调用around的增强方法
return invokeAdviceMethod(pjp, jpm, null, null);
}
}
MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor 类
注意观察执行过程,后面的类类似
public class MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor, BeforeAdvice, Serializable {
private final MethodBeforeAdvice advice;
public MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor(MethodBeforeAdvice advice) {
Assert.notNull(advice, "Advice must not be null");
this.advice = advice;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {
// 1 执行前置通知
this.advice.before(mi.getMethod(), mi.getArguments(), mi.getThis());
// 2 进入下一个拦截器
return mi.proceed();
}
}
AspectJAfterAdvice 类
public class AspectJAfterAdvice extends AbstractAspectJAdvice
implements MethodInterceptor, AfterAdvice, Serializable {
public AspectJAfterAdvice(
Method aspectJBeforeAdviceMethod, AspectJExpressionPointcut pointcut, AspectInstanceFactory aif) {
super(aspectJBeforeAdviceMethod, pointcut, aif);
}
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {
try {
// 1 先执行下一个拦截器链 在try-finally中
return mi.proceed();
}
finally {
// 2 调用最终通知方法
invokeAdviceMethod(getJoinPointMatch(), null, null);
}
}
}
AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor 类
public class AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor, AfterAdvice, Serializable {
private final AfterReturningAdvice advice;
public AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor(AfterReturningAdvice advice) {
Assert.notNull(advice, "Advice must not be null");
this.advice = advice;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {
//1 先执行下一个拦截器,等待返回结果
Object retVal = mi.proceed();
// 2 后执行返回通知
this.advice.afterReturning(retVal, mi.getMethod(), mi.getArguments(), mi.getThis());
// 3 返回通知处理后的结果
return retVal;
}
}
AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice 类
public class AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice extends AbstractAspectJAdvice
implements MethodInterceptor, AfterAdvice, Serializable {
public AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice(
Method aspectJBeforeAdviceMethod, AspectJExpressionPointcut pointcut, AspectInstanceFactory aif) {
super(aspectJBeforeAdviceMethod, pointcut, aif);
}
@Override
public boolean isBeforeAdvice() {
return false;
}
@Override
public boolean isAfterAdvice() {
return true;
}
@Override
public void setThrowingName(String name) {
setThrowingNameNoCheck(name);
}
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {
try {
// 1 先执行下一个通知链 在try-catch
return mi.proceed();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (shouldInvokeOnThrowing(ex)) {
// 2 后执行异常抛出后通知
invokeAdviceMethod(getJoinPointMatch(), null, ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
/**
* 通知类型是否和@AfterThrowing.throwing配置的通知类型匹配
*/
private boolean shouldInvokeOnThrowing(Throwable ex) {
return getDiscoveredThrowingType().isAssignableFrom(ex.getClass());
}
}
图解模拟
单个切面5个通知
- 紫色:拦截器链自上而下递归执行
- 蓝色:目标方法无异常,拦截器链自下而上递归返回
- 红色:目标方法有异常,拦截器链自下而上递归返回
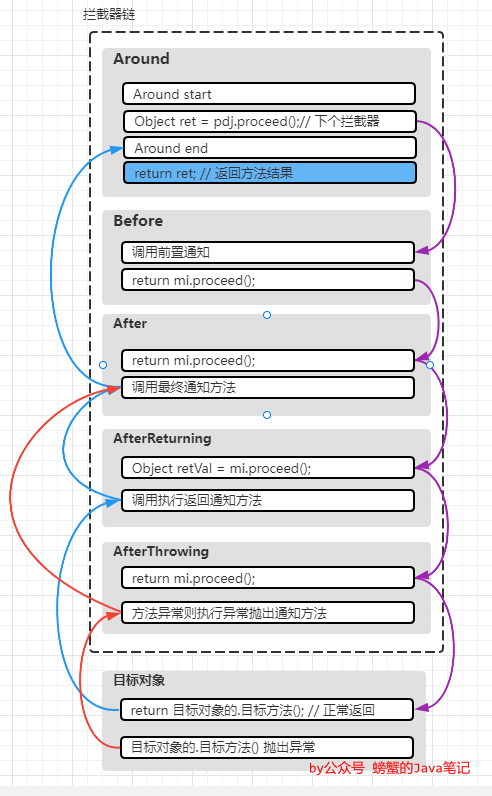
结合上面的图和5个通知的invoke方法逻辑,伪代码如下:
{
Around start
{
Before invoke()
{
try{
{
{
try{
目标方法执行()
}catche(Throwable ex){
AfterThrowing.invoke()
}
}
AfterReturning invoke()
}
} finally{
After invoke()
}
}
}
Around end
}
2个切面10个通知
2个切面10个通知的执行图解如下:
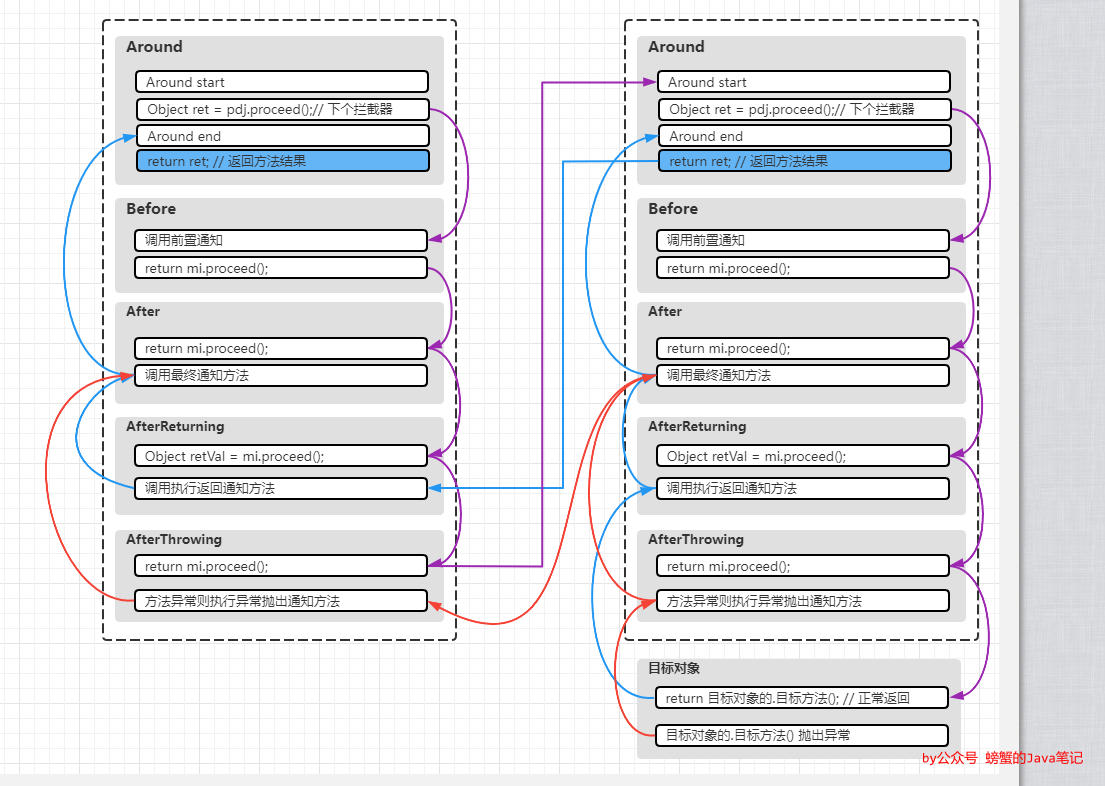
结合上面的图和5个通知的invoke方法逻辑,伪代码如下:
{
Around start
{
Before invoke()
{
try{
{
{
try{
// 目标方法执行() 此处套娃下一个切面的通知
{
Around2 start
{
Before2 invoke()
{
try{
{
{
try{
目标方法执行()
}catche(Throwable ex){
AfterThrowing2.invoke()
}
}
AfterReturning2 invoke()
}
} finally{
After2 invoke()
}
}
}
Around2 end
}
}catche(Throwable ex){
AfterThrowing.invoke()
}
}
AfterReturning invoke()
}
} finally{
After invoke()
}
}
}
Around end
}
总结
本文介绍如何声明通知、如何传递参数到通知方法中、多种通知多个切面的通知顺序源码分析与图解。
本篇源码地址:https://github.com/kongxubihai/pdf-spring-series/blob/main/spring-series-aop/src/main/java/com/crab/spring/aop/demo03/advice
知识分享,转载请注明出处。学无先后,达者为先!