1.安装
DOS在线安装:
python -m pip install pytest
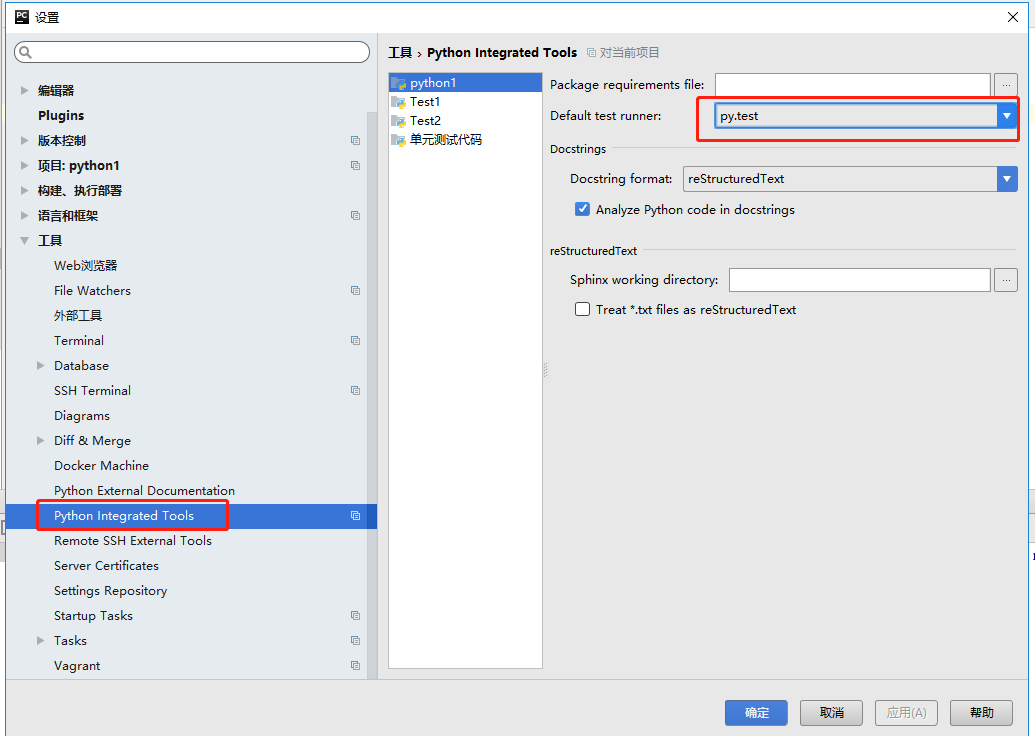
注意:在pycharm上运行pytest脚本前,需要修改pycharm配置:
文件---配置---工具---Default test runner:修改为py.test
2.Pytest断言
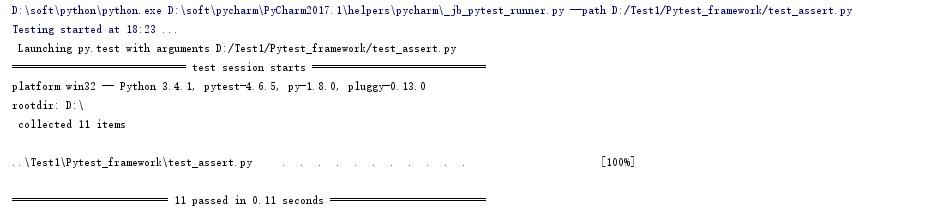
import pytest # 功能:用于计算a 与 b 相加的和 def add(a, b): return a + b # 功能:用于判断素数 def is_prime(n): if n <= 1: return False for i in range(2, n): if n % i == 0: return False return True # 测试相等 def test_add_1(): assert add(3, 4) == 7 # 测试不相等 def test_add_2(): assert add(17, 22) != 50 # 测试大于等于 def test_add_3(): assert add(17, 22) <= 50 # 测试小于等于 def test_add_4(): assert add(17, 22) >= 38 # 测试包含 def test_in(): a = 'hello' b = 'he' assert b in a # 测试不包含 def test_not_in(): a = 'hello' b = 'hi' assert b not in a # 判断是否为True def test_true_1(): assert is_prime(13) # 判断是否为True def test_true_2(): assert is_prime(7) is True # 判断是否不为True def test_true_3(): assert not is_prime(4) # 判断是否不为True def test_true_4(): assert is_prime(6) is not True # 判断是否为False def test_false_1(): assert is_prime(8) is False if __name__ == '__main__': pytest.main()
运行结果:
3.Fixture
用来对测试方法,测试函数,测试类和整个测试文件进行初始化或还原测试环境
import pytest # 功能函数 def multiply(a, b): return a * b class TestMultiply: # ========= Fixture ======== @classmethod def setup_class(cls): # 在当前测试类的开始执行 print("setup_class ==========>") def teardown_class(cls): # 在当前测试类的结束执行 print("teardown_class==========>") def setup_method(self, method): # 在每个测试方法开始执行 print("setup_method------>") def teardown_mehod(self, method): # 在每个测试方法结束执行 print("teardown_method------>") def setup(self): # 在每个测试方法之前执行,等效于setup_method() print("setup---->") def teardown(self): # 在每个测试方法之后执行,等效于teardown_method(function) print("teardown------>") # ========= 测试用例 ======== def test_multiply_3_4(self): print("test_number_3_4") assert multiply(3, 4) == 12 def test_multiply_a_3(self): print("test_string_a_3") assert multiply('a', 3) == 'aaa' if __name__ == '__main__': pytest.main()
运行结果为:

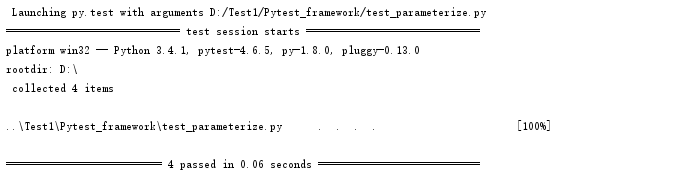
4.参数化
import pytest import math # pytest参数化 @pytest.mark.parametrize( "base, exponent, expected", # 定义参数名称 [(2, 2, 4), (2, 3, 8), (1, 9, 1), (0, 9, 0)], ids=["case1", "case2", "case3", "case4"] # 定义测试用例名称 ) def test_pow(base, exponent, expected): assert math.pow(base, exponent) == expected if __name__ == '__main__': pytest.main()
运行结果: