Flex布局相对于以前我们经常所用到的布局方式要好的很多,在做微信小程序的时候要既能符合微信小程序的文档开发要求,又能使用不同以往的居中方式并减少css的相关样式声明。
先来看看关于flex的一张图:
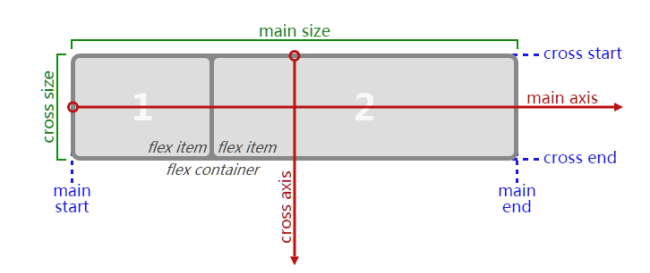
从上面可以看到一些flexbox的相关信息,
main axis 和 cross axis 指的是flexbox内部flex项目(flex item)的排列方向,通俗点说就是,里面的flex项目是按照横轴或者纵轴排列的顺序方向。
main start 和 main end 是指项目的开始和项目的结束是按照排列方向的起点和终点。
再来看看flex的相关属性:
我们给定一个结构:
<div class="container"> <div class="item1"></div> <div class="item2"></div> <div class="item3"></div> ... </div>
在微信小程序里面可以是这样的结构:
<view class="container"> <view class="item1"></view> <view class="item2"></view> <view class="item3"></view> ... </view>
当我们要用时这个布局的时候对于外层的结构,我们对他的css样式设定:
<style type="text/css"> .container{ display: flex; /*or inline-flex*/ } </style>
接下来我们就需要来规定这个item排列的方向了,依旧对外层结构css设定:
.container{ display: flex; /*or inline-flex*/ flex-direction: row; }
flex-direction这个属性是用来规定flex项目在轴方向上面排列的顺序,
他有这样几个属性:
flex-direction: row | row-reverse | column | column-reverse;
row
如果规定的方向是 ltr(left to right)项目一次从左往右排列,
如果规定的方向是 rtl(right to left)项目一次从右往左排列,
row是默认值。
row-reverse
如果规定的方向是 ltr(left to right)项目一次从右往左排列,
如果规定的方向是 rtl(right to left)项目一次从左往右排列,
row 和 row-reverse 是相反的。
column 跟row是类似的,只不过是从上到下的方向排列的。
column-reverse 跟row-reverse 是类似的,只不过是从下到上的方向排列的。
对于有时候,并不想让所有的项目都在一行排列的话(多行显示),我们添加flex-wrap:
.container{ display: flex; /*or inline-flex*/ flex-direction: row; flex-wrap:wrap; }
lex-wrap是决定项目是否多行显示的属性,项目默认情况下是在一行下显示的。
flex-wrap: nowrap | wrap | wrap-reverse;
nowrap 指的是在一行显示不换行;
wrap 指的是多行显示;
wrap-reverse 指的是多行显示,但是跟规定排列方向相反;
flex-flow是 flex-direction 和 flex-wrap 的缩写
flex-flow: <‘flex-direction’> || <‘flex-wrap’>
上面css即:
.container{ display: flex; /*or inline-flex*/ flex-flow:row wrap; }
在我们一些需要构建的布局里,我们还需要去让他能够自由的伸缩,这也是flex布局的优势之一,能够极大的方便我们去提升效率。
用于在主轴上对齐伸缩的项目属性:justify-content。他的属性有:
justify-content: flex-start | flex-end | center | space-between | space-around;
不同属性值下他的表现:
css样式为:
.container{ width: 100%; height: 400px; background-color: #ccc; display: flex; /*or inline-flex*/ flex-flow:row wrap; justify-content:flex-start; } .item{ flex:0 0 30%; } .item1{background-color:#0074e0;} .item{background-color:#008c00;} .item3{background-color:#be0000;}
flex-start

flex-end

center

space-between

space-around

flex-start(默认值),项目向起始位置靠齐,第一个项目所在轴的起点位置对齐,后面的项目与前一个项目的边外边对齐。
flex-end,项目向结束位置,最后一个项目所在轴的终点位置对齐,前面的项目与后一个项目的边外边对齐。
center,项目向一行的中间位置对齐,可以说成是此行的居中对齐。在某些居中需求下的css样式布局既可以选择这个样式声明
space-between,项目会平均的分布在一行里面。项目的第一项和最后一项会与轴的起点和终点边靠齐。其他的项目则平均分布早剩余的空间里面。
space-around,项目会平均分布在一行里。两端会保留一半的空间。
在多行存在的情况,有一个和justify-content类似的属性,只不过他是作用在相对于轴的垂直方向上的。属性值如下:
align-content: flex-start | flex-end | center | space-between | space-around | stretch;
不同属性值下的表现:(横轴上规定的是 flex-start)
css样式为:
.container{ width: 100%; height: 400px; background-color: #ccc; display: flex;/*or inline-flex*/ flex-flow:row wrap; justify-content:flex-start; align-content: flex-start; } .item{ flex:0 0 30%; min-height: 100px; } .item1,.item6{background-color:#0074e0;} .item2{background-color:#008c00;} .item5{background-color:#234567;} .item3,.item4{background-color:#be0000;}
flex-start

flex-end
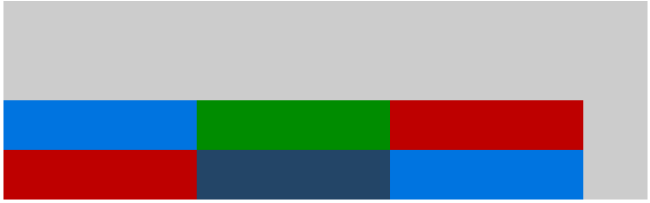
center
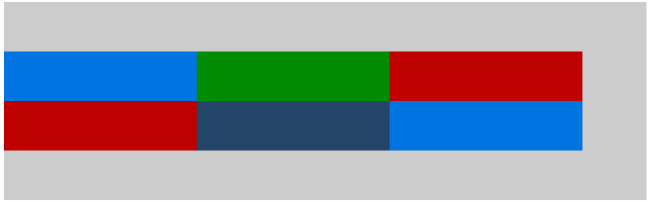
space-between
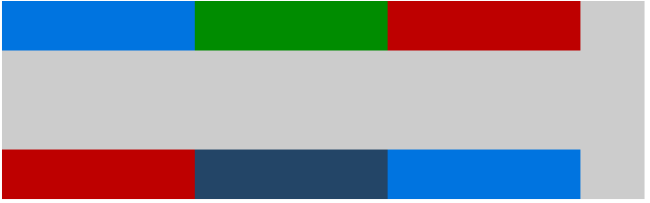
space-around
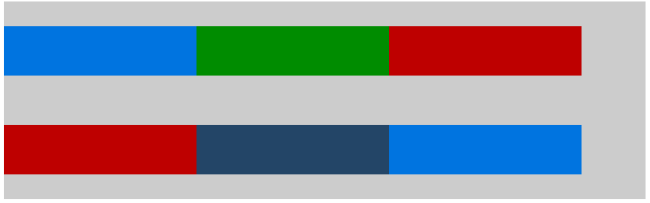
flex-start(默认值),项目向起始位置靠齐,第一个项目所在轴的起点位置对齐,后面的项目与前一个项目的边外边对齐。
flex-end,项目向结束位置,最后一个项目所在轴的终点位置对齐,前面的项目与后一个项目的边外边对齐。
center,项目向一行的中间位置对齐,可以说成是此行的居中对齐。在某些居中需求下的css样式布局既可以选择这个样式声明
space-between,项目会平均的分布在一行里面。项目的第一项和最后一项会与轴的起点和终点边靠齐。其他的项目则平均分布早剩余的空间里面。
space-around,项目会平均分布在一行里。两端会保留一半的空间。
虽然方式跟justify-content是一样的,但是因为轴的不同起始点和终点是不同的,所以显示的方式是一直的,但是方向上的效果看起来会有点差异。
关于stretch 由于上面的项目设定了高度,当项目的高度不是固定值得时候,stretch的表现如下:

也就是说侧轴的长度是不是固定值得时候,各行会扩大占据剩下的空间。
接下来 在介绍两个属性,align-items 和 align-self
align-items: flex-start | flex-end | center | baseline | stretch;
align-self: auto | flex-start | flex-end | center | baseline | stretch;
align-items是在所有项目上的对齐方式。
align-self是在单独的项目上的对齐方式。
不同属性值下的表现:(横轴上规定的是 flex-start)
css样式为:
.container{ width: 100%; height: 400px; background-color: #ccc; display: flex;/*or inline-flex*/ flex-flow:row wrap; justify-content:flex-start; align-items: flex-start; } .item{ flex:0 0 30%; min-height: 100px; }
align-items: flex-start

align-self: flex-start

修改样式:(后面的修改下同)
.container{ width: 100%; height: 400px; background-color: #ccc; display: flex;/*or inline-flex*/ flex-flow:row wrap; justify-content:flex-start; /*align-items: flex-start;*/ } .item{ flex:0 0 30%; min-height: 100px; max-height: 300px; } .item:nth-child(2){ max-height: 200px; align-self: flex-start; }
align-items: flex-end

align-self: flex-end

align-items: center;

align-self: center;

align-items:baseline;

align-self:baseline;(为了更好的能看出效果这里限制所有的项目最小高度为100px最大高度不定)

align-items: stretch; / align-self: stretch;
侧轴的长度属性为auto 这个值会使外边距盒子的尺寸按照min/max 的长度接近所在行的尺寸
另外:float clear vertical-align 在flex布局里里面是无效的。
属性介绍到这里,就来先看看这个布局的灵活性是如何体现的。
当只有一个flex项目的时候,结构如此下:
<div class="container"> <div class="item1"></div> </div>
在微信小程序里面可以是这样的结构:
<view class="container"> <view class="item1"></view> </view>
给他设定才css样式,
.container{ width: 100%; height: 400px; background-color: #ccc; display: flex; flex-flow:row wrap; justify-content:flex-start; } .item1{ background-color: #0074e0; width: 50px; height: 50px; }
显示是这样的:

但是要让他完全居中的样子,比如:

css样式设定如下
.container{ width: 100%; height: 400px; background-color: #ccc; display: flex; flex-flow:row wrap; justify-content:center; /*样式修改在这里*/ align-items: center; /*样式修改在这里*/ } .item1{ background-color: #0074e0; width: 100px; height:100px; }
现在让他在右下角显示如下:

CSS样式设置:
.container{ width: 100%; height: 400px; background-color: #ccc; display: flex; flex-flow:row wrap; justify-content:flex-end; /*样式修改在这里*/ align-items:flex-end; /*样式修改在这里*/ } .item1{ background-color: #0074e0; width: 100px; height:100px; }
在加上一个项目:(后面新增不再赘述)
<div class="container"> <div class="item1"></div> <div class="item2"></div> </div>
在微信小程序里面可以是这样的结构:
<view class="container"> <view class="item1"></view> <view class="item2"></view> </view>
左上横排

.container{ width: 100%; height: 400px; background-color: #ccc; display: flex; flex-flow:row wrap; justify-content:flex-start; align-items:flex-start; }
水平方向居中

.container{ width: 100%; height: 400px; background-color: #ccc; display: flex; flex-flow:row wrap; justify-content:center; align-items:flex-start; }
两个项目不贴在一起

.container{ width: 100%; height: 400px; background-color: #ccc; display: flex; flex-flow:row wrap; justify-content:space-around; align-items:flex-start; }
从上面的列子看来,仅仅只是就该某些css的属性,就能达到以前需要花大量css样式的声明才能达到的效果。
跟新。。。写糊涂了。再次感谢指出错误。
再来看看下面这个
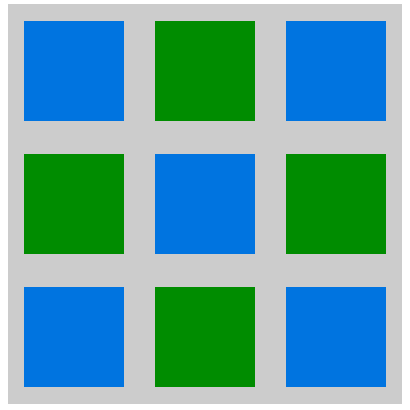
html的结构如下:
<div class="container"> <div class="row"> <div class="item1"></div> <div class="item2"></div> <div class="item1"></div> </div> <div class="row"> <div class="item2"></div> <div class="item1"></div> <div class="item2"></div> </div> <div class="row"> <div class="item1"></div> <div class="item2"></div> <div class="item1"></div> </div> </div>
css样式如下:
.container{ width: 400px; height: 400px; background-color: #ccc; display: flex; flex-wrap: wrap; align-content: space-around; } .row{ display:flex; flex-basis: 100%; justify-content:space-around; } .item1, .item2{ width: 100px; height:100px; } .item1{ background-color: #0074e0; } .item2{ background-color: #008c00; }
仅仅只是添加下一条css样式,然后增加项目个数,修改下外框的宽高度就有这样的效果显示。
一些基本的flex布局的样式就说到这里了,这只是一个很小的点,其他的更多的是体现出这布局项目里面的伸缩的计算方式 排列方式,如:order flex-grow flex-shrink flex-basis 等。更多的技巧则需要自己去深层次的探索。这里仅仅只是基础,大神们无视就好。
附加:简单的说下flex-basis: 100%; 这个属性定义了Flex项目在分配Flex容器剩余空间之前的一个默认尺寸。