1 接口
1-1 基本接口说明
Springboot启动源码
package com.village.dog;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
private static final Logger logging = LoggerFactory.getLogger(Application.class);
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(Application.class,args);
}
}
BeanFactory接口:用于访问Spring容器的根接口
简介:实现BeanFactory接口的Object容纳多个bean definition,
每个bean definition通过唯一的字符串名称进行区别。
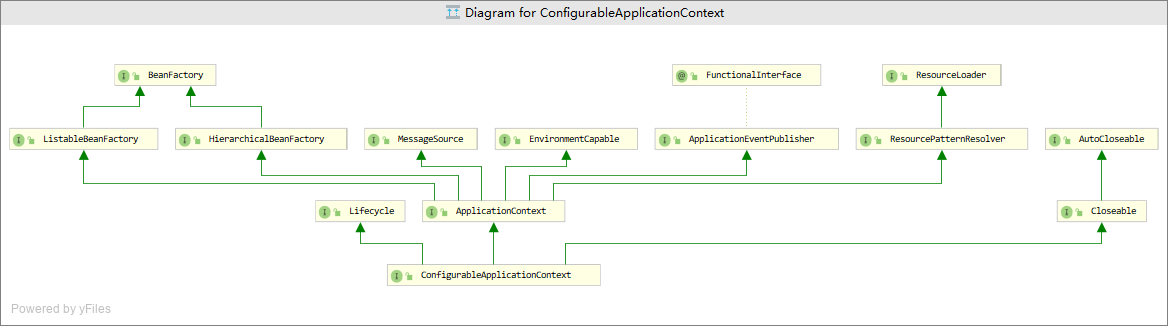
ApplicationContext接口:为应用提供配置的核心接口
| 接口支持功能 | 所对应的父接口 |
|---|---|
| 用于访问应用组件的工厂方法 | org.springframework.beans.factory.ListableBeanFactory |
| 加载文件资源的能力 | org.springframework.core.io.ResourceLoader |
| 向已注册的监听对象发布事件的能力 | ApplicationEventPublisher |
| 解析消息,支持国际化 | MessageSource |
说明:类图中可看到ApplicationContext接口继承BeanFactory接口,此外还继承了其他很多接口。
Java中接口可通过extends关键字继承一个或多个接口
1-2 BeanFactory实现类
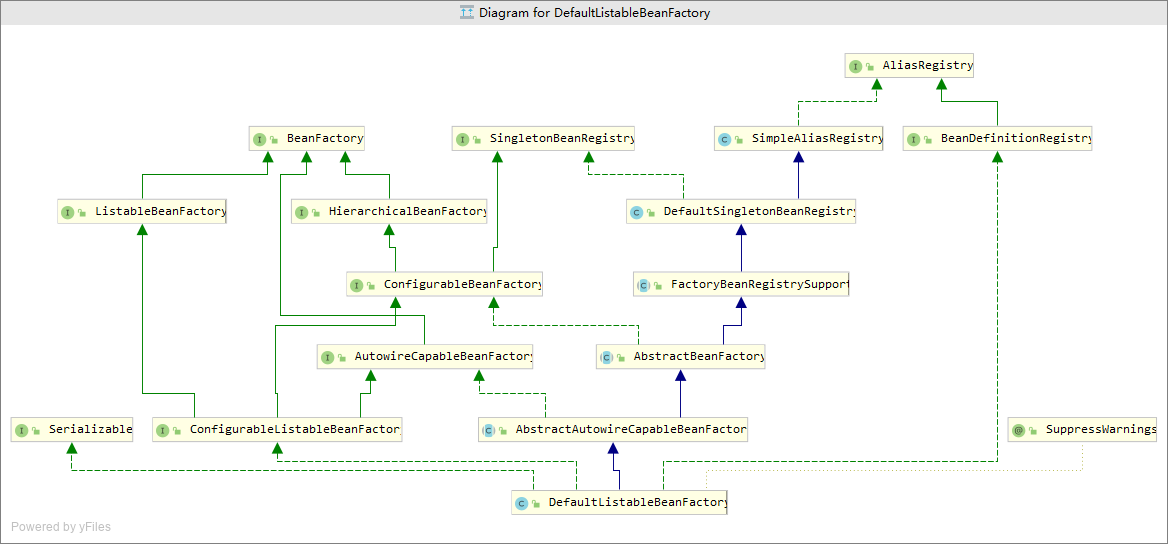
DefaultLisableBeanFactory:spring中的默认接口实现类
- 继承父类:DefaultSingletonBeanRegister:用于共享bean实例的通用注册类,其允许能够通过bean name获得单例对象。
// 说明:DefaultSingletonBeanRegister中定义了存放所有单例对象的concurrentHashMap
public class DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry extends SimpleAliasRegistry implements SingletonBeanRegistry {
/** Cache of singleton objects: bean name to bean instance. */
private final Map<String, Object> singletonObjects = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(256);
需求:打印 ”存放单例对象的map“中特定的单例对象
package com.village.dog;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
// springboot默认是单例对象
@Component
public class Component1 {
}
package com.village.dog;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Component2 {
}
package com.village.dog;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.Map;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
private static final Logger logging = LoggerFactory.getLogger(Application.class);
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException {
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(Application.class,args);
/*
需求:通过反射的方式获取存储单例对象的concurrentMap,打印处Map中我们自己注入的
两个单例对象Component1和Component2.
*/
Field singletonObjects = DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry.class.getDeclaredField("singletonObjects");
singletonObjects.setAccessible(true);
// 获取现有的BeanFactory实现类
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory();
// 获取该实现类的singletonObjects属性,也就是存放单例对象的map
Map<String,Object> map = (Map<String, Object>) singletonObjects.get(beanFactory);
map.entrySet().stream().filter(e->e.getKey().startsWith("component")).forEach(
e-> System.out.println(e.getKey()+"="+e.getValue())
);
}
}
运行结果
component1=com.village.dog.Component1@601cbd8c
component2=com.village.dog.Component2@7180e701
1-3 ApplicationContext接口特点
图2中ApplicationContext的父接口如下
ListableBeanFactory和HierarchicalBeanFactory:BeanFactory的扩展
MessageSource: 用于解析消息的策略接口,支持消息参数化和国际化(国际化能力)
EnvironmentCapable:环境信息,包括yaml,xml等类型文件中的配置信息
ApplicationEventPublisher:事件对象发布能力
ResourcePatternResolver:基于通配符匹配资源
说明:可以发现Application除了获取Bean实例对象这一基本的功能外,还支持国际化,环境信息获取、
基于通配符匹配资源和发布事件对象这四种能力。
四种扩展功能测试代码
package com.village.dog;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.context.event.EventListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
// springboot默认是单例对象
@Component
public class Component1 {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(Component1.class);
/*
通过事件分发器,可以实现业务上解耦:
比如用户注册,后续操作可能有短信验证码,邮件验证码
这个时候模块的功能的协同可以通过事件发布框架进行接口
*/
@EventListener
public void testMonitor(UserRegisterEvent event){
log.info("收到发送的消息{}",event);
}
}
package com.village.dog;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEvent;
public class UserRegisterEvent extends ApplicationEvent {
public UserRegisterEvent(Object source){
super(source);
}
}
package com.village.dog;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.core.io.Resource;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Locale;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application_Extension {
private static final Logger logging = LoggerFactory.getLogger(Application_Extension.class);
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException, IOException {
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(Application_Extension.class,args);
/*
1) ApplicationContext国际化功能:
========该继承于父接口MessageSource=====
getMessage方法:同一key获取不同语言的value,从而实现国际化
实际开发中,语言可以从浏览器的请求头获取
注意:配置文件内容的编码方式需要设置的方式一致,IDEA中可以在setting中设置properties文件的编码方式为UTF8
*/
System.out.println("1 国际化功能测试");
System.out.println(context.getMessage("hi",null, Locale.CHINA));
System.out.println(context.getMessage("hi",null,Locale.ENGLISH));
System.out.println(context.getMessage("hi",null, Locale.JAPANESE));
System.out.println();
/*
2) ApplicationContext:获取资源文件
========继承于于父接口MessageSource=====
*/
System.out.println("2 获取资源测试");
Resource[] resources = context.getResources("classpath:application.properties");
for(Resource resource:resources){
System.out.println(resource);
}
/*采用通配符获取jar包中名称为spring.factories的文件路径
spring.factories的作用:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/444331676
*/
Resource[] re = context.getResources("classpath*:META-INF/spring.factories");
for(Resource resource:re){
System.out.println(resource);
}
System.out.println();
/*
3) applicationContext的环境信息获取能力
=============继承于父接口EnvironmentCapable====
*/
// 配置信息获取:通过application获取windows系统环境变量Java_Home以及application.properties中的server.port属性
System.out.println("3 环境信息获取测试");
System.out.println(context.getEnvironment().getProperty("Java_Home"));
System.out.println(context.getEnvironment().getProperty("server.port"));
System.out.println();
/*
4) applicationContext的事件发布能力
==============继承于父接口ApplicationEventPublisher===
*/
System.out.println("4 事件对象发布测试");
context.publishEvent(new UserRegisterEvent(context));
}
}
运行结果
1 国际化功能测试
你好
Hello
こんにちは
2 获取资源测试
class path resource [application.properties]
URL [jar:file:/C:/Users/Administrator/.m2/repository/org/springframework/boot/spring-boot/2.5.5/spring-boot-2.5.5.jar!/META-INF/spring.factories]
URL [jar:file:/C:/Users/Administrator/.m2/repository/org/springframework/boot/spring-boot-autoconfigure/2.5.5/spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.5.5.jar!/META-INF/spring.factories]
URL [jar:file:/C:/Users/Administrator/.m2/repository/org/springframework/spring-beans/5.3.10/spring-beans-5.3.10.jar!/META-INF/spring.factories]
URL [jar:file:/C:/Users/Administrator/.m2/repository/org/springframework/boot/spring-boot-test/2.5.5/spring-boot-test-2.5.5.jar!/META-INF/spring.factories]
3 环境信息获取测试
C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_131
9006
4 事件对象发布测试
[2022-05-17 16:03:06] [INFO ] -- 收到发送的消息com.village.dog.UserRegisterEvent[source=org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.context.AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext@67080771
2 实现类
2-1 BeanFactory实现类特点
特点1:底层类,相较于Application不支持以下功能
不会主动调用BeanFactory的后处理器
不会主动添加Bean后处理器(解析@Autowired @Resource注入依赖)
不会主动初始化单例
不会解析${}和#{}(EL表达式)
特点2:Bean的后置处理器支持排序功能
BeanFactory实现类特点展示代码
package com.village.dog;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanFactoryPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanDefinition;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionBuilder;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigUtils;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
public class TestBeanFactory {
private static void printBeanDefinitionsNames(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory){
for(String name:beanFactory.getBeanDefinitionNames()){
System.out.println(name);
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory();
/*
容器创建实例对象前必须存储对象的beanDefinition
beanDefinition包含class、scope、初始化、销毁信息
*/
AbstractBeanDefinition beanDefinition =
BeanDefinitionBuilder.genericBeanDefinition(Config.class).setScope("singleton").getBeanDefinition();
beanFactory.registerBeanDefinition("config",beanDefinition);
/*
打印容器类中BeanDefinition的名称,从打印结果可以发现
容器类并没有对Bean的内容进行进一步解析。
*/
System.out.println("step1:当前容器所包含的BeanDefinition");
printBeanDefinitionsNames(beanFactory);
// 为容器添加处理器
System.out.println("step2:容器添加处理器后,所包含的BeanDefinition");
AnnotationConfigUtils.registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(beanFactory);
printBeanDefinitionsNames(beanFactory);
System.out.println("step3:执行BeanFactoryPostProcessor逻辑后,添加的BeanDefinition,创建的实例对象和");
// 执行BeanFactoryPostProcessor的逻辑
beanFactory.getBeansOfType(BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class);
beanFactory.getBeansOfType(BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class).values().forEach(beanFactoryPostProcessor ->{
beanFactoryPostProcessor.postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
});
printBeanDefinitionsNames(beanFactory);
// 为null,说明此时@Autowired的,如果在执行BeanPostProcessor前获取bean,那么后续即便
// 调用BeanPostProcessor也无法注入依赖
//System.out.println(beanFactory.getBean(Bean1.class).getBean2());
// 执行BeanPostProcessor的逻辑,将依赖注入到容器的bean中,针对bean的生命周期的各个阶段提供扩展
// 例如@Autowired或@Resource
System.out.println("step4:执行BeanPostProcessor,创建的实例对象");
beanFactory.getBeansOfType(BeanPostProcessor.class).values().forEach(beanFactory::addBeanPostProcessor);
// DefaultListableBeanFactory默认是延迟创建单例,可以通过preInstantiateSingletons提前创建
beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons();
System.out.println("=============================");
System.out.println(beanFactory.getBean(Bean1.class).getBean2());
/*
总结:BeanFactory的特点:
1.不会主动调用BeanFactory的后处理器
2.不会主动添加Bean后处理器
3.不会主动初始化单例
4.不会解析EL表达式
*/
}
@Configuration
static class Config{
@Bean
public Bean1 bean1(){return new Bean1();}
@Bean
public Bean2 bean2(){return new Bean2();}
}
static class Bean1{
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(Bean1.class);
public Bean1(){
log.debug("构造Bean1()");
}
@Autowired
private Bean2 bean2;
public Bean2 getBean2(){return bean2;}
}
static class Bean2{
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(Bean2.class);
public Bean2(){
log.debug("构造Bean2()");
}
}
}
程序输出结果
step1:当前容器所包含的BeanDefinition
config
step2:容器添加处理器后,所包含的BeanDefinition
config
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalConfigurationAnnotationProcessor
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalAutowiredAnnotationProcessor
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalCommonAnnotationProcessor
org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerProcessor
org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerFactory
step3:执行BeanFactoryPostProcessor逻辑后,添加的BeanDefinition,创建的实例对象和
[2022-05-19 20:43:30] [DEBUG] -- Creating shared instance of singleton bean 'org.springframework.context.annotation.internalConfigurationAnnotationProcessor'
[2022-05-19 20:43:30] [DEBUG] -- Creating shared instance of singleton bean 'org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerProcessor'
[2022-05-19 20:43:30] [DEBUG] -- Creating shared instance of singleton bean 'org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerFactory'
config
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalConfigurationAnnotationProcessor
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalAutowiredAnnotationProcessor
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalCommonAnnotationProcessor
org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerProcessor
org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerFactory
bean1
bean2
step4:执行BeanPostProcessor,创建的实例对象
[2022-05-19 20:43:30] [DEBUG] -- Creating shared instance of singleton bean 'org.springframework.context.annotation.internalAutowiredAnnotationProcessor'
[2022-05-19 20:43:30] [DEBUG] -- Creating shared instance of singleton bean 'org.springframework.context.annotation.internalCommonAnnotationProcessor'
[2022-05-19 20:43:30] [DEBUG] -- Creating shared instance of singleton bean 'config'
[2022-05-19 20:43:30] [DEBUG] -- Creating shared instance of singleton bean 'bean1'
[2022-05-19 20:43:30] [DEBUG] -- 构造Bean1()
[2022-05-19 20:43:30] [DEBUG] -- Creating shared instance of singleton bean 'bean2'
[2022-05-19 20:43:30] [DEBUG] -- 构造Bean2()
=============================
com.village.dog.TestBeanFactory$Bean2@61862a7f
实例程序说明
DefaultListableBeanFactory()是BeanFactory接口实现,这个类也就是
产生Bean的工厂,该工厂能够创建bean的实例对象供外部程序使用。为创建
Bean的实例对象,该工厂需要解析每个bean的class对象,从而为每个bean生成
beanDefinition存放在工厂中(BeanDefinition是对bean实例的描述,包括属性值、构造参数值等)。
显然"如何从Bean得到BeanDefinition"对于BeanFactory非常重要,只要我们保证能够正确解析Bean Class获取BeanDefinition实例对象,那么就能够保证我们能够正确的创建想要的bean。
实际开发中,我们可以通过注解的方式将我们定义的Bean放入的容器中,具体的工作实际上是由Spring中的BeanFactoryPostProcessor去解析Bean生成BeanDefinition,通过BeanPostProcessor为bean实例对象注入依赖。
-
BeanFactoryPostProcessor: Factory hook that allows for custom modification of an application context's bean definitions, adapting the bean property values of the context's underlying bean factory.(工厂钩子程序用于自定义的应用上下文BeanDefinition修改,
调整上下文的底层bean工厂的bean属性值,只针对beanDefinition) -
BeanPostProcessor:Factory hook that allows for custom modification of new bean instances
for example, checking for marker interfaces or wrapping beans with proxies.(bean的解析,有的处理器处理@Autowired注解,有的处理器处理@Resource注解)
设计思想:在程序的固定固定位置通过hook程序的定义修改实现灵活的功能,是开闭原则的一种体现
Bean后处理器的排序
package com.village.dog;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanFactoryPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanDefinition;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionBuilder;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigUtils;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
public class TestBeanFactory {
public static void main(String[] args) {
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory();
AbstractBeanDefinition beanDefinition =
BeanDefinitionBuilder.genericBeanDefinition(Config.class).setScope("singleton").getBeanDefinition();
beanFactory.registerBeanDefinition("config",beanDefinition);
// 为容器添加处理器
AnnotationConfigUtils.registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(beanFactory);
// 执行BeanFactoryPostProcessor的逻辑
beanFactory.getBeansOfType(BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class);
beanFactory.getBeansOfType(BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class).values().forEach(beanFactoryPostProcessor ->{
beanFactoryPostProcessor.postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
});
beanFactory.getBeansOfType(BeanPostProcessor.class).values().forEach(beanFactory::addBeanPostProcessor);
// beanFactory.getBeansOfType(BeanPostProcessor.class).values().forEach(beanPostProcessor->{
// System.out.println("BeanFactory中的BeanPostProcessor:"+beanPostProcessor);
// beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(beanPostProcessor); // 先添加的processor先执行
// });
// 重新定义BeanPostProcessor的顺序
beanFactory.getBeansOfType(BeanPostProcessor.class).values().stream().sorted(beanFactory.getDependencyComparator()).
forEach(beanPostProcessor->{
System.out.println("BeanFactory中的BeanPostProcessor:"+beanPostProcessor);
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(beanPostProcessor); // 先添加的processor先执行
});
System.out.println(beanFactory.getBean(Bean1.class).getBean3());
}
@Configuration
static class Config{
@Bean
public Bean1 bean1(){return new Bean1();}
@Bean
public Bean2 bean2(){return new Bean2();}
@Bean
public Bean3 bean3(){return new Bean3();}
@Bean
public Bean4 bean4(){return new Bean4();}
}
/*
Bean1中Inter bean3,Inter接口有两个实现类
Bean3,Bean4,
情况1:
@Autowired
Inter bean3
会根据bean3名称匹配到Bean3
情况2:
@Resource(name="bean4")
Inter bean3;
会根据name匹配到bean4
上述如果两个注解一起用,都可以匹配,但最终匹配的是Bean3,原因是
@Autowired对应的BeanPostProcessor在执行顺序上优于
@Resource对应的BeanPostProcessor
我们可以通过定义排序规则,让@Resource对应的BeanPostProcessor的执行顺序优于
@Autowired对应的BeanPostProcessor
*/
static class Bean1{
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(Bean1.class);
public Bean1(){
log.debug("构造Bean1()");
}
@Autowired
private Bean2 bean2;
public Bean2 getBean2(){return bean2;}
@Autowired
@Resource(name="bean4")
Inter bean3;
public Inter getBean3(){return bean3;}
}
static class Bean2{
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(Bean2.class);
public Bean2(){
log.debug("构造Bean2()");
}
}
interface Inter{
void get();
}
static class Bean3 implements Inter{
@Override
public void get() {}
}
static class Bean4 implements Inter{
@Override
public void get() {
}
}
}
2-2 ApplicationContext接口的实现类
背景:Spring中ApplicationContext接口有以下四个较为常见的实现类
| 容器类名 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| ClassPathXmlApplication | 加载classpath路径下的xml进行配置 |
| FileSystemXmlApplicationContext | 加载磁盘路径下的xml文件进行配置 |
| AnnotationConfigApplicationContext | 基于Java配置类创建 |
| AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext | 基于Java配置类创建,适用于web环境 |
四种实现类测试代码
package com.village.dog;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.ListableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.DispatcherServletRegistrationBean;
import org.springframework.boot.web.embedded.tomcat.TomcatServletWebServerFactory;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.context.AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.server.ServletWebServerFactory;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.Controller;
public class TestApplicationContext {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("测试ClassPathXmlApplicationContext");
testClassPathXmlApplicationContext();
/*
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory();
// ==================ClassPathXmlApplication的内部机制流程=================
printBeanDefinitionNames(beanFactory);
XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory);
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(new ClassPathResource("b01.xml"));
printBeanDefinitionNames(beanFactory);
*/
System.out.println("测试AnnotationConfigApplicationContext");
testAnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
System.out.println("测试AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext");
testAnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext();
}
/*
ClassPathXmlApplication:加载classpath路径下的xml进行配置
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext:加载磁盘路径下的xml文件进行配置
*/
private static void testClassPathXmlApplicationContext(){
// FileSystemXmlApplicationContext context = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("xxx.xml");
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("b01.xml");
printBeanDefinitionNames(context);
System.out.println(context.getBean(Bean2.class).getBean1());
System.out.println();
}
private static void testAnnotationConfigApplicationContext(){
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Config.class);
/*
从输出可以看出:相较于ClassPathXmlApplication容器,该容器中除了配置类中配置的
Bean1和Bean2,还有Config以及用于解析不同注解的5个工具类,作为bean的后处理器(如下所示):
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalConfigurationAnnotationProcessor
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalAutowiredAnnotationProcessor
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalCommonAnnotationProcessor
org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerProcessor
org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerFactory
如果ClassPathXmlApplication加载的xml文件中包含<context:annotation-config/>,则也能引入上述5个后置处理器
*/
printBeanDefinitionNames(context);
System.out.println(context.getBean(Bean2.class).getBean1());
System.out.println();
}
/*
AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext:
该容器也是基于Java配置类创建,主要用于web环境
*/
private static void testAnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext(){
// 内嵌Tomcat容器配合DispatchServlet实现简单的web应用
// 最小系统: web容器,servlet对象,容器注册类,控制类处理请求
AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext (WebConfig.class);
printBeanDefinitionNames(context);
System.out.println();
}
@Configuration
static class WebConfig{
@Bean
public ServletWebServerFactory servletWebServerFactory(){ // 创建内嵌Tomcat容器
return new TomcatServletWebServerFactory();
}
@Bean
public DispatcherServlet dispatcherServlet(){ // 创建Servlet对象
return new DispatcherServlet();
}
// 将dispatchServlet注册到Tomcat容器中
@Bean
public DispatcherServletRegistrationBean registrationBean(DispatcherServlet dispatcherServlet){
return new DispatcherServletRegistrationBean(dispatcherServlet,"/");
}
// 这里将/后面的bean名称作为访问路径
@Bean("/hello")
public Controller controller1(){
return (request,response)->{
response.getWriter().print("Response Message:Hello");
return null;
};
}
}
@Configuration
static class Config{
@Bean
public Bean1 bean1(){
return new Bean1();
}
@Bean
public Bean2 bean2(Bean1 bean1){
Bean2 bean2 = new Bean2();
bean2.setBean1(bean1); // 注入依赖
return bean2;
}
}
static class Bean1{}
static class Bean2{
private Bean1 bean1;
public void setBean1(Bean1 bean1){
this.bean1 = bean1;
}
public Bean1 getBean1(){
return bean1;
}
}
private static void printBeanDefinitionNames(ListableBeanFactory beanFactory){
System.out.println("==============beanDefinitions==================");
for(String name:beanFactory.getBeanDefinitionNames()){
System.out.println(name);
}
System.out.println("================================");
}
}
日志输出
测试ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
[2022-06-01 20:26:57] [DEBUG] -- Refreshing org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext@5afa04c
[2022-06-01 20:26:57] [DEBUG] -- Loaded 2 bean definitions from class path resource [b01.xml]
[2022-06-01 20:26:57] [DEBUG] -- Creating shared instance of singleton bean 'bean1'
[2022-06-01 20:26:57] [DEBUG] -- Creating shared instance of singleton bean 'bean2'
==============beanDefinitions==================
bean1
bean2
================================
com.village.dog.TestApplicationContext$Bean1@475e586c
测试AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
[2022-06-01 20:26:57] [DEBUG] -- Refreshing org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext@5c1a8622
[2022-06-01 20:26:57] [DEBUG] -- Creating shared instance of singleton bean 'org.springframework.context.annotation.internalConfigurationAnnotationProcessor'
[2022-06-01 20:26:57] [DEBUG] -- Creating shared instance of singleton bean 'org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerProcessor'
[2022-06-01 20:26:57] [DEBUG] -- Creating shared instance of singleton bean 'org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerFactory'
[2022-06-01 20:26:57] [DEBUG] -- Creating shared instance of singleton bean 'org.springframework.context.annotation.internalAutowiredAnnotationProcessor'
[2022-06-01 20:26:57] [DEBUG] -- Creating shared instance of singleton bean 'org.springframework.context.annotation.internalCommonAnnotationProcessor'
[2022-06-01 20:26:57] [DEBUG] -- Creating shared instance of singleton bean 'testApplicationContext.Config'
[2022-06-01 20:26:57] [DEBUG] -- Creating shared instance of singleton bean 'bean1'
[2022-06-01 20:26:57] [DEBUG] -- Creating shared instance of singleton bean 'bean2'
[2022-06-01 20:26:57] [DEBUG] -- Autowiring by type from bean name 'bean2' via factory method to bean named 'bean1'
==============beanDefinitions==================
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalConfigurationAnnotationProcessor
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalAutowiredAnnotationProcessor
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalCommonAnnotationProcessor
org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerProcessor
org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerFactory
testApplicationContext.Config
bean1
bean2
================================
com.village.dog.TestApplicationContext$Bean1@21b2e768
测试AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext
[2022-06-01 20:26:57] [DEBUG] -- Refreshing org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.context.AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext@11c9af63
[2022-06-01 20:26:57] [DEBUG] -- Creating shared instance of singleton bean 'org.springframework.context.annotation.internalConfigurationAnnotationProcessor'
[2022-06-01 20:26:58] [DEBUG] -- Creating shared instance of singleton bean 'org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerProcessor'
[2022-06-01 20:26:58] [DEBUG] -- Creating shared instance of singleton bean 'org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerFactory'
[2022-06-01 20:26:58] [DEBUG] -- Creating shared instance of singleton bean 'org.springframework.context.annotation.internalAutowiredAnnotationProcessor'
[2022-06-01 20:26:58] [DEBUG] -- Creating shared instance of singleton bean 'org.springframework.context.annotation.internalCommonAnnotationProcessor'
[2022-06-01 20:26:58] [DEBUG] -- Unable to locate ThemeSource with name 'themeSource': using default [org.springframework.ui.context.support.ResourceBundleThemeSource@be35cd9]
[2022-06-01 20:26:58] [DEBUG] -- Creating shared instance of singleton bean 'servletWebServerFactory'
[2022-06-01 20:26:58] [DEBUG] -- Creating shared instance of singleton bean 'testApplicationContext.WebConfig'
[2022-06-01 20:27:00] [DEBUG] -- Code archive: C:\Users\Administrator\.m2\repository\org\springframework\boot\spring-boot\2.5.5\spring-boot-2.5.5.jar
[2022-06-01 20:27:00] [DEBUG] -- Code archive: C:\Users\Administrator\.m2\repository\org\springframework\boot\spring-boot\2.5.5\spring-boot-2.5.5.jar
[2022-06-01 20:27:00] [DEBUG] -- None of the document roots [src/main/webapp, public, static] point to a directory and will be ignored.
[2022-06-01 20:27:00] [INFO ] -- Tomcat initialized with port(s): 8080 (http)
六月 01, 2022 8:27:00 下午 org.apache.coyote.AbstractProtocol init
信息: Initializing ProtocolHandler ["http-nio-8080"]
六月 01, 2022 8:27:00 下午 org.apache.catalina.core.StandardService startInternal
信息: Starting service [Tomcat]
六月 01, 2022 8:27:00 下午 org.apache.catalina.core.StandardEngine startInternal
信息: Starting Servlet engine: [Apache Tomcat/9.0.53]
六月 01, 2022 8:27:00 下午 org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationContext log
信息: Initializing Spring embedded WebApplicationContext
[2022-06-01 20:27:00] [DEBUG] -- Published root WebApplicationContext as ServletContext attribute with name [org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext.ROOT]
[2022-06-01 20:27:00] [INFO ] -- Root WebApplicationContext: initialization completed in 2448 ms
[2022-06-01 20:27:00] [DEBUG] -- Creating shared instance of singleton bean 'registrationBean'
[2022-06-01 20:27:00] [DEBUG] -- Creating shared instance of singleton bean 'dispatcherServlet'
[2022-06-01 20:27:00] [DEBUG] -- Autowiring by type from bean name 'registrationBean' via factory method to bean named 'dispatcherServlet'
[2022-06-01 20:27:00] [DEBUG] -- Mapping filters:
[2022-06-01 20:27:00] [DEBUG] -- Mapping servlets: dispatcherServlet urls=[/]
[2022-06-01 20:27:00] [DEBUG] -- Creating shared instance of singleton bean '/hello'
[2022-06-01 20:27:00] [DEBUG] -- Starting beans in phase 2147483646
六月 01, 2022 8:27:00 下午 org.apache.coyote.AbstractProtocol start
信息: Starting ProtocolHandler ["http-nio-8080"]
[2022-06-01 20:27:00] [INFO ] -- Tomcat started on port(s): 8080 (http) with context path ''
[2022-06-01 20:27:00] [DEBUG] -- Successfully started bean 'webServerStartStop'
[2022-06-01 20:27:00] [DEBUG] -- Starting beans in phase 2147483647
[2022-06-01 20:27:00] [DEBUG] -- Successfully started bean 'webServerGracefulShutdown'
==============beanDefinitions==================
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalConfigurationAnnotationProcessor
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalAutowiredAnnotationProcessor
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalCommonAnnotationProcessor
org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerProcessor
org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerFactory
testApplicationContext.WebConfig
servletWebServerFactory
dispatcherServlet
registrationBean
/hello
================================
总结:四种ApplicationContext接口的实现类包含两种配置容器的方式,一种是基于xml文件,另外一种是通过添加配置注解的配置类。通常我们适用配置类的方式配置容器更多一点。通过打印容器中beanDefinition。可以发现采用配置类的容器类对于@Autowired等注解的解析是通过容器中所添加的后置bean处理器实现的。
此外,web环境下的容器类至少包含 web容器、servlet对象、web容器注册对象。
小结
问题1:BeanFactory与ApplicationContext的作用和关系
1)BeanFactory是spring容器的核心接口,也是ApplicationContext的父接口。
2)ApplicationContext组合BeanFactory的功能,更加确切地ApplicationContext接口的实现类内部
有一个成员变量是BeanFactory接口的实现类,然后通过内部BeanFactory的实现类调用BeanFactory接口方法。
说明:org.springframework.context.support.GenericApplicationContexts是ApplicationContext接口的实现类,其包含成员变量DefaultListableBeanFactory,该变量实现BeanFactory接口。因此Application接口本质上组合了BeanFactory接口。
public class GenericApplicationContext extends AbstractApplicationContext implements BeanDefinitionRegistry {
private final DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory;
...
}
问题2:ApplicationContext在BeanFactory扩展哪些功能?
ApplicationContext除了继承BeanFactory,还继承了其他接口,从而
支持以下四种功能:
1)国际化功能
2)根据统配符加载Resouce的功能
3)获取配置信息(环境变量)的功能
4)发送事件对象的功能
问题3:ApplicationContext的事件解耦功能如何得到支持?
事件解耦本质上是观察者模式的体现,通过消息,实现功能的解耦。
ApplicationContext的父接口ApplicationContext提供了该功能。
Spring 事件驱动模型实现业务解耦
观察者模式与订阅发布模式的区别
问题4:BeanFactory实现类的特点?
属于底层类,相较于Application不支持以下功能
- 不会主动调用BeanFactory的后处理器
- 不会主动添加Bean后处理器(解析@Autowired @Resource注入依赖)
- 不会主动初始化单例
- 不会解析${}和#{}(EL表达式)
问题5:ApplicationContext的常见实现和使用方法
四种ApplicationContext接口的实现类包含两种配置容器的方式,一种是基于xml文件,另外一种是通过添加配置注解的配置类。