我们可以在Spring的bean中轻松的注入HttpServletRequest,使用@Autowired HttpServletRequest request;就可以了。
但是,为什么我们可以直接这样用呢?
原因肯定是Spring在容器初始化的时候就将HttpServletRequest注册到了容器中。
那么我们就查原码,发现在WebApplicationContextUtils.registerWebApplicationScopes(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory, ServletContext)中实现了这个功能。
这个方法是在AbstractApplicationContext.refresh()中进行调用的,也就是在Spring容器初始化的时候,将web相关的对象注册到了容器中。
具体可以看下面的原码图片:



调用处:

问题:
注入 HttpServletRequest 为什么每次都能拿到最新的?bean 的依耐关系不是容器启动后就确定了吗?
解析:
spring 注册的 HttpServletRequest 类型的 bean 是一个 RequestObjectFactory,如果进行依赖注入时是通过 RequestObjectFactory.getObject() 获取 request 对象的话,那么依赖关系在这个时候就确定了,这样肯定不能达到每次 http 请求都拿到一个新的 HttpServletRequest 对象的目的。
写一个 controller ,注入 HttpServletRequest,打断点查看注入的对象是一个 JDK 代理对象, 对应的 InvocationHandler 是 AutowireUtils$ObjectFactoryDelegatingInvocationHandler。通过查找 ObjectFactoryDelegatingInvocationHandler 使用的地方,发现是在 AutowireUtils.resolveAutowiringValue() 时创建的代理对象。再在这个方法上打个断点,重新启动容器,就可以发现,HttpServletRequest 是在 XxController 这个 bean 注入依赖属性时 (populateBean() )调用的 AutowireUtils.resolveAutowiringValue() 创建的代理。
这样就说的通了:因为 spring 在注入 HttpServletRequest 时,发现如果注入的是 一个 ObjectFactory 类型的对象时,就会将注入的 bean 替换成一个 JDK 动态代理对象,代理对象在执行 HttpServletRequest 对象里的方法时,就会通过 RequestObjectFactory.getObject() 获取一个 新的 request 对象来执行。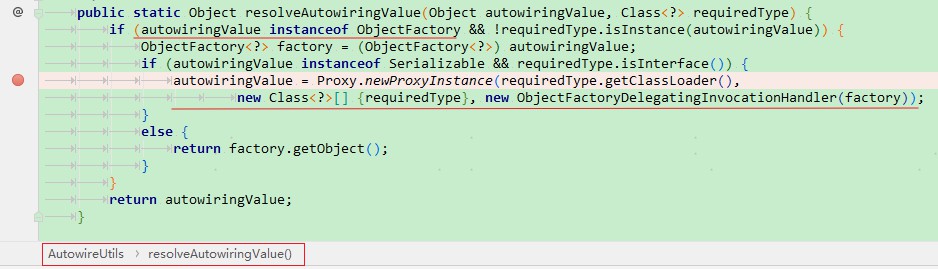
RequestObjectFactory

1 private static class RequestObjectFactory implements ObjectFactory<ServletRequest>, Serializable { 2 @Override 3 public ServletRequest getObject() { 4 return currentRequestAttributes().getRequest(); 5 } 6 7 @Override 8 public String toString() { 9 return "Current HttpServletRequest"; 10 } 11 }
ObjectFactoryDelegatingInvocationHandler

1 private static class ObjectFactoryDelegatingInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler, Serializable { 2 3 private final ObjectFactory<?> objectFactory; 4 5 public ObjectFactoryDelegatingInvocationHandler(ObjectFactory<?> objectFactory) { 6 this.objectFactory = objectFactory; 7 } 8 9 @Override 10 public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { 11 String methodName = method.getName(); 12 if (methodName.equals("equals")) { 13 // Only consider equal when proxies are identical. 14 return (proxy == args[0]); 15 } 16 else if (methodName.equals("hashCode")) { 17 // Use hashCode of proxy. 18 return System.identityHashCode(proxy); 19 } 20 else if (methodName.equals("toString")) { 21 return this.objectFactory.toString(); 22 } 23 try { 24 return method.invoke(this.objectFactory.getObject(), args); 25 } 26 catch (InvocationTargetException ex) { 27 throw ex.getTargetException(); 28 } 29 } 30 }
附:
1. Spring能实现在多线程环境下,将各个线程的request进行隔离,且准确无误的进行注入,奥秘就是ThreadLocal

2. Spring中还可以直接注入ApplicationContext
