Dubbo 服务调用
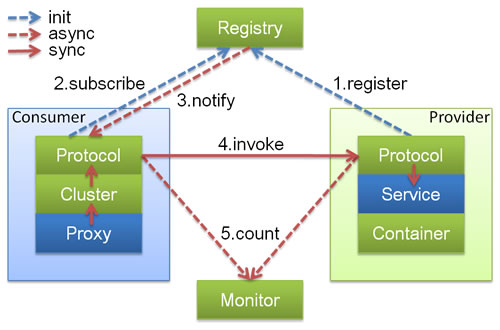

根据上图,可以看出,服务调用过程为:
-
Consumer 端的 Proxy 调用 Cluster 层选择集群中的某一个 Invoker(负载均衡)
-
Invoker 最终会调用 Protocol 层进行 RPC 通讯(netty,tcp 长连接),将服务调用信息和配置信息进行传递
-
Provider 端 Protocol 层接收到服务调用信息后,最终会调用真实的服务实现
Consumer 端调用过程
通过前面 Dubbo 服务发现&引用 的学习,我们知道,Consumer 端的调用过程大体如下:
-
执行 FailoverClusterInvoker#invoke(Invocation invocation) (负载均衡。当有多个 provider 时走这一步,没有的话,就跳过)
-
执行 Filter#invoke(Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) (所有 group="provider" 的 Filter)
-
执行 DubboInvoker#invoke(Invocation inv)
所以,最终的通讯过程是由 DubboInvoker 来完成的:
protected Result doInvoke(final Invocation invocation) throws Throwable { RpcInvocation inv = (RpcInvocation) invocation; final String methodName = RpcUtils.getMethodName(invocation); inv.setAttachment(Constants.PATH_KEY, getUrl().getPath()); inv.setAttachment(Constants.VERSION_KEY, version); // 选择 ExchangeClient(一般情况下只有一个) ExchangeClient currentClient; if (clients.length == 1) { currentClient = clients[0]; } else { currentClient = clients[index.getAndIncrement() % clients.length]; } try { boolean isAsync = RpcUtils.isAsync(getUrl(), invocation); boolean isOneway = RpcUtils.isOneway(getUrl(), invocation); int timeout = getUrl().getMethodParameter(methodName, Constants.TIMEOUT_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_TIMEOUT); if (isOneway) { boolean isSent = getUrl().getMethodParameter(methodName, Constants.SENT_KEY, false); currentClient.send(inv, isSent); RpcContext.getContext().setFuture(null); return new RpcResult(); } else if (isAsync) { // dubbo 异步调用 ResponseFuture future = currentClient.request(inv, timeout); RpcContext.getContext().setFuture(new FutureAdapter<Object>(future)); return new RpcResult(); } else { // 服务调用分支 RpcContext.getContext().setFuture(null); return (Result) currentClient.request(inv, timeout).get(); } } catch (TimeoutException e) { throw new RpcException(RpcException.TIMEOUT_EXCEPTION, "Invoke remote method timeout. method: " + invocation.getMethodName() + ", provider: " + getUrl() + ", cause: " + e.getMessage(), e); } catch (RemotingException e) { throw new RpcException(RpcException.NETWORK_EXCEPTION, "Failed to invoke remote method: " + invocation.getMethodName() + ", provider: " + getUrl() + ", cause: " + e.getMessage(), e); } }
阅读源码可以发现,获取 Rpc 调用结果的方法是: ExchangeClient#request(inv, timeout).get(), 最终会调用 NettyChannel#send(Object message, false) 去写消息。而消息的编解码是通过 com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.protocol.dubbo.DubboCodec 来处理的。
// 对 Request 消息进行编码(DubboCodec.class) protected void encodeRequestData(Channel channel, ObjectOutput out, Object data) throws IOException { RpcInvocation inv = (RpcInvocation) data; out.writeUTF(inv.getAttachment(Constants.DUBBO_VERSION_KEY, DUBBO_VERSION)); out.writeUTF(inv.getAttachment(Constants.PATH_KEY)); out.writeUTF(inv.getAttachment(Constants.VERSION_KEY)); out.writeUTF(inv.getMethodName()); // 写出调用方法的名称 out.writeUTF(ReflectUtils.getDesc(inv.getParameterTypes())); // 写出调用方法的参数 Object[] args = inv.getArguments(); if (args != null) for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) { out.writeObject(encodeInvocationArgument(channel, inv, i)); // 写出调用的实参 } out.writeObject(inv.getAttachments()); // 写出 attachments }
Provider 端调用过程
Provider 端接收到 Consumer 端的消息后,会通过 DubboCodec#decodeBody(Channel channel, InputStream is, byte[] header)处理,将消息转化为 RpcInvocation。最终通过预先设置好的 netty 的 handler 来将 RpcInvocation 转化为 Invoker 的调用。
通过 Dubbo 服务发现&引用 的学习,我们知道,这个 handler 最终会调用 DubboProtocol#requestHandler 来处理,最终将 Invocation 转化为 Invoker 的调用。
调用完成后,返回结果通过DubboCodec#encodeResponseData(Channel channel, ObjectOutput out, Object data)进行编码,最终写回到 Consumer 端:
// 对返回结果进行编码 protected void encodeResponseData(Channel channel, ObjectOutput out, Object data) throws IOException { Result result = (Result) data; Throwable th = result.getException(); if (th == null) { Object ret = result.getValue(); if (ret == null) { out.writeByte(RESPONSE_NULL_VALUE); } else { out.writeByte(RESPONSE_VALUE); out.writeObject(ret); } } else { out.writeByte(RESPONSE_WITH_EXCEPTION); out.writeObject(th); } }
Conmuser 端接收到调用的返回数据后,会由 DubboCodec#decodeBody(Channel channel, InputStream is, byte[] header)将数据转化成 RpcResult。
ExchangeClient#request(inv, timeout).get() 最终会调用 DefaultFuture#get() 来获取 Response 中的返回数据。DefaultFuture#get() 使用了同步阻塞的方式来等待 provider 端的返回数据。
官方如是说:
满眼都是 Invoker
由于 Invoker 是 Dubbo 领域模型中非常重要的一个概念,很多设计思路都是向它靠拢。这就使得 Invoker渗透在整个实现代码里,对于刚开始接触 Dubbo 的人,确实容易给搞混了。 下面我们用一个精简的图来说明最重要的两种 Invoker:服务提供 Invoker 和服务消费 Invoker: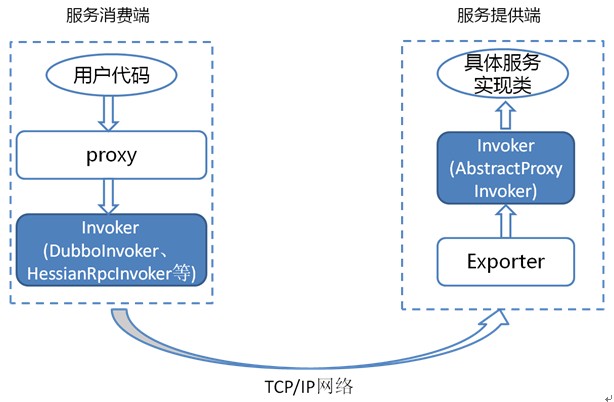

服务提供 Invoker:DubboInvoker(默认)、HessianRpcInvoker等(视协议而定)
服务消费 Invoker
如果想了解更多Dubbo源码的知识,请移步 Dubbo源码解读——通向高手之路 的视频讲解:
http://edu.51cto.com/sd/2e565