在入门一、入门二我们实现了一个完整的API保护的过程。需要保护的API只需在其Controler上应用[Authorize]特性,来显式指定受保护的资源。而我们实现的这个例子,所应用的模式叫“Client Credentials”,在Config.cs中有这么一段代码
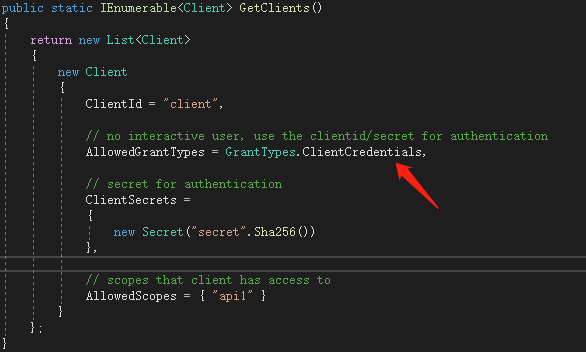
“Client Credentials”(客户端凭证)模式,是最简单的授权模式,因为授权的流程仅发生在Client与Identity Server之间。
该模式的适用场景为服务器与服务器之间的通信。比如对于一个电子商务网站,将订单和物流系统分拆为两个服务分别部署。物流系统需要获取需要派送的物品,而订单系统需要跟踪物流信息。而这两个系统之间服务的授权就可以通过这种模式来实现。
官方客户授权几种说明:https://identityserver4.readthedocs.io/en/latest/topics/clients.html
OAuth2.0 定义了四种授权模式:
- Implicit:简化模式;直接通过浏览器的链接跳转申请令牌。
- Client Credentials:客户端凭证模式;该方法通常用于服务器之间的通讯;该模式仅发生在Client与Identity Server之间。
- Resource Owner Password Credentials:密码模式
- Authorization Code:授权码模式;
Implicit
就是认证服务器提供网页进行登录。受保护的网站使用该模式,访问需要授权的网页时如果没认证的会自动跳转到认证服务器的登录界面,登录后自动回到原来访问的授权页面。
Resource Owner Password Credentials
用户需要向客户端提供自己的用户名和密码。客户端使用这些信息,向"服务商提供商"索要授权。
在这种模式中,用户必须把自己的密码给客户端,这通常用在用户对客户端高度信任的情况下,比如客户端是操作系统的一部分,或由一个著名公司出品。一般不建议使用该模式。认证服务器只有在其他授权模式无法执行的情况下,才应考虑使用这种模式。
Authorization Code
我们使用第三方使用QQ帐号进行登录的例子说明
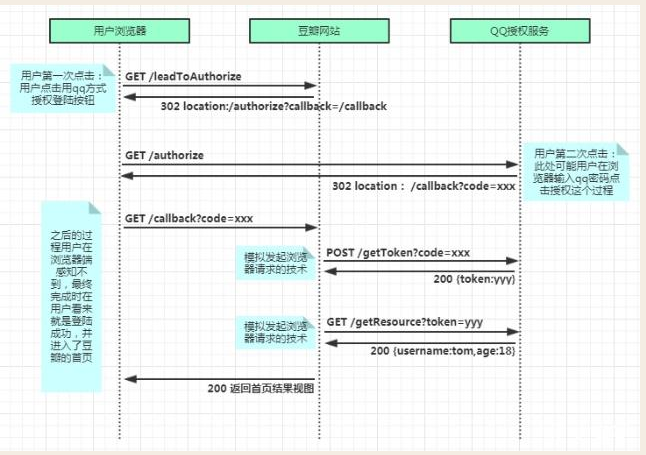
这有一篇不错的说明,上图也来自该网页
https://www.cnblogs.com/alittlesmile/p/11531577.html
一个认证服务器,可以应用两种模式吗?
可以的。后面的例子,我们要为入门一的例子上加上Implicit模式。下面源码中的将是一个新的web的网站,使用44302端口
public static IEnumerable<Client> GetClients()
{
return new List<Client>
{
new Client
{
ClientId = "client",
// no interactive user, use the clientid/secret for authentication
AllowedGrantTypes = GrantTypes.ClientCredentials,
// secret for authentication
ClientSecrets =
{
new Secret("secret".Sha256())
},
// scopes that client has access to
AllowedScopes = { "api1" }
},
new Client
{
ClientId = "mvc",
ClientName = "MVC Client",
AllowedGrantTypes = GrantTypes.Hybrid,
AllowOfflineAccess = true,
ClientSecrets = { new Secret("secret".Sha256()) },
RedirectUris = { "https://localhost:44302/signin-oidc" },
PostLogoutRedirectUris = { "https://localhost:44302/" },
FrontChannelLogoutUri = "https://localhost:44302/signout-oidc",
AllowedScopes =
{
IdentityServerConstants.StandardScopes.OpenId,
IdentityServerConstants.StandardScopes.Profile,
IdentityServerConstants.StandardScopes.Email,
"api1", "api2.read_only"
},
}
};
}
各个模式的Client源码,可以在这找
https://identityserver4.readthedocs.io/en/latest/topics/clients.html