单用户OS和多用户OS?
Linux是多用户OS,Windows是单用户OS。很多人会疑惑? Windows7也可以创建多个用户啊,怎么能说是单用户OS呢?
这里的多用户指的是OS同时可以被多个人访问,单用户指的是OS一次只能被一个用户的访问。
Windows里面,win7、winxp都是单用户OS;Windows server 2008,2003等是多用户OS。
Linux环境下使用who命令可以知道当前有多少用户
[root@51cto ~]# who root tty1 2018-05-31 02:44 root pts/0 2018-05-31 02:44 (192.168.80.1)
whoami可以知道当前登陆用户是谁
[root@51cto ~]# whoami root
无论单用户OS还是多用户OS都可以再系统上创建多个账户。
用户类别
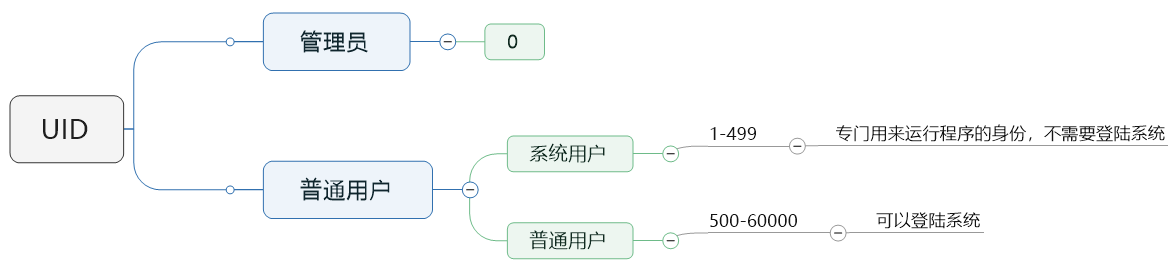
UID的取值范围再配置文件/etc/login.defs里面定义了
[root@51cto ~]# cat /etc/login.defs | grep -v '^#' MAIL_DIR /var/spool/mail PASS_MAX_DAYS 99999 PASS_MIN_DAYS 0 PASS_MIN_LEN 5 PASS_WARN_AGE 7 UID_MIN 500 UID_MAX 60000 GID_MIN 500 GID_MAX 60000 CREATE_HOME yes UMASK 077 USERGROUPS_ENAB yes ENCRYPT_METHOD SHA512
组类别
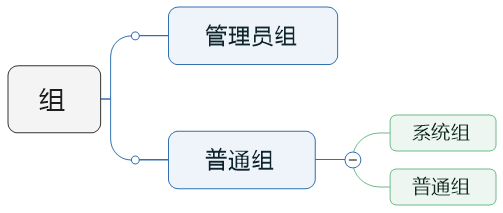
使用组简化授权
基本组:优先使用基本组,用户只能属于一个基本组。基本组也叫默认组。
附加组:基本组不能满足授权要求时,创建附加组。用户可以属于多个附加组。
私有组:创建用户是如果没有指定所属的组 系统会自动为其创建一个同名的组
Linux环境下用户信息保存在/etc/passwd,每一行代表一个用户。
[root@51cto ~]# cat /etc/passwd root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash bin:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin daemon:x:2:2:daemon:/sbin:/sbin/nologin adm:x:3:4:adm:/var/adm:/sbin/nologin lp:x:4:7:lp:/var/spool/lpd:/sbin/nologin sync:x:5:0:sync:/sbin:/bin/sync shutdown:x:6:0:shutdown:/sbin:/sbin/shutdown halt:x:7:0:halt:/sbin:/sbin/halt mail:x:8:12:mail:/var/spool/mail:/sbin/nologin uucp:x:10:14:uucp:/var/spool/uucp:/sbin/nologin operator:x:11:0:operator:/root:/sbin/nologin games:x:12:100:games:/usr/games:/sbin/nologin gopher:x:13:30:gopher:/var/gopher:/sbin/nologin ftp:x:14:50:FTP User:/var/ftp:/sbin/nologin nobody:x:99:99:Nobody:/:/sbin/nologin vcsa:x:69:69:virtual console memory owner:/dev:/sbin/nologin saslauth:x:499:76:"Saslauthd user":/var/empty/saslauth:/sbin/nologin postfix:x:89:89::/var/spool/postfix:/sbin/nologin sshd:x:74:74:Privilege-separated SSH:/var/empty/sshd:/sbin/nologin wangyan:x:500:500::/home/wangyan:/bin/bash

- Username field: This field denotes the User (or User Account) Name. According to the man page of
useraddcommand, "Usernames may only be up to 32 characters long". This username must be used at the time of logging in to the system. - Password field: Second field is the Password field, not denoting the actual password though. A 'x' in this field denotes the password is encrypted and saved in the
/etc/shadowfile. - UID field: Whenever a new user account is created, it is assigned with a user id or UID (UID for the user '
mandar' is 500, in this case) and this field specifies the same. - GID field: Similar to the UID field, this field specifies which group the user belongs to, the group details being present in
/etc/groupfile. - Comment/Description/User Info field: This field is the short comment/description/information of the user account (For this example, user account '
mandar' belongs to the userMandar Shinde, hence this comment). - User Home Directory: Whenever a user logs in to the system, he is taken to his Home directory, where all his personal files reside. This field provides the absolute path to the user's home directory (
/home/mandarin this case). - Shell: This field denotes, the user has access to the shell mentioned in this field (user '
mandar' has been given access to/bin/bashor simplybashshell).
查看Linux系统中有哪些shell可以用
[root@51cto ~]# cat /etc/shells /bin/sh /bin/bash /sbin/nologin /bin/dash
用户密码在/etc/shadow文件中
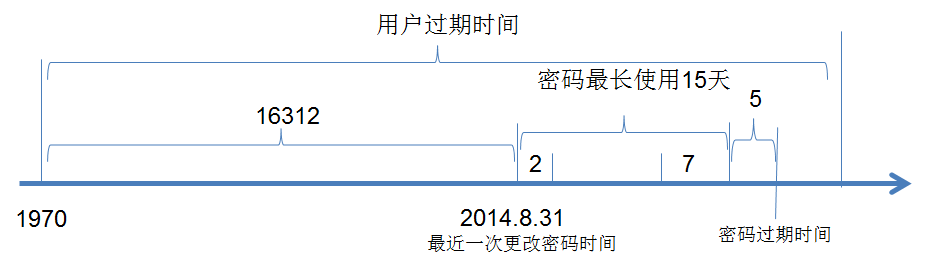
[root@51cto ~]# cat /etc/shadow root:$6$5B2lQCfHQp5kBP8L$yA9etUiORX6Zxn663OARZcp/:17675:0:99999:7::: bin:*:15615:0:99999:7::: daemon:*:15615:0:99999:7::: adm:*:15615:0:99999:7::: lp:*:15615:0:99999:7::: sync:*:15615:0:99999:7::: shutdown:*:15615:0:99999:7::: halt:*:15615:0:99999:7::: mail:*:15615:0:99999:7::: uucp:*:15615:0:99999:7::: operator:*:15615:0:99999:7::: games:*:15615:0:99999:7::: gopher:*:15615:0:99999:7::: ftp:*:15615:0:99999:7::: nobody:*:15615:0:99999:7::: vcsa:!!:17675:::::: saslauth:!!:17675:::::: postfix:!!:17675:::::: sshd:!!:17675:::::: wangyan:!!:17680:0:99999:7::: [root@WebServer ~]# tail -1 /etc/shadow wangyan:$6$PDZ2U4mgN89wtWFfCYFB.:16312:2:15:7:5:16600:
用户登录名
加密后的密码
从1970 年到最近一次更改密码时间之间过了多少天
密码最少使用几天
密码最长使用多少天
密码到期前几天提醒用户更改密码
密码过期时间
用户过期时间
chage
更改用户密码过期信息
-d 设置最近一次更改密码时间
-E 设置账户过期时间
-I 设置密码过期时间
-l --list 列出用户账户密码信息
-m 设置用户最短密码使用时间
-M 设置用户最常密码使用时间
-W 设置密码更改警告时间