基于大小相似,摆放规整的水表图片的 数字表盘的识别

识别效果:

# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- """ Created on Tue Sep 17 19:00:45 2019 @author: xxr """ from cv2 import cv2 #因为cv2里面还有cv2 所以要这样干! import numpy as np #读取原始图片 image= cv2.imread('shuibiao1.jpg') #图片的缩小,记住比例 的缩放 r = 500.0 / image.shape[1] dim = (500, int(image.shape[0] * r)) image = cv2.resize(image, dim, interpolation = cv2.INTER_AREA) #图像灰度化处理 grayImage = cv2.cvtColor(image,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) #基于Canny的边沿检测(生成的也是二值图) canny=cv2.Canny(grayImage,30,180) cv2.imshow('canny', canny) # 运用OpenCV findContours函数检测图像所有轮廓 contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(canny,cv2.RETR_CCOMP,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE) # 对于检测出的轮廓,contourArea限制轮廓所包围的面积的大小,boundingRect识别出正矩形,通过矩形的宽度和高度筛选出想要的图片区域。 # count=0 # minx=10000 # miny=10000 # height=0 # weight=0 for cnt in contours: if cv2.contourArea(cnt)>800: #筛选出面积大于30的轮廓 [x,y,w,h] = cv2.boundingRect(cnt) #x,y是左上角的坐标,h,w是高和宽 if h > 28 and h < 50: # 根据期望获取区域,即数字区域的实际高度预估28至50之间 # if(minx>x): # minx=x # if(miny>y): # miny=y # count+=1 # height+=h # weight+=w cv2.rectangle(image,(x,y),(x+w,y+h),(0,255,0),2) # #截取特定区域 # imagehh = image[miny:miny+height,minx:minx+weight] cv2.imshow("hh",image) # print(str(count)+"jjjjjjjj") cv2.waitKey(0) cv2.destroyAllWindows()
对水表图片进行的hough(霍夫)直线检测
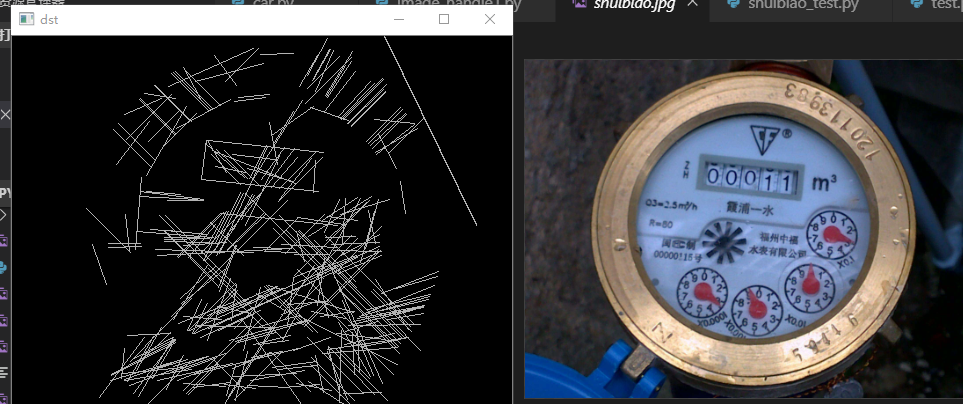
1 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- 2 """ 3 Created on Tue Sep 17 19:00:45 2019 4 5 @author: xxr 6 """ 7 from cv2 import cv2 #因为cv2里面还有cv2 所以要这样干! 8 import numpy as np 9 10 #读取原始图片 11 image= cv2.imread('shuibiao.jpg') 12 13 #读入一张白色的图 14 image2=cv2.imread('white.png') 15 image3=image2 16 17 #图片的缩小,记住比例 的缩放 18 r = 500.0 / image.shape[1] 19 dim = (500, int(image.shape[0] * r)) 20 image = cv2.resize(image, dim, interpolation = cv2.INTER_AREA) 21 image2=cv2.resize(image2, dim, interpolation = cv2.INTER_AREA) 22 23 #图像灰度化处理 24 grayImage = cv2.cvtColor(image,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) 25 #基于Canny的边沿检测(生成的也是二值图) 26 canny=cv2.Canny(grayImage,30,180) 27 #cv2.imshow("canny_image",canny) 28 #再canny处理图像以后 用hough直线检测 29 #统计概率霍夫线变换 30 31 32 # 步长 阈值 最小直线长度 最大构成直线的点的间隔 33 lines = cv2.HoughLinesP(canny, 1, np.pi / 180, 60, minLineLength=30, maxLineGap=8) 34 for line in lines: 35 x1, y1, x2, y2 = line[0] 36 cv2.line(image2, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), (0, 0, 255), 1) 37 38 39 40 #这里进行矩形的轮廓检测 !!!应该找 白色的矩形框 41 image2 = cv2.cvtColor(image2,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) 42 #黑白颜色颠倒 43 height, width = image2.shape 44 dst = np.zeros((height,width,1), np.uint8) 45 for i in range(0, height): 46 for j in range(0, width): 47 grayPixel = image2[i, j] 48 dst[i, j] = 255-grayPixel 49 50 51 #高斯滤波(使图像模糊,平滑) 52 #dst=cv2.GaussianBlur(dst,(7,7),0) 53 54 cv2.imshow('dst', dst) 55 contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(dst,cv2.RETR_CCOMP,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE) 56 57 # #绘制直线 58 # max=0 59 # max_i=0 60 # print(len(contours[2])) 61 # for i in range(len(contours)): 62 # if(5==len(contours[i])): 63 # max_i=i 64 # cv2.drawContours(image3,contours,-1,(0,255,255),3) 65 # cv2.imshow("draw_img0", image3) 66 67 # #绘制矩形 68 # for i in range(0,len(contours)): 69 # x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(contours[i]) 70 # cv2.rectangle(image3, (x,y), (x+w,y+h), (153,153,0), 5) 71 #cv2.imshow("draw_img0", image3) 72 73 #打印矩形 74 # for i in range(0,len(contours)): 75 # x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(contours[i]) 76 # print(contours[0]) 77 # cv2.rectangle(image3, (x,y), (x+w,y+h), (255,153,0), 5) 78 79 #标准霍夫线变换(但在这里不太实用) 80 # lines = cv2.HoughLines(canny, 1, np.pi/180, 150) 81 # for line in lines: 82 # rho, theta = line[0] #line[0]存储的是点到直线的极径和极角,其中极角是弧度表示的。 83 # a = np.cos(theta) #theta是弧度 84 # b = np.sin(theta) 85 # x0 = a * rho #代表x = r * cos(theta) 86 # y0 = b * rho #代表y = r * sin(theta) 87 # x1 = int(x0 + 1000 * (-b)) #计算直线起点横坐标 88 # y1 = int(y0 + 1000 * a) #计算起始起点纵坐标 89 # x2 = int(x0 - 1000 * (-b)) #计算直线终点横坐标 90 # y2 = int(y0 - 1000 * a) #计算直线终点纵坐标 注:这里的数值1000给出了画出的线段长度范围大小,数值越小,画出的线段越短,数值越大,画出的线段越长 91 # cv2.line(image, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), (0, 0, 255), 2) #点的坐标必须是元组,不能是列表。 92 # cv2.imshow("image-lines", image) 93 94 # 二值化图片 95 # #自适应阈值化能够根据图像不同区域亮度分布,改变阈值 96 # #threshold_pic = cv2.adaptiveThreshold(grayImage, 255, cv2.ADAPTIVE_THRESH_GAUSSIAN_C,cv2.THRESH_BINARY, 25, 10) 97 # ret,threshold_pic=cv2.threshold(grayImage,127, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY) 98 # cv2.imshow("threshold_image",threshold_pic) 99 #等待显示(不添加这两行将会报错) 100 cv2.waitKey(0) 101 cv2.destroyAllWindows()
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Tue Sep 17 19:00:45 2019
@author: xxr
"""
from cv2 import cv2 #因为cv2里面还有cv2 所以要这样干!
import numpy as np
#读取原始图片
image= cv2.imread('shuibiao.jpg')
#读入一张白色的图
image2=cv2.imread('white.png')
image3=image2
#图片的缩小,记住比例 的缩放
r = 500.0 / image.shape[1]
dim = (500, int(image.shape[0] * r))
image = cv2.resize(image, dim, interpolation = cv2.INTER_AREA)
image2=cv2.resize(image2, dim, interpolation = cv2.INTER_AREA)
#图像灰度化处理
grayImage = cv2.cvtColor(image,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
#基于Canny的边沿检测(生成的也是二值图)
canny=cv2.Canny(grayImage,30,180)
#cv2.imshow("canny_image",canny)
#再canny处理图像以后 用hough直线检测
#统计概率霍夫线变换
# 步长 阈值 最小直线长度 最大构成直线的点的间隔
lines = cv2.HoughLinesP(canny, 1, np.pi / 180, 60, minLineLength=30, maxLineGap=8)
for line in lines:
x1, y1, x2, y2 = line[0]
cv2.line(image2, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), (0, 0, 255), 1)
#这里进行矩形的轮廓检测 !!!应该找 白色的矩形框
image2 = cv2.cvtColor(image2,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
#黑白颜色颠倒
height, width = image2.shape
dst = np.zeros((height,width,1), np.uint8)
for i in range(0, height):
for j in range(0, width):
grayPixel = image2[i, j]
dst[i, j] = 255-grayPixel
#高斯滤波(使图像模糊,平滑)
#dst=cv2.GaussianBlur(dst,(7,7),0)
cv2.imshow('dst', dst)
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(dst,cv2.RETR_CCOMP,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
# #绘制直线
# max=0
# max_i=0
# print(len(contours[2]))
# for i in range(len(contours)):
# if(5==len(contours[i])):
# max_i=i
# cv2.drawContours(image3,contours,-1,(0,255,255),3)
# cv2.imshow("draw_img0", image3)
# #绘制矩形
# for i in range(0,len(contours)):
# x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(contours[i])
# cv2.rectangle(image3, (x,y), (x+w,y+h), (153,153,0), 5)
#cv2.imshow("draw_img0", image3)
#打印矩形
# for i in range(0,len(contours)):
# x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(contours[i])
# print(contours[0])
# cv2.rectangle(image3, (x,y), (x+w,y+h), (255,153,0), 5)
#标准霍夫线变换(但在这里不太实用)
# lines = cv2.HoughLines(canny, 1, np.pi/180, 150)
# for line in lines:
# rho, theta = line[0] #line[0]存储的是点到直线的极径和极角,其中极角是弧度表示的。
# a = np.cos(theta) #theta是弧度
# b = np.sin(theta)
# x0 = a * rho #代表x = r * cos(theta)
# y0 = b * rho #代表y = r * sin(theta)
# x1 = int(x0 + 1000 * (-b)) #计算直线起点横坐标
# y1 = int(y0 + 1000 * a) #计算起始起点纵坐标
# x2 = int(x0 - 1000 * (-b)) #计算直线终点横坐标
# y2 = int(y0 - 1000 * a) #计算直线终点纵坐标 注:这里的数值1000给出了画出的线段长度范围大小,数值越小,画出的线段越短,数值越大,画出的线段越长
# cv2.line(image, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), (0, 0, 255), 2) #点的坐标必须是元组,不能是列表。
# cv2.imshow("image-lines", image)
# 二值化图片
# #自适应阈值化能够根据图像不同区域亮度分布,改变阈值
# #threshold_pic = cv2.adaptiveThreshold(grayImage, 255, cv2.ADAPTIVE_THRESH_GAUSSIAN_C,cv2.THRESH_BINARY, 25, 10)
# ret,threshold_pic=cv2.threshold(grayImage,127, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
# cv2.imshow("threshold_image",threshold_pic)
#等待显示(不添加这两行将会报错)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()