大纲:
使用注解的好处;
注解的概念;
Java中的常见注解;
注解的分类;
自定义注解;
注解的好处:让编程更加简洁,代码更加清晰;
注解的概念:Java提供了一种原程序中的元素关联任何信息和任何元数据的途径和方法;
Java中的常见注解:
JDK自带的注解:
@Override:
@Deprecated:会和@Suppvisewarnings一起使用;
@Suppvisewarnings:

1 /** 2 * @Deprecated 和 @SuppressWarnings 两个注解的使用 3 */ 4 package annotation; 5 6 public class AnnotationTest01 7 { 8 @SuppressWarnings("deprecation") 9 public void test01() 10 { 11 Person p = new Child(); 12 13 // 加了横线,表示这个方法已经过时了,有一个警告; 14 // 但为了去掉警告(一般公司都会要求),可以加上 @SuppressWarnings("deprecation") 注解,表示忽略这种警告 15 // 注意,注解必须加在方法上面 16 p.sing(); 17 } 18 } 19 20 interface Person 21 { 22 public String name(); 23 24 public int age(); 25 26 // 表示这个方法已经过时了,方法名上会多一个横线 27 @Deprecated 28 public void sing(); 29 } 30 31 class Child implements Person 32 { 33 // 实现了父类接口,就要重写(覆盖)父类的方法,使用 @Override 注解 34 @Override 35 public String name() 36 { 37 return null; 38 } 39 40 @Override 41 public int age() 42 { 43 return 0; 44 } 45 46 @Override 47 public void sing() 48 { 49 50 } 51 }
Spring中的常用注解:
@Autowired:
@Service:
@Repository:
SpringMVC中的常用注解:
MyBatis中的常用注解:
@InsertProvider:
@UpdateProvider:
@Options:
注解的分类:
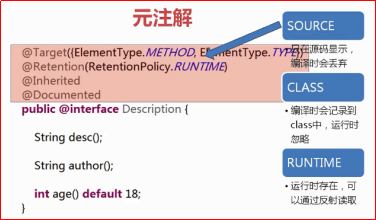
按照运行机制区分:
源码注解:注解只在源码中存在,编译成.class文件就不存在了;
编译时注解:在源码和.class文件中都存在;
运行时注解:在运行阶段还起作用,甚至会影响运行逻辑的注解;
按照来源区分:
来自JDK的注解:
来自第三方的注解:比如来自Spring、MyBatis等;
自定义的注解:
自定义注解:
语法:


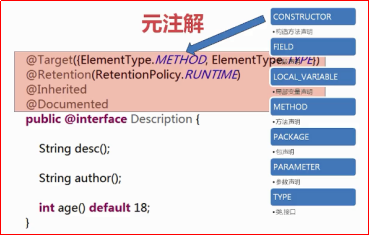



1 /** 2 * 自定义注解 3 */ 4 package annotation; 5 6 import java.lang.annotation.Documented; 7 import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; 8 import java.lang.annotation.Inherited; 9 import java.lang.annotation.Retention; 10 import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; 11 import java.lang.annotation.Target; 12 13 @Target({ElementType.METHOD,ElementType.TYPE}) 14 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) 15 @Inherited 16 @Documented 17 public @interface Description 18 { 19 String desc(); 20 21 String author(); 22 23 int age() default 18; 24 }
元注解:对注解进行注解的注解; 注意:使用继承注解时,只能继承类上面的注解(即不能继承接口上面的注解,也不能继承父类中方法上的注解)
使用自定义注解:


1 /** 2 * 使用自定义注解 3 */ 4 package annotation; 5 6 public class AnnotationTest02 7 { 8 @Description(desc="I an eyeColor",author="Mooc boy",age=20) 9 public String eyeColor() 10 { 11 return "red"; 12 } 13 14 public static void main(String[] args) 15 { 16 AnnotationTest02 test = new AnnotationTest02(); 17 System.out.println(test.eyeColor()); 18 } 19 } 20 21 /* 22 结果打印如下: 23 24 red 25 */
解析注解:
通过反射获取类、函数或成员上的运行时注解信息,从而实现动态控制程序运行的逻辑;

1 /** 2 * 解析注解 3 */ 4 package annotation; 5 6 import java.lang.annotation.Annotation; 7 import java.lang.reflect.Method; 8 9 public class AnnotationTest03 10 { 11 public static void main(String[] args) 12 { 13 try 14 { 15 // 1.使用类加载器加载类 16 Class c = Class.forName("annotation.ParseAnnotation"); 17 18 // 2.找到类上面的注解 19 // 判断这个类上有没有Description这个注解 20 boolean isExit = c.isAnnotationPresent(Description.class); 21 22 if(isExit) 23 { 24 // 3.拿到注解实例 25 Description d = (Description)c.getAnnotation(Description.class); 26 27 // 4.解析注解,获得的是类注解的解析信息 28 System.out.println("desc=" + d.desc() + ",author=" + d.author() + ",age=" + d.age()); 29 30 // 5.解析方法注解 31 Method[] m = c.getMethods(); // 先找到所有方法 32 for(Method ms : m) 33 { 34 boolean isExit2 =ms.isAnnotationPresent(Description.class); 35 if(isExit2) 36 { 37 Description d2 = (Description)ms.getAnnotation(Description.class); 38 System.out.println("desc=" + d2.desc() + ",author=" + d2.author() + ",age=" + d2.age()); 39 } 40 41 } 42 43 // 6.另外一种解析方法 44 for(Method ms2 : m) 45 { 46 Annotation[] a = ms2.getAnnotations(); // 获得方法上的所有注解 47 for(Annotation an : a) 48 { 49 if(an instanceof Description) // 判断此注解是不是 Description 注解 50 { 51 Description d3 = (Description)an; 52 System.out.println("desc=" + d3.desc() + ",author=" + d3.author() + ",age=" + d3.age()); 53 } 54 } 55 } 56 } 57 } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) 58 { 59 e.printStackTrace(); 60 } 61 } 62 } 63 64 @Description(desc="I am class annotation",author="Mooc boy") 65 class ParseAnnotation 66 { 67 @Description(desc="I am method annotation",author="Mooc boy") 68 public String name() 69 { 70 return null; 71 } 72 }
