HTTP REQUESTS
BASIC INFORMATION FLOW
- The user clicks on a link.
- HTML website generates a request(client-side)
- The request is sent to the server.
- The server performs the requests(server-side)
- Sends response back.
GET vs POST
Two main methods used to send data to the web application:
1. Through the URL(Usually using GET).
a. http://webisite.com/news.php?id=1
b. http://website.com/?id=1
2. Through input elements(Usually using POST).
a. Search boxes.
b. Login boxes.
c. ..etc.
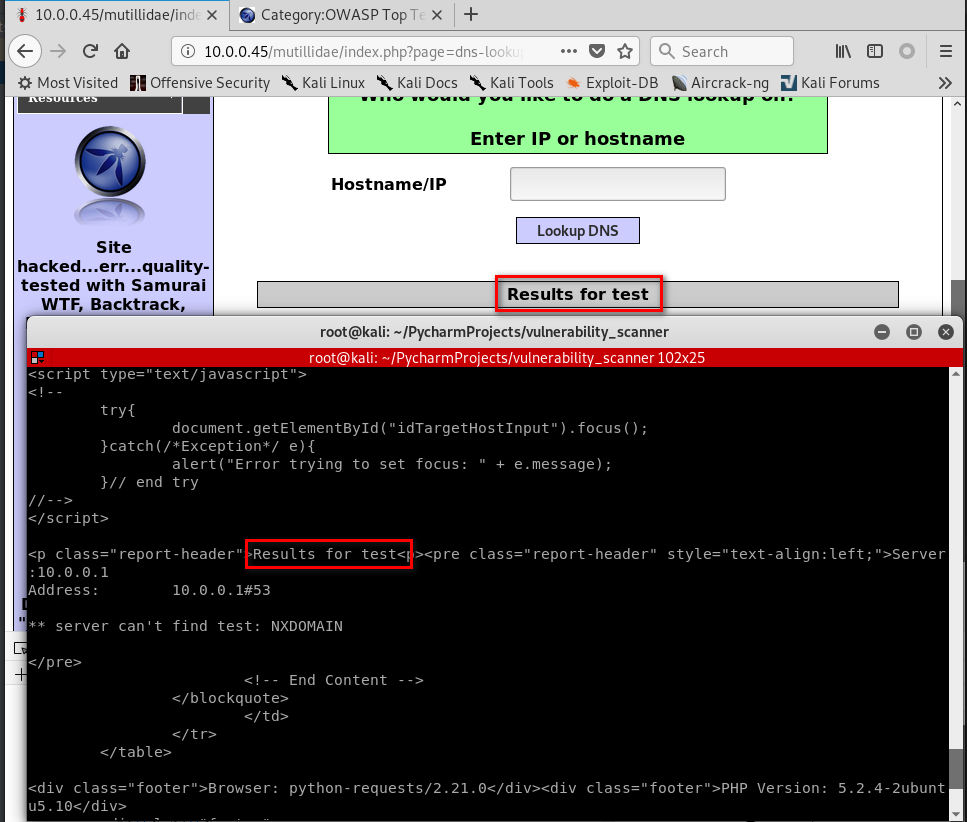
Target website:http://10.0.0.45/mutillidae/index.php?page=dns-lookup.php

#!/usr/bin/env python import requests from bs4 import BeautifulSoup from urllib.parse import urljoin def request(url): try: return requests.get(url) except requests.exceptions.ConnectionError: pass target_url = "http://10.0.0.45/mutillidae/index.php?page=dns-lookup.php" response = request(target_url) parsed_html = BeautifulSoup(response.content.decode()) forms_list = parsed_html.findAll("form") for form in forms_list: action = form.get("action") post_url = urljoin(target_url, action) method = form.get("method") inputs_list = form.findAll("input") post_data = {} for input in inputs_list: input_name = input.get("name") input_type = input.get("type") input_value = input.get("value") if input_type == "text": input_value = "test" post_data[input_name] = input_value result = requests.post(post_url, data=post_data) print(result.content.decode())
Run the Python Code successfully.