CSS Combinators
CSS Pseudo-classes
p:first-child = p element 同时它是某个 element 的 first child
CSS Pseudo-elements
伪元素用双分号 ::
比较常看到的使用场景, 第一个字特别大
p::first-letter { color: #ff0000; font-size: xx-large; }
前 / 后插入图片
h1::before { content: url(smiley.gif); }
user selection
::selection { color: red; background: yellow; }
不是所有 element 都可以插入伪元素的, 比如 img 就不行.
参考: stackoverflow – Does :before not work on img elements?
CSS Image Sprites
以前常用于把多个 icon 放到 1 个 image 里.
通过 background-image + position 调出图片然后显示某个区域而已
CSS Attribute Selectors
[target] = 有 attribute "target"
[target="_blank"] = 有 attribute "target" 同时 attribute value 是 "_blank"
[title~="flower"] = attribute "title" 同时 value contains a space-separated list of "flower" (e.g. "flower abc", "abc flower", not ok: "abc-flower", "flowerAbc")
[title*="flower"] = attribute "title" 同时 value contains "flower" (没有 space-separated 概念)
[class|="top"] = attribute "class" 同时 value starts with top (必须是完整字, 或者 hypen, e.g. "top", "top-abc", "top-xyz", not ok: "topcontent,", "topAbc") 注: 所以 class 最好还是用 hypen 不要用 camelcase 嘛.
[class^="top"] = attribute "class" 同时 value starts with top 了 "不需要完整字"
[class$="test"] = attribute "class" 同时 ends with test "不需要完整字"
*, ^, $, contains, starts with, ends with 和正则一样, 很好记.
~, | contains, starts with 比较怪.
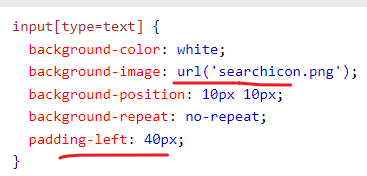
CSS Forms
input + icon

用 background-image + padding 来做的
去掉 textarea resize
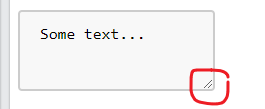
{ resize: none; }
CSS Counters
可以用 CSS 来做 index

CSS 长这样

CSS Units
Absolute Lengths
px, cm, mm
in (inch) 1in = 96px = 2.54cm (电脑 dpi 的情况)
pt (point) 1 pt = 1/72 inch
pc (1pc = 12 pt)
Relative Lengths
em, rem, %,
vw, vh (对应 viewport 的 percentage, 1vw = 1% of viewport width)
冷门的: ex, ch, vmin, vmax
Default Unit
没有 default unit 的, 除了 0 可以不用放 unit, 其它都得放. 参考: CSS Default Units
CSS Specificity
CSS 的优先级是有点复杂的.
它有一个跑分机制
4 个 Levels:
Inline styles,
IDs, Classes,
attributes and pseudo-classes,
Elements and pseudo-elements
Start at 0, add 1000 for style attribute, add 100 for each ID, add 10 for each attribute, class or pseudo-class, add 1 for each element name or pseudo-element.
如果同分那就下面覆盖上面.
例子: 一个 div 有 id 也有 class
<div id="dada" class="tata">asdd</div>
CSS
#dada { background-color: green; } .tata { background-color: red; }
最终结果是 green, 虽然 .tata 在下面, 但是由于 id add 100, class 只是 add 10, 所以 id 分数比较高.
虽然说 add 10 for each attribute, 按理说我只要有超过 10 个 attribute 就可以超越 id 的 100 分, 但我测试了没有.
所以它的累加只是在平级的时候可以区分, 不是拿来越级的.
!important
#myid { background-color: blue !important; }
important 就无视跑分了, 但是如果 2 个 !important 的话就依然看分数
CSS Math Functions
calc, max, min
常用方式
calc(100% - 100px);
max(50%, 300px);