1. 本周学习总结
1.1 以你喜欢的方式(思维导图或其他)归纳总结集合与泛型相关内容。
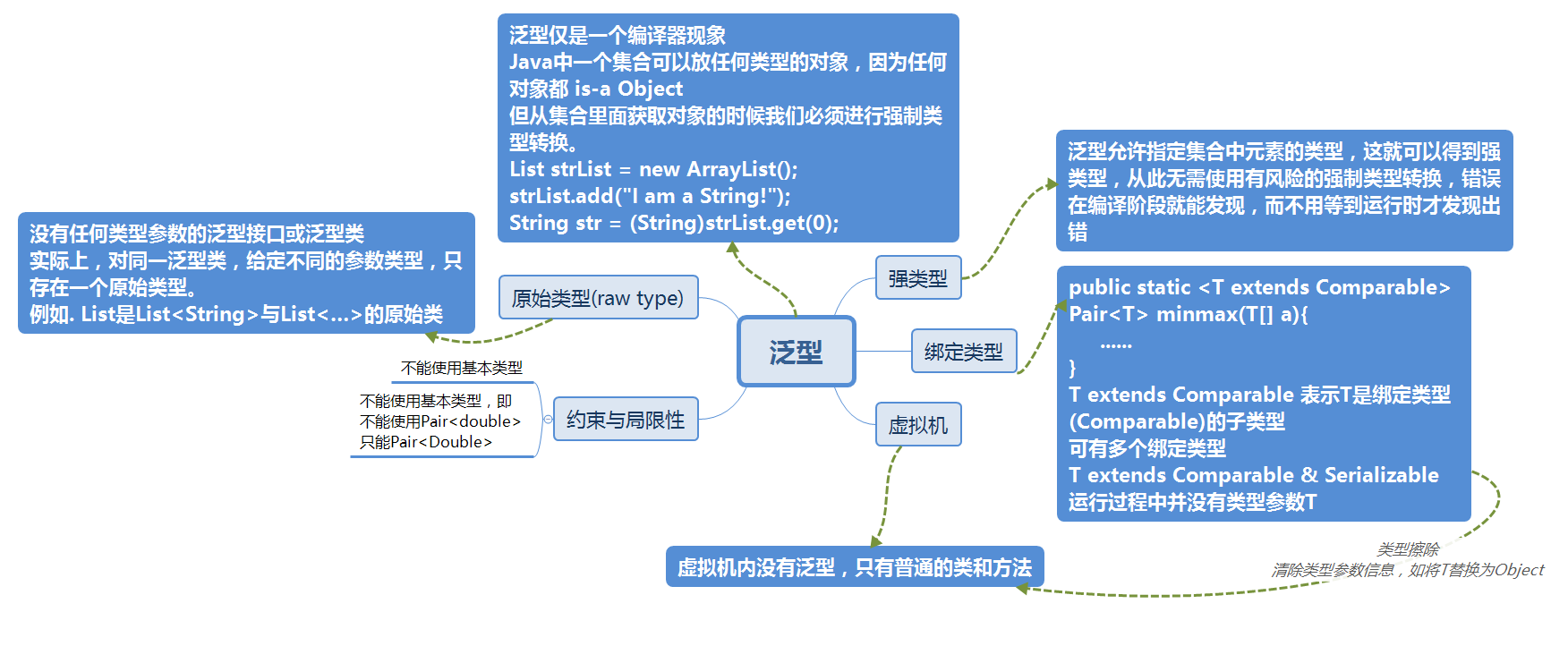
2. 书面作业
本次作业题集集合
List中指定元素的删除(题目4-1)
1.1 实验总结
答:

在老师的详细讲解下,对泛型有了一定了解,要注意的是,在打开一个list后,要使用sc.close();将其关闭。
统计文字中的单词数量并按出现次数排序(题目5-3)
2.1 伪代码(简单写出大体步骤)
答:
1.读入一串字符,用while判断是否结束
while(str!="!!!!!")
2.将字符串分割成一个个单词的小字符串存储并统计单词(key)出现的次数(value)
if(cnt==null){
map.put(key, 1);
}
else{
map.put(key, cnt+1);
}
3.实现Comparato接口,为单词排序
List<Map.Entry<String,Integer>> entryList = new ArrayList<>(map.entrySet());
Collections.sort(entryList, new Comparator<Map.Entry<String,Integer>>(){
public int compare(Entry<String, Integer> o1, Entry<String, Integer> o2) {
if(o1.getValue()<o2.getValue())
else if(o1.getKey().compareTo(o2.getKey())>0)
return 0;
}
}
4.输出前10组数据
for (Map.Entry<String,Integer> entry :arrayList)
{
if(i==10)
{
break;
}
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + "=" + entry.getValue());
i++;
}
2.2 实验总结
根据如上步骤顺序依次写出代码,一步一步来,写代码前的逻辑整理很重要,乍一看很难的题目拆分后其实也不难。
倒排索引(题目5-4)
3.1 截图你的提交结果(出现学号)
答:还未编译通过,凌乱ing
3.2 伪代码(简单写出大体步骤)
答:
1.读取输入,存储
2.用HashMap统计单词出现的次数
3.转化成list,用Comparato接口实现排序,输出
4.输入另一串文字,储存
5.存放在另一个HashMap
6.如果找到,输出行集与行集内每一行的内容,如果没找到输出found 0 results
3.3 实验总结
答:与上一题类似的输入、存储和排序,匿名内部类还需要再熟悉一下。
Stream与Lambda
编写一个Student类,属性为:
private Long id;
private String name;
private int age;
private Gender gender;//枚举类型
private boolean joinsACM; //是否参加过ACM比赛
创建一集合对象,如List,内有若干Student对象用于后面的测试。
4.1 使用传统方法编写一个方法,将id>10,name为zhang, age>20, gender为女,参加过ACM比赛的学生筛选出来,放入新的集合。在main中调用,然后输出结果。
答:
public static void main(String[] args){
ArrayList<Student> list=new ArrayList<Student>();
Student e1=new Student(11L,"zhang",21,Gender.female,true);
Student e2=new Student(9L,"zhang",21,Gender.female,true);
list.add(e1);
list.add(e2);
for (Student student : list) {
System.out.println(student.find());
}
}
4.2 使用java8中的stream(), filter(), collect()编写功能同4.1的函数,并测试。
答:
ArrayList<Student> arrayList2 = (ArrayList<Student>) arrayList.parallelStream()
.filter(student -> (student.getId() > 10L && student.getName().equals("zhang")
&& student.getAge() > 20 &&
student.getGender().equals(Gender.female)
&& student.isJoinsACM()))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
4.3 构建测试集合的时候,除了正常的Student对象,再往集合中添加一些null,然后重新改写4.2,使其不出现异常。
答:判断student是否为null,若为null就舍去。
泛型类:GeneralStack(题目5-5)
5.1 截图你的提交结果(出现学号)
答:

终于。。。
5.2 GeneralStack接口的代码
答:
interface GeneralStack<E> {
public E push(E item);//如果item为null或者栈满都会返回null
public E pop();//出栈,如为空,则返回null
public E peek();//获得栈顶元素,如果为空则返回null
public boolean empty();//判断是否栈空,如果为空则返回true
public int size();//返回栈中元素数量
}
5.3 结合本题,说明泛型有什么好处
答:消除源代码中的许多强制类型转换,使得代码更加可读,减少了出错机会,还能让一个类应用于多种类型,调用时,就可以创建多个不同类型的类。
泛型方法
基础参考文件GenericMain,在此文件上进行修改。
6.1 编写方法max,该方法可以返回List中所有元素的最大值。List中的元素必须实现Comparable接口。编写的max方法需使得String max = max(strList)可以运行成功,其中strList为List类型。也能使得Integer maxInt = max(intList);运行成功,其中intList为List类型。
答:
class Max {
public static <T extends Comparable<T>> T max(List<T> list){
T max = list.get(0);
for (T t : list) {
if ( t.compareTo( max ) > 0 ){
max = t;
}
}
return max;//返回List中所有元素的最大值
}
6.2 选做:现有User类,其子类为StuUser,且均实现了Comparable接口。编写方法max1,基本功能同6.1,并使得max1(stuList);可以运行成功,其中stuList为List
6.3 选做:编写int myCompare(T o1, T o2, Comparator c)方法,该方法可以比较User对象及其子对象,传入的比较器c既可以是Comparator
选做:逆向最大匹配分词算法
集合实验文件中的第07次实验(集合).doc文件,里面的题目6.
7.1 写出伪代码
7.2 实验总结
选做:JavaFX入门
完成其中的作业1、作业2。内有代码,可在其上进行适当的改造。建议按照里面的教程,从头到尾自己搭建。
3. 码云上代码提交记录及PTA实验总结
题目集:jmu-Java-05-集合
3.1. 码云代码提交记录
在码云的项目中,依次选择“统计-Commits历史-设置时间段”, 然后搜索并截图
答:

3.2. PTA实验
函数(4-1),编程(5-3,5-4,5-5)
实验总结已经在作业中体现,不用写。