Weighted Quick Union即:
在Quick Union的基础上对结点加权(weighted),在parent[i]基础上增加一个size[i].
用来存储该结点(site)的所有子结点数目.(size[i] == number of sites in subtree rooted at i)
具体操作步骤:
仅仅在union() operation改变,在改变parent前,增加一个步骤:
比较两个结点的size,谁更轻谁就在下面,
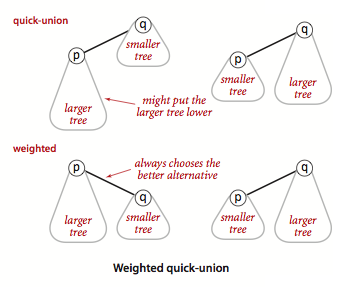
具体看代码:
1 class WeightedQuickUnion(): 2 __count = int() #number of components 3 __parent = list() #__parent[i] parent of i 4 __size = list() #size[i] number of sites in subtree rooted at i 5 #Each site is initially in its own component 6 def __init__(self,N): 7 self.__count = N 8 for i in range(0,self.__count): 9 self.__parent.append(i) 10 self.__size.append(1) 11 #Return the component identifier for the component containing site 12 def find(self,p): 13 self.validate(p) 14 while (p != self.__parent[p]): 15 p = self.__parent[p] 16 return p 17 def connected(self,p,q): 18 return self.find(p) == self.find(q) 19 #Merges the component containig site p with 20 #the component containing site q 21 def union(self,p,q): 22 rootP=self.find(p) 23 rootQ=self.find(q) 24 if (rootP == rootQ): 25 return 26 if (self.__size[rootP] < self.__size[rootQ]): 27 self.__parent[rootP] = rootQ 28 self.__size[rootQ] += self.__size[rootP] 29 else: 30 self.__parent[rootQ] = rootP 31 self.__size[rootP] += self.__size[rootQ] 32 self.__count-=1 33 def validate(self, p): 34 n = len(self.__parent) 35 if (p < 0 or p >= n): 36 raise ValueError("index", p, "is not between 0 and", (n - 1)) 37 def traversal(self): 38 for i in self.__parent: 39 print(i,end=' ') 40 WQU = WeightedQuickUnion(8) 41 WQU.union(0,1) 42 WQU.union(2,1) 43 WQU.union(2,4) 44 WQU.union(3,7) 45 print(WQU.connected(0,4)) 46 WQU.traversal()
实例同上一文Quick Find一样,
连接0-1-2-4 3-7,并调用connected()方法验证0-4是否连接
最后遍历
输出:
True
0 0 0 3 0 5 6 3
根据输出可以反应出树形图:
0 3 5 6
/ | |
1 2 4 7
程序中:union()方法里,把size的比较分为两种情况,小于以及大于+等于.
union(0,1)的时候0是p,1是q,他们的size都是1,所以会执行
1 self.__parent[rootQ] = rootP 2 self.__size[rootP] += self.__size[rootQ]
也就是q(1)会成为p(0)的子节点.
union(3,7)同理.
其它情况由于size不同,会按照程序写的那样,把轻的作重的子节点