直接上代码
注: 代码来自于 Java 9
put方法
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
- 当调用put(),首先会根据key生成一个 hash值,原理如下:
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
//key 是 null 直接返回 0
//key 不是null,先计算key对应的hashCode,赋值给 h
//并将 h 与 h >>> 16 做异或(相同为0 不同为1)运算 ,作为hash值返回
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}
-
下图举例说明了位运算的过程,至于原理解释,参考本文引用

-
拿到了hash值后,调用 putVal(),做了如下操作
- 将对象table赋值给tab,并以tab是否为空作为是否第一次调用此方法的判断,是则resize()并给tab,n赋值;
- 获取tab的第i个元素:根据 (n - 1) & hash 算法 ,计算出i找到,如果为空,调用newNode() ,赋值给tab第i个;
- 如果不为空,可能存在2种情况:hash值重复了,也就是put过程中,发现之前已经有了此key对应的value,则暂时e = p;
至于另外一种情况就是位置冲突了,即根据(n - 1) & hash算法发生了碰撞,再次分情况讨论;
1.以链表的形式存入;
2.如果碰撞导致链表过长(大于等于TREEIFY_THRESHOLD),就把链表转换成红黑树; - 最后,如果e不为空,将e添加到table中(e.value 被赋值为 putVal()中的参数 value);
代码如下:
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
//hashmap对象中 tabel属性为空--->第一次put---->resize()
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
//发现tab[i] 没有值,直接存入即可
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
//tab[i]取到值了,莫慌,先定义下方2个变量
Node<K,V> e; K k;
//如果是 key 重复了 很简单,直接e = p
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
// 该链为树
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
// 该链为链表
else {
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
//几种情况都处理,可以添加元素 了
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
get方法
public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V> e;
return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? null : e.value;
}
- 还是先根据key获取hash值,其他没什么可说的,有值value,没有值返回null,直接进入getNode()
final Node<K,V> getNode(int hash, Object key) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> first, e; int n; K k;
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
if (first.hash == hash && // always check first node
((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return first;
if ((e = first.next) != null) {
if (first instanceof TreeNode)
return ((TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key);
do {
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
return null;
}
- 不难发现,此方法明显没有putVal复杂,并且参数比较简单:一个int型的hash值,一个Object的key;
- 先定义几个变量:
- 1个Node的数组 tab,两个Node对象,first,e,一个int n,一个K k;
- 进入方法的if判断,如果不走此if,直接返回null;
- 判断了如下内容,并且用 && 连接(同时满足,并且有短路)
(tab = table) != null, 只要进行过 put 操作,即满足;(n = tab.length) > 0,要求map集合中有元素(与上一个条件不同:先put再remove,此判断不成立);(first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null,还是与put时同样的计算索引方法,!=null 代表tab数组对应索引有元素;
- 满足最外层的if后,再次需要分2种情况讨论;
- 别找了 hash值也是first的hash值,传入的key也是那个key(==直接返回true,重写了 equal后 返回true也可以)
此时,直接返回first即可; - 树中还是链表中?做出不同处理
1.红黑树:直接调用getTreeNode(),不做深究
2.链表:通过.next() 循环获取,知道找到满足条件的key为止
- 别找了 hash值也是first的hash值,传入的key也是那个key(==直接返回true,重写了 equal后 返回true也可以)
- 最后,可以返回之前定义的 Node对象 e啦。
再来两张图,加深理解
-
从结构实现来讲,HashMap是数组+链表+红黑树(JDK1.8增加了红黑树部分)实现的,如下如所示。
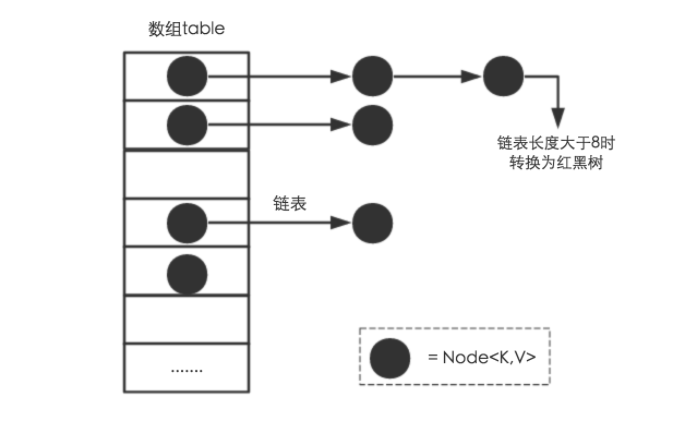
-
HashMap的put方法执行过程可以通过下图来理解。
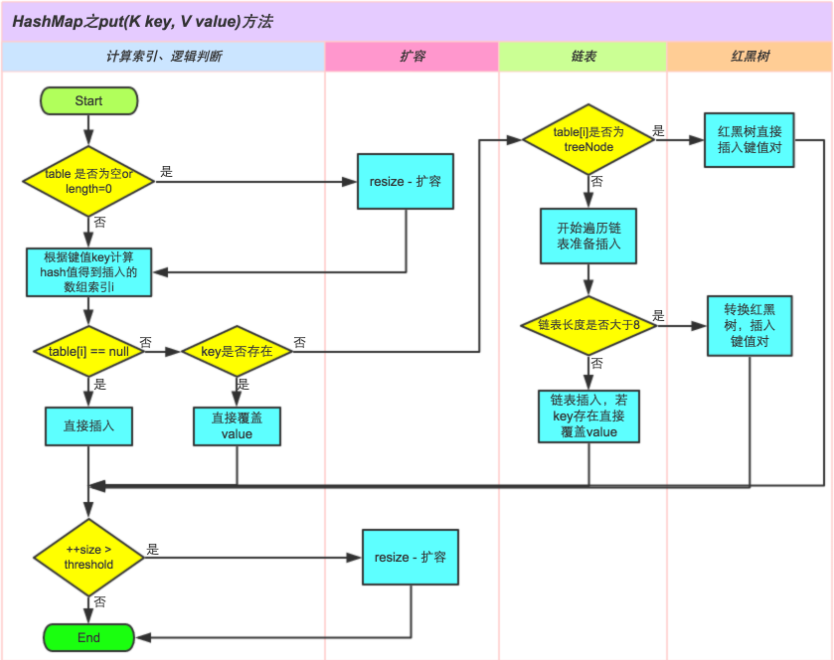
本文参考:http://yikun.github.io/2015/04/01/Java-HashMap工作原理及实现/
http://www.importnew.com/20386.html